C语言编写s函数
S函数简单介绍
为什么要编写S函数?因为MALTAB提供的模型不能满足用户需求。
Simulink与一个C MEX S-Function之间的相互关系:是通过调用S-Function中的回调函数来实现的。说白了就是调用API函数的过程。
Simulink S函数运行过程:初始化完成之后进入循环,直至结束。初始化设置输入输出参数,采样时间等。循环是更新状态,进行运算等。
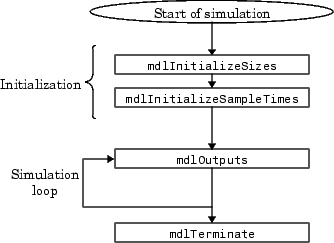
主要使用到的函数
初始化设置使用到的两个函数:
static void mdlInitializeSizes(SimStruct *S),用于指定输入,输出,以及状态等等
static void mdlInitializeSampleTimes(SimStruct *S),用于指定采样时间
初始化状态:
static void mdlStart(SimStruct *S),此函数在模型执行开始时调用一次。自己需要初始化的函数可以放在这里面。
输出函数:
static void mdlOutputs(SimStruct *S, int_T tid),用于计算S函数的输出,算法一般是在这里实现的。
结束函数:
static void mdlTerminate(SimStruct *S), 函数结束时执行的操作,例如释放内存,更新变量等必要操作。
注意事项:
变量设置:mdlOutputs()变量需要全局变量,否则会出现不可知错误。
数据类型需要是real_T 类型。real_T 类型tmwtypes.h中定义。这样定义可以灵活适应更多的平台。可以在16、32、64位的平台使用。real_T的用法基本与和double的用法一致。同理int_T和int用法一致。
S函数代码分析
我们在maltab的工作台的路径下先创建一个test.c,然后在C文件写入代码。
代码写入,使用MEX命令编译C文件,创建C-MEX文件
在simulink中的S-Function调用C-MEX文件。
#include"math.h"
//********************************PID算法部分************************************//
#define OUT_MIN -1000
#define OUT_MAX 1000
int Error;//偏差
/****************************************************************************************/
//定义PID结构体//
/****************************************************************************************/
typedef struct
{
volatile double Proportion; // 比例常数 Proportional Const
volatile double Integral; // 积分常数 Integral Const
volatile double Derivative; // 微分常数 Derivative Const
volatile double Error1; // Error[n-1]
volatile double Error2; // Error[n-2]
volatile double iError; // Error[n]
volatile double Error_sum;
volatile double index; //积分分离标志
} PID;
//PID指针
PID pid_increase;
PID* sptr_increase=&pid_increase;
//PID初始化
void PID_Init(PID *sptr)
{
sptr->Derivative=0;//Kd
sptr->Proportion=0;//Kp
sptr->Integral=0;//Ki
sptr->Error2=0;
sptr->Error1=0;
sptr->iError=0;
sptr->Error_sum=0;
sptr->index=1;
}
//PID输出限幅处理
double PID_OutputLimit(double output)
{
if (output < OUT_MIN)
{
output = (double)OUT_MIN;
}
else if (output > OUT_MAX)
{
output = (double)OUT_MAX;
}
return output;
}
/****************************************************************************************/
// 位置式PID //
// pwm=Kp*e(k)+Ki*∑e(k)+Kd[e(k)-e(k-1)]
// //
/****************************************************************************************/
double PID_increase(int iError,PID* