之前的Blog【SpringBoot学习笔记 一】SpringBoot基本概念和项目初始化里我提到,SpringBoot初始化的项目结构包含如下四部分,也就是只要包含如下四部分就可以启动一个最简单的SpringBoot
- 一个配置文件:application.properties ,管理相关配置信息,在【SpringBoot学习笔记 二】YAML格式文件配置方式详解中介绍到SpringBoot的YAML配置是如何编写又是如何自动绑定到代码实体中的
- 一个测试类:SpringbootApplicationTests,用来进行项目测试,这个暂时还没有用到,不过也不涉及核心机制
- 一个Maven的坐标文件: pom.xml,项目的相关依赖坐标,在【SpringBoot学习笔记 一】SpringBoot基本概念和项目初始化中介绍到了什么是场景启动器,SpringBoot的依赖是如何管理的
- 程序的主启动类:SpringbootApplication,是程序的启动入口,也是SpringBoot自动化配置的出发点。
我们回顾下原来搭建一个springmvc的hello-word的web项目(xml配置的)我们需要在pom中导入各种依赖,然后各个依赖有可能还会存在版本冲突需要各种排除。当你历尽千辛万苦的把依赖解决了,然后还需要编写web.xml、springmvc.xml配置文件等。我们只想写个hello-word项目而已,却把一大把的时间都花在了配置文件和jar包的依赖上面。大大的影响了我们开发的效率,以及加大了web开发的难度。为了简化这复杂的配置、以及各个版本的冲突依赖关系,SpringBoot就应运而生。我们现在通过idea创建一个springboot项目只要分分钟就解决了,你不需要关心各种配置(基本实现零配置),让你真正的实现了开箱即用,这都要归功于 Spring Boot 的自动化配置,也是SpringBoot的核心原理,搞懂了这个就搞懂了SpringBoot到底是怎么实现的。
Spring Factories 机制
Spring Boot 的自动配置是基于 Spring Factories 机制实现的。Spring Factories 机制是 Spring Boot 中的一种服务发现机制,这种扩展机制与 Java SPI 机制十分相似。Spring Boot 会自动扫描所有 Jar 包类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories 文件,并读取其中的内容,进行实例化,这种机制也是 Spring Boot Starter 的基础
Spring Factories文件格式
spring.factories 文件本质上与 properties 文件相似,其中包含一组或多组键值对(key=vlaue)
- key 的取值为接口的完全限定名
- value 的取值为接口实现类的完全限定名
- 一个接口可以设置多个实现类,不同实现类之间使用
,隔开
以Spring的TestContext框架配置为例:
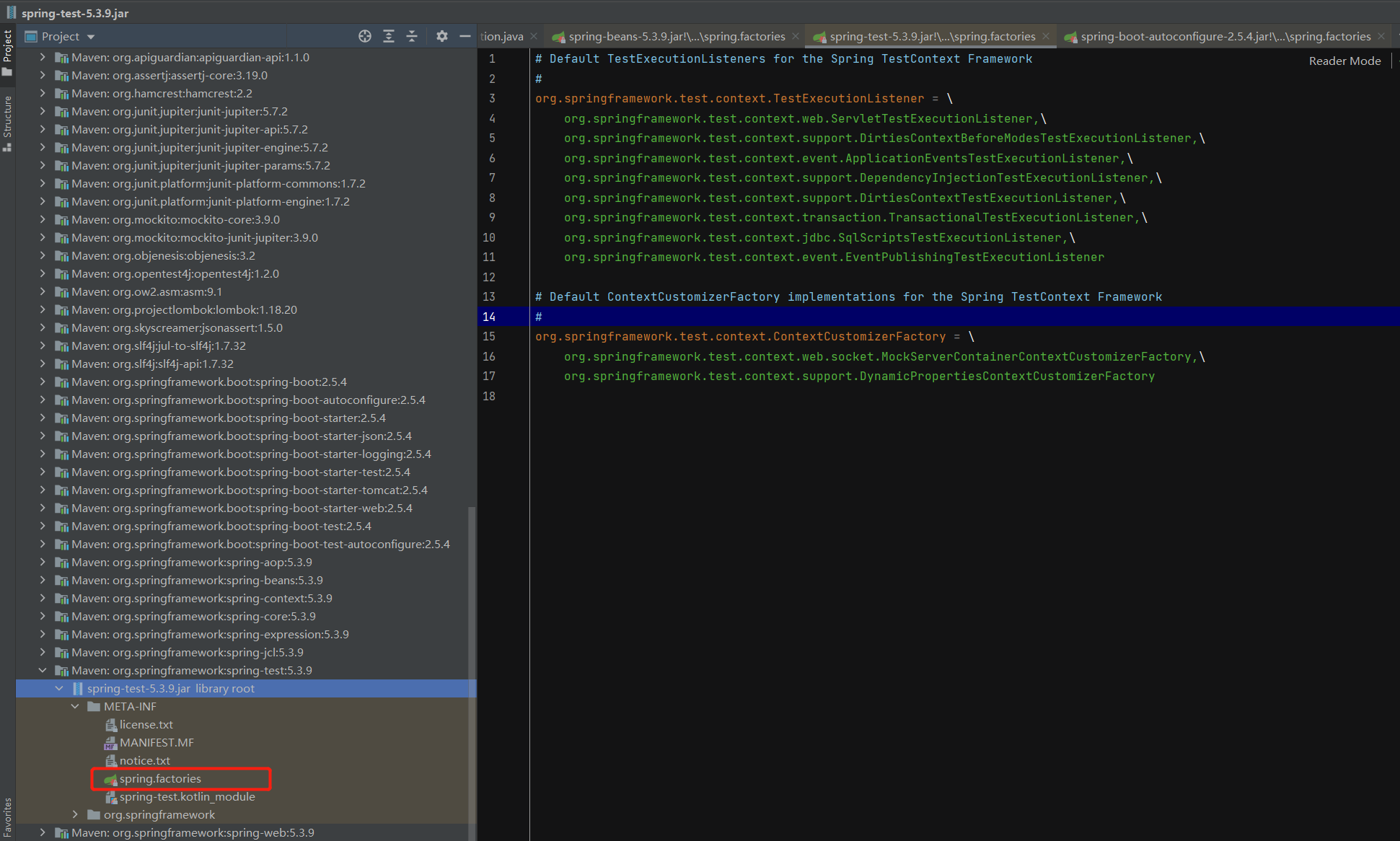
文件的格式如下:
# Default TestExecutionListeners for the Spring TestContext Framework
#
org.springframework.test.context.TestExecutionListener =
org.springframework.test.context.web.ServletTestExecutionListener,
org.springframework.test.context.support.DirtiesContextBeforeModesTestExecutionListener,
org.springframework.test.context.event.ApplicationEventsTestExecutionListener,
org.springframework.test.context.support.DependencyInjectionTestExecutionListener,
org.springframework.test.context.support.DirtiesContextTestExecutionListener,
org.springframework.test.context.transaction.TransactionalTestExecutionListener,
org.springframework.test.context.jdbc.SqlScriptsTestExecutionListener,
org.springframework.test.context.event.EventPublishingTestExecutionListener
# Default ContextCustomizerFactory implementations for the Spring TestContext Framework
#
org.springframework.test.context.ContextCustomizerFactory =
org.springframework.test.context.web.socket.MockServerContainerContextCustomizerFactory,
org.springframework.test.context.support.DynamicPropertiesContextCustomizerFactory
文件中配置的内容过长,为了阅读方便而手动换行时,为了防止内容丢失可以使用
。
Spring Factories 实现原理
spring-core 包里定义了 SpringFactoriesLoader 类,这个类会扫描所有 Jar 包类路径下的 META-INF/spring.factories 文件,并获取指定接口的配置。
loadFactories方法能够获取指定接口的实现类对象,它调用loadFactoryNames方法
