Rasa 聊天机器人框架使用流程(详细!!)
简述:
Rasa是一个能用于构建机器人对话系统的框架,基于Rasa框架搭建机器人对话系统,可以使用于工业各类语音智能服务场景,如:远程医疗问诊、智能客户服务、保险产品销售、金融催收服务、手机智能助手等领域。支持基于规则、填槽和机器学习来构建对话系统。主要模块包括:NLU(意图识别和实体提取)和Core(基于模型及规则进行回复)。提供了搭建对话系统的脚手架。
常用命令有:
rasa init # 创建项目
rasa train # 训练NLU和Core模型
rasa run actions # 启动动作服务(主要是自己写的动作,系统默认的动作,不需要单独启动)
rasa shell # 启动对话机器人 (会自动启动默认动作服务)
rasa x # 启动rasa x可视化服务
1.新建工程
第一步,执行下面命令创建一个新的工程:
rasa init
或
rasa init --no-prompt
rasa init命令会创建Rasa工程需要的全部文件,并在初始化样本数据上训练简单的聊天机器人。如果命令没有携带–no-prompt标志,你会遇到一些关于工程设置的提问。
使用rasa init 创建mybot项目,目录结果如下:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-dgtIKq2l-1645008096429)(/Users/liuzepei/Library/Application Support/typora-user-images/image-20220216181439694.png)]
以下文件将会被创建:
| init.py | 帮助python找到你的功能的空文件 |
|---|---|
| actions.py | 该文件中你可以自定义执行动作的代码 |
| config.yml ‘*’ | Rasa NLU和Rasa Core模型配置文件 |
| credentials.yml | 连接到其他服务的详细配置 |
| data/nlu.yml ‘*’ | Rasa NLU训练数据 |
| data/stories.yml ‘*’ | 故事编写文件 |
| domain.yml ‘*’ | 智能助手功能定义领域文件 |
| endpoints.yml | 连接到像fb messenger通道的详细配置 |
| models/.tar.g | 初始化模型 |
‘*’标记的是非常重要的文件,在该教程里有它们详细的解释。
2.查看和构建NLU训练数据
Rasa智能助手第一部分就是NLU模型。NLU是Natural Language Understanding的简称,它的意思就是把用户各种信息转换为结构化数据。要使用Rasa完成该功能,你需要提供训练语料,Rasa能够通过这些语料学习如何理解用户信息。并且Rasa能使用这些语料训练模型。
在rasa init 命令新建工程目录里,运行下面命令查看训练配置文件:
cat data/nlu.yml
数据样例:
nlu.yml 用于训练nlu模型的训练数据
version: "2.0"
nlu:
- intent: greet
examples: |
- 你好
- 上午好
- 中午好
- 嗨
- intent: goodbye
examples: |
- 再见
- 回头见
- 晚安
- intent: affirm
examples: |
- 是的
- 有
- 当然
- 听上去不错
- intent: deny
examples: |
- 不
- 不要
- 没有
- 没有
- 我不喜欢
- intent: mood_great
examples: |
- 太好了
- 感觉不错
- 非常好
- intent: mood_unhappy
examples: |
- 不开心
- 感到沮丧
- 不高兴
- 不太好
- intent: bot_challenge
examples: |
- 你是个机器人吗?
- 你是人类吗?
- 我是在和机器人讲话吗?
- 我是在和人类讲话吗?
- intent: request_names
examples: |
- 我想告诉你姓名
- 你知道我的姓名吗?
