2021年12月
北京
xxd
五、Netty核心模块
1、Bootstrap、ServerBootstrap
Bootstrap 意思是引导,一个 Netty 应用通常由一个 Bootstrap 开始,主要作用是配置整个 Netty 程序,串联各个组件,Netty 中 Bootstrap 类是客户端程序的启动引导类,ServerBootstrap 是服务端启动引导类。
常见的方法有
public ServerBootstrap group(EventLoopGroup parentGroup, EventLoopGroup childGroup),:该方法用于服务器端,用来设置两个 EventLoop
public B group(EventLoopGroup group),:该方法用于客户端,用来设置一个 EventLoop
public B channel(Class<? extends C> channelClass),:该方法用来设置一个服务器端的通道实现
public <T> B option(ChannelOption<T> option, T value),:用来给 ServerChannel 添加配置
public <T> ServerBootstrap childOption(ChannelOption<T> childOption, T value),:用来给接收到的通道添加配置
public ServerBootstrap childHandler(ChannelHandler childHandler),:该方法用来设置业务处理类(自定义的handler)
public ChannelFuture bind(int inetPort),:该方法用于服务器端,用来设置占用的端口号
public ChannelFuture connect(String inetHost, int inetPort),:该方法用于客户端,用来连接服务器端
2、Future、ChannelFuture
Netty 中所有的 IO 操作都是异步的,不能立刻得知消息是否被正确处理。但是可以过一会等它执行完成或者直接注册一个监听,具体的实现就是通过 Future 和 ChannelFutures,他们可以注册一个监听,当操作执行成功或失败时监听会自动触发注册的监听事件
常见的方法有
Channel channel(),返回当前正在进行 IO 操作的通道
ChannelFuture sync(),等待异步操作执行完毕
3、Channel
Netty 网络通信的组件,能够用于执行网络 I/O 操作。
通过 Channel 可获得当前网络连接的通道的状态
通过 Channel 可获得网络连接的配置参数(例如接收缓冲区大小)
Channel 提供异步的网络 I/O 操作(如建立连接,读写,绑定端口),异步调用意味着任何 I/O 调用都将立即返回,并且不保证在调用结束时所请求的 I/O 操作已完成
调用立即返回一个 ChannelFuture 实例,通过注册监听器到 ChannelFuture 上,可以 I/O 操作成功、失败或取消时回调通知调用方
支持关联 I/O 操作与对应的处理程序
不同协议、不同的阻塞类型的连接都有不同的 Channel 类型与之对应,常用的 Channel 类型:
NioSocketChannel,异步的客户端 TCP Socket 连接。
NioServerSocketChannel,异步的服务器端 TCP Socket 连接。
NioDatagramChannel,异步的 UDP 连接。
NioSctpChannel,异步的客户端 Sctp 连接。
NioSctpServerChannel,异步的 Sctp 服务器端连接,这些通道涵盖了 UDP 和 TCP 网络 IO 以及文件 IO。
4、Selector
Netty 基于 Selector 对象实现 I/O 多路复用,通过 Selector 一个线程可以监听多个连接的 Channel 事件。
当向一个 Selector 中注册 Channel 后,Selector 内部的机制就可以自动不断地查询(Select)这些注册的 Channel 是否有已就绪的 I/O 事件(例如可读,可写,网络连接完成等),这样程序就可以很简单地使用一个线程高效地管理多个 Channel
5、ChannelHandler 及其实现类
ChannelHandler是一个接口,处理 I/O 事件或拦截 I/O 操作,并将其转发到其 ChannelPipeline(业务处理链)中的下一个处理程序。ChannelHandler本身并没有提供很多方法,因为这个接口有许多的方法需要实现,方便使用期间,可以继承它的子类
几个重要的实现类和方法
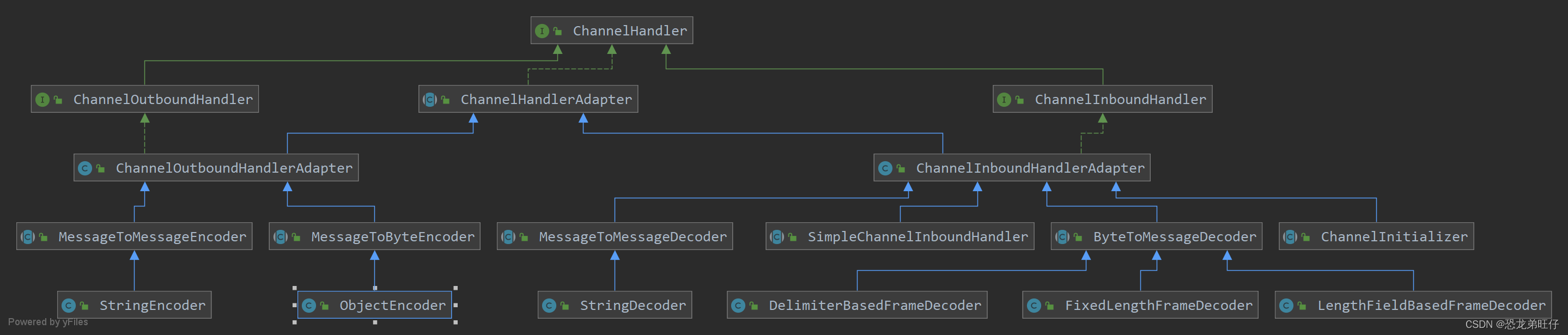
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter的一些简单的方法,其他的channelHandler中也大致都有这些方法
public class ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter extends ChannelHandlerAdapter implements ChannelInboundHandler {
/**
* 将通道注册到selector中
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void channelUnregistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
}
/**
* 通道就绪事件
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
}
/**
*
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
}
/**
* 通道读取数据事件
* @param ctx
* @param msg
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
}
/**
* 数据读取完毕事件
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void channelWritabilityChanged(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
}
}
6、Pipeline 和 ChannelPipeline
ChannelPipeline 是一个重点:
ChannelPipeline 是一个 Handler 的集合,它负责处理和拦截 inbound 或者 outbound 的事件和操作,相当于一个贯穿 Netty 的链。
(也可以这样理解:ChannelPipeline 是保存 ChannelHandler 的 List,用于处理或拦截 Channel 的入站事件和出站操作)
ChannelPipeline 实现了一种高级形式的拦截过滤器模式,使用户可以完全控制事件的处理方式,以及 Channel 中各个的 ChannelHandler 如何相互交互
在 Netty 中每个 Channel 都有且仅有一个 ChannelPipeline 与之对应,它们的组成关系如下
一个channel包含一个Channelpipeline,而Channelpipeline中又维护了一个由ChannelHnadlerContext组成的双向链表,并且每个ChannelHandlerContext中又关联着一个ChannelHandler
入栈事件和出栈事件在一个双向链表中,入栈事件会从链表head往后传递到最后一个入栈的handler,出栈事件会从链表tail往前传递到最后一个出栈的handler,两种类型的handler互补干扰,
