本文主要讲述在Ubuntu系统下用vim、gcc、Makefile命令对C程序进行编译运行。本文还包括对刚下载的Ubuntu进行网络配置,apt源的更换。
一、网络配置
1.以DHCP方式配置网卡
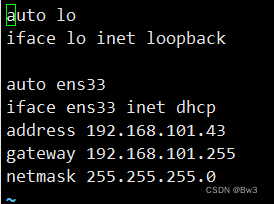
输入sudo vi /etc/network/interfaces
将其内容改为
2.更换apt源
输入sudo vim /etc/apt/sources.list
将内容更换为
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-updates main restricted universe multiverse
# deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ bionic-backports main restricted universe multiverse
输入sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
等待加载完毕即可
二、C语言编写输出hello word的程序
1,输入sudo apt-get install vim下载vim编辑器
2,输入sudo apt-get install gcc下载gcc编译器
下载完成之后实验vim编辑器编写bw.c的C程序。
输入vim bw.c进行编辑
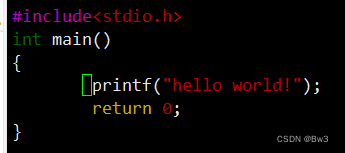
保存退出以后输入
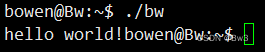
gcc bw.c -o bw
./bw
输出结果为
三、gcc编译C程序与Windows编译C程序
1,gcc编译
-
编写main1.c
#include<stdio.h> #include"sub1.h" float bb(int a,int b); int main() { int a,b; a=9; b=2; printf("a/b= %f",bb(a,b)); return 0; } -
编写sub1.h
float bb(int a,int b) { float c=(float)a; float d=(float)b; return c/d; }之后输入命令运行
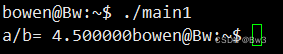
gcc main1.c sub1.h -o main1./main1运行结果为
2,Windows编译
-
编写main1.c
#include<stdio.h> #include"sub1.h" int main() { int a,b; a=9; b=2; printf("a/b= %f",bb(a,b)); return 0; } -
编写sub1.h
float bb(int a,int b) { float c=(float)a; float d=(float)b; return c/d; }运行结果
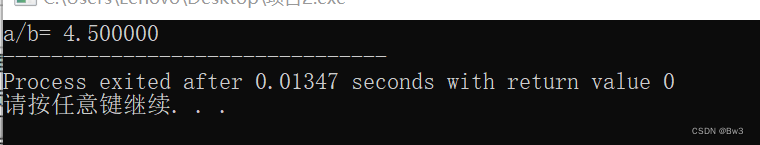
四、Makefile方式进行编译主程序
1,安装make
sudo apt-get install make
2,make的介绍
make在当前目录下寻找“Makefile”或“makefile”文件
若找到,查找文件中的第一个目标文件.o
若目标文件不存在,根据依赖关系查找.s文件
若.s文件不存在,根据依赖关系查找.i文件
若.i文件不存在,根据依赖关系查找.c文件,此时.c文件一定存在,于是生成一个.o文件,再去执行
3,makefile文件规则
<目标>: <前置条件>
[Tab]<命令>
目标是必须存在的;前置条件和命令可以只选择一个。
例如
clean:
rm *.o
该代码的作用便是删除所有的.o文件
4,编辑makefile文件
输入vim makefile进行编辑
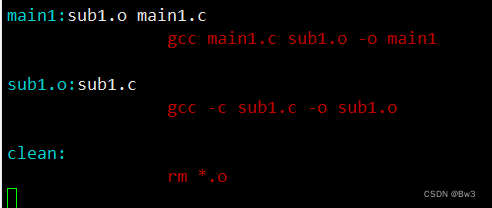
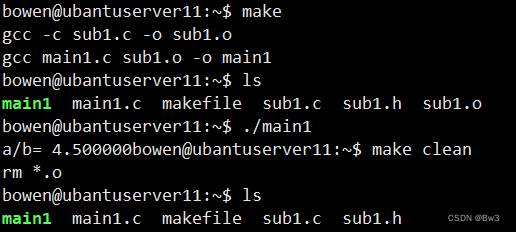
之后输入make,运行结果如下
五,总结
这次作业主要是回顾了一下Linux的内容,关于vim,gcc,make等命令的学习,特别令我印象深刻的是gcc对C程序的处理步骤。还有makefile的优点,极大提高了效率。
最后
以上就是高贵哈密瓜最近收集整理的关于Ubuntu系统下运用vim、gcc、Makefile命令简单编译运行C程序的全部内容,更多相关Ubuntu系统下运用vim、gcc、Makefile命令简单编译运行C程序内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复