第一讲Spring源码 BeanFactory的初探,我们已经对Spring的bean工厂和环境有了一个初步的认y有了第一篇对BeanFactory的初探的基础知识积累,那我们今天就接着分析,refresh做了什么操作
/**
* 在创建 IOC 容器前,如果已经有容器存在,则需要把已有的容器销毁和
* 关闭,以保证在 refresh 之后使用的是新建立起来的 IOC 容器。它类似于对 IOC 容器的重启,在新建立
* 好的容器中对容器进行初始化,对 Bean 配置资源进行载入。
* @throws BeansException
* @throws IllegalStateException
*/
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
//1、调用容器准备刷新的方法,获取容器的当时时间,同时给容器设置同步标识
prepareRefresh();
//2 告诉子类启动refreshBeanFactory()方法,Bean定义资源文件的载入从子类的refreshBeanFactory()启动
//这步比较关键,这步完成后,配置文件就会解析成一个个Bean定义,注册到BeanFactory
//当然这里面的bean还没有初始化,只是配置信息提取出来了
// 注册信息都存在了注册中心(beanName--> BeanDefinition)的concurrentHashMap里面
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
//3、为 BeanFactory 配置容器特性,例如类加载器、事件处理器等
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
//4、为容器的某些子类指定特殊的 BeanPost 事件处理器
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//5、调用所有注册的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的 Bean
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//6、为 BeanFactory 注册 BeanPost 事件处理器.
//BeanPostProcessor 是 Bean 后置处理器,用于监听容器触发的事件
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//7、初始化信息源,和国际化相关
initMessageSource();
//8、初始化容器事件传播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
//9、调用子类的某些特殊 Bean 初始化方法
onRefresh();
//10、为事件传播器注册事件监听器.
registerListeners();
//11、初始化所有剩余的单例 Bean
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//12、初始化容器的生命周期事件处理器,并发布容器的生命周期事件
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}//1、调用容器准备刷新的方法,获取容器的当时时间,同时给容器设置同步标识
prepareRefresh(); 这个虽然也很重要,但是不是我们要研究的我们可以看下第二个方法做了什么
2 返回一个工厂,对工厂进行初始化,因为我们是注解的形式,里面的代码就很简单,基本就初始化一个工厂
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
/**
* obtain:获得
* @return
*/
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
// 具体实现调用子类容器的refreshBeanFactory()方法
refreshBeanFactory();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException {
if (!this.refreshed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"GenericApplicationContext does not support multiple refresh attempts: just call 'refresh' once");
}
this.beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
}3.我们来分析prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);,来准备工厂,为工厂设置一些属性
/**
* 配置其标准的特征,比如上下文的加载器ClassLoader和post-processors回调
* Configure the factory's standard context characteristics,
* such as the context's ClassLoader and post-processors.
* @param beanFactory the BeanFactory to configure
* 此处的beanFactory参数等于DefaultListableFactory
*/
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
//bean表达式解释器,后面说 能够获取bean当中的属性在前台页面
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
//对象与string类型的转换 <property red="dao">
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
//添加一个后置管理器
//ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
// 能够在bean中获得到各种*Aware(*Aware都有其作用)
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
//意思是如果自定义的Bean中没有名为"systemProperties"和"systemEnvironment"的Bean,
// 则注册两个Bena,Key为"systemProperties"和"systemEnvironment",Value为Map,
// 这两个Bean就是一些系统配置和系统环境信息
// Register default environment beans.