public static <T> List<T> loadFactories(Class<T> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.notNull(factoryType, "'factoryType' must not be null");
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoader == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
// 调用loadFactoryNames获取接口的实现类
List<String> factoryImplementationNames = loadFactoryNames(factoryType, classLoaderToUse);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded [" + factoryType.getName() + "] names: " + factoryImplementationNames);
}
// 遍历 factoryNames 数组,创建实现类的对象
List<T> result = new ArrayList(factoryImplementationNames.size());
Iterator var5 = factoryImplementationNames.iterator();
//排序
while(var5.hasNext()) {
String factoryImplementationName = (String)var5.next();
result.add(instantiateFactory(factoryImplementationName, factoryType, classLoaderToUse));
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(result);
return result;
}
loadFactoryNames方法能够根据接口获取其实现类类名的集合,它调用loadSpringFactories方法
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoader == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
//获取自动配置类
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
loadSpringFactories方法能够读取该项目中所有 Jar 包类路径下
META-INF/spring.factories文件的配置内容,并以 Map 集合的形式返回
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
Map<String, List<String>> result = (Map)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
HashMap result = new HashMap();
try {
//扫描所有 Jar 包类路径下的 META-INF/spring.factories 文件
Enumeration urls = classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
//将扫描到的 META-INF/spring.factories 文件中内容包装成 properties 对象
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<?, ?> entry = (Map.Entry)var6.next();
//提取 properties 对象中的 key 值
String factoryTypeName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim();
//提取 proper 对象中的 value 值(多个类的完全限定名使用逗号连接的字符串)
// 使用逗号为分隔符转换为数组,数组内每个元素都是配置类的完全限定名
String[] factoryImplementationNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue());
String[] var10 = factoryImplementationNames;
int var11 = factoryImplementationNames.length;
//遍历配置类数组,并将数组转换为 list 集合
for(int var12 = 0; var12 < var11; ++var12) {
String factoryImplementationName = var10[var12];
((List)result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, (key) -> {
return new ArrayList();
})).add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
//将 propertise 对象的 key 与由配置类组成的 List 集合一一对应存入名为 result 的 Map 中
result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> {
return (List)implementations.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList));
});
cache.put(classLoader, result);
//返回 result
return result;
} catch (IOException var14) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var14);
