
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
using namespace std;
vector<int> getRandomSample(int n, int num)
{
vector<int> sample;
vector<int> total_set;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
total_set.push_back(i);
for(int i = 0; i < num; ++i)
{
int j = rand()%total_set.size();
sample.push_back( total_set[j] );
total_set.erase( total_set.begin()+j );
}
return sample;
}
//k次函数
double funcX(double* a, double x, int k)
{
double xx = 1.0;
double y = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
y = y + a[i]*xx;
xx *= x;
}
return y;
}
vector<int> get_inliners(vector<cv::Point2d>& points, double* a, int k)
{
double inlier_threshold = 5;
vector<int> inliers;
for(int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++)
{
cv::Point2d p = points[i];
double y_predict = funcX(a, p.x, k);
if( fabs(p.y - y_predict) < inlier_threshold)
inliers.push_back( i );
}
cout << "inliers:" << inliers.size() << "n";
return inliers;
}
bool estimateLine(vector<cv::Point2d>& points, vector<int>&active, double* a, int k)
{
const double learning_rate = 0.1;
const int N = active.size();
double J[k*N] = {0};
double residual[N] = {0};
static double rr_last = 0;
static int iter = 0;
double rr = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
cv::Point2d p = points[ active[i] ];
double hx = funcX(a, p.x, k);
double xx = 1;
for(int j = 0; j < k; ++j)
{
J[k*i+j] = xx;
xx *= p.x;
}
residual[i] = (p.y - hx);
rr += residual[i]*residual[i];
}
rr /= N;
//cout << " r = " << rr << " ";
if(fabs(rr-rr_last) < 1e-4 || iter > 50)
{
cout << " r = " << rr << " ";
return true;
}
rr_last = rr;
//J^TJ * deltaA = J^T*r
//H*deltaA = g*r
// Eigen::Matrix2d H;
// Eigen::Vector2d G;
// Eigen::Vector2d deltaA;
Eigen::Matrix3d H;
Eigen::Vector3d G;
Eigen::Vector3d deltaA;
for(int j = 0; j < k; ++j)
{
for (int m = 0; m < k; ++m)
{
double h = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
h += J[k*i+m]*J[k*i+j];
H(m,j) = h;
}
double g = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
g += J[k*i+j]*residual[i];
G(j) = g;
}
deltaA = H.inverse() * G;
for (int m = 0; m < k; ++m)
a[m] += deltaA(m) * learning_rate;
return false;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
const int K = 3;
srand((unsigned int)time(0));
ofstream out;
out.open("/home/ha/ws_ipython/my_ransac_line.txt");
double a[K];
cout << "a = ";
for(int i = 0; i < K; i++)
{
a[i] = rand()%100/5.0 + 3;
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
cout << "truen";
vector<cv::Point2d> points;
for(size_t i = 0; i < 20; ++i)
{
cv::Point2d p;
p.x = i+rand()%10;
p.y = funcX(a, p.x, K) + rand()%100/15.0 - rand()%100/15.0;
points.push_back( p );
out << "point1,"<<p.x<<","<<p.y<<endl;
if( i%4 == 0)
{
p.x = i + 3 + rand()%20;
p.y += rand()%100;
points.push_back( p );
out << "point1,"<<p.x<<","<<p.y<<endl;
p.x = i - 3 + rand()%20;
p.y += rand()%100;
points.push_back( p );
out << "point1,"<<p.x<<","<<p.y<<endl;