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
前三行代码可以看我上面的注释,就不啰嗦一遍了,我们来看一个新知识点,也是我们这篇博客
的主人公之一的:BeanPostProcess
//添加一个后置管理器
//ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
// 能够在bean中获得到各种*Aware(*Aware都有其作用)
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));好了,讲到这,我们可以先停下源码的分析,来讲一讲什么是BeanPostProcess
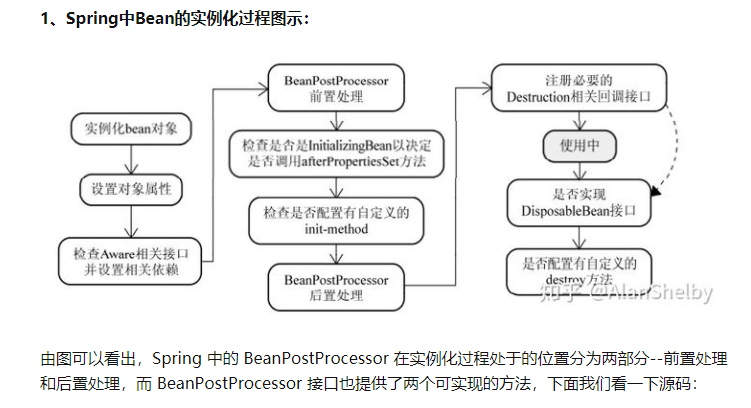
BeanPostProcess:Spring框架的提供的一个扩展类点(不止一个)通过实现BeanPostProcessor接口,程序员就可插手bean实例化的过程,从而减轻了beanFactory的负担
这里引用网上的一个bean实例化过程中,beanPostProcess所处的位置的图:
/**
* BeanPostProcessor是Spring框架的提供的一个扩展类点(不止一个)
* 通过实现BeanPostProcessor接口,程序员就可插手bean实例化的过程,从而减轻了beanFactory的负担
* 值得说明的是这个接口可以设置多个,会形成一个列表,然后依次执行
* (但是spring默认的怎么办?set)
* 比如AOP就是在bean实例后期间将切面逻辑织入bean实例中的
* AOP也正是通过BeanPostProcessor和IOC容器建立起了联系
* (由spring提供的默认的PostPorcessor,spring提供了很多默认的PostProcessor,下面我会一一介绍这些实现类的功能)
* 可以来演示一下 BeanPostProcessor 的使用方式(把动态代理和IOC、aop结合起来使用)
* 在演示之前先来熟悉一下这个接口,其实这个接口本身特别简单,简单到你发指
* 但是他的实现类特别复杂,同样复杂到发指!
* 可以看看spring提供哪些默认的实现(前方高能)
* 查看类的关系图可以知道spring提供了以下的默认实现,因为高能,故而我们只是解释几个常用的
* 1、ApplicationContextAwareProcessor (acap)
* acap后置处理器的作用是,当应用程序定义的Bean实现ApplicationContextAware接口时注入ApplicationContext对象
* 当然这是他的第一个作业,他还有其他作用,这里不一一列举了,可以参考源码
* 我们可以针对ApplicationContextAwareProcessor写一个栗子
* 2、InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
* 用来处理自定义的初始化方法和销毁方法
* 上次说过Spring中提供了3种自定义初始化和销毁方法分别是
* 一、通过@Bean指定init-method和destroy-method属性
* 二、Bean实现InitializingBean接口和实现DisposableBean
* 三、@PostConstruct:@PreDestroy
* 为什么spring通这三种方法都能完成对bean生命周期的回调呢?
* 可以通过InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的源码来解释
* 3、InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
* 4、CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
* 5、AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
* 6 、RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
* 7、BeanValidationPostProcessor
* 8、AbstractAutoProxyCreator
* ......
* 后面会一一解释
*/
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* 在bean初始化之前执行
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
/**
* 初始化之后
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
由方法名字也可以看出,前者在实例化及依赖注入完成后、在任何初始化代码(比如配置文件中的init-method)调用之前调用;后者在初始化代码调用之后调用。此处需要注意的是:接口中的两个方法都要将传入的 bean 返回,而不能返回 null,如果返回的是 null 那么我们通过 getBean() 方法将得不到目标。
我们来搞一个自定义的玩一下:上代码
@Component
public class CarryProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* 在类的初始化之前
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean.getClass().getSimpleName().equals("IndexDao")) {
System.out.println("before");
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean.getClass().getSimpleName().equals("IndexDao")) {
System.out.println("after");
}
return bean;
}
}@Repository
public class IndexDao implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public IndexDao() {
System.out.println("构造.....");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("init");
}
public void query() {
System.out.println("index dao query");
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
System.out.println(applicationContext);
}
}我们可以看下代码的执行结果:
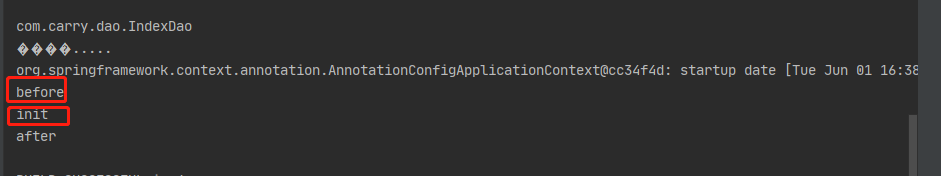
postProcessBeforeInitialization会在init方法之前执行
不知道大家有没有注意到,我这次自定义演示beanPostProcess的时候,还加了一个IndexDao去实现ApplicationContextAware接口,,实现里面的里面有一个private ApplicationContext applicationContext; 然后重写它的setApplicationContext方法进行赋值.
你们可以想想这个有啥用?这个作用可大了,你想想你都能
拿到它的applicationContext了,不是能做很多事.
spring有一个这个的应用场景,就是spring中single的bean注入了一个prototype的Bean的解决方案
你们不知道的可以看下我的这篇博客,清晰明了:
spring中single的bean注入了一个prototype的Bean的解决方案
好了,回到正题,我们是不是已经知道了什么是beanPostProcess了,回到spring的源码
//添加一个后置处理器:ApplicationContextAwareProcessor 将spring容器赋值给bean对象的applicationContext属性
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));刚讲完了这行代码,来看下面做了什么,下面就是在往BeanFactory里面设置了几个忽略自动装配的接口
后面好像也没有啥重要的代码了,大家可以详细看我上面这个prepareBeanFactory方法的全部代码的注释就可以了.
这个prepareBeanFactory方法执行完毕,我们来看下个方法,点进去一看是空的,那挺好,不用讲了,这个肯定是给子类实现的,为容器的某些子类指定特殊的 BeanPost 事件处理器
来看下一个方法:invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
从方法名上可以得出:执行spring环境的BeanFactorypostProcess(程序员自定义的和spring内部定义的)
那么问题来了,什么是BeanFactorypostProcess?这又是spring的一个扩展点,我们来简单的讲解一下:
BeanFactoryPostProcessor:BeanFactory后置处理器,是对BeanDefinition对象进行修改
来写一个demo分析一下:
@Component
public class CarryBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
BeanDefinition indexDao = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("indexDao");
indexDao.setScope("prototype");
String beanClassName = indexDao.getBeanClassName();
System.out.println(beanClassName);
}
}我们可以拿到这个bena工厂哦,可以修改这个bd
好,回到正题,来接着分析这个方法
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
//自定义的beanFactoryPostProcessors
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {//BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor BeanfactoryPostProcessor
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
//这个currentRegistryProcessors 放的是spring内部自己实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的对象
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
//BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 等于 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
//getBeanNamesForType 根据bean的类型获取bean的名字ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
//这个地方可以得到一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,因为是spring默认在最开始自己注册的
//为什么要在最开始注册这个呢?
//因为spring的工厂需要许解析去扫描等等功能
//而这些功能都是需要在spring工厂初始化完成之前执行
//要么在工厂最开始的时候、要么在工厂初始化之中,反正不能再之后
//因为如果在之后就没有意义,因为那个时候已经需要使用工厂了
//所以这里spring'在一开始就注册了一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,用来插手springfactory的实例化过程
//在这个地方断点可以知道这个类叫做ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
//ConfigurationClassPostProcessor那么这个类能干嘛呢?可以参考源码
//下面我们对这个牛逼哄哄的类(他能插手spring工厂的实例化过程还不牛逼吗?)重点解释
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
//排序不重要,况且currentRegistryProcessors这里也只有一个数据
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
//合并list,不重要(为什么要合并,因为还有自己的)
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
//最重要。注意这里是方法调用
//执行所有BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
//执行完成了所有BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
//这个list只是一个临时变量,故而要清除
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
//执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor的回调,前面不是吗?
//前面执行的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子类BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的回调
//这是执行的是BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessBeanFactory
//ConfuguratuonClassPpostProcssor
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
//自定义BeanFactoryPostProcessor
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
//ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}这个方法确实有点长,我们来一点点分析,抓大放小,把它攻克掉.