ChannelPipeline addFirst(ChannelHandler… handlers),把一个业务处理类(handler)添加到链中的第一个位置ChannelPipeline addLast(ChannelHandler… handlers),把一个业务处理类(handler)添加到链中的最后一个位置
7、ChannelHandlerContext
保存 Channel 相关的所有上下文信息,同时关联一个 ChannelHandler 对象
即 ChannelHandlerContext 中包含一个具体的事件处理器 ChannelHandler,同时 ChannelHandlerContext 中也绑定了对应的 pipeline 和 Channel 的信息,方便对 ChannelHandler 进行调用。
常用方法
ChannelFuture close(),关闭通道
ChannelOutboundInvoker flush(),刷新
ChannelFuture writeAndFlush(Object msg),将数据写到
ChannelPipeline 中当前 ChannelHandler 的下一个 ChannelHandler 开始处理(出站)
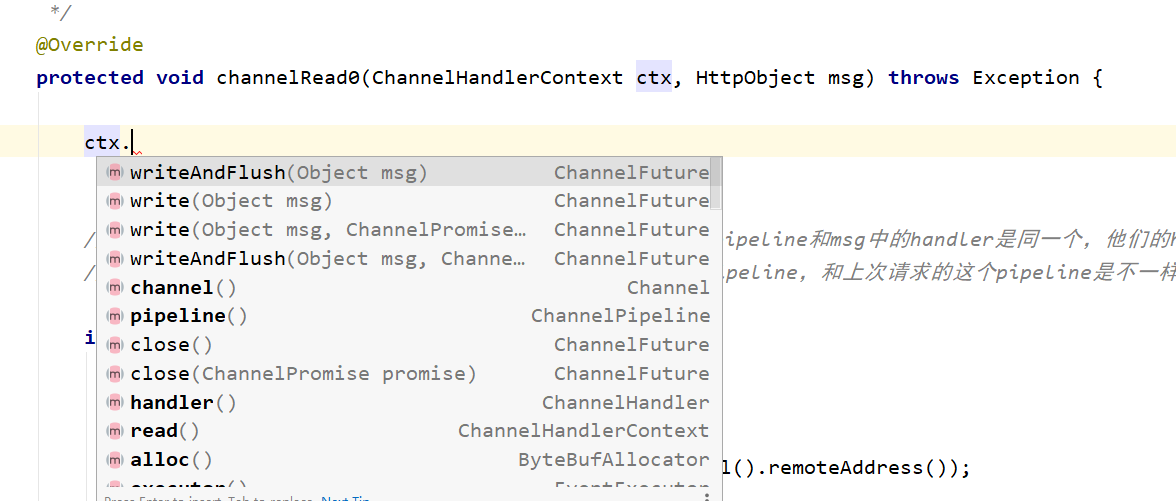
从这个对应的context中可以获取到channel和pipeline。然后从这个handler或者是pipeline中的pro或者next中又可以找到其他的handler或者pipeline。
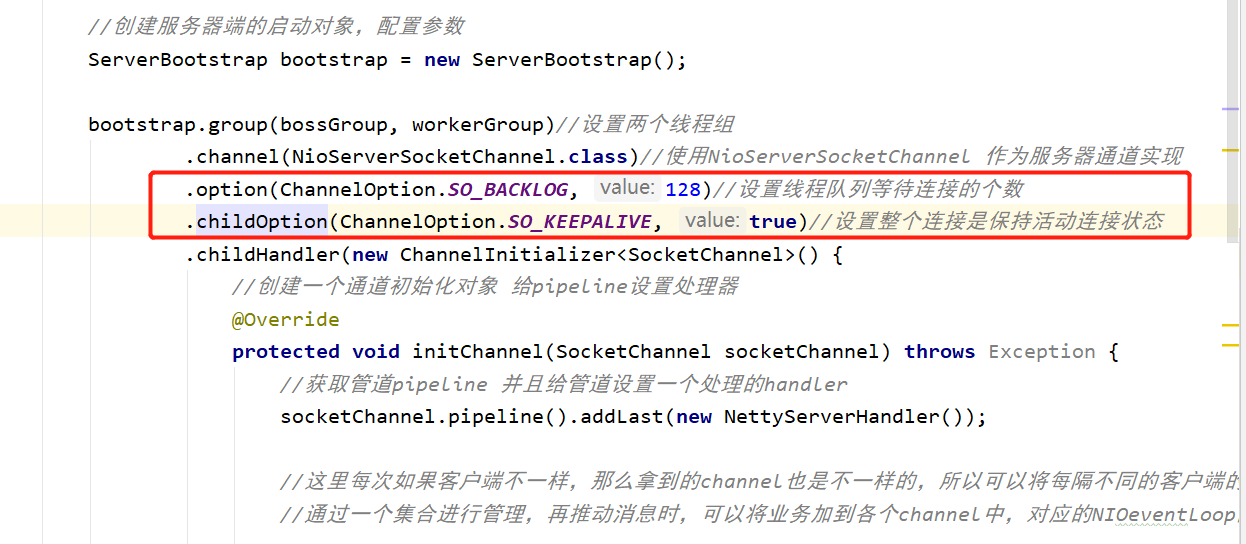
8、ChannelOption
在链式编程中
Netty 在创建 Channel 实例后,一般都需要设置 ChannelOption 参数。
在创建客户端的启动的时候,就需要设置这个oprion参数。
9、EventLoopGroup 和 NioEventLoopGroup
EventLoopGroup 是一组 EventLoop 的抽象,Netty 为了更好的利用多核 CPU 资源,一般会有多个 EventLoop 同时工作,每个 EventLoop 维护着一个 Selector 实例。
EventLoopGroup 提供 next 接口,可以从组里面按照一定规则获取其中一个 EventLoop 来处理任务。在 Netty 服务器端编程中,我们一般都需要提供两个 EventLoopGroup,例如:BossEventLoopGroup 和 WorkerEventLoopGroup。
通常一个服务端口即一个 ServerSocketChannel 对应一个 Selector 和一个 EventLoop 线程。BossEventLoop 负责接收客户端的连接并将 SocketChannel 交给 WorkerEventLoopGroup 来进行 IO 处理。
常用方法
public NioEventLoopGroup(),构造方法
public Future<?> shutdownGracefully(),断开连接,关闭线程
10、Unpooled 类
Netty 提供一个专门用来操作缓冲区(即 Netty 的数据容器)的工具类
主要是利用内部的一些处理将 这个buffer分成了三个区域,可读,可写,已读这样三个区域。
而普通的buffer是通过反转实现单独的读或者单独的写操作的。
11、Netty 心跳检测机制案例
netty内部已经封装了心跳检测的机制,我们可以自己设置,当一定的时间内没有发生读操作、写操作、读写操作的时候,就会触发相应的心跳检测。(读写操作都是针对于服务器端的,客户端向服务器端发送数据,服务器端此时就是读操作)
案例
- 编写一个
Netty心跳检测机制案例,当服务器超过3秒没有读时,就提示读空闲 - 当服务器超过
5秒没有写操作时,就提示写空闲 - 实现当服务器超过
7秒没有读或者写操作时,就提示读写空闲
服务端开启日志,同时开启心跳检测机制。
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);//1个
NioEventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();//8个
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))//在bossGroup端增加一个日志处理器
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
/**
* 加入一个netty提供的处理空闲状态的处理器
* readeridelTime :表示有多久时间没有读了,就会发送一个心跳检测包,检测是否还是连接状态
* writerIdelTime :表示还有多长时间没有写了,超过时间就会发送一个心跳检测包
* allIdelTime : 表示多长时间没有读和写了,超过时间发送心跳检测
* 当每一额 IdelTime被出发后机会传递给下一个handler去处理相关的内容
* 会通过下一个handler的userEventTiggered去处理
*
*/
pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(3,5,7, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
pipeline.addLast(new MyServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(7000).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
服务器端对应的处理器
public class MyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/**
*
* @param ctx 上下文
* @param evt 事件
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception {
if(evt instanceof IdleStateEvent){
IdleStateEvent event = (IdleStateEvent) evt;
String eventType = "";
switch (event.state()){
case ALL_IDLE:
eventType = "读写空闲";
break;
case READER_IDLE:
eventType = "读空闲";
break;
case WRITER_IDLE:
eventType = "写空闲";
break;
}
System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress()+"----超时事件发生:"+eventType);
System.out.println("服务器做相应的处理...");
}
}
}
12、编码解码器 protobuf使用
-
是一种轻便高效的结构化数据存储格式,可以用于结构化数据串行化(序列化) 很适合做数据存储或者是RPC (remote procedure call 远程过程调用)数据交换格式。
http+json -> protobuf+tcp 向这样的数据交互格式进行转型,
-
protobuf是以message来做数据管理的。
-
支持跨平台,跨语言。
使用
导入依赖
<!--protobuf 做编码解码操作的-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.protobuf</groupId>
