默认情况下,c++编译器至少给一个类添加3个函数
默认构造函数(无参,函数体为空)
默认析构函数(无参,函数体为空)
默认拷贝构造函数,对属性进行值拷贝
构造函数调用规则
1.如果用户定义了有参构造函数,c++不在提供默认无参构造,但是会提供默认拷贝构造函数
2.如果用户定义拷贝构造函数,c++不会再提供其他构造函数
验证编译器是否会自动提供拷贝构造函数:
class Person
{
public:
Person()
{
cout << "Person的默认构造函数调用" << endl;
}
Person(int age)
{
cout << "Person的有参构造函数调用" << endl;
m_Age = age;
}
Person(const Person& p)
{
cout << "Person的拷贝构造函数调用" << endl;
m_Age = p.m_Age;
}
~Person()
{
cout << "Person的析构构函数调用" << endl;
}
int m_Age;
};
void test01()
{
Person p;
p.m_Age = 18;
Person p2(p);
cout << "p2的年龄为:" << p2.m_Age << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
如果将15~19行代码删掉,再次调用test01函数时,编译器会自动给我们提供拷贝构造函数,这个函数内只会执行“m_Age=p.m_Age;”这行代码,此时控制台会输出以下内容:

1.如果我们写了有参构造函数,编译器就不再提供默认构造,依然提供拷贝构造
class Person
{
public:
Person(int age)
{
cout << "Person的有参构造函数调用" << endl;
m_Age = age;
}
~Person()
{
cout << "Person的析构构函数调用" << endl;
}
int m_Age;
};
void test02()
{
Person p;
}
int main()
{
test02();
return 0;
}当编译器执行这段代码时,由于这段代码写了有参构造函数,而在test02中“Person P”没有提供参数,编译器也不提供默认构造函数,因此代码会出错
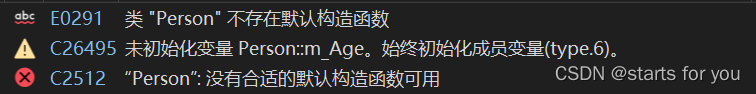
仍然使用上述代码,但对test02进行修改,这样代码就可以正常运行了,Person p2(p);是为了测试编译器是否会提供拷贝构造函数
void test02()
{
Person p(28);
Person p2(p);
}2.如果我们写了拷贝构造函数,编译器就不会再提供其他普通构造函数了,用下面这段代码来做验证:
class Person
{
public:
Person(const Person& p)
{
cout << "Person的拷贝构造函数调用" << endl;
m_Age = p.m_Age;
}
~Person()
{
cout << "Person的析构构函数调用" << endl;
}
int m_Age;
};
void test02()
{
Person p;
Person p2(p);
}
int main()
{
test02();
return 0;
}此时执行这段代码编译器会报错

最后
以上就是单薄狗最近收集整理的关于C++中构造函数调用规则的全部内容,更多相关C++中构造函数调用规则内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复