- lookup: names
examples: |
- 猪八戒
- 孙悟空
- 沙悟净
- 唐三藏
rules.yml 规则,根据用户意图,进行具体的动作(包括查询、填槽、回复等)
version: "2.0"
rules:
- rule: Say goodbye anytime the user says goodbye
steps:
- intent: goodbye
- action: utter_goodbye
- rule: Say 'I am a bot' anytime the user challenges
steps:
- intent: bot_challenge
- action: utter_iamabot
- rule: Activate form
steps:
- intent: request_names
- action: name_form
- active_loop: name_form
- rule: Submit form
condition:
- active_loop: name_form
steps:
- action: name_form
- active_loop: null
- slot_was_set:
- requested_slot: null
- action: utter_submit
- action: utter_slots_values
3.定义模型配置
通过配置文件定义你的模型需要用到的Rasa NLU和Rasa Core的组件。在该例子中,NLU模型将使用supervised_embeddings 管道。你可以通过页面here了解不同的NLU 管道。
通过下面命令查看模型配置文件:
cat config.yml # 即对NLU和Core模型的配置
cat domain.yml # 领域配置
credentials.yml # 证书配置,用于调用语音通道的接口
endpoints.yml # 端点配置,如:机器人要使用的模型、动作、存储服务等
language 和 pipeline主要确定应该如何构建Rasa NLU模型。policies主要定义Rasa Core模型使用的策略policies。
涉及配置文件有:
config.yml 即对NLU和Core模型的配置
# Configuration for Rasa NLU.
# https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/nlu/components/
language: zh
pipeline:
# # No configuration for the NLU pipeline was provided. The following default pipeline was used to train your model.
# # If you'd like to customize it, uncomment and adjust the pipeline.
# # See https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/tuning-your-model for more information.
# - name: WhitespaceTokenizer
- name: JiebaTokenizer #支持中文
- name: RegexFeaturizer
- name: LexicalSyntacticFeaturizer
- name: CountVectorsFeaturizer
- name: CountVectorsFeaturizer
analyzer: char_wb
min_ngram: 1
max_ngram: 4
- name: DIETClassifier
epochs: 100
constrain_similarities: true
- name: EntitySynonymMapper
- name: ResponseSelector
epochs: 100
constrain_similarities: true
- name: FallbackClassifier
threshold: 0.3
ambiguity_threshold: 0.1
# Configuration for Rasa Core.
# https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/core/policies/
policies:
# # No configuration for policies was provided. The following default policies were used to train your model.
# # If you'd like to customize them, uncomment and adjust the policies.
# # See https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/policies for more information.
- name: MemoizationPolicy
- name: TEDPolicy
max_history: 5
epochs: 100
constrain_similarities: true
- name: RulePolicy
domain.yml 领域配置
version: '2.0'
config:
store_entities_as_slots: true
session_config:
session_expiration_time: 60
carry_over_slots_to_new_session: true
intents:
- greet:
use_entities: true
- deny:
use_entities: true
- request_names:
use_entities: true
- goodbye:
use_entities: true
- affirm:
use_entities: true
- mood_great:
use_entities: true
- mood_unhappy:
use_entities: true
- bot_challenge:
use_entities: true
entities: []
slots:
first_name:
type: rasa.shared.core.slots.TextSlot
initial_value: null
auto_fill: true
influence_conversation: true
last_name:
type: rasa.shared.core.slots.TextSlot
initial_value: null
auto_fill: true
influence_conversation: true
name_spelled_correctly:
type: rasa.shared.core.slots.BooleanSlot
initial_value: null
auto_fill: true
influence_conversation: true
requested_slot:
type: rasa.shared.core.slots.UnfeaturizedSlot
initial_value: null
auto_fill: true
influence_conversation: false
responses:
utter_greet:
- text: 嗨,你好吗?
utter_cheer_up:
- image: https://i.imgur.com/nGF1K8f.jpg
text: '这是某些使你嗨起来的东西:'
utter_did_that_help:
- text: 这对你有帮助吗?
utter_happy:
- text: 好极了,继续!
utter_goodbye:
- text: 再见
utter_iamabot:
- text: 我是个机器人,由Rasa框架提供支持.
utter_ask_first_name:
- text: 你贵姓?
utter_ask_last_name:
- text: 你的名字?
utter_ask_name_spelled_correctly:
- buttons:
- payload: /affirm
title: 是
- payload: /deny
title: 否
text: 姓 {first_name} 拼写对了吗?
utter_submit:
- text: 好的,谢谢!
utter_slots_values:
- text: 我记住你了, {first_name} {last_name}!
