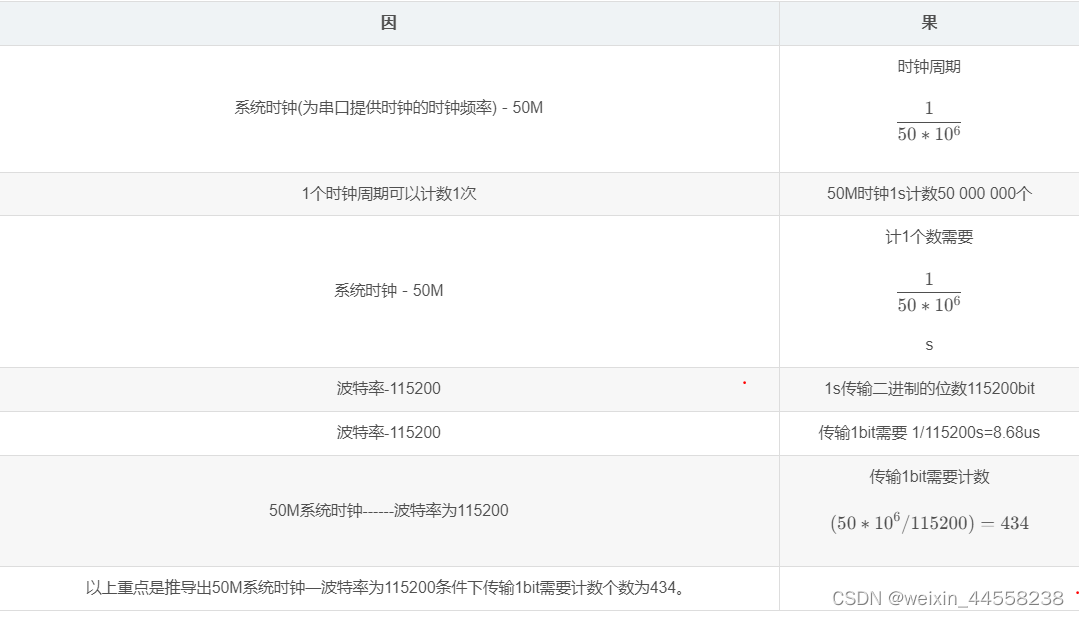
波特率技术举例:
1.串口发送原理:
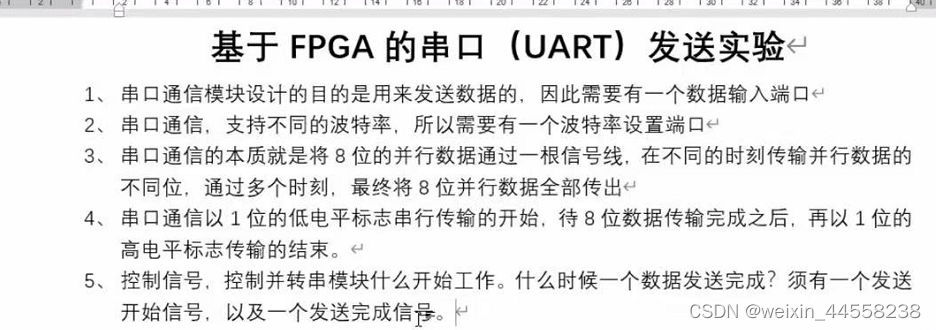
设计框图
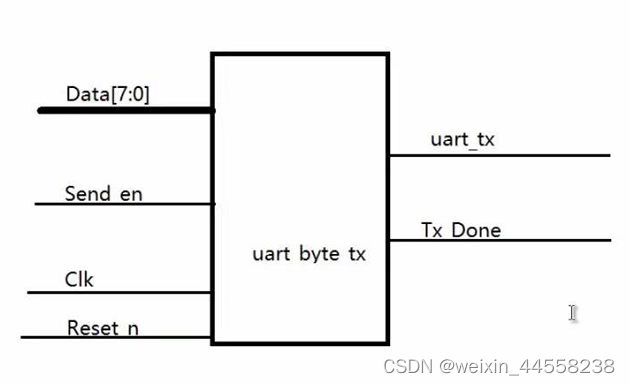
时序图:bps_clk为波特率时钟
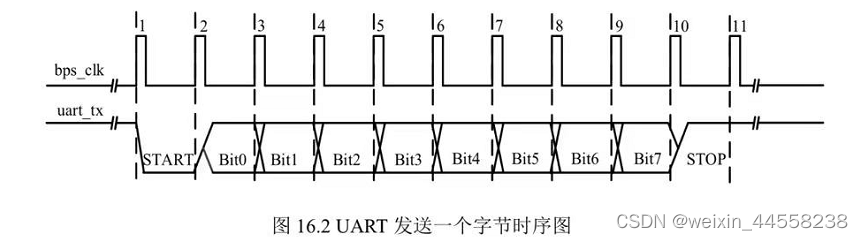
串口发送模块代码:
//时钟频率是50Mhz,也就是周期是20ns
module uart_byte_tx(
input [7:0] Data, //将要发送的数据
input En, //发送数据的使能信号
input clk, //系统时钟
input rst, //复位信号
input [2:0] Baud_set, //8种波特率模式
output reg uart_tx, //发送后接受到的串行数据 起始位+数据+停止位
output reg Tx_Done //数据发送完成的标志
);
reg [17:0] cnt; // 用来分频得到波特率时钟
reg [17:0] Baud; //Baud由Bund_set决定,用来控制波特率
reg [3:0] counter_1; //对发送的第几位数据进行计数
wire [9:0] data_last;//加上起始位和停止位的数据
assign data_last = {1'd1,Data,1'd0};
//Baud
always@(Baud_set)
case(Baud_set)
3'd0:Baud=18'd166666;//波特率为300
3'd1:Baud=18'd41666;//波特率为1200
3'd2:Baud=18'd20833;//波特率为2400
3'd3:Baud=18'd5208;//波特率为9600
3'd4:Baud=18'd2604;//波特率为19200
3'd5:Baud=18'd1302;//波特率为38400
3'd6:Baud=18'd868;//波特率为57600
3'd7:Baud=18'd434;//波特率为115200
endcase
//波特率分频
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(!rst) cnt <=0;
else if(En==1)
begin
if (cnt==Baud-1) cnt<=0;
else cnt<=cnt +1;
end
else cnt <=0;
//always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)
// if(!rst) Baud_clk <=0;
// else if (cnt==Baud/2-1) Baud_clk<=!Baud_clk;
// else if (cnt==Baud-1) Baud_clk<=!Baud_clk;
// else Baud_clk<=Baud_clk ;
//对发送的数据进行计数
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(!rst) counter_1<=0;
else if(En==1)
begin
if(cnt==Baud-1&&cnt==Baud-1)
begin
if(counter_1==9) counter_1<=0;
else counter_1<=counter_1+1;
end
else counter_1<=counter_1;
end
else counter_1<=0;
//控制Tx_Done
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(!rst) Tx_Done<=0;
else if(counter_1==9&&cnt==Baud-1) Tx_Done<=1;
else Tx_Done<=0;
//发送数据