}
}
}
SpringBoot自动配置实现原理
Spring Boot 自动化配置就是基于 Spring Factories 机制实现的,我们从注解开始一步一步跟进去:
@SpringBootApplication 注解
了解了Spring-Factories机制,我们再回过头来看看SpringBoot是如何利用该机制实现自动配置的。所有 Spring Boot 项目的主启动程序类上都使用了一个 @SpringBootApplication 注解,该注解是 Spring Boot 中最重要的注解之一 ,也是 Spring Boot 实现自动化配置的关键。
package com.example.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}
@SpringBootApplication 是一个组合元注解,其内容如下:
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanNameGenerator;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringBootConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.context.TypeExcludeFilter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.FilterType;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan.Filter;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(
excludeFilters = {@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}
), @Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class}
)}
) //自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件或者bean , 将这个bean定义加载到IOC容器中
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
@AliasFor(
annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class
)
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class
)
String[] excludeName() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ComponentScan.class,
attribute = "basePackages"
)
String[] scanBasePackages() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ComponentScan.class,
attribute = "basePackageClasses"
)
Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ComponentScan.class,
attribute = "nameGenerator"
)
Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> nameGenerator() default BeanNameGenerator.class;
@AliasFor(
annotation = Configuration.class
)
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
}
@EnableAutoConfiguration 注解
如上所述@SpringBootApplication 是一个组合元注解,还有@SpringBootConfiguration 和 @EnableAutoConfiguration,其中 @EnableAutoConfiguration 注解是 SpringBoot 自动化配置的核心所在。@EnableAutoConfiguration 注解用于开启 Spring Boot 的自动配置功能
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
String[] excludeName() default {};
}
它使用 Spring 框架提供的 @Import 注解通过 AutoConfigurationImportSelector类(选择器)给容器中导入自动配置组件
AutoConfigurationImportSelector 类
AutoConfigurationImportSelector 类实现了 DeferredImportSelector 接口,AutoConfigurationImportSelector 中还包含一个静态内部类 AutoConfigurationGroup,它实现了 DeferredImportSelector 接口的内部接口 Group,AutoConfigurationImportSelector 类中包含 3 个主要方法
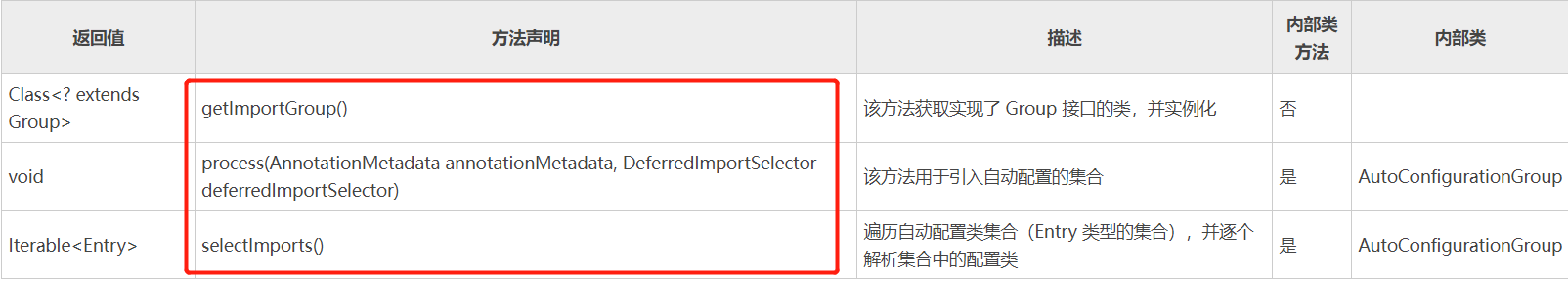
1 getImportGroup方法主要用于获取实现了 DeferredImportSelector.Group 接口的类
public Class<? extends Group> getImportGroup() {
//获取实现了 DeferredImportSelector.Gorup 接口的 AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationGroup 类
return AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationGroup.class;
}
2 process 方法通过调用 getAutoConfigurationEntry() 方法读取 spring.factories 文件中的内容,获得自动配置类的集合
public void process(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, DeferredImportSelector deferredImportSelector) {
Assert.state(deferredImportSelector instanceof AutoConfigurationImportSelector, () -> {
return String.format("Only %s implementations are supported, got %s", AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class.getSimpleName(), deferredImportSelector.getClass().getName());
});
//拿到 META-INF/spring.factories中的EnableAutoConfiguration,并做排除、过滤处理
//AutoConfigurationEntry里有需要引入配置类和排除掉的配置类,最终只要返回需要配置的配置类
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = ((AutoConfigurationImportSelector)deferredImportSelector).getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);
//加入缓存,List<AutoConfigurationEntry>类型
this.autoConfigurationEntries.add(autoConfigurationEntry);
Iterator var4 = autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations().iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
String importClassName = (String)var4.next();
//加入缓存,Map<String, AnnotationMetadata>类型
this.entries.putIfAbsent(importClassName, annotationMetadata);
}
}
getAutoConfigurationEntry方法通过调用 getCandidateConfigurations() 方法来获取自动配置类的完全限定名,并在经过排除、过滤等处理后,将其缓存到成员变量中
protected AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!this.isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
} else {
//获取注解元数据中的属性设置
AnnotationAttributes attributes = this.getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
//获取自动配置类
List<String> configurations = this.getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
//删除list 集合中重复的配置类
configurations = this.removeDuplicates(configurations);
//获取导入的配置类
Set<String> exclusions = this.getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
//检查是否还存在排除配置类
this.checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
//删除排除的配置类
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
//获取过滤器,过滤配置类
configurations = this.getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
//出发自动化配置导入事件
this.fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
}
在 getCandidateConfigurations方法中,根据 Spring Factories 机制调用 SpringFactoriesLoader 的 loadFactoryNames方法
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
根据 EnableAutoConfiguration.class (自动配置接口)获取其实现类(自动配置类)的类名的集合
protected Class<?> getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass() {
return EnableAutoConfiguration.class;
}
这个接口和类的映射关系在 spring-boot-autoconfigure-xxx.jar 类路径下的 META-INF/spring.factories 中设置如下:
.......