<artifactId>protobuf-java</artifactId>
<version>3.16.1</version>
</dependency>
下载对应的protobuf的软件
下载地址
这里需要注意的是,在maven里面导入依赖的时候,选择的版本需要和这个一致,不然就会导致后面生成的java代码报错,缺少相关的类 我这里都使用的是 3.16.1 后续使用测试都可
protoc-3.16.1-win32.zip
编写对应的proto文件
这里直接使用的是多对象的方式,单对象基本类似,只是更加简单。
创建两个对象 student worker
syntax = "proto3";
option optimize_for = SPEED;
option java_package = "cn.nssc.netty.codec2";
option java_outer_classname = "MyDataInfo";
//proto可以使用message管理其他message
message MyMessage{
enum DataType{
StudentType = 0;//从proto3后要求编号从0开始
WorkerType = 1;
}
//用data_type 来标识传递进来的是哪一个属性
DataType data_type = 1;
//表示每次枚举类型最多只能出现这两种类型其中的一个,可以及节省空间
oneof dataBody{
Student student = 2;
Worker worker = 3;
}
}
message Student{
int32 id = 1;
string name = 2;
}
message Worker{
string name = 1;
int32 age = 2;
}
生成java文件命令
protoc.exe --java_out=. Student.proto
服务端server
public class NettyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
/**
* 创建BossGroup workGroup
* 创建两个线程组,bossGroup只处理连接请求,真正的客户端业务处理都交给workGroup处理
* 这两个线程都是死循环
*/
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();//默认实际创建cpu核心数 *2 个线程
//workerGroup默认实际创建cpu核心数 *2 个线程 分配机制 默认采用子线程轮询处理客户端的数据通信
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
//创建服务器端的启动对象,配置参数
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)//设置两个线程组
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)//使用NioServerSocketChannel 作为服务器通道实现
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)//设置线程队列等待连接的个数
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)//设置整个连接是保持活动连接状态
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
//创建一个通道初始化对象 给pipeline设置处理器
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
//加入解码器
//需要指定对那种对象进行解码
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast("decoder",new ProtobufDecoder(MyDataInfo.MyMessage.getDefaultInstance()));
//获取管道pipeline 并且给管道设置一个处理的handler
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new NettyServerHandler());
//这里每次如果客户端不一样,那么拿到的channel也是不一样的,所以可以将每隔不同的客户端的channel
//通过一个集合进行管理,再推动消息时,可以将业务加到各个channel中,对应的NIOeventLoop的taskQueue或者scheduleTakQueue
}
});//设置处理器给workGroup的EventLoop 对应的管道设置处理器
System.out.println("server is really.....");
//设置保持活动连接状态
//绑定一个端口 并且同步,生成一个channelFuture对象 启动服务器
ChannelFuture cf = bootstrap.bind(6688).sync();
//自己加一个监听器
cf.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception {
if(channelFuture.isSuccess()){
System.out.println("监听端口6688成功");
}else{
System.out.println("监听端口6688失败");
}
}
});
//对关闭通道进行监听 当有关闭通道的事件的时候才会关闭
cf.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
//优雅的关闭work和boss
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
server处理handler
public class NettyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/**
* 当通道就绪就会触发这个方法
*
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
int random = new Random().nextInt(3);
MyDataInfo.MyMessage myMessage = null;
if (random == 0) {
myMessage = MyDataInfo.MyMessage.newBuilder()
.setDataType(MyDataInfo.MyMessage.DataType.StudentType)
.setStudent(MyDataInfo.Student.newBuilder().setId(5).setName("多对象测试...").build())
.build();
} else {
myMessage = MyDataInfo.MyMessage.newBuilder()
.setDataType(MyDataInfo.MyMessage.DataType.WorkerType)
.setWorker(MyDataInfo.Worker.newBuilder().setName("测试-worker").setAge(25).build())
.build();
}
//将数据刷写出去
ctx.writeAndFlush(myMessage);
}
/**
* 拿到服务器端回复的消息
* channelRead 表示有数据可读了
*
* @param ctx
* @param msg
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//正常阻塞处理原始数据接收发送
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("服务器回复的消息2: " + buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("服务器端地址: " + ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
//使用taskQueue进行优化
//这里是接授客户端的数据信息,但是如果出现了这里的处理逻辑非常负责,这时候我们可以采用异步的方式,来处理这个请求
//NIOEventLoop 的taskQueue中
//用户自定义任务,进行异步执行 任务都会提交到对应的taskQueue中
ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("服务器回复的消息1: " + buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
});
//用户自定义定时任务,进行异步执行,任务都会提交到sceduleTaskQueue中
ctx.channel().eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("隔5秒异步执行一次,服务端回复的消息3...");
}
}, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/**
* 发生异常关闭客户端
*
* @param ctx
* @param cause
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
ctx.close();
}
}
客户端client
public class NettyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//创建客户端的循环事件组
NioEventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//创建一个客户端的启动对象
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
try {
//设置相关参数
bootstrap.group(eventLoopGroup)//设置线程组
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)//设置客户端通道的实现类
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
//在pipeline中加入protobufEncoder
pipeline.addLast("encoder",new ProtobufEncoder());
pipeline.addLast(new NettyClientHandler());//加入自己的处理器
}
});
System.out.println("client is ok....");
//启动客户端连接服务器端 channelFuture涉及到netty的异步模型
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 6688).sync();
//给关闭通道增加一个连接 进行监听 r如果出现了关闭事件 则关闭通道
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
eventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
客户端处理 clientHandler
public class NettyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/**
* 当通道就绪就会触发这个方法
*
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
int random = new Random().nextInt(3);
MyDataInfo.MyMessage myMessage = null;
if (random == 0) {
myMessage = MyDataInfo.MyMessage.newBuilder()
.setDataType(MyDataInfo.MyMessage.DataType.StudentType)
.setStudent(MyDataInfo.Student.newBuilder().setId(5).setName("多对象测试...").build())
.build();
} else {
myMessage = MyDataInfo.MyMessage.newBuilder()
.setDataType(MyDataInfo.MyMessage.DataType.WorkerType)
.setWorker(MyDataInfo.Worker.newBuilder().setName("测试-worker").setAge(25).build())
.build();
}
//将数据刷写出去
ctx.writeAndFlush(myMessage);
}
/**
* 拿到服务器端回复的消息
* channelRead 表示有数据可读了
*
* @param ctx
* @param msg
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//正常阻塞处理原始数据接收发送
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("服务器回复的消息2: " + buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("服务器端地址: " + ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
//使用taskQueue进行优化
//这里是接授客户端的数据信息,但是如果出现了这里的处理逻辑非常负责,这时候我们可以采用异步的方式,来处理这个请求
//NIOEventLoop 的taskQueue中
//用户自定义任务,进行异步执行 任务都会提交到对应的taskQueue中
ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("服务器回复的消息1: " + buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
});
//用户自定义定时任务,进行异步执行,任务都会提交到sceduleTaskQueue中
ctx.channel().eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("隔5秒异步执行一次,服务端回复的消息3...");
}
}, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/**
* 发生异常关闭客户端
*
* @param ctx
* @param cause
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
ctx.close();
}
}
服务端打印结果:
server is really.....
监听端口6688成功
stu: 5多对象测试...
stu: 5多对象测试...