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(!rst) begin uart_tx<=1;end
else if(En==1&&Tx_Done==0)
begin
if(counter_1==9) uart_tx<=1;
else
uart_tx<=data_last[counter_1];
end
else
uart_tx<=1;
endmodule 2.完成5个字节的数据发送
因为串口通信协议只能完成8位比特的发送(8bit=1byte),因此发送5个字节的数据需要将5个字节的数据拆分成一个字节一个字节来依次发送。即最先发送[7:0]位,然后发送[15:8]位,直至发送至[39:32]位。
多个 字节发送的模块图:
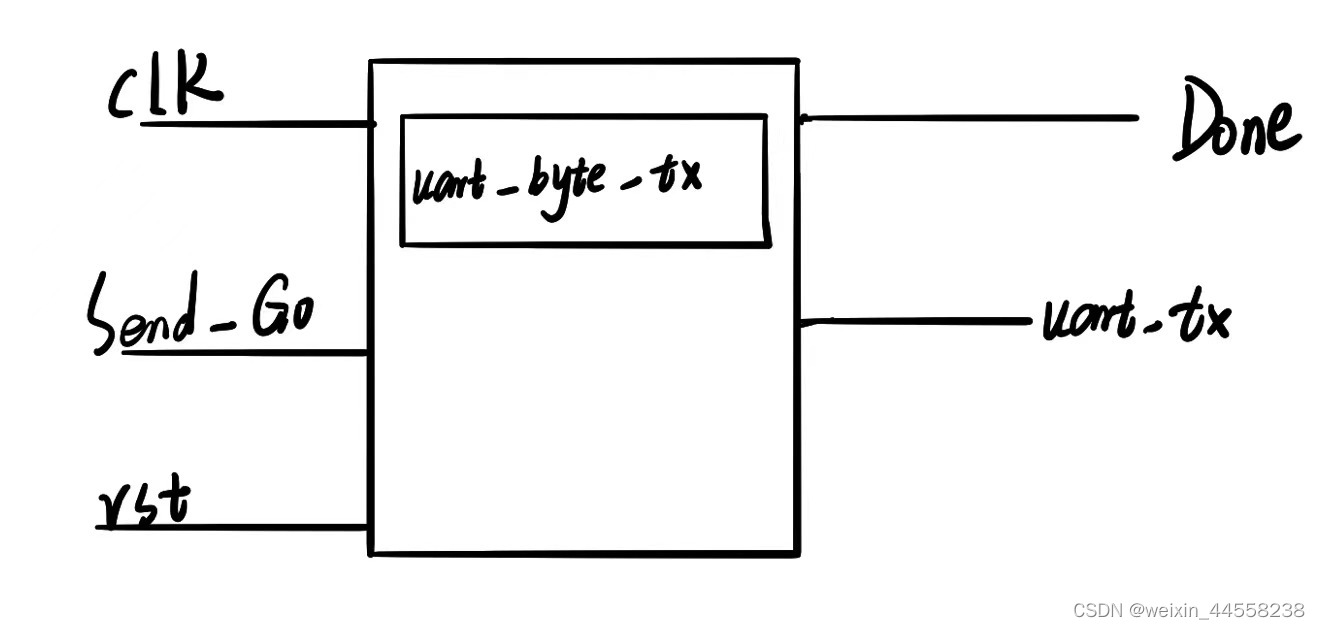
采用状态机的思想来设计多个字节的发送:
状态0:此时没有接收到发送数据请求信号,该模块处于空闲状态
状态1:该模块接收到发送数据请求信号(Trans_Go),开始发送数据的第一个字节,第一个字节发送完成后,转移到状态2
状态2:发送数据[15:8]
状态3:发送数据[23:16]
状态4:发送数据[31:24]
状态5:发送数据[39:32],发送完数据的最后一个字节后,回到零状态,等待数据请求信号(Trans_Go)的来临。
源文件
//采用状态机的思想发送5个字节的数据
//
module top_2(
input clk,
input Trans_Go, //请求发送
input [39:0] Send_Data,
input rst,
output reg Done, //5个字节发送完成
output uart_tx
);
reg [7:0] Data;
reg En;
wire Tx_Done;
reg [2:0] state;
//例化串口模块
uart_byte_tx uart_nux_byte_Inst (
.Data(Data),
.En(En),
.clk(clk),
.rst(rst),
.Baud_set(3'd7),
.uart_tx(uart_tx),
.Tx_Done(Tx_Done)
);
//开始状态转移
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(!rst)
begin
Done<=0;
state<=0;
Data<=0;
En<=0;
end
else if(state==0)
begin
if(Trans_Go) begin
if(Tx_Done) state<=3'd1;
else begin En<=1;Data<=Send_Data[7:0]; end
end
else begin state<=state;Data<=0;En<=0; Done<=0;end
end
else if(state==3'd1)
begin
if(Tx_Done) state<=3'd2;
else begin
En<=1;
Data<=Send_Data[15:8];
end
end
else if(state==3'd2)
begin
if(Tx_Done) state<=3'd3;
else begin
En<=1;
Data<=Send_Data[23:16];
end
end
else if(state==3'd3)
begin
if(Tx_Done) state<=3'd4;
else begin
En<=1;
Data<=Send_Data[31:24];
end
end
else if(state==3'd4)
begin
if(Tx_Done) begin state<=3'd0;Done<=1;En=0;end
else begin
En<=1;
Data<=Send_Data[39:32];
end
end
endmodule激励文件
module top_2_test();
reg clk;