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.LifecycleAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ReactiveElasticsearchRestClientAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jdbc.JdbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcDataAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.r2dbc.R2dbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisReactiveAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRestClientAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.codec.CodecsAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.influx.InfluxDbAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jsonb.JsonbAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.availability.ApplicationAvailabilityAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoReactiveAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.neo4j.Neo4jAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.netty.NettyAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.quartz.QuartzAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.R2dbcAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.R2dbcTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketRequesterAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketServerAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.rsocket.RSocketStrategiesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveSecurityAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveUserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.rsocket.RSocketSecurityAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.saml2.Saml2RelyingPartyAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.servlet.OAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.servlet.OAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sql.init.SqlInitializationAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskSchedulingAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.ClientHttpConnectorAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.reactive.WebSocketReactiveAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.client.WebServiceTemplateAutoConfiguration
.......
以上配置中,value 取值是由多个 xxxAutoConfiguration (使用逗号分隔)组成,每个 xxxAutoConfiguration 都是一个自动配置类。Spring Boot 启动时,会利用 Spring-Factories 机制,将这些 xxxAutoConfiguration 实例化并作为组件加入到容器中,以实现 Spring Boot 的自动配置
3 selectImports将 process 方法处理后得到的自动配置类,进行过滤、排除,最后将所有自动配置类添加到容器中
public Iterable<DeferredImportSelector.Group.Entry> selectImports() {
if (this.autoConfigurationEntries.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
} else {
//获取所有需要排除的配置类
Set<String> allExclusions = (Set)this.autoConfigurationEntries.stream().
map(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry::getExclusions).flatMap(Collection::stream).collect(Collectors.toSet());
//获取所有经过自动化配置过滤器的配置类
Set<String> processedConfigurations = (Set)this.autoConfigurationEntries.stream().map(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.
AutoConfigurationEntry::getConfigurations).flatMap(Collection::stream).collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedHashSet::new));
//排除过滤后配置类中需要排除的类
processedConfigurations.removeAll(allExclusions);
return (Iterable)this.sortAutoConfigurations(processedConfigurations,
this.getAutoConfigurationMetadata()).stream().map((importClassName) -> {
return new DeferredImportSelector.Group.Entry((AnnotationMetadata)this.entries.get(importClassName), importClassName);
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
SpringBoot自动配置绑定和修改
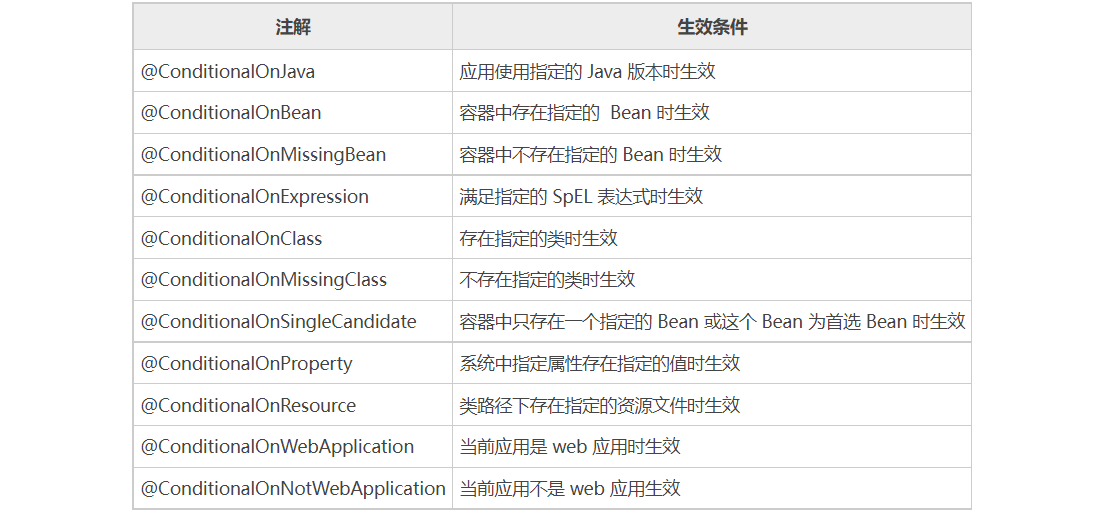
spring.factories 文件中的所有自动配置类(xxxAutoConfiguration),都是必须在一定的条件下才会作为组件添加到容器中,配置的内容才会生效。这些限制条件在 Spring Boot 中以 @Conditional 派生注解的形式体现
下面我们以 ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration 为例,介绍 Spring Boot 自动配置是如何生效的
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration自动配置类
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration配置类的代码如下:
@Configuration( //表示这是一个配置类,与 xml 配置文件等价,也可以给容器中添加组件
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
@AutoConfigureOrder(-2147483648)
@ConditionalOnClass({ServletRequest.class})//判断当前项目有没有 ServletRequest 这个类
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(// 判断当前应用是否是 web 应用,如果是,当前配置类生效
