跟着上节,以tick中断为例,探究liunx时间子系统
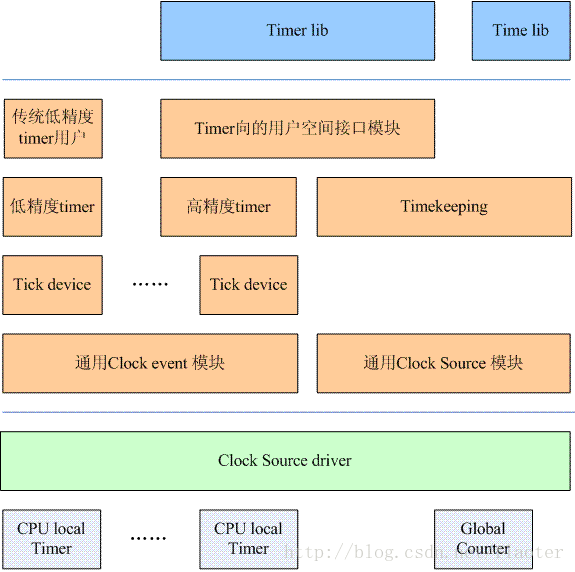
linux 时间子系统分层框架
图片出处http://blog.csdn.net/flaoter
最底层是硬件和驱动层,每个cpu core都有自己的cpu local timer,此外SOC内部肯定会有一个用于全局的global counter。
■ 中间层是linux内核层,内核抽象出了时钟源(clocksource), 时钟事件设备(clock_event_device), tick设备(tick_device)用于时间管理。分为左右两部分,
• 右边实现计时功能。linux内核有各种time line, 包括real time clock, monotonic clock, monotonic raw clock等。clocksource提供了一个单调增加的计时器产生tick,为timeline提供时钟源。timekeeper是内核提供时间服务的基础模块,负责选择并维护最优的clocksource。
• 左边实现定时功能。clock event管理可产生event或是触发中断的定时器,** 一般而言,每个CPU形成自己的一个小系统,也就要管理自己的clock event**。tick device是基于clock event设备进行工作的,cpu管理自己的调度、进程统计等是基于tick设备的。低精度timer和高精度timer都是基于tick device生成的定时器设备,关于它们的事件和周期信号的关系在上面的图中有一个大体的介绍。
■ 最上层是linux应用层。基于timekeeping设备的是时间管理的库time lib,基于定时器设备的是定时管理的库timer lib。
出处http://blog.csdn.net/flaoter
探究tick中断路由
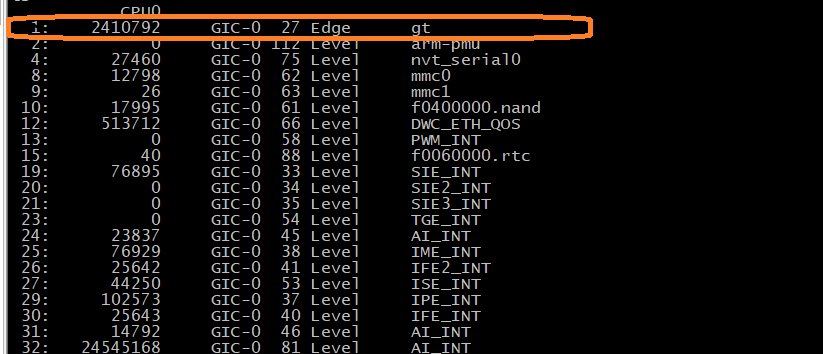
接着上章,我们知道tick中断的handler是tick_handle_periodic,来看看 tick中断是如何运行到这里的。arm中有一个global timer的全局定时器。我们来看看arm global timer中断驱动程序:
在linux下cat /proc/interrupts
arm global timer驱动是作为一个clocksource驱动在drivers/clocksource目录下;arm_global_timer.c中:
从驱动入口函数:global_timer_of_register开始
static int __init global_timer_of_register(struct device_node *np)
{
struct clk *gt_clk;
int err = 0;
/*
* In A9 r2p0 the comparators for each processor with the global timer
* fire when the timer value is greater than or equal to. In previous
* revisions the comparators fired when the timer value was equal to.