worker: 测试-worker25
六、Netty应用实例-群聊系统
案例
编写一个 Netty 群聊系统,实现服务器端和客户端之间的数据简单通讯(非阻塞)
实现多人群聊
服务器端:可以监测用户上线,离线,并实现消息转发功能
客户端:通过 channel 可以无阻塞发送消息给其它所有用户,同时可以接受其它用户发送的消息(有服务器转发得到
服务器端
public class GroupChatServer {
private int port;
public GroupChatServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
//编写run方法 处理客户端请求
public void run() throws InterruptedException {
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);//1个
NioEventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();//8个
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
try {
bootstrap.group(bossGroup,workGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,true)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
//向pipeline中添加一个解码器
pipeline.addLast("decoder",new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder",new StringEncoder());
//加入自己的业务处理handler
pipeline.addLast(new GroupChatServerHandler());
}
});
System.out.println("netty服务器启动");
//关闭
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
//异步关闭
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//启动服务端
GroupChatServer groupChetServer = new GroupChatServer(7000);
groupChetServer.run();
}
}
服务端的handler
public class GroupChatServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String> {
//定义一个channel组 管理所有的cchannel
//GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE是一个全局的事件执行器,是一个单例
private static ChannelGroup channelGroup = new DefaultChannelGroup(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE);
public static HashMap<String,Channel> channels = new HashMap<>();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
/**
* 表示连接建立,第一个被执行
*
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//将当前的channel加入到ChannelGroup
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
//将该客户加入聊天的信息之后,推送给其他客户端
ctx.writeAndFlush("[客户端]" + channel.remoteAddress() + "加入聊天n");//将channelGroup中所有的channel遍历,并且发送消息,不需要我们自己遍历
channelGroup.add(channel);
channels.put(channel.remoteAddress().toString(),channel);
}
/**
* 断开连接
*
* @param ctx
*/
@Override
public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
channelGroup.writeAndFlush("客户端" + channel.remoteAddress() + "离开了....n");
System.out.println("当前群聊活动人数: " + channelGroup.size());
}
/**
* 表示channel处于活动状态 提示xxx上线了
*
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + " 上线了...");
}
/**
* 提示离线
*
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + " 下线了...");
}
/**
* 读取数据 转发给客户端数据
*
* @param ctx
* @param msg
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception {
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
//遍历channelGroup 根据不同情况,处理
channelGroup.forEach(ch -> {
if (channel != ch) {//不是本人
ch.writeAndFlush("[客户]" + channel.remoteAddress() + " " + sdf.format(new Date()) + " 发送消息 " + msg + "n");
} else {
ch.writeAndFlush("[自己] 发送了消息 " + " " + sdf.format(new Date()) + " " + msg + "n");
}
});
}
/**
* 异常关闭通道
*
* @param ctx
* @param cause
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
ctx.channel().close();
}
}
客户端
public class GroupChatClient {
private String host;
private int port;
public GroupChatClient() {
}
public GroupChatClient(String host, int port) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
public void run() throws InterruptedException {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
try {
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
pipeline.addLast(new GroupChatClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect(host, port).sync();
Channel channel = channelFuture.channel();
System.out.println("channelLocal:" + channel.remoteAddress());
//客户端需要输入信息
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNext()) {
String msg = scanner.nextLine();
channel.writeAndFlush(msg + "rn");
}
channelFuture.channel().close();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
GroupChatClient groupChatClient = new GroupChatClient("127.0.0.1", 7000);
groupChatClient.run();
}
}
客户端的handler
public class GroupChatClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("msg: "+msg.trim());
}
}
七、WebSocket长链接
服务器端,使用netty其他的大致一样,主要是在handler中的处理,还有往pipeline中添加的处理流不一样
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpObjectAggregator;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpServerCodec;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.WebSocketServerProtocolHandler;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import io.netty.handler.stream.ChunkedWriteHandler;
/**
* @Author: kelezhu2020@163.com
* @Date: 2022/1/9 8:09
*/
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);//1个
NioEventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();//8个
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))//在bossGroup端增加一个日志处理器
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
/**
* 基于http的协议 webSocket来实现
*/
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
//是以块进行处理的,添加一个chunkWriterHandler处理器
pipeline.addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler());
/**
* 因为http的数据在传输的过程中是分段的
* HttpObjectAggregator就是可以将多个段聚合起来
* 当浏览器发生大量的数据的时候,就会发出多次http请求
*/
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(8192));
/**
* 对于webSocket的数据而言是以帧(frame)的形式传递的
* webSocketFrame下面有6个子类
* 浏览器请求 ws://localhost:7000/xxx 表示请求的一个uri
* WebSocketServerProtocolHandler 核心是将http的协议升级为一个ws协议(长链接)
*
* 原理: 通过一个状态码101来进行切换的
*
*/
pipeline.addLast(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/hello"));
//自定义handler,处理ws的协议数据
pipeline.addLast(new MyWebSocketServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(7000).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
handler处理
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.TextWebSocketFrame;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
/**
* @Author: kelezhu2020@163.com
* @Date: 2022/1/9 8:23
* TextWebSocketFrame 表示是一个文本帧(frame)
*/
public class MyWebSocketServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<TextWebSocketFrame> {
/**
* 接收消息
* @param ctx
* @param msg
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, TextWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("服务器端收到消息: "+msg.text());
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame("服务器端时间"+ LocalDateTime.now()+"msg: "+msg.text()));
}
/**
* 当web客户端连接后出发方法
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//id表示唯一的值, LongText是唯一的 ShortText不一定唯一
System.out.println("handler被调用"+ctx.channel().id().asLongText());
System.out.println("handler被调用"+ctx.channel().id().asShortText());
}
/**
* 当handler被移除之后调用
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("handlerRemove被调用"+ctx.channel().id().asLongText());
}
/**
* 异常处理
* @param ctx
* @param cause
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
System.out.println("发生异常,关闭服务端....");
ctx.close();
}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>webSocket-test</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var socket;
//判断当前浏览器是否支持websocket
if(window.WebSocket) {
//go on
socket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:7000/hello");
//相当于channelRead0, ev 收到服务器端回送的消息
socket.onmessage = function (ev) {
var rt = document.getElementById("responseText");
rt.value = rt.value + "n" + ev.data;
}
//相当于连接开启(感知到连接开启)
socket.onopen = function (ev) {
var rt = document.getElementById("responseText");
rt.value = "连接开启了.."
}
//相当于连接关闭(感知到连接关闭)
socket.onclose = function (ev) {
var rt = document.getElementById("responseText");
rt.value = rt.value + "n" + "连接关闭了.."