actions:
- utter_greet
- utter_slots_values
- utter_submit
- validate_name_form
forms:
name_form:
first_name:
- type: from_text
last_name:
- type: from_text
e2e_actions: []
credentials.yml 证书配置,用于调用语音通道的接口
# This file contains the credentials for the voice & chat platforms
# which your bot is using.
# https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/messaging-and-voice-channels
rest:
# # you don't need to provide anything here - this channel doesn't
# # require any credentials
#facebook:
# verify: "<verify>"
# secret: "<your secret>"
# page-access-token: "<your page access token>"
#slack:
# slack_token: "<your slack token>"
# slack_channel: "<the slack channel>"
# slack_signing_secret: "<your slack signing secret>"
#socketio:
# user_message_evt: <event name for user message>
# bot_message_evt: <event name for bot messages>
# session_persistence: <true/false>
#mattermost:
# url: "https://<mattermost instance>/api/v4"
# token: "<bot token>"
# webhook_url: "<callback URL>"
# This entry is needed if you are using Rasa X. The entry represents credentials
# for the Rasa X "channel", i.e. Talk to your bot and Share with guest testers.
rasa:
url: "http://localhost:5002/api"
endpoints.yml 端点配置,如:机器人要使用的模型、动作、存储服务等
# This file contains the different endpoints your bot can use.
# Server where the models are pulled from.
# https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/model-storage#fetching-models-from-a-server
#models:
# url: http://my-server.com/models/default_core@latest
# wait_time_between_pulls: 10 # [optional](default: 100)
# Server which runs your custom actions.
# https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/custom-actions
#action_endpoint:
# url: "http://localhost:5055/webhook"
action_endpoint:
url: "http://localhost:5055/webhook"
# Tracker store which is used to store the conversations.
# By default the conversations are stored in memory.
# https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/tracker-stores
#tracker_store:
# type: redis
# url: <host of the redis instance, e.g. localhost>
# port: <port of your redis instance, usually 6379>
# db: <number of your database within redis, e.g. 0>
# password: <password used for authentication>
# use_ssl: <whether or not the communication is encrypted, default false>
#tracker_store:
# type: mongod
# url: <url to your mongo instance, e.g. mongodb://localhost:27017>
# db: <name of the db within your mongo instance, e.g. rasa>
# username: <username used for authentication>
# password: <password used for authentication>
tracker_store:
type: SQL
dialect: sqlite
db: trackers.db
# Event broker which all conversation events should be streamed to.
# https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/event-brokers
#event_broker:
# url: localhost
# username: username
# password: password
# queue: queue
event_broker:
type: SQL
dialect: sqlite
db: events.db
names.txt 本案例使用的姓名列表
孙悟空
猪八戒
唐三藏
沙悟净
诸葛青云
4.编写你的第一个故事
在这一节,你要教你的助手如何响应你的消息。这被称作对话管理,由你的Rasa Core模型来处理。Rasa Core模型以训练”stories”方式从真实的会话数据中学习。一个故事代表用户和助手之间真实的会话过程。
intents和entities行反应了用户的输入,action names 展示助手如何响应用户输入。
一个对话的例子。用户说hello,助手也回复hello。这就是为什么它看起来像一个故事。你可以在 Stories中查看详细信息。
以 - 开始的行是助手的action(执行动作)。在这个会话中,所有的action是把用户的信息原样返回,像utter_greet。但是,通常action可以做任何事情,包括调用api,与外部交互等。
运行下面的命令可以查看data/stories.md文件下的故事例子:
cat data/stories.md
stories.yml 故事情节,描述对话的流程
version: "2.0"
stories:
- story: happy path
steps:
- intent: greet
- action: utter_greet
- intent: mood_great
- action: utter_happy
- story: sad path 1
steps:
- intent: greet
- action: utter_greet
- intent: mood_unhappy
- action: utter_cheer_up
- action: utter_did_that_help
- intent: affirm
- action: utter_happy
- story: sad path 2
steps:
- intent: greet
- action: utter_greet
- intent: mood_unhappy
- action: utter_cheer_up
- action: utter_did_that_help
- intent: deny
- action: utter_goodbye
- story: interactive_story_1
steps:
- intent: greet
- action: utter_greet
- intent: request_names
- action: name_form
- active_loop: name_form
- slot_was_set:
- requested_slot: first_name
- slot_was_set:
- name_spelled_correctly: None
- slot_was_set:
- first_name: None
- slot_was_set:
- requested_slot: last_name
- slot_was_set:
- name_spelled_correctly: None
- slot_was_set:
- last_name: None
- slot_was_set:
- requested_slot: null
- active_loop: null
- action: utter_submit
- action: utter_slots_values
5.定义领域
接下来我们要定义一个领域。这个领域定义了你的助手所能处理的边界:希望用户输入什么样的信息,能够预测哪些执行动作,如何响应用户,存储什么样的信息。助手的领域存储在文件domain.yml中:
cat domain.yml
那么不同部分的意思是什么?