*/
if (read_cpuid_part() == ARM_CPU_PART_CORTEX_A9
&& (read_cpuid_id() & 0xf0000f) < 0x200000) {
pr_warn("global-timer: non support for this cpu version.n");
return -ENOSYS;
}
gt_ppi = irq_of_parse_and_map(np, 0);
if (!gt_ppi) {
pr_warn("global-timer: unable to parse irqn");
return -EINVAL;
}
gt_base = of_iomap(np, 0);
if (!gt_base) {
pr_warn("global-timer: invalid base addressn");
return -ENXIO;
}
gt_clk = of_clk_get(np, 0);
if (!IS_ERR(gt_clk)) {
err = clk_prepare_enable(gt_clk);
if (err)
goto out_unmap;
} else {
pr_warn("global-timer: clk not foundn");
err = -EINVAL;
goto out_unmap;
}
gt_clk_rate = clk_get_rate(gt_clk);
gt_evt = alloc_percpu(struct clock_event_device); /*分配一个clock_event_device*/
if (!gt_evt) {
pr_warn("global-timer: can't allocate memoryn");
err = -ENOMEM;
goto out_clk;
}
err = request_percpu_irq(gt_ppi, gt_clockevent_interrupt,
"gt", gt_evt); /*1. 申请中断处理函数,绑定一个clock_event_device*/
if (err) {
pr_warn("global-timer: can't register interrupt %d (%d)n",
gt_ppi, err);
goto out_free;
}
/* Register and immediately configure the timer on the boot CPU */
err = gt_clocksource_init(); /*注册一个clocksource*/
if (err)
goto out_irq;
err = cpuhp_setup_state(CPUHP_AP_ARM_GLOBAL_TIMER_STARTING,
"clockevents/arm/global_timer:starting",
gt_starting_cpu, gt_dying_cpu); /*cpu hotplug,cpu热插拔绑定handler,当CPUHP_AP_ARM_GLOBAL_TIMER_STARTING时间触发时调用gt_starting_cpu*/
if (err)
goto out_irq;
gt_delay_timer_init();
return 0;
out_irq:
free_percpu_irq(gt_ppi, gt_evt);
out_free:
free_percpu(gt_evt);
out_clk:
clk_disable_unprepare(gt_clk);
out_unmap:
iounmap(gt_base);
WARN(err, "ARM Global timer register failed (%d)n", err);
return err;
}
/* Only tested on r2p2 and r3p0 */
TIMER_OF_DECLARE(arm_gt, "arm,cortex-a9-global-timer",
global_timer_of_register); /*声明一个驱动树节点*/
我们注意到三个步骤,
1.申请一个clock_event_device,
2.注册中断处理函数,绑定clock_event_device,中断处理函数是gt_clockevent_interrupt,且在其中会调用clock_event_device的evt_handler处理中断;
3.注册一个clocksource
4.绑定cpu热插拔时间,gt_starting_cpu,cpuhotplug我们后面在学,现在多核系统,一个主cpu (boot cpu)之外的cpu(AP cpu)可以当作一个外设来看待,在业务没那么繁忙时可以将其关掉,关闭和开启会触发cpu hotplug事件,在cpu起来时会注册一个AP global timer,并触发CPUHP_AP_ARM_GLOBAL_TIMER_STARTING事件,并调用handler:gt_starting_cpu。
我们依次来看这几个函数:
gt_clocksource_init:
static int __init gt_clocksource_init(void)
{
writel(0, gt_base + GT_CONTROL);
writel(0, gt_base + GT_COUNTER0);
writel(0, gt_base + GT_COUNTER1);
/* enables timer on all the cores */
writel(GT_CONTROL_TIMER_ENABLE, gt_base + GT_CONTROL);
#ifdef CONFIG_CLKSRC_ARM_GLOBAL_TIMER_SCHED_CLOCK
sched_clock_register(gt_sched_clock_read, 64, gt_clk_rate);
#endif
return clocksource_register_hz(>_clocksource, gt_clk_rate);
}
- 写timer的寄存器;2.clocksource_register_hz()
clocksource_register_hz() 是 __clocksource_register_scale()的包装
在include/linux/clocksource.h
static inline int clocksource_register_hz(struct clocksource *cs, u32 hz)
{
return __clocksource_register_scale(cs, 1, hz);
}
__clocksource_register_scale在kernel/time/clocksource.c中
int __clocksource_register_scale(struct clocksource *cs, u32 scale, u32 freq)
{
unsigned long flags;
/* Initialize mult/shift and max_idle_ns */
__clocksource_update_freq_scale(cs, scale, freq);
/* Add clocksource to the clocksource list */
mutex_lock(&clocksource_mutex);
clocksource_watchdog_lock(&flags);
clocksource_enqueue(cs);
clocksource_enqueue_watchdog(cs);
clocksource_watchdog_unlock(&flags);
clocksource_select();
clocksource_select_watchdog(false);