reg Trans_Go; //请求发送
reg rst;
reg [39:0] Send_Data;
wire Done; //5个字节发送完成
wire uart_tx;
top_2 top_2_test(
.clk(clk),
.Trans_Go(Trans_Go),
.Send_Data(Send_Data),
.rst(rst),
. Done(Done),
.uart_tx(uart_tx)
);
initial
begin
Send_Data = 40'h0;
Trans_Go=0;
clk=1;
rst=0;
#10000 rst=1;
Send_Data = 40'h1234567899;
#5000 Trans_Go=1;
@(posedge Done)
Trans_Go=0;
#10000
Send_Data= 40'h1187654321;
Trans_Go=1;
@(posedge Done)
Trans_Go=0;
end
always #10 clk=~clk;
endmodule代码优化:采用2个或者3个状态机发送数据,并且容易修改成发送任意字节的数据。
状态1:空闲状态,没有发送数据,当数据请求信号Trans_Go来临时,转为状态1
状态2:正在发送数据
源文件
//采用2个或者3个状态机实现任意字节数据的发送
//
module top_3(
clk,
Trans_Go, //请求发送
Send_Data, //最多能发送20个字节的数据
rst,
Done, //5个字节发送完成
uart_tx
);
parameter Num_Byte = 7; //发送数据的字节数
parameter Num_bit = Num_Byte*8; //发送数据的位数
input [Num_bit-1:0] Send_Data;
input clk;
input Trans_Go; //请求发送
input rst;
output reg Done; //数据发送完成
output uart_tx;
reg [0:1] state; //状态
reg [Num_bit-1:0] Data_1;
reg [2:0] counter_byte; //对发送的字节数进行计数
reg [7:0] Data;
reg En;
wire Tx_Done;
uart_byte_tx uart_nux_byte_Inst (
.Data(Data),
.En(En),
.clk(clk),
.rst(rst),
.Baud_set(3'd7),
.uart_tx(uart_tx),
.Tx_Done(Tx_Done)
);
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(!rst) begin state<=0;Done<=0;Data<=0;En<=0;Data_1<=0;counter_byte <= 0;end
else if(state==0)
begin
if(Trans_Go==1&&Done==0) begin state<=1;Data_1<=Send_Data;end
else begin
Data_1<=0;
state<=0;
Done<=0;
Data<=0;
En<=0;
counter_byte <= 0;
end
end
else if(state==1)
begin
if(Tx_Done)
begin
if(counter_byte==Num_Byte-1) begin state<=0; Done<=1;En<=0;counter_byte<=0;end
else
begin
counter_byte <= counter_byte+1;
Data_1 <={Data_1[7:0],Data_1[Num_bit-1:8]};
Data <=Data_1[7:0];
Done<=0;
end
end
else if(!Tx_Done)
begin
Data <=Data_1[7:0];