这个方法的前面定义了几个list用来存放 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 和BeanFactoryPostProcessor (你自己手动add进去的和spring内部维护的)
我们可以断点到这一行代码看一下:
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();到底有什么值,很重要哦
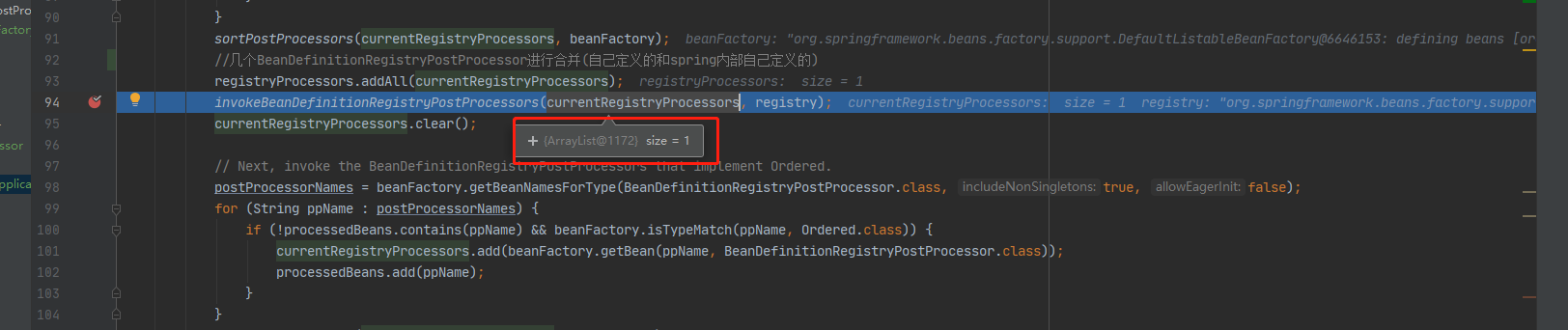
只有一个,你们知道是哪个吗?从我博客的第一篇看过来的肯定知道是哪个BeanFactoryPostProcessor
就是我之前提到过的,在reader构造方法里面添加的一个类:
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor这个类的作用很大,我把这个类,贴出来,大家都好好看看
/**
* 扫描、解析注解、imprt
* {@link BeanFactoryPostProcessor} used for bootstrapping processing of
* {@link Configuration @Configuration} classes.
*
*/
public class ConfigurationClassPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,
PriorityOrdered, ResourceLoaderAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware {
private static final String IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME =
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class.getName() + ".importRegistry";
private final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
private SourceExtractor sourceExtractor = new PassThroughSourceExtractor();
private ProblemReporter problemReporter = new FailFastProblemReporter();
@Nullable
private Environment environment;
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();
@Nullable
private ClassLoader beanClassLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
private MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory();
private boolean setMetadataReaderFactoryCalled = false;
private final Set<Integer> registriesPostProcessed = new HashSet<>();
private final Set<Integer> factoriesPostProcessed = new HashSet<>();
@Nullable
private ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader reader;
private boolean localBeanNameGeneratorSet = false;
/* Using short class names as default bean names */
private BeanNameGenerator componentScanBeanNameGenerator = new AnnotationBeanNameGenerator();
/* Using fully qualified class names as default bean names */
private BeanNameGenerator importBeanNameGenerator = new AnnotationBeanNameGenerator() {
@Override
protected String buildDefaultBeanName(BeanDefinition definition) {
String beanClassName = definition.getBeanClassName();
Assert.state(beanClassName != null, "No bean class name set");
return beanClassName;
}
};
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE; // within PriorityOrdered
}
/**
* Set the {@link SourceExtractor} to use for generated bean definitions
* that correspond to {@link Bean} factory methods.
*/
public void setSourceExtractor(@Nullable SourceExtractor sourceExtractor) {
this.sourceExtractor = (sourceExtractor != null ? sourceExtractor : new PassThroughSourceExtractor());
}
public void setProblemReporter(@Nullable ProblemReporter problemReporter) {
this.problemReporter = (problemReporter != null ? problemReporter : new FailFastProblemReporter());
}
public void setMetadataReaderFactory(MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) {
Assert.notNull(metadataReaderFactory, "MetadataReaderFactory must not be null");
this.metadataReaderFactory = metadataReaderFactory;
this.setMetadataReaderFactoryCalled = true;
}
public void setBeanNameGenerator(BeanNameGenerator beanNameGenerator) {
Assert.notNull(beanNameGenerator, "BeanNameGenerator must not be null");
this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet = true;
this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = beanNameGenerator;
this.importBeanNameGenerator = beanNameGenerator;
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");
this.environment = environment;
}
@Override
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Assert.notNull(resourceLoader, "ResourceLoader must not be null");
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
if (!this.setMetadataReaderFactoryCalled) {
this.metadataReaderFactory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory(resourceLoader);
}
}
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader beanClassLoader) {
this.beanClassLoader = beanClassLoader;
if (!this.setMetadataReaderFactoryCalled) {
this.metadataReaderFactory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory(beanClassLoader);
}
}
/**
* 手动调用的
* Derive further bean definitions from the configuration classes in the registry.