__clocksource_suspend_select(cs);
mutex_unlock(&clocksource_mutex);
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(__clocksource_register_scale);
clocksource_enqueue将cs加入全局clocksource_list的队列中。
中断处理函数
static irqreturn_t gt_clockevent_interrupt(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
struct clock_event_device *evt = dev_id;
if (!(readl_relaxed(gt_base + GT_INT_STATUS) &
GT_INT_STATUS_EVENT_FLAG))
return IRQ_NONE;
/**
* ERRATA 740657( Global Timer can send 2 interrupts for
* the same event in single-shot mode)
* Workaround:
* Either disable single-shot mode.
* Or
* Modify the Interrupt Handler to avoid the
* offending sequence. This is achieved by clearing
* the Global Timer flag _after_ having incremented
* the Comparator register value to a higher value.
*/
if (clockevent_state_oneshot(evt))
gt_compare_set(ULONG_MAX, 0); /*如果oneshot 则比较时间*/
writel_relaxed(GT_INT_STATUS_EVENT_FLAG, gt_base + GT_INT_STATUS);
evt->event_handler(evt); /*调用event_device的event_handler*/
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
中断函数中调用clock_event_device的event_handler()处理。
那clock_event_device的event_handler在何处设置呢?
我们来看gt_starting_cpu()函数做了些什么。
static int gt_starting_cpu(unsigned int cpu)
{
struct clock_event_device *clk = this_cpu_ptr(gt_evt);
clk->name = "arm_global_timer";
clk->features = CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_PERIODIC | CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_ONESHOT |
CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_PERCPU;
clk->set_state_shutdown = gt_clockevent_shutdown;
clk->set_state_periodic = gt_clockevent_set_periodic;
clk->set_state_oneshot = gt_clockevent_shutdown;
clk->set_state_oneshot_stopped = gt_clockevent_shutdown;
clk->set_next_event = gt_clockevent_set_next_event;
clk->cpumask = cpumask_of(cpu);
clk->rating = 300;
clk->irq = gt_ppi;
clockevents_config_and_register(clk, gt_clk_rate,
1, 0xffffffff); /*注册一个clock_event_device*/
enable_percpu_irq(clk->irq, IRQ_TYPE_NONE);
return 0;
}
clockevents_config_and_register() 在kernel/time/clockevents.c
void clockevents_register_device(struct clock_event_device *dev)
{
unsigned long flags;
/* Initialize state to DETACHED */
clockevent_set_state(dev, CLOCK_EVT_STATE_DETACHED);
if (!dev->cpumask) {
WARN_ON(num_possible_cpus() > 1);
dev->cpumask = cpumask_of(smp_processor_id());
}
if (dev->cpumask == cpu_all_mask) {
WARN(1, "%s cpumask == cpu_all_mask, using cpu_possible_mask insteadn",
dev->name);
dev->cpumask = cpu_possible_mask;
}
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&clockevents_lock, flags);
list_add(&dev->list, &clockevent_devices);
tick_check_new_device(dev); /*检查并添加tick device*/
clockevents_notify_released();
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&clockevents_lock, flags);
}
tick_check_new_device() 在kernel/time/tick-common.c
void tick_check_new_device(struct clock_event_device *newdev)
{
struct clock_event_device *curdev;
struct tick_device *td;
int cpu;
cpu = smp_processor_id();
td = &per_cpu(tick_cpu_device, cpu); /*tick_device是percpu*/
curdev = td->evtdev;
/* cpu local device ? */
if (!tick_check_percpu(curdev, newdev, cpu))
goto out_bc;
/* Preference decision */
if (!tick_check_preferred(curdev, newdev))
goto out_bc;
if (!try_module_get(newdev->owner))
return;
/*
* Replace the eventually existing device by the new
* device. If the current device is the broadcast device, do
* not give it back to the clockevents layer !