}
} else {
alert("当前浏览器不支持websocket")
}
//发送消息到服务器
function send(message) {
if(!window.socket) { //先判断socket是否创建好
return;
}
if(socket.readyState == WebSocket.OPEN) {
//通过socket 发送消息
socket.send(message)
} else {
alert("连接没有开启");
}
}
</script>
<form onsubmit="return false">
<textarea name="message" style="height: 300px; width: 300px"></textarea>
<input type="button" value="发送消息" onclick="send(this.form.message.value)">
<textarea id="responseText" style="height: 300px; width: 300px"></textarea>
<input type="button" value="清空内容" onclick="document.getElementById('responseText').value=''">
</form>
</body>
</html>
服务器端后台调用展示,当浏览器启动一个之后就会生成唯一的id。然后当浏览器关闭当前窗口的时候,这个removeHandler就会被调用
一月 09, 2022 9:06:44 上午 io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler channelRead
信息: [id: 0xb1961bd5, L:/0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:7000] READ: [id: 0x195ad594, L:/0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1:7000 - R:/0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1:1097]
一月 09, 2022 9:06:44 上午 io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler channelReadComplete
信息: [id: 0xb1961bd5, L:/0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0:7000] READ COMPLETE
handler被调用005056fffec00001-00005190-00000004-1e4d24ea4a9d97ef-195ad594
handler被调用195ad594
服务器端收到消息: msg send success
handlerRemove被调用005056fffec00001-00005190-00000004-1e4d24ea4a9d97ef-195ad594
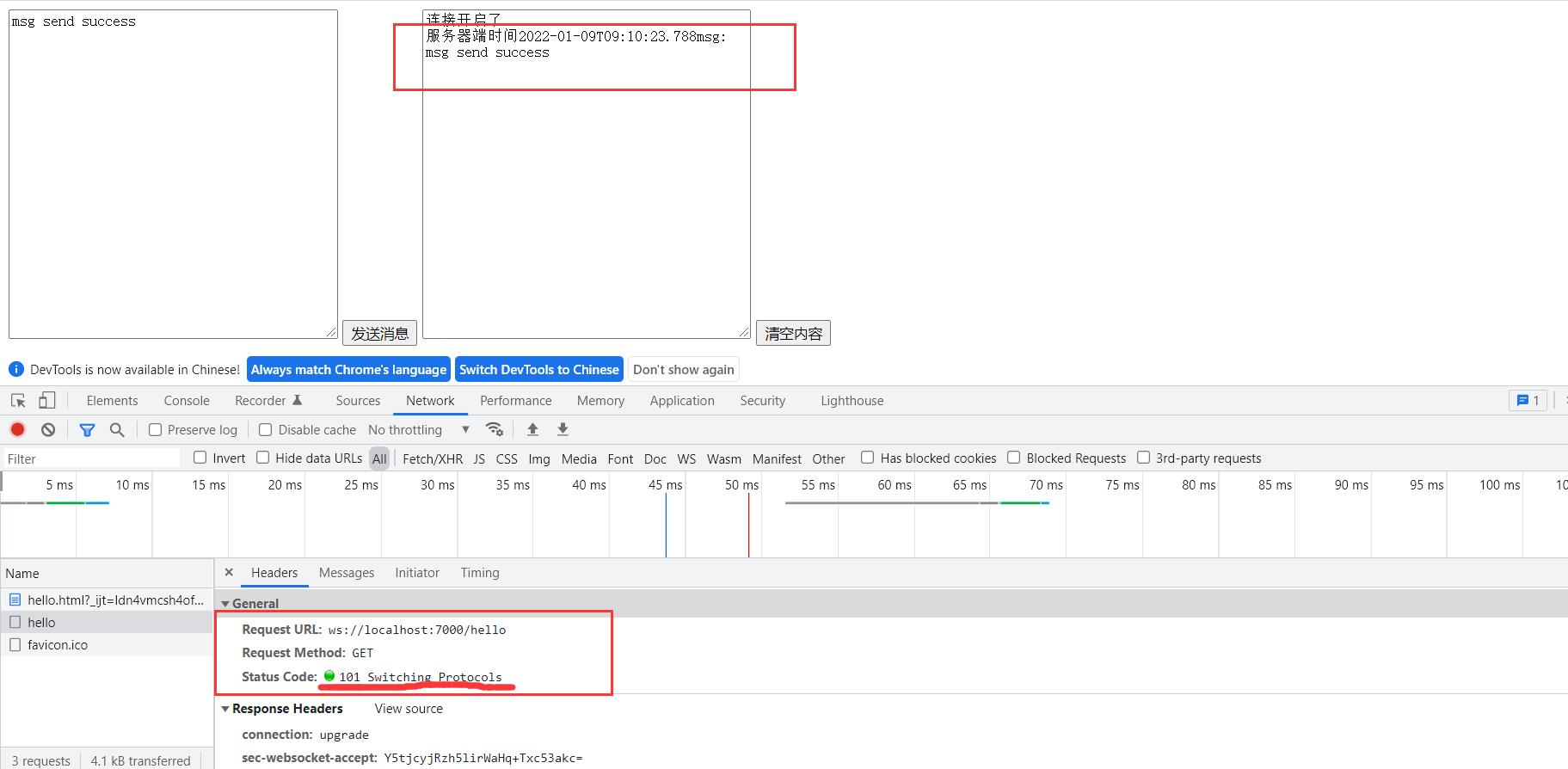
同时当服务器端关闭了之后,前端也会自动感知到。通过保持这样一个长链接,可以很轻松的实现前后端数据的持续交互。
八、Netty 编解码器和 Handler 调用机制
Netty 的组件设计:Netty 的主要组件有 Channel、EventLoop、ChannelFuture、ChannelHandler、ChannelPipe 等