*/
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
int registryId = System.identityHashCode(registry);
if (this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
}
if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
}
this.registriesPostProcessed.add(registryId);
processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry);
}
/**
* Prepare the Configuration classes for servicing bean requests at runtime
* by replacing them with CGLIB-enhanced subclasses.
*/
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
int factoryId = System.identityHashCode(beanFactory);
if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(factoryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + beanFactory);
}
this.factoriesPostProcessed.add(factoryId);
if (!this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(factoryId)) {
// BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor hook apparently not supported...
// Simply call processConfigurationClasses lazily at this point then.
processConfigBeanDefinitions((BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory);
}
//给配置类产生cglib代理
//为什么需要产生cglib代理?
enhanceConfigurationClasses(beanFactory);
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor(beanFactory));
}
/**
* Build and validate a configuration model based on the registry of
* {@link Configuration} classes.
*/
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//定义一个list存放app 提供的bd(项目当中提供了@Compent)
List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
//获取容器中注册的所有bd名字
//7个
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
/**
* Full
* Lite
*/
for (String beanName : candidateNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef) ||
ConfigurationClassUtils.isLiteConfigurationClass(beanDef)) {
//果BeanDefinition中的configurationClass属性为full或者lite,则意味着已经处理过了,直接跳过
//这里需要结合下面的代码才能理解
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef);
}
}
//判断是否是Configuration类,如果加了Configuration下面的这几个注解就不再判断了
// 还有 add(Component.class.getName());
// candidateIndicators.add(ComponentScan.class.getName());
// candidateIndicators.add(Import.class.getName());
// candidateIndicators.add(ImportResource.class.getName());
//beanDef == appconfig
else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
//BeanDefinitionHolder 也可以看成一个数据结构
configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));
}
}
// Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found
if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// 排序,根据order,不重要
// Sort by previously determined @Order value, if applicable
configCandidates.sort((bd1, bd2) -> {
int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition());
int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition());
return Integer.compare(i1, i2);
});
// Detect any custom bean name generation strategy supplied through the enclosing application context
SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null;
//如果BeanDefinitionRegistry是SingletonBeanRegistry子类的话,
// 由于我们当前传入的是DefaultListableBeanFactory,是SingletonBeanRegistry 的子类
// 因此会将registry强转为SingletonBeanRegistry
if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) {
sbr = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry;
if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet) {//是否有自定义的
BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR);
//SingletonBeanRegistry中有id为 org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationBeanNameGenerator
//如果有则利用他的,否则则是spring默认的
if (generator != null) {
this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator;
this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator;
}
}
}
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();
}
// Parse each @Configuration class
//实例化ConfigurationClassParser 为了解析各个配置类
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
//实例化2个set,candidates用于将之前加入的configCandidates进行去重
//因为可能有多个配置类重复了
//alreadyParsed用于判断是否处理过
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates);
Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size());
do {
parser.parse(candidates);
parser.validate();
//map.keyset
Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);
// Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content
if (this.reader == null) {
this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(
registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,
this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
/**
* 这里值得注意的是扫描出来的bean当中可能包含了特殊类
* 比如ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar那么也在这个方法里面处理
* 但是并不是包含在configClasses当中
* configClasses当中主要包含的是importSelector
* 因为ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar在扫描出来的时候已经被添加到一个list当中去了
*/
//bd 到 map 除却普通
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);
candidates.clear();
//由于我们这里进行了扫描,把扫描出来的BeanDefinition注册给了factory
//但是
if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {
String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames));
Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>();
for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {
alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {
if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {
BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&
!alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) {
candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName));
}
}
}
candidateNames = newCandidateNames;
}
}
while (!candidates.isEmpty());
// Register the ImportRegistry as a bean in order to support ImportAware @Configuration classes
if (sbr != null && !sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) {
sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) {
// Clear cache in externally provided MetadataReaderFactory; this is a no-op
// for a shared cache since it'll be cleared by the ApplicationContext.