| intents | 你希望用户说的 |
|---|---|
| actions | 助手能做的和说的 |
| templates | 助手说的话术模板 |
这些是如何组合的呢?Rasa Core的工作就是在会话的每一步选择一个正确的action去执行。在该例子中,我们的actions只是简单的发送一个消息给用户。这些简单的话语执行的就是domain中以utter_开头的actions。助手将从templates中选择一个模板响应消息。参考 Custom Actions创建自定义action。
涉及的配置文件在上文已经逐一列出,下面看看自定义的action是如何写的,主要完成了输入验证的过程,默认的action是以utter_打头,系统默认支
import yaml
import pathlib
from typing import Text, List, Any, Dict, Optional
from rasa_sdk import Tracker, FormValidationAction
from rasa_sdk.executor import CollectingDispatcher
from rasa_sdk.types import DomainDict
names = pathlib.Path("names.txt").read_text().split("n")
class ValidateNameForm(FormValidationAction):
def name(self) -> Text:
return "validate_name_form"
async def required_slots(
self,
slots_mapped_in_domain: List[Text],
dispatcher: "CollectingDispatcher",
tracker: "Tracker",
domain: "DomainDict",
) -> Optional[List[Text]]:
first_name = tracker.slots.get("first_name")
if first_name is not None:
if first_name not in names:
return ["name_spelled_correctly"] + slots_mapped_in_domain
return slots_mapped_in_domain
async def extract_name_spelled_correctly(
self, dispatcher: CollectingDispatcher, tracker: Tracker, domain: Dict
) -> Dict[Text, Any]:
intent = tracker.get_intent_of_latest_message()
return {"name_spelled_correctly": intent == "affirm"}
def validate_name_spelled_correctly(
self,
slot_value: Any,
dispatcher: CollectingDispatcher,
tracker: Tracker,
domain: DomainDict,
) -> Dict[Text, Any]:
"""Validate `first_name` value."""
if tracker.get_slot("name_spelled_correctly"):
return {"first_name": tracker.get_slot("first_name"), "name_spelled_correctly": True}
return {"first_name": None, "name_spelled_correctly": None}
def validate_first_name(
self,
slot_value: Any,
dispatcher: CollectingDispatcher,
tracker: Tracker,
domain: DomainDict,
) -> Dict[Text, Any]:
"""Validate `first_name` value."""
# If the name is super short, it might be wrong.
print(f"姓 = {slot_value} 长度 = {len(slot_value)}")
if len(slot_value) <=1:
dispatcher.utter_message(text=f"姓太短了,你确定拼写对了?")
return {"first_name": None}
else:
return {"first_name": slot_value}
def validate_last_name(
self,
slot_value: Any,
dispatcher: CollectingDispatcher,
tracker: Tracker,
domain: DomainDict,
) -> Dict[Text, Any]:
"""Validate `last_name` value."""