En<=1;
Done<=0;
end
end
endmodule
激励文件
module top_3_test();
parameter Num_Byte = 7;
parameter Num_bit = Num_Byte*8;
reg clk;
reg Trans_Go; //请求发送
reg rst;
reg [Num_bit-1:0] Send_Data;
wire Done; //5个字节发送完成
wire uart_tx;
top_3 top_3_test(
.clk(clk),
.Trans_Go(Trans_Go),
.Send_Data(Send_Data),
.rst(rst),
. Done(Done),
.uart_tx(uart_tx)
);
initial
begin
Send_Data = 56'h0;
Trans_Go=0;
clk=1;
rst=0;
#10000 rst=1;
Send_Data = 56'h12345678991234;
#5000 Trans_Go=1;
@(posedge Done)
Trans_Go=0;
#10000
Send_Data= 56'h11876543214321;
Trans_Go=1;
@(posedge Done)
Trans_Go=0;
end
always #10 clk=~clk;
endmodule
板级测试文件,实现1分钟发送一个数据
//多个字节发送板级测试文件
//
module top4(
input clk,
input rst,
output uart_tx
);
//例化
wire Done;
reg Trans_Go;
parameter Num_Byte = 7;
parameter Num_bit =Num_Byte*8;
reg [Num_bit-1:0] Send_Data;
reg [Num_bit-1:0] Data_chuzhi=56'h1234567891234;
top_3 top_3_Inst(
.clk(clk),
.rst(rst),
.Send_Data(Send_Data),
.Trans_Go(Trans_Go),
.Done(Done),
.uart_tx(uart_tx)
);
//10ms计数
parameter MCNT = 33'd3000000000;// 2s计数值
reg [32:0] counter_10ms;
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(!rst) counter_10ms<=0;
else if(counter_10ms==MCNT-1) counter_10ms<=0;
else counter_10ms<=counter_10ms+1;
//每隔10ms发送一个数据
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(!rst) Trans_Go<=0;
else if(counter_10ms==1) Trans_Go<=1;
else if(Done) Trans_Go<=0;
else Trans_Go<=Trans_Go;
//对发送的数据加1
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)
if(!rst) Send_Data<=Data_chuzhi;
else if(Done) Send_Data<=Send_Data+1;
else Send_Data<=Send_Data;
endmodule测试成功
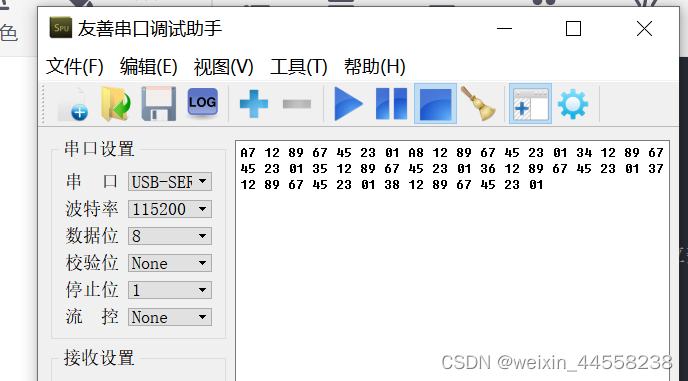
最后
以上就是朴实秋天最近收集整理的关于FPGA串口发送学习的全部内容,更多相关FPGA串口发送学习内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复