type = Type.SERVLET
)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ServerProperties.class})
//启动指定类的属性配置(ConfigurationProperties)功能;将配置文件中对应的值和 ServerProperties 绑定起来;并把 ServerProperties 加入到ioc容器中
@Import({ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class, EmbeddedTomcat.class, EmbeddedJetty.class, EmbeddedUndertow.class})
public class ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration {
public ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration() {
}
@Bean //给容器中添加一个组件,这个组件的某些值需要从properties中获取
public ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer servletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(ServerProperties serverProperties, ObjectProvider<WebListenerRegistrar> webListenerRegistrars) {
return new ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(serverProperties, (List) webListenerRegistrars.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnClass(
name = {"org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat"}
)
public TomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer tomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(ServerProperties serverProperties) {
return new TomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer(serverProperties);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingFilterBean({ForwardedHeaderFilter.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(
value = {"server.forward-headers-strategy"},
havingValue = "framework"
)
public FilterRegistrationBean<ForwardedHeaderFilter> forwardedHeaderFilter() {
ForwardedHeaderFilter filter = new ForwardedHeaderFilter();
FilterRegistrationBean<ForwardedHeaderFilter> registration = new FilterRegistrationBean(filter, new ServletRegistrationBean[0]);
registration.setDispatcherTypes(DispatcherType.REQUEST, new DispatcherType[]{DispatcherType.ASYNC, DispatcherType.ERROR});
registration.setOrder(-2147483648);
return registration;
}
public static class BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, BeanFactoryAware {
private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
public BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar() {
}
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
if (beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
this.beanFactory = (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) beanFactory;
}
}
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (this.beanFactory != null) {
this.registerSyntheticBeanIfMissing(registry, "webServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor", WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor.class, WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor::new);
this.registerSyntheticBeanIfMissing(registry, "errorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor", ErrorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor.class, ErrorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor::new);
}
}
private <T> void registerSyntheticBeanIfMissing(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, String name, Class<T> beanClass, Supplier<T> instanceSupplier) {
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(beanClass, true, false))) {
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(beanClass, instanceSupplier);
beanDefinition.setSynthetic(true);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(name, beanDefinition);
}
}
}
}
该类使用了以下注解:
@Configuration:用于定义一个配置类,可用于替换 Spring 中的 xml 配置文件;@Bean:被 @Configuration 注解的类内部,可以包含有一个或多个被 @Bean 注解的方法,用于构建一个 Bean,并添加到 Spring 容器中;该注解与 spring 配置文件中 等价,方法名与 的 id 或 name 属性等价,方法返回值与 class 属性等价;- 除了 @Configuration 和 @Bean 注解外,该类还使用 5 个 @Conditional 衍生注解:
@ConditionalOnClass({ServletRequest.class}):判断当前项目是否存在 ServletRequest 这个类,若存在,则该配置类生效。@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET):判断当前应用是否是 Web 应用,如果是的话,当前配置类生效。@ConditionalOnClass(name = {"org.apache.catalina.startup.Tomcat"}):判断是否存在 Tomcat 类,若存在则该方法生效。@ConditionalOnMissingFilterBean({ForwardedHeaderFilter.class}):判断容器中是否有 ForwardedHeaderFilter 这个过滤器,若不存在则该方法生效。@ConditionalOnProperty(value = {"server.forward-headers-strategy"},havingValue = "framework"):判断配置文件中是否存在 server.forward-headers-strategy = framework,若不存在则该方法生效。
那么我们想要给自动配置类中属性什么样的值又是怎么实现的呢?