ChannelHandler 充当了处理入站和出站数据的应用程序逻辑的容器。例如,实现 ChannelInboundHandler 接口(或 ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter),你就可以接收入站事件和数据,这些数据会被业务逻辑处理。当要给客户端发送响应时,也可以从 ChannelInboundHandler 冲刷数据。业务逻辑通常写在一个或者多个 ChannelInboundHandler 中。ChannelOutboundHandler 原理一样,只不过它是用来处理出站数据的
ChannelPipeline 提供了 ChannelHandler 链的容器。以客户端应用程序为例,如果事件的运动方向是从客户端到服务端的,那么我们称这些事件为出站的,即客户端发送给服务端的数据会通过 pipeline 中的一系列 ChannelOutboundHandler,并被这些 Handler 处理,反之则称为入站的。
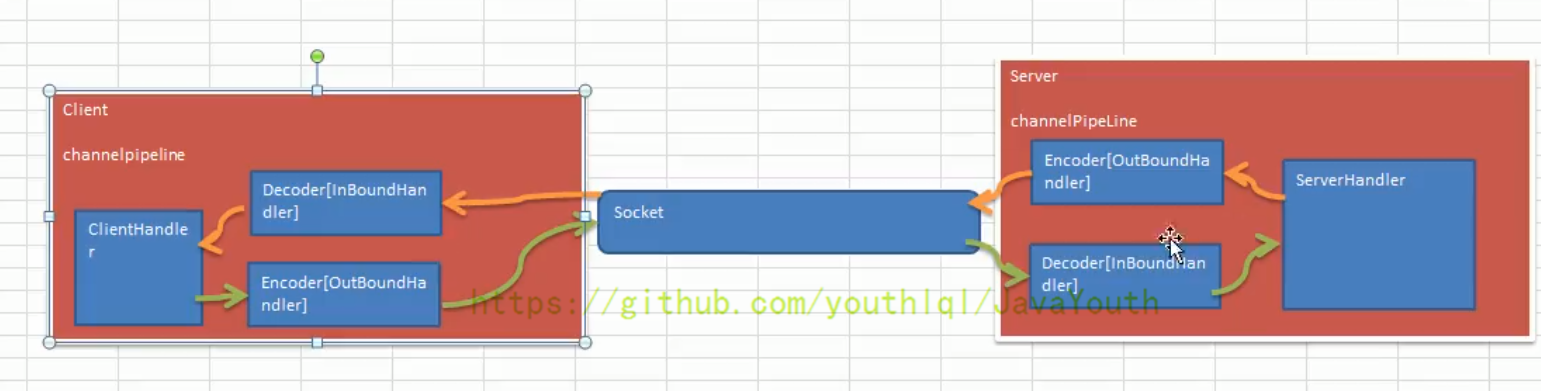
编码解码器
当 Netty 发送或者接受一个消息的时候,就将会发生一次数据转换。入站消息会被解码:从字节转换为另一种格式(比如 java 对象);如果是出站消息,它会被编码成字节。
Netty 提供一系列实用的编解码器,他们都实现了 ChannelInboundHadnler 或者 ChannelOutboundHandler 接口。在这些类中,channelRead 方法已经被重写了。以入站为例,对于每个从入站 Channel 读取的消息,这个方法会被调用。随后,它将调用由解码器所提供的 decode() 方法进行解码,并将已经解码的字节转发给 ChannelPipeline 中的下一个 ChannelInboundHandler。
解码器 - ByteToMessageDecoder
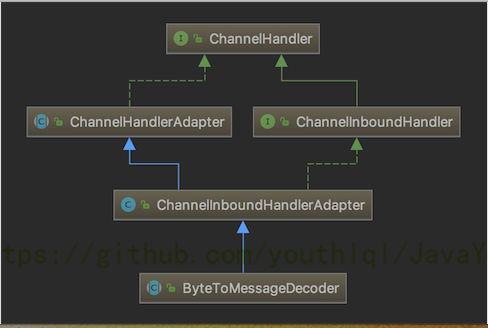
- 由于不可能知道远程节点是否会一次性发送一个完整的信息,
tcp有可能出现粘包拆包的问题,这个类会对入站数据进行缓冲,直到它准备好被处理.【后面有说TCP的粘包和拆包问题】 - 一个关于
ByteToMessageDecoder实例分析
/**
* @param channelHandlerContext 上下文对象
* @param byteBuf 入栈的bytebuf
* @param list list集合,将解码后的数据传给下一个handler
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf byteBuf, List<Object> list) throws Exception {
//long 8个字节
//这里判断,需要有8个字节之后才能读取一个long
if(byteBuf.readableBytes() >= 8){
list.add(byteBuf.readLong());
}
Netty的handler链的调用机制
出站入站
关于出站入站,很多人可能有点迷糊
1)客户端有出站入站,服务端也有出站入站
2)以客户端为例,如果有服务端传送的数据到达客户端,那么对于客户端来说就是入站;
如果客户端传送数据到服务端,那么对于客户端来说就是出站;
同理,对于服务端来说,也是一样的,有数据来就是入站,有数据输出就是出站
3)为什么服务端和客户端的Serverhandler都是继承SimpleChannelInboundHandler,而没有ChannelOutboundHandler出站类?