((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this.metadataReaderFactory).clearCache();
}
}
/**
* Post-processes a BeanFactory in search of Configuration class BeanDefinitions;
* any candidates are then enhanced by a {@link ConfigurationClassEnhancer}.
* Candidate status is determined by BeanDefinition attribute metadata.
* @see ConfigurationClassEnhancer
*/
public void enhanceConfigurationClasses(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
Map<String, AbstractBeanDefinition> configBeanDefs = new LinkedHashMap<>();
for (String beanName : beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
//判断是否是一个全注解类
//扫描是全注解类?full和lite的关系
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef)) {
if (!(beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition '" +
beanName + "' since it is not stored in an AbstractBeanDefinition subclass");
}
else if (logger.isWarnEnabled() && beanFactory.containsSingleton(beanName)) {
logger.warn("Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition '" + beanName +
"' since its singleton instance has been created too early. The typical cause " +
"is a non-static @Bean method with a BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor " +
"return type: Consider declaring such methods as 'static'.");
}
configBeanDefs.put(beanName, (AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef);
}
}
if (configBeanDefs.isEmpty()) {
// nothing to enhance -> return immediately
return;
}
ConfigurationClassEnhancer enhancer = new ConfigurationClassEnhancer();
for (Map.Entry<String, AbstractBeanDefinition> entry : configBeanDefs.entrySet()) {
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDef = entry.getValue();
// If a @Configuration class gets proxied, always proxy the target class
beanDef.setAttribute(AutoProxyUtils.PRESERVE_TARGET_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE);
try {
// Set enhanced subclass of the user-specified bean class
Class<?> configClass = beanDef.resolveBeanClass(this.beanClassLoader);
if (configClass != null) {
//完成对全注解类的cglib代理
Class<?> enhancedClass = enhancer.enhance(configClass, this.beanClassLoader);
if (configClass != enhancedClass) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(String.format("Replacing bean definition '%s' existing class '%s' with " +
"enhanced class '%s'", entry.getKey(), configClass.getName(), enhancedClass.getName()));
}
beanDef.setBeanClass(enhancedClass);
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot load configuration class: " + beanDef.getBeanClassName(), ex);
}
}
}
private static class ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor extends InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter {
private final BeanFactory beanFactory;
public ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(
PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) {
// Inject the BeanFactory before AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor's
// postProcessPropertyValues method attempts to autowire other configuration beans.
if (bean instanceof EnhancedConfiguration) {
((EnhancedConfiguration) bean).setBeanFactory(this.beanFactory);
}
return pvs;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean instanceof ImportAware) {
ImportRegistry ir = this.beanFactory.getBean(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, ImportRegistry.class);
AnnotationMetadata importingClass = ir.getImportingClassFor(bean.getClass().getSuperclass().getName());
if (importingClass != null) {
((ImportAware) bean).setImportMetadata(importingClass);
}
}
return bean;
}
}
}
好了,我们接着分析:
进去这个 invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors方法
/**
* Invoke the given BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor beans.