# If the name is super short, it might be wrong.
print(f"名字 = {slot_value} 长度 = {len(slot_value)}")
if len(slot_value) <= 1:
dispatcher.utter_message(text=f"名字太短了,你确定拼写对了?")
return {"last_name": None}
else:
return {"last_name": slot_value}
6.训练模型
一旦我们添加了新的NLU或Core数据,或者更新领域或配置,就要在样本故事和NLU数据上重新训练神经网络。可以通过使用下面命令重新训练神经网络。该命令将调用Rasa 的Core和NLU训练功能并且把训练好的模型存储到models/文件夹下。该命令将自动重新训练Rasa的数据或配置改变部分的模型。
rasa train
rasa train命令将查找NLU和CORE的数据并训练组合模型。
图示:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-qVfxKaYp-1645008096430)(/Users/liuzepei/Library/Application Support/typora-user-images/image-20220216182032542.png)]
7.使用你的助手
恭喜!你刚刚建立了一个完全由机器学习驱动的助手。
下一步就是测试它!如果你在本机学习该教程,开始通过下面命令启动和使用你的助手吧:
rasa shell
启动机器人进行对话
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-xHbgqHxW-1645008096430)(/Users/liuzepei/Library/Application Support/typora-user-images/image-20220216182605475.png)]
8.创建 rasa x
你可以使用Rasa X收集更多会话来改进你的助手:

在项目目录下启动rasa X 命令如下:
rasa x
启动示例:
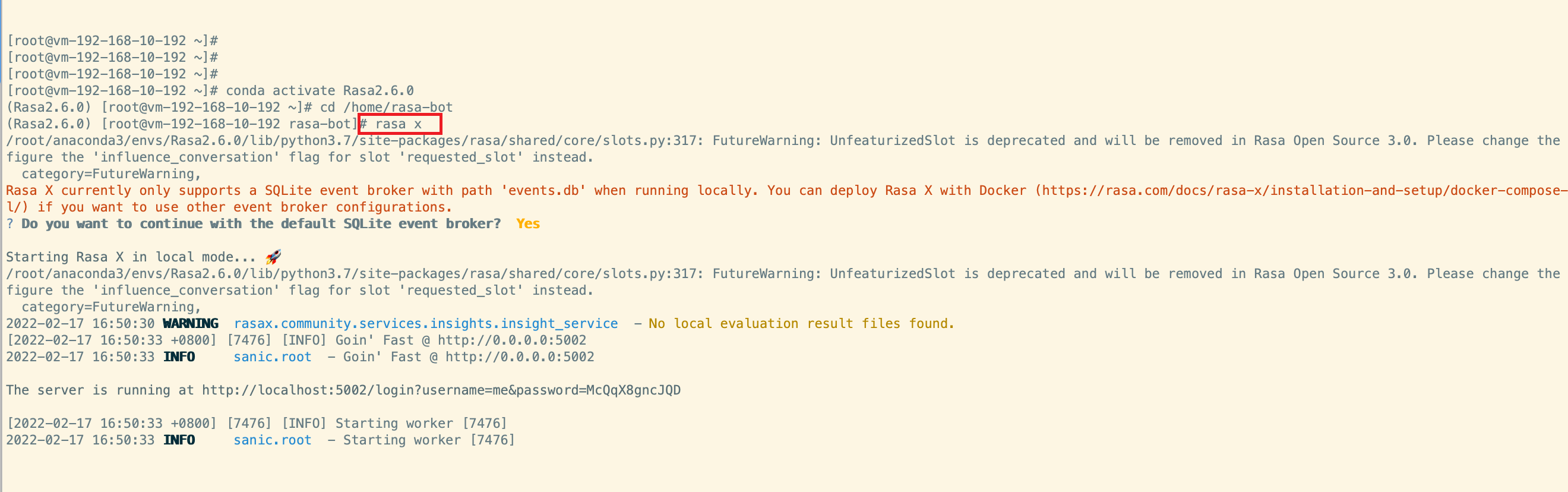
如果是在服务器上开启服务,IE浏览器登录时填上服务器的ip地址,例如:192.168.10.192:5002
输入密码图示:
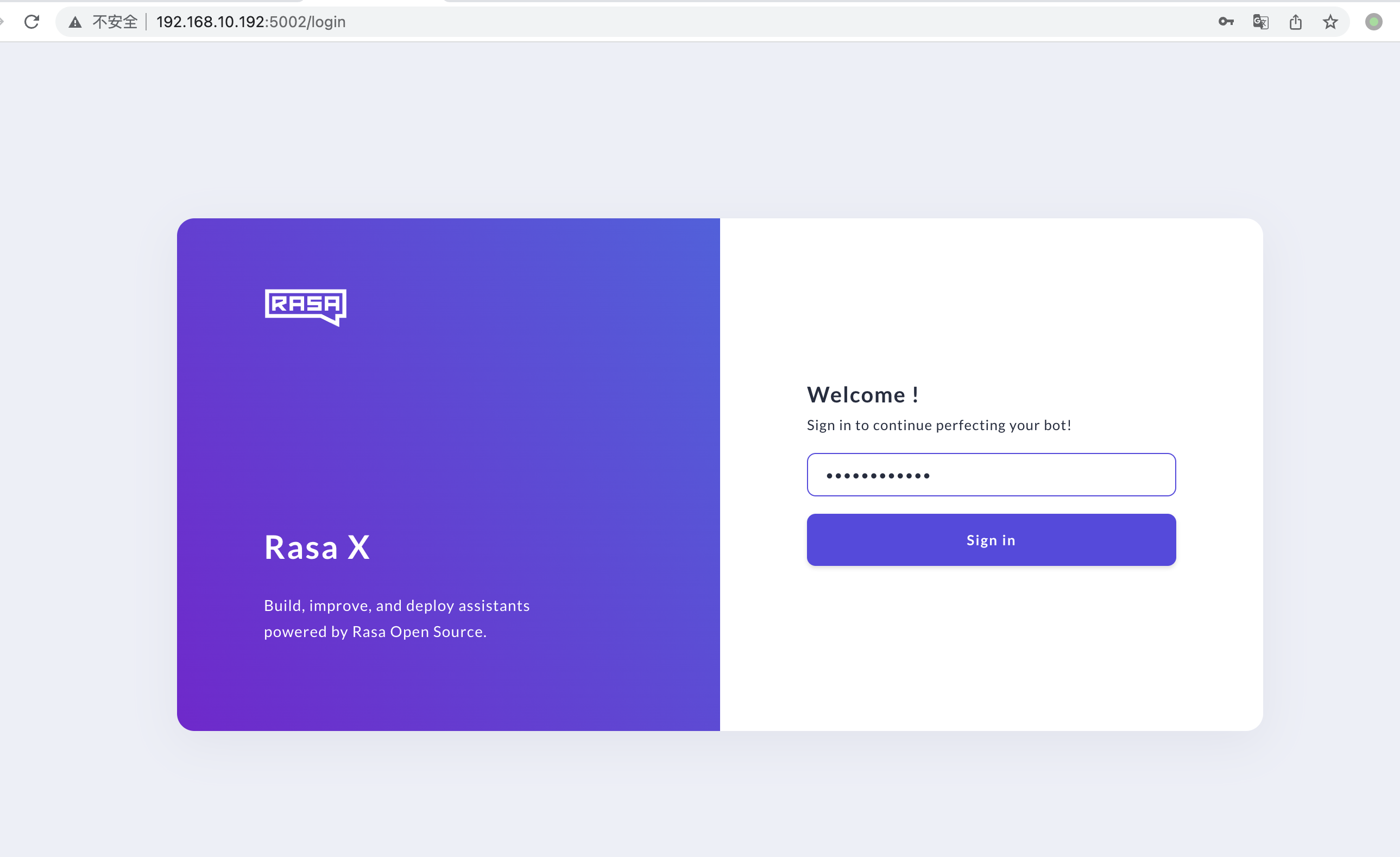