ServerProperties 类
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration 类还使用了一个 @EnableConfigurationProperties 注解,通过该注解导入了一个 ServerProperties 类,其部分源码如下
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "server",
ignoreUnknownFields = true
)
public class ServerProperties {
private Integer port;
private InetAddress address;
@NestedConfigurationProperty
private final ErrorProperties error = new ErrorProperties();
private ServerProperties.ForwardHeadersStrategy forwardHeadersStrategy;
private String serverHeader;
private DataSize maxHttpHeaderSize = DataSize.ofKilobytes(8L);
private Shutdown shutdown;
@NestedConfigurationProperty
private Ssl ssl;
@NestedConfigurationProperty
private final Compression compression;
@NestedConfigurationProperty
private final Http2 http2;
private final ServerProperties.Servlet servlet;
private final ServerProperties.Tomcat tomcat;
private final ServerProperties.Jetty jetty;
private final ServerProperties.Netty netty;
private final ServerProperties.Undertow undertow;
public ServerProperties() {
this.shutdown = Shutdown.IMMEDIATE;
this.compression = new Compression();
this.http2 = new Http2();
this.servlet = new ServerProperties.Servlet();
this.tomcat = new ServerProperties.Tomcat();
this.jetty = new ServerProperties.Jetty();
this.netty = new ServerProperties.Netty();
this.undertow = new ServerProperties.Undertow();
}
....
}
我们看到,ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration 使用了一个 @EnableConfigurationProperties 注解,通过该注解导入了一个 ServerProperties 类,而 ServerProperties 类上则使用了一个 @ConfigurationProperties 注解。这其实是 Spring Boot 自动配置机制中的通用用法。
自动配置实现步骤
@ConfigurationProperties 注解的作用,是将这个类的所有属性与配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定,以便于获取或修改配置,但是 @ConfigurationProperties 功能是由容器提供的,被它注解的类必须是容器中的一个组件,否则该功能就无法使用。而 @EnableConfigurationProperties 注解的作用正是将指定的类以组件的形式注入到 IOC 容器中,并开启其 @ConfigurationProperties 功能。因此,@ConfigurationProperties + @EnableConfigurationProperties 组合使用,便可以为 XxxProperties 类实现配置绑定功能。整体回顾下:
- SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