*/
private static void invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(
Collection<? extends BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> postProcessors, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
for (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
}
}这个其实就是遍历这个list,主要就是调用里面的方法
进最重要的一个方法:processConfigBeanDefinitions这个方法很重要,我们来分析下这个方法里面做了什么事
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//定义一个list存放app 提供的bd(项目当中提供了@Compent)
List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
//获取容器中注册的所有bd名字
//7个
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
/**
* Full
* Lite
*/
for (String beanName : candidateNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef) ||
ConfigurationClassUtils.isLiteConfigurationClass(beanDef)) {
//果BeanDefinition中的configurationClass属性为full或者lite,则意味着已经处理过了,直接跳过
//这里需要结合下面的代码才能理解
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef);
}
}
//判断是否是Configuration类,如果加了Configuration下面的这几个注解就不再判断了
// 还有 add(Component.class.getName());
// candidateIndicators.add(ComponentScan.class.getName());
// candidateIndicators.add(Import.class.getName());
// candidateIndicators.add(ImportResource.class.getName());
//beanDef == appconfig
else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
//BeanDefinitionHolder 也可以看成一个数据结构
configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));
}
}
// Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found
if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// 排序,根据order,不重要
// Sort by previously determined @Order value, if applicable
configCandidates.sort((bd1, bd2) -> {
int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition());
int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition());
return Integer.compare(i1, i2);
});
// Detect any custom bean name generation strategy supplied through the enclosing application context
SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null;
//如果BeanDefinitionRegistry是SingletonBeanRegistry子类的话,
// 由于我们当前传入的是DefaultListableBeanFactory,是SingletonBeanRegistry 的子类
// 因此会将registry强转为SingletonBeanRegistry
if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) {
sbr = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry;
if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet) {//是否有自定义的
BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR);
//SingletonBeanRegistry中有id为 org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationBeanNameGenerator
//如果有则利用他的,否则则是spring默认的
if (generator != null) {
this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator;
this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator;
}
}
}
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();
}
// Parse each @Configuration class
//实例化ConfigurationClassParser 为了解析各个配置类
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
//实例化2个set,candidates用于将之前加入的configCandidates进行去重
//因为可能有多个配置类重复了
//alreadyParsed用于判断是否处理过
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates);
Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size());
do {
parser.parse(candidates);
parser.validate();
//map.keyset
Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);
// Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content
if (this.reader == null) {
this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(
registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,
this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
/**
* 这里值得注意的是扫描出来的bean当中可能包含了特殊类
* 比如ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar那么也在这个方法里面处理
* 但是并不是包含在configClasses当中
* configClasses当中主要包含的是importSelector
* 因为ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar在扫描出来的时候已经被添加到一个list当中去了
*/
//bd 到 map 除却普通
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);
candidates.clear();
//由于我们这里进行了扫描,把扫描出来的BeanDefinition注册给了factory
//但是
if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {
String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames));
Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>();
for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {
alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {
if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {
BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&
!alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) {
candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName));
}
}
}
candidateNames = newCandidateNames;
}
}
while (!candidates.isEmpty());
// Register the ImportRegistry as a bean in order to support ImportAware @Configuration classes
if (sbr != null && !sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) {
sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) {
// Clear cache in externally provided MetadataReaderFactory; this is a no-op
// for a shared cache since it'll be cleared by the ApplicationContext.
((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this.metadataReaderFactory).clearCache();
}
}
//所有的bean的名字
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();这个其实就是我们上节博客记录的,放在factory里面的七个类然后遍历这七个类
我们看这段代码
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef) ||
ConfigurationClassUtils.isLiteConfigurationClass(beanDef)) {
//果BeanDefinition中的configurationClass属性为full或者lite,则意味着已经处理过了,直接跳过
//这里需要结合下面的代码才能理解
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef);
}
}我这这边先暂时记下两个单词:full和lite后面会慢慢分析
继续往下走:
//判断是否是Configuration类,如果加了Configuration下面的这几个注解就不再判断了
// 还有 add(Component.class.getName());
// candidateIndicators.add(ComponentScan.class.getName());
// candidateIndicators.add(Import.class.getName());
// candidateIndicators.add(ImportResource.class.getName());
//beanDef == appconfig
else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
//BeanDefinitionHolder 也可以看成一个数据结构
configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));
}进ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)方法看下:
public static boolean checkConfigurationClassCandidate(BeanDefinition beanDef, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) {
String className = beanDef.getBeanClassName();
if (className == null || beanDef.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return false;
}
AnnotationMetadata metadata;
if (beanDef instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition &&
className.equals(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef).getMetadata().getClassName())) {
// Can reuse the pre-parsed metadata from the given BeanDefinition...
//如果BeanDefinition 是 AnnotatedBeanDefinition的实例,并且className 和 BeanDefinition中 的元数据 的类名相同
// 则直接从BeanDefinition 获得Metadata
metadata = ((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef).getMetadata();
}
else if (beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef).hasBeanClass()) {
// Check already loaded Class if present...
// since we possibly can't even load the class file for this Class.
