以下内容节选自https://bitesofcode.wordpress.com/2017/09/12/augmented-reality-with-python-and-opencv-part-1/comment-page-1/#comment-61

对于上图中,怎么估计(begin{bmatrix}h_{11} & h_{12} & h_{13} \ h_{21} & h_{22} & h_{23} \ h_{31} & h_{32} & h_{33} end{bmatrix})?
我们可以使用Random Aample Consebsus(RANSAC)
RANSAC算法过程如下:
- 均匀随机选择点集合中的一部分点;
- Fit a model to subset
- find all remaining points that are "close" to the model and reject the rest as outliers
- do this many times and choose the best model
举个例子,假设我们有一下点集,我们想用使用RANSAC来用一条直线拟合:
算法过程如下:
- sample (randomly) the number of points required to fit the model
- solve for model params using samples
- Score by the fraction of inliers within a present threshold 't' of the model
- repeat 1-3 until the best model is found with high confidence
运行这个算法的结果图如下,显示了第一次迭代的前三个步骤, 之后的是Score步骤:
对于我们homograpy estimation,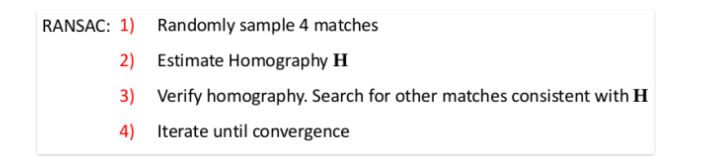
在Opencv中
# assuming matches stores the matches found and
# returned by bf.match(des_model, des_frame)
# differenciate between source points and destination points
src_pts = np.float32([kp_model[m.queryIdx].pt for m in matches]).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
dst_pts = np.float32([kp_frame[m.trainIdx].pt for m in matches]).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
# compute Homography
M, mask = cv2.findHomography(src_pts, dst_pts, cv2.RANSAC, 5.0)以上代码中5.0是阈值距离来决定一个匹配是否跟预估的Homography 一致,在预估了homography之后,我们可以投影四个角点:
# Draw a rectangle that marks the found model in the frame
h, w = model.shape
pts = np.float32([[0, 0], [0, h - 1], [w - 1, h - 1], [w - 1, 0]]).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
# project corners into frame
dst = cv2.perspectiveTransform(pts, M)
# connect them with lines
img2 = cv2.polylines(img_rgb, [np.int32(dst)], True, 255, 3, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.imshow('frame', cap)
cv2.waitKey(0)结果如下:
转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/rogerjin/p/7852472.html
最后
以上就是贪玩茉莉最近收集整理的关于Homography estimation(旋转估计)的全部内容,更多相关Homography内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复