登录后图示:
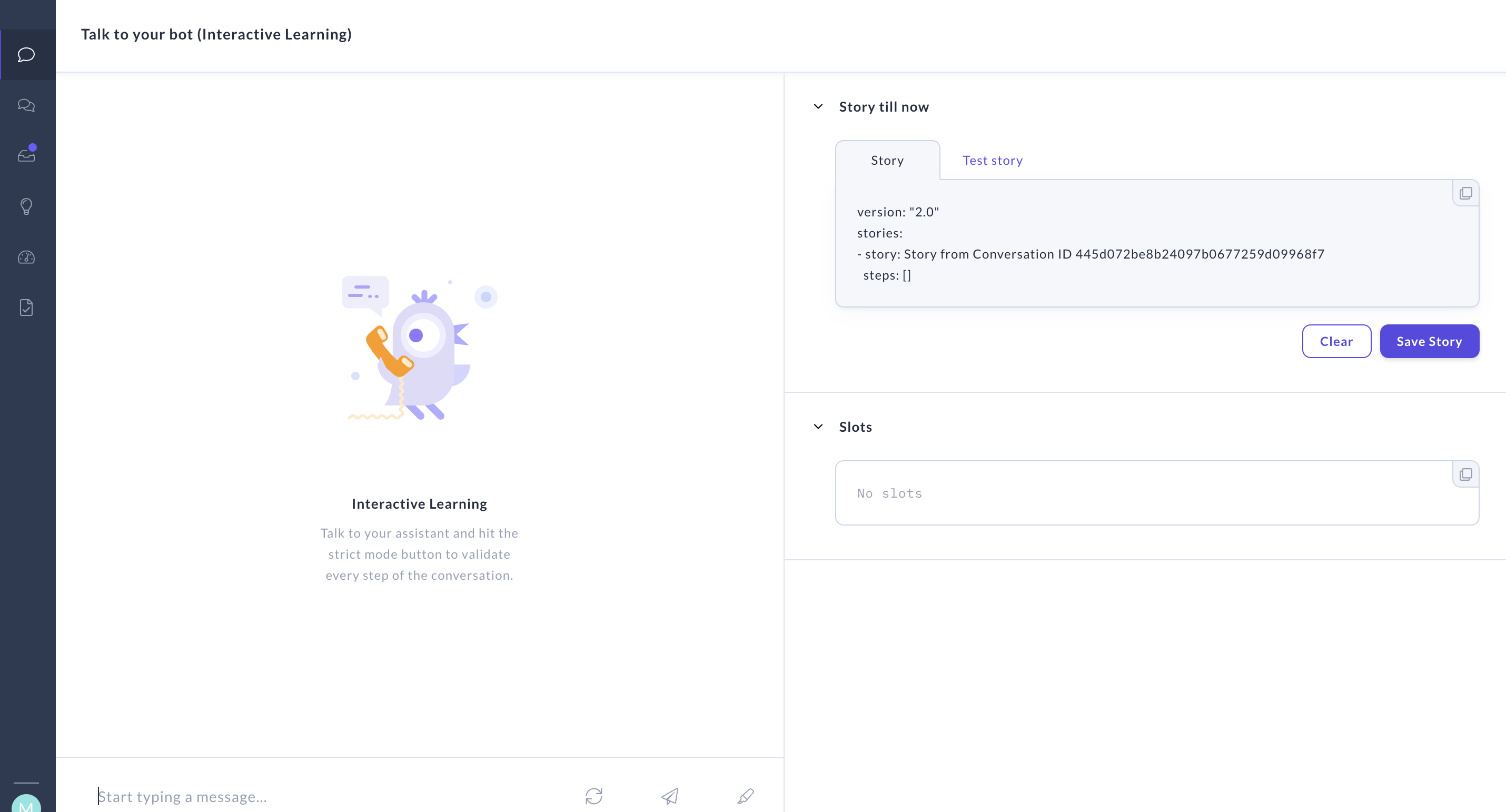
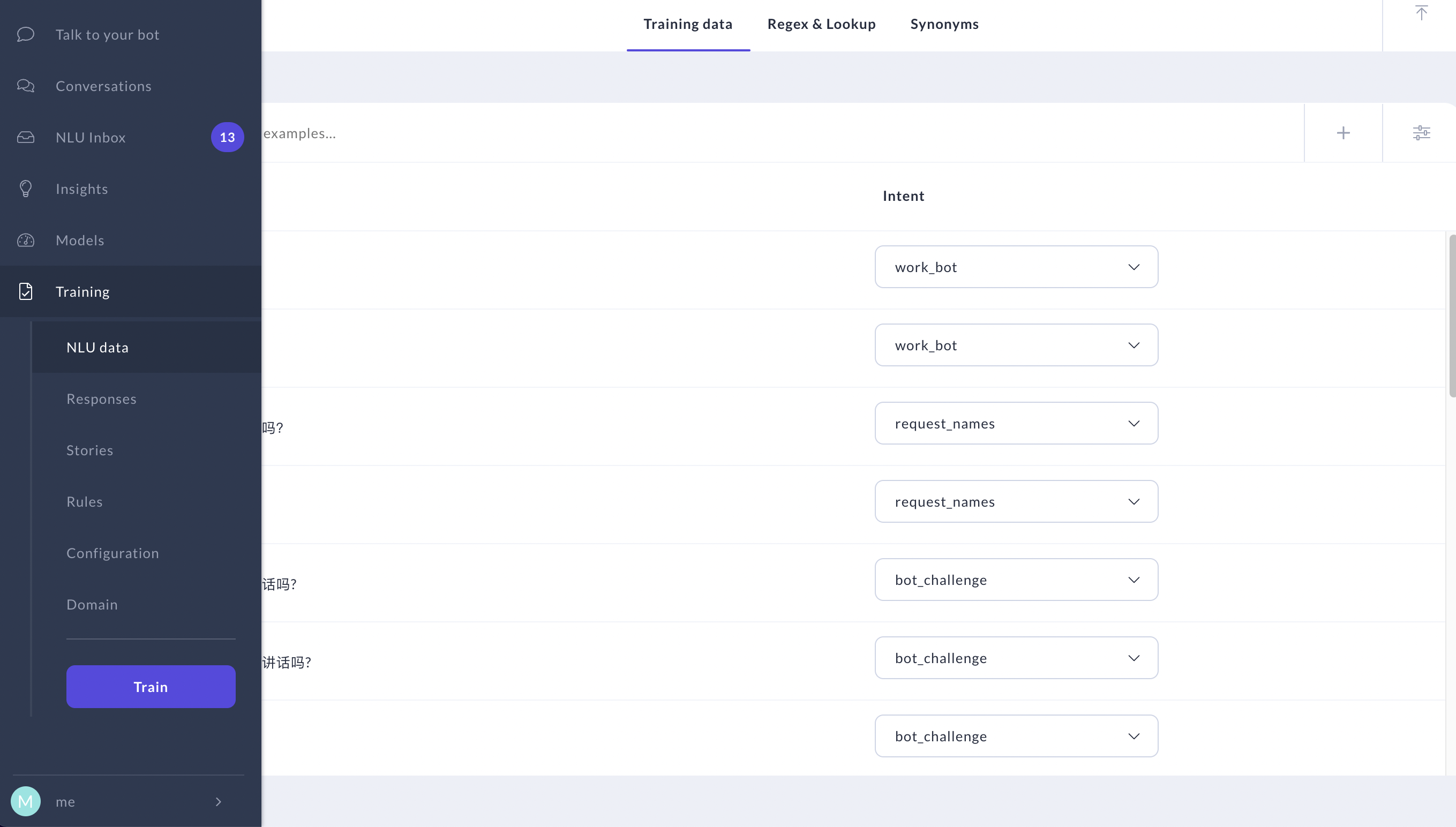
功能展示界面:
最后
以上就是高高红酒最近收集整理的关于Rasa 聊天机器人框架使用流程Rasa 聊天机器人框架使用流程(详细!!)的全部内容,更多相关Rasa内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
![自制QQ机器人插件笔记[nonebot2部署于ubuntu系统服务器]](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg2.png)







发表评论 取消回复