- 我们看我们需要的功能有没有在SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类当中
- 我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件,(只要我们要用的组件存在在其中,我们就不需要再手动配置了)
- 给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性。我们只需要在配置文件中指定这些属性的值即可
而这一切机制都是通过SpringBoot主启动类启动时的自动发现机制实现的。
其实SpringBoot的IOC和DI管理就是通过@Configuration纯注解方式实现的,提前编写好自动配置类,通过Spring Factories 机制发现导入,然后再读取配置文件中的值并绑定就可以直接使用或修改了。
自动配置类 XxxAutoConfiguration 负责使用 XxxProperties 中属性进行自动配置,而 XxxProperties 则负责将自动配置属性与配置文件的相关配置进行绑定,以便于用户通过配置文件修改默认的自动配置。也就是说,真正限制我们可以在配置文件中配置哪些属性的类就是这些 XxxxProperties 类,它与配置文件中定义的 prefix 关键字开头的一组属性是唯一对应的,这也是为什么我们在yaml这篇Blog【SpringBoot学习笔记 三】Profile多环境配置及配置优先级中提到的servler配置会自动生效。
Spring Boot 中为我们提供了大量的自动配置类 XxxAutoConfiguration 以及 XxxProperties,每个自动配置类 XxxAutoConfiguration 都使用了 @EnableConfigurationProperties 注解,而每个 XxxProperties 上都使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解,再回顾下我在这篇Blog中【SpringBoot学习笔记 二】YAML格式文件配置方式详解提到的Person配置为什么能被读取,就是因为这其实就是一个手动的配置,我们自己写配置,自己绑定配置与组件
手动写配置
person:
name: tml
age: 30
pets:
-dog
-cat
-pig
car:
name: 蔚来es6
url:
domain: www.baidu.com
location: china
手动注册组件,手动将配置与组件绑定
package com.example.springboot.model;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.List;
/**
* * @Name Person
* * @Description
* * @author tianmaolin
* * @Data 2021/9/27
*/
@Component
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:application.properties")
public class Person {
//@ConfigurationProperties配置yaml自动JavaBean注入
private String name;
private Integer age;
private List<String> pets;
private Car car;
//@Value配置yaml属性引入,SPEL表达式获取值
@Value("${url.domain}")
private String url;
@Value("${url.location}")
private String location;
//@Value配置外部配置文件属性绑定
@Value("${spring.application.name}")
private String appName;
}
总结一下
话不多说,通过学习理解整理了如下的流程图,也就是为什么SpringBoot可以基本实现零配置启动,其实并不是零配置,而是Spring提前给我们做好了一切而已。
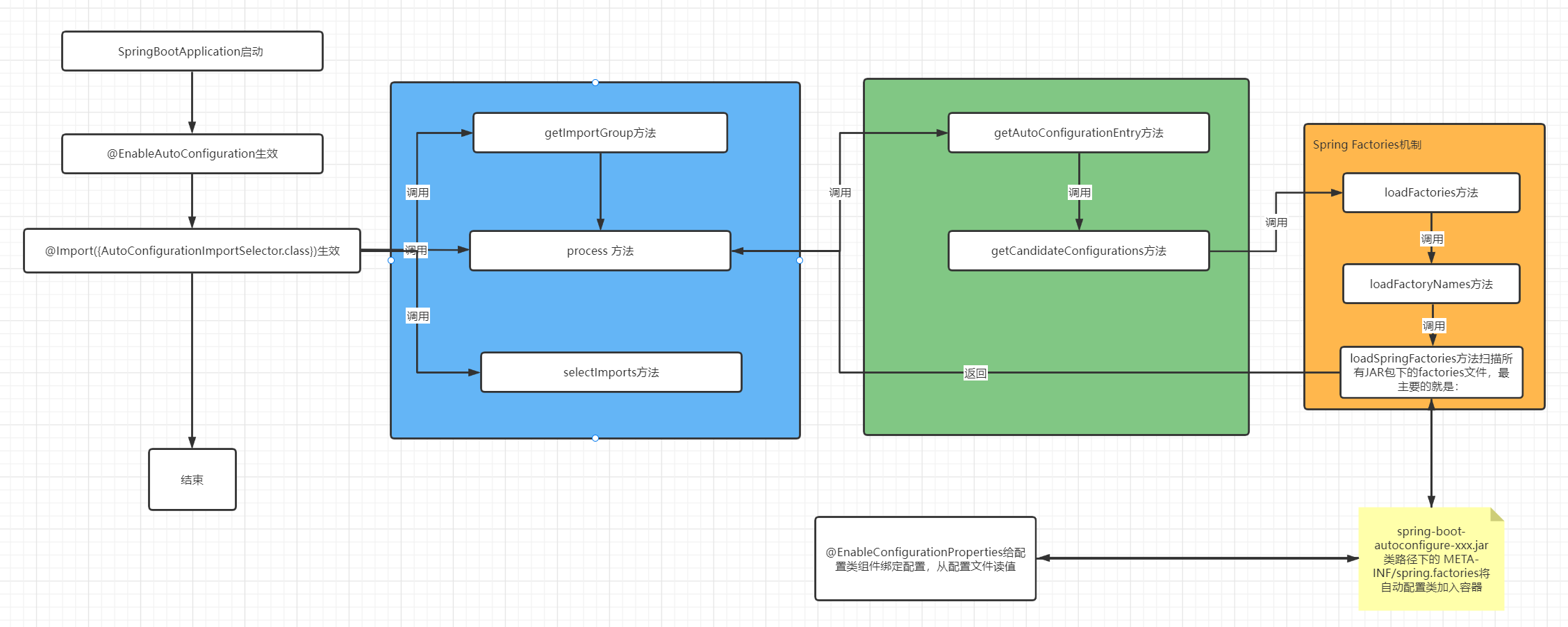
最后
以上就是甜蜜长颈鹿最近收集整理的关于【SpringBoot学习笔记 四】SpringBoot自动配置原理Spring Factories 机制SpringBoot自动配置实现原理SpringBoot自动配置绑定和修改总结一下的全部内容,更多相关【SpringBoot学习笔记内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复