//如果BeanDefinition 是 AbstractBeanDefinition的实例,并且beanDef 有 beanClass 属性存在
//则实例化StandardAnnotationMetadata
Class<?> beanClass = ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef).getBeanClass();
metadata = new StandardAnnotationMetadata(beanClass, true);
}
else {
try {
MetadataReader metadataReader = metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(className);
metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
}
catch (IOException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not find class file for introspecting configuration annotations: " + className, ex);
}
return false;
}
}
//判断当前这个bd中存在的类是不是加了@Configruation注解
//如果存在则spring认为他是一个全注解的类
if (isFullConfigurationCandidate(metadata)) {
//如果存在Configuration 注解,则为BeanDefinition 设置configurationClass属性为full
beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_FULL);
}
//判断是否加了以下注解,摘录isLiteConfigurationCandidate的源码
// candidateIndicators.add(Component.class.getName());
// candidateIndicators.add(ComponentScan.class.getName());
// candidateIndicators.add(Import.class.getName());
// candidateIndicators.add(ImportResource.class.getName());
//如果不存在Configuration注解,spring则认为是一个部分注解类
else if (isLiteConfigurationCandidate(metadata)) {
beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_LITE);
}
else {
return false;
}
// It's a full or lite configuration candidate... Let's determine the order value, if any.
Integer order = getOrder(metadata);
if (order != null) {
beanDef.setAttribute(ORDER_ATTRIBUTE, order);
}
return true;
}我们来分析一下这个方法
前面的代码大概就是判断这个bd属于哪种类型的,从不同类型的bd获取Metadata
主要来分析这个:
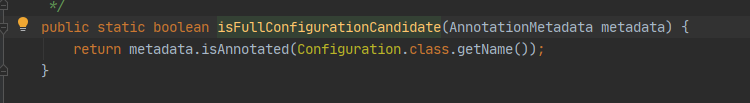
//判断当前这个bd中存在的类是不是加了@Configruation注解
//如果存在则spring认为他是一个全注解的类
if (isFullConfigurationCandidate(metadata)) {
//如果存在Configuration 注解,则为BeanDefinition 设置configurationClass属性为full
beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_FULL);
}
这个就是我们上面的我们记下的full和lite,具体啥作用,下次再分析,现在我们知道了,如果一个类,被加了@Configuration,就会被标记full,如果大家跟着我的博客,一点点debug,应该知道,我们现在BeanFactory里面,有几个类就会被标记成full?一个,没错,就是我们的AppConfig
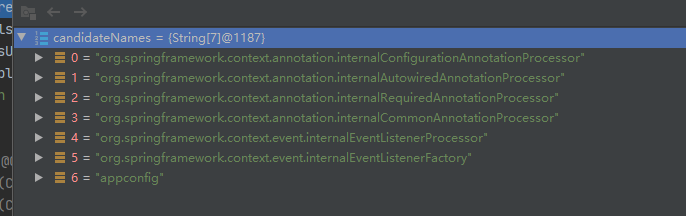
再次请大家记住我们现在有几个bd
//判断是否加了以下注解,摘录isLiteConfigurationCandidate的源码
// candidateIndicators.add(Component.class.getName());
// candidateIndicators.add(ComponentScan.class.getName());
// candidateIndicators.add(Import.class.getName());
// candidateIndicators.add(ImportResource.class.getName());
//如果不存在Configuration注解,spring则认为是一个部分注解类
else if (isLiteConfigurationCandidate(metadata)) {
beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_LITE);
}public static boolean isLiteConfigurationCandidate(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
// Do not consider an interface or an annotation...
if (metadata.isInterface()) {
return false;
}
// Any of the typical annotations found?
for (String indicator : candidateIndicators) {
if (metadata.isAnnotated(indicator)) {
return true;
}
}
// Finally, let's look for @Bean methods...
try {
return metadata.hasAnnotatedMethods(Bean.class.getName());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Failed to introspect @Bean methods on class [" + metadata.getClassName() + "]: " + ex);
}
return false;
}
}
private static final Set<String> candidateIndicators = new HashSet<>(8);
static {
candidateIndicators.add(Component.class.getName());
candidateIndicators.add(ComponentScan.class.getName());
candidateIndicators.add(Import.class.getName());
candidateIndicators.add(ImportResource.class.getName());
}
如果一个类被加上了@Component @ComponentScan @Import @InportResource将会标记成lite
checkConfigurationClassCandidate这个方法我们现在也知道干了什么事
好了,这篇博客就先到这,下一篇接着分析org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#processConfigBeanDefinitions这个牛逼哄哄的类和牛逼哄哄的方法
最后
以上就是忐忑百褶裙最近收集整理的关于Spring源码分析,bean的BeanPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor的的全部内容,更多相关Spring源码分析,bean内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复