}
}
vector<int> inliers;
double best_a[K];
for(int j = 0; j < 10; j++)
{
double a_result[K] = {1};
for (int i = 0; i < K; ++i)
a_result[i] = a[i] - 1.0;
vector<int> samples = getRandomSample(points.size(), 5);
while(true)
{
if(estimateLine(points, samples, a_result, K) )
break;
}
vector<int> inliers_curr = get_inliners(points, a_result, K);
if(inliers.size() < inliers_curr.size())
{
inliers = inliers_curr;
for(int i = 0; i < K; i++)
best_a[i] = a_result[i];
}
}
for(vector<int>::iterator iter = inliers.begin(); iter != inliers.end(); ++iter)
out << "point2,"<<points[*iter].x<<","<<points[*iter].y<<endl;
//最后再来一次估计
if(inliers.size() > 10)
{
vector<int> samples = getRandomSample(inliers.size(), 6);
for(int i = 0; i < samples.size(); i++)
samples[i] = inliers[i];
while(true)
{
if(estimateLine(points, samples, best_a, K) )
break;
}
}
cout << " best a: ";
for(int i = 0; i < K; i++)
cout << best_a[i] << ",";
cout <<endl;
cout << "true ";
for(int i = 0; i < K; i++)
cout << a[i] << ",";
cout <<endl;
cout << "line ransac finished..n";
return 1;
}
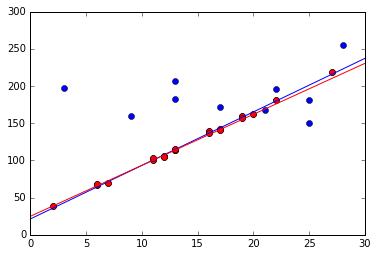
一次函数
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
file = open("my_ransac_line.txt");
datas1 = []
datas2 = []
while( True ):
line = file.readline();
if not line:
break;
if line.find("point") != -1:
in_str = line[0:-1].split(",") #[0:-1]是为了去掉字符串后面的换行符号
in_data = [float(i) for i in in_str[1::]]#去除第一个
if line.find("point1") != -1:
datas1.append(in_data)
if line.find("point2") != -1:
datas2.append(in_data)
for pos in datas1:
plt.plot(pos[0], pos[1], c='b',marker="o")
for pos in datas2:
plt.plot(pos[0], pos[1], c='r',marker="o")
trueA = [21.2, 7.2]
bestA = [24.7817,6.85777]
x = np.linspace(0,30,100)
y = trueA[1]*x + trueA[0]
plt.plot(x,y,'b') #真实曲线
y2 = bestA[1]*x + bestA[0]
plt.plot(x,y2,'r') #拟合出来的曲线
plt.show()
二次函数
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
file = open("my_ransac_line.txt");
datas1 = []
datas2 = []
while( True ):
line = file.readline();
if not line:
break;
if line.find("point") != -1:
in_str = line[0:-1].split(",") #[0:-1]是为了去掉字符串后面的换行符号
in_data = [float(i) for i in in_str[1::]]#去除第一个
if line.find("point1") != -1:
datas1.append(in_data)
if line.find("point2") != -1:
datas2.append(in_data)
for pos in datas1:
plt.plot(pos[0], pos[1], c='b',marker="o")
for pos in datas2:
plt.plot(pos[0], pos[1], c='r',marker="o")
trueA = [10,14.4,6.2]
bestA = [9.41402,13.1826,6.33986]
x = np.linspace(0,30,100)
y = trueA[2]*x*x + trueA[1]*x + trueA[0]
plt.plot(x,y,'b') #真实曲线
y2 = bestA[2]*x*x + bestA[1]*x + bestA[0]
plt.plot(x,y2,'r') #拟合出来的曲线
plt.show()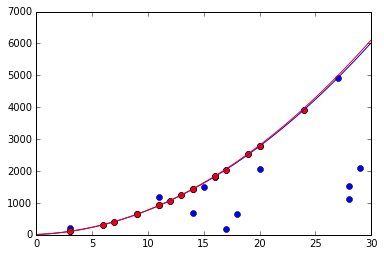
参考
// http://blog.csdn.net/haoliliang88/article/details/52932397
// https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gauss%E2%80%93Newton_algorithm
最后
以上就是俭朴月亮最近收集整理的关于RANSAC 加Guass-newton拟合曲线的全部内容,更多相关RANSAC内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复