By now, you're familiar with a module, which is a circuit that interacts with its outside through input and output ports. Larger, more complex circuits are built by composing bigger modules out of smaller modules and other pieces (such as assign statements and always blocks) connected together. This forms a hierarchy, as modules can contain instances of other modules.
到目前为止,您已经熟悉了一个模块,它是一个通过输入和输出端口与其外部交互的电路。更大、更复杂的电路是通过将更大的模块从更小的模块和连接在一起的其他部分(例如分配语句和 always 块)组成的来构建的。这形成了一个层次结构,因为模块可以包含其他模块的实例。
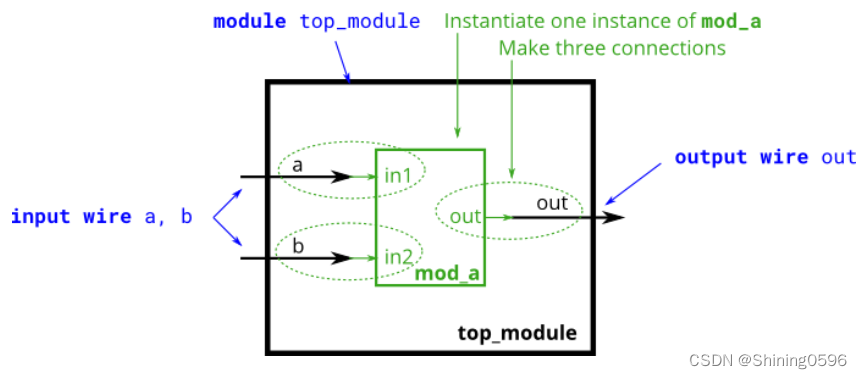
The figure below shows a very simple circuit with a sub-module. In this exercise, create one instance of module mod_a, then connect the module's three pins (in1, in2, and out) to your top-level module's three ports (wires a, b, and out). The module mod_a is provided for you — you must instantiate it.
下图显示了一个带有子模块的非常简单的电路。在本练习中,创建模块 mod_a 的一个实例,然后将模块的三个引脚(in1、in2 和 out)连接到顶层模块的三个端口(线 a、b 和 out)。模块 mod_a 是为您提供的——您必须实例化它。
When connecting modules, only the ports on the module are important. You do not need to know the code inside the module. The code for module mod_a looks like this:
连接模块时,只有模块上的端口很重要。您不需要知道模块内的代码。模块 mod_a 的代码如下所示:
module mod_a ( input in1, input in2, output out );
// Module body
endmodule
图片1 戳链接图片
The hierarchy of modules is created by instantiating one module inside another, as long as all of the modules used belong to the same project (so the compiler knows where to find the module). The code for one module is not written inside another module's body (Code for different modules are not nested).
You may connect signals to the module by port name or port position. For extra practice, try both methods.
模块的层次结构是通过在另一个模块中实例化一个模块来创建的,只要使用的所有模块都属于同一个项目(因此编译器知道在哪里可以找到该模块)。一个模块的代码没有写在另一个模块的主体中(不同模块的代码没有嵌套)。您可以通过端口名称或端口位置将信号连接到模块。如需额外练习,请尝试两种方法。
图片2 戳链接
Connecting Signals to Module Ports
There are two commonly-used methods to connect a wire to a port: by position or by name.
将信号连接到模块端口将电线连接到端口有两种常用的方法:按位置或按名称。
By position
The syntax to connect wires to ports by position should be familiar, as it uses a C-like syntax. When instantiating a module, ports are connected left to right according to the module's declaration. For example:
按位置按位置将电线连接到端口的语法应该很熟悉,因为它使用类似 C 的语法。实例化模块时,端口根据模块的声明从左到右连接。
mod_a instance1 ( wa, wb, wc );This instantiates a module of type mod_a and gives it an instance name of "instance1", then connects signal wa (outside the new module) to the first port (in1) of the new module, wb to the second port (in2), and wc to the third port (out). One drawback of this syntax is that if the module's port list changes, all instantiations of the module will also need to be found and changed to match the new module.
实例化一个 mod_a 类型的模块,并给它一个实例名称“instance1”,然后将信号 wa(在新模块外部)连接到新模块的第一个端口(in1),将 wb 连接到第二个端口(in2),然后wc 到第三个端口(出)。这种语法的一个缺点是,如果模块的端口列表发生更改,则还需要找到并更改模块的所有实例以匹配新模块。
By name
Connecting signals to a module's ports by name allows wires to remain correctly connected even if the port list changes. This syntax is more verbose, however.
按名称将信号连接到模块的端口可以使电线保持正确连接,即使端口列表发生更改。然而,这种语法更加冗长。
mod_a instance2 ( .out(wc), .in1(wa), .in2(wb) );The above line instantiates a module of type mod_a named "instance2", then connects signal wa (outside the module) to the port named in1, wb to the port named in2, and wc to the port named out. Notice how the ordering of ports is irrelevant here because the connection will be made to the correct name, regardless of its position in the sub-module's port list. Also notice the period immediately preceding the port name in this syntax.
上面的行实例化了一个名为“instance2”的 mod_a 类型的模块,然后将信号 wa(模块外部)连接到名为 in1 的端口,将 wb 连接到名为 in2 的端口,将 wc 连接到名为 out 的端口。请注意这里的端口顺序是如何无关的,因为无论其在子模块端口列表中的位置如何,都将使用正确的名称进行连接。还要注意此语法中端口名称之前的句点。
Module Declaration
module top_module ( input a, input b, output out );
module top_module (
input a,
input b,
output out
);
// Create an instance of "mod_a" named "inst1", and connect ports by name:
mod_a inst1 (
.in1(a), // Port"in1"connects to wire "a"
.in2(b), // Port "in2" connects to wire "b"
.out(out) // Port "out" connects to wire "out"
// (Note: mod_a's port "out" is not related to top_module's wire "out".
// It is simply coincidence that they have the same name)
);
/*
// Create an instance of "mod_a" named "inst2", and connect ports by position:
mod_a inst2 ( a, b, out ); // The three wires are connected to ports in1, in2, and out, respectively.
*/
endmodule
最后
以上就是潇洒魔镜最近收集整理的关于Verilog之Module模块 Connecting Signals to Module Ports的全部内容,更多相关Verilog之Module模块 Connecting内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复