实际上当我们在handler中调用ctx.writeAndFlush()方法后,就会将数据交给ChannelOutboundHandler进行出站处理,只是我们没有去定义出站类而已,若有需求可以自己去实现ChannelOutboundHandler出站类
4)总结就是客户端和服务端都有出站和入站的操作
**服务端发数据给客户端:**服务端—>出站—>Socket通道—>入站—>客户端
**客户端发数据给服务端:**客户端—>出站—>Socket通道—>入站—>服务端
解码器 - ReplayingDecoder
public abstract class ReplayingDecoder<S> extends ByteToMessageDecoder
ReplayingDecoder 扩展了 ByteToMessageDecoder 类,使用这个类,我们不必调用 readableBytes() 方法,也就不用判断还有没有足够的数据来读取。参数 S 指定了用户状态管理的类型,其中 Void 代表不需要状态管理
package com.atguigu.netty.inboundhandlerandoutboundhandler;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.ReplayingDecoder;
import java.util.List;
public class MyByteToLongDecoder2 extends ReplayingDecoder<Void> {
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyByteToLongDecoder2 被调用");
//在 ReplayingDecoder 不需要判断数据是否足够读取,内部会进行处理判断
out.add(in.readLong());
}
}
ReplayingDecoder 使用方便,但它也有一些局限性:
并不是所有的 ByteBuf 操作都被支持,如果调用了一个不被支持的方法,将会抛出一个 UnsupportedOperationException。
ReplayingDecoder 在某些情况下可能稍慢于 ByteToMessageDecoder,例如网络缓慢并且消息格式复杂时,消息会被拆成了多个碎片,速度变慢
其他解码器
LineBasedFrameDecoder:这个类在 Netty 内部也有使用,它使用行尾控制字符(n或者rn)作为分隔符来解析数据。
DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder:使用自定义的特殊字符作为消息的分隔符。
HttpObjectDecoder:一个 HTTP 数据的解码器
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder:通过指定长度来标识整包消息,这样就可以自动的处理黏包和半包消息。
九、TCP 粘包和拆包及解决方案
基本介绍
TCP 是面向连接的,面向流的,提供高可靠性服务。收发两端(客户端和服务器端)都要有一一成对的 socket,因此,发送端为了将多个发给接收端的包,更有效的发给对方,使用了优化方法(Nagle 算法),将多次间隔较小且数据量小的数据,合并成一个大的数据块,然后进行封包。这样做虽然提高了效率,但是接收端就难于分辨出完整的数据包了,因为面向流的通信是无消息保护边界的
由于 TCP 无消息保护边界,需要在接收端处理消息边界问题,也就是我们所说的粘包、拆包问题,看一张图
TCP 粘包、拆包图解
TCP 粘包和拆包解决方案
常用方案:使用自定义协议+编解码器来解决
关键就是要解决服务器端每次读取数据长度的问题,这个问题解决,就不会出现服务器多读或少读数据的问题,从而避免的 TCP 粘包、拆包。
一个案例
-
要求客户端发送
5个Message对象,客户端每次发送一个Message对象 -
服务器端每次接收一个
Message,分5次进行解码,每读取到一个Message,会回复一个Message对象给客户端。
MessageProtocol
//协议包
public class MessageProtocol {
private int len; //关键
private byte[] content;
public int getLen() {
return len;
}
public void setLen(int len) {
this.len = len;
}
public byte[] getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(byte[] content) {
this.content = content;
}
}
MyServer
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).childHandler(new MyServerInitializer()); //自定义一个初始化类
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(7000).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
MyServerInitializer
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
public class MyServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new MyMessageDecoder());//解码器
pipeline.addLast(new MyMessageEncoder());//编码器
pipeline.addLast(new MyServerHandler());
}
}
MyServerHandler
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.UUID;
//处理业务的handler
public class MyServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<MessageProtocol>{
private int count;
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
//cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageProtocol msg) throws Exception {
//接收到数据,并处理
int len = msg.getLen();
byte[] content = msg.getContent();
System.out.println("服务器接收到信息如下");
System.out.println("长度=" + len);
System.out.println("内容=" + new String(content, Charset.forName("utf-8")));
System.out.println("服务器接收到消息包数量=" + (++this.count));
//回复消息
System.out.println("服务端开始回复消息------");
String responseContent = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
int responseLen = responseContent.getBytes("utf-8").length;
byte[] responseContent2 = responseContent.getBytes("utf-8");
//构建一个协议包
MessageProtocol messageProtocol = new MessageProtocol();
messageProtocol.setLen(responseLen);
messageProtocol.setContent(responseContent2);
ctx.writeAndFlush(messageProtocol);
}
}
MyClient
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
public class MyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new MyClientInitializer()); //自定义一个初始化类
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 7000).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
MyClientInitializer
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
public class MyClientInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new MyMessageEncoder()); //加入编码器
pipeline.addLast(new MyMessageDecoder()); //加入解码器
pipeline.addLast(new MyClientHandler());
}
}
MyClientHandler
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class MyClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<MessageProtocol> {
private int count;
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//使用客户端发送10条数据 "今天天气冷,吃火锅" 编号
for(int i = 0; i< 5; i++) {
String mes = "今天天气冷,吃火锅";
byte[] content = mes.getBytes(Charset.forName("utf-8"));
int length = mes.getBytes(Charset.forName("utf-8")).length;
//创建协议包对象
MessageProtocol messageProtocol = new MessageProtocol();
messageProtocol.setLen(length);
messageProtocol.setContent(content);
ctx.writeAndFlush(messageProtocol);
}
}
// @Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageProtocol msg) throws Exception {
int len = msg.getLen();
byte[] content = msg.getContent();
System.out.println("客户端接收到消息如下");
System.out.println("长度=" + len);
System.out.println("内容=" + new String(content, Charset.forName("utf-8")));
System.out.println("客户端接收消息数量=" + (++this.count));
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
System.out.println("异常消息=" + cause.getMessage());
ctx.close();
}
}
MyMessageDecoder
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.ReplayingDecoder;
import java.util.List;
public class MyMessageDecoder extends ReplayingDecoder<Void> {
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("MyMessageDecoder decode 被调用");
//需要将得到二进制字节码-> MessageProtocol 数据包(对象)
int length = in.readInt();
byte[] content = new byte[length];
in.readBytes(content);
//封装成 MessageProtocol 对象,放入 out, 传递下一个handler业务处理
MessageProtocol messageProtocol = new MessageProtocol();
messageProtocol.setLen(length);
messageProtocol.setContent(content);
//放入out传给下一个hanlder进行处理
out.add(messageProtocol);
}
}
MyMessageEncoder
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToByteEncoder;
public class MyMessageEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<MessageProtocol> {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageProtocol msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyMessageEncoder encode 方法被调用");
out.writeInt(msg.getLen());
out.writeBytes(msg.getContent());
}
}
尚硅谷课程自己做的笔记 韩老师主讲
参考文章
https://blog.csdn.net/Youth_lql/article/details/115524052
文章typora (md)文档放在了阿里云盘需要自取
https://www.aliyundrive.com/s/Ff9JJZ55LRh
参考的尚硅谷的netty的资料 阿里云盘
https://www.aliyundrive.com/s/cxroPfwweyu
文章全文共4篇:
篇1: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43349416/article/details/122890716
篇2:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43349416/article/details/122890890
篇3:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43349416/article/details/122890914
篇4:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43349416/article/details/122890958
水平有限,有什么错误的地方欢迎留言指出,抱拳。
最后
以上就是务实故事最近收集整理的关于Netty学习笔记 - 2 (带源码分析部分)五、Netty核心模块六、Netty应用实例-群聊系统七、WebSocket长链接八、Netty 编解码器和 Handler 调用机制九、TCP 粘包和拆包及解决方案的全部内容,更多相关Netty学习笔记内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复