*/
if (tick_is_broadcast_device(curdev)) {
clockevents_shutdown(curdev);
curdev = NULL;
}
clockevents_exchange_device(curdev, newdev);
tick_setup_device(td, newdev, cpu, cpumask_of(cpu));
/*添加tick_device*/
if (newdev->features & CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_ONESHOT)
tick_oneshot_notify();
return;
out_bc:
/*
* Can the new device be used as a broadcast device ?
*/
tick_install_broadcast_device(newdev);
}
已经进入tick模块,tick_setup_device()
static void tick_setup_device(struct tick_device *td,
struct clock_event_device *newdev, int cpu,
const struct cpumask *cpumask)
{
void (*handler)(struct clock_event_device *) = NULL;
ktime_t next_event = 0;
/*
* First device setup ?
*/
if (!td->evtdev) {
/*
* If no cpu took the do_timer update, assign it to
* this cpu:
*/
if (tick_do_timer_cpu == TICK_DO_TIMER_BOOT) {
if (!tick_nohz_full_cpu(cpu))
tick_do_timer_cpu = cpu;
else
tick_do_timer_cpu = TICK_DO_TIMER_NONE;
tick_next_period = ktime_get();
tick_period = NSEC_PER_SEC / HZ;
}
/*
* Startup in periodic mode first.
*/
td->mode = TICKDEV_MODE_PERIODIC;
/*如果是第一个evt_handler,则则设置未周期模式*/
} else {
handler = td->evtdev->event_handler; /*不是第一个event_hdanler,则获取上一个event_handler*/
next_event = td->evtdev->next_event;
td->evtdev->event_handler = clockevents_handle_noop;
}
td->evtdev = newdev;
/*
* When the device is not per cpu, pin the interrupt to the
* current cpu:
*/
if (!cpumask_equal(newdev->cpumask, cpumask))
irq_set_affinity(newdev->irq, cpumask);
/*
* When global broadcasting is active, check if the current
* device is registered as a placeholder for broadcast mode.
* This allows us to handle this x86 misfeature in a generic
* way. This function also returns !=0 when we keep the
* current active broadcast state for this CPU.
*/
if (tick_device_uses_broadcast(newdev, cpu))
return;
if (td->mode == TICKDEV_MODE_PERIODIC)
tick_setup_periodic(newdev, 0); /*如果tick_device模式是周期的*/
else
tick_setup_oneshot(newdev, handler, next_event);
/*tick_device模式是oneshot模式,该handler是tick_device的老的event_handler*/
}
用面向对象的思想,tick_device是clock_event_device的“子类”
struct tick_device {
struct clock_event_device *evtdev;
enum tick_device_mode mode;
};
每个cpu都有自己的tick_device;
tick_check_new_device()中
td = &per_cpu(tick_cpu_device, cpu);
tick_setup_device()给该cpu的tick_device设置一个clock_event_device;
tick_device 模式分为periodic和one shot模式
如果是初次设置,则为periodic模式,调用tick_setup_periodic(); 不是第一次设置则走one shot模式tick_setup_oneshot():
tick_setup_periodic()分支就是我们在中断子系统章节的入口了,后面在细看,先来看tick_setup_oneshot()分支:
kernel/time/tick-oneshot.c中
void tick_setup_oneshot(struct clock_event_device *newdev,
void (*handler)(struct clock_event_device *),
ktime_t next_event)
{
newdev->event_handler = handler; /*设置event_handler*/
clockevents_switch_state(newdev, CLOCK_EVT_STATE_ONESHOT); /*设置clock_event_device 的state为oneshot模式*/
clockevents_program_event(newdev, next_event, true);
}
clockevents_program_event():
int clockevents_program_event(struct clock_event_device *dev, ktime_t expires,
bool force)
{
unsigned long long clc;
int64_t delta;
int rc;
if (unlikely(expires < 0)) {
WARN_ON_ONCE(1);
return -ETIME;
}
dev->next_event = expires;
if (clockevent_state_shutdown(dev))
return 0;
/* We must be in ONESHOT state here */
WARN_ONCE(!clockevent_state_oneshot(dev), "Current state: %dn",
clockevent_get_state(dev));
/* Shortcut for clockevent devices that can deal with ktime. */
if (dev->features & CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_KTIME)
return dev->set_next_ktime(expires, dev);
delta = ktime_to_ns(ktime_sub(expires, ktime_get()));
if (delta <= 0)
return force ? clockevents_program_min_delta(dev) : -ETIME;
delta = min(delta, (int64_t) dev->max_delta_ns);
delta = max(delta, (int64_t) dev->min_delta_ns);
clc = ((unsigned long long) delta * dev->mult) >> dev->shift;
rc = dev->set_next_event((unsigned long) clc, dev);
/*设置下一次触发事件的时刻*/
return (rc && force) ? clockevents_program_min_delta(dev) : rc;
}
clock_source_device 中set_next_event是在和时设置?
回到gt_starting_cpu() dricers/clockcource/arm_global_timer.c
clk->set_next_event = gt_clockevent_set_next_event;
我们来看gt_clockevent_set_next_event()做了什么?
static int gt_clockevent_set_next_event(unsigned long evt,
struct clock_event_device *unused)
{
gt_compare_set(evt, 0);
return 0;
}
static void gt_compare_set(unsigned long delta, int periodic)
{
u64 counter = gt_counter_read();
unsigned long ctrl;
counter += delta;
ctrl = GT_CONTROL_TIMER_ENABLE;
writel_relaxed(ctrl, gt_base + GT_CONTROL);
writel_relaxed(lower_32_bits(counter), gt_base + GT_COMP0);
writel_relaxed(upper_32_bits(counter), gt_base + GT_COMP1);
if (periodic) {
writel_relaxed(delta, gt_base + GT_AUTO_INC);
ctrl |= GT_CONTROL_AUTO_INC;
}
ctrl |= GT_CONTROL_COMP_ENABLE | GT_CONTROL_IRQ_ENABLE;
writel_relaxed(ctrl, gt_base + GT_CONTROL);
}
硬件寄存器操作,设置下一次中断产生的时刻。设置下一次中断产生调用tick_device的老的event_handler。
我们再看看periodic分支
tick_setup_periodic():
void tick_setup_periodic(struct clock_event_device *dev, int broadcast)
{
tick_set_periodic_handler(dev, broadcast); /*设置event_hdanler*/
/* Broadcast setup ? */
if (!tick_device_is_functional(dev))
return;
if ((dev->features & CLOCK_EVT_FEAT_PERIODIC) &&
!tick_broadcast_oneshot_active()) {
clockevents_switch_state(dev, CLOCK_EVT_STATE_PERIODIC);
} else {
unsigned long seq;
ktime_t next;
do {
seq = read_seqbegin(&jiffies_lock);
next = tick_next_period;
} while (read_seqretry(&jiffies_lock, seq));
clockevents_switch_state(dev, CLOCK_EVT_STATE_ONESHOT);
for (;;) {
if (!clockevents_program_event(dev, next, false))
return;
next = ktime_add(next, tick_period);
}
}
}
tick_setup_periodic(dev, broadcast); 设置clock_event_device的event_handler 为tick_handle_periodic
kernel/time/tick-internal.h
static inline void tick_set_periodic_handler(struct clock_event_device *dev, int broadcast)
{
dev->event_handler = tick_handle_periodic;
}
这样timer中断中调用clock_event_device->event_handler,就进入tick_handle_periodic()函数。
低速时钟使用periodic模式。这样tick中断的路由就已完成,接下来进入tick_handle_periodic()处理一些cpu调度和统计信息,我们在调度子系统中学习。
高速时钟概念待补充
tick_init()函数
https://www.cnblogs.com/arnoldlu/p/7078228.html
https://blog.csdn.net/cc289123557/article/details/53728173
https://www.jb51.net/article/133579.htm
最后
以上就是迷你学姐最近收集整理的关于小张学linux内核:二. 时间子系统的全部内容,更多相关小张学linux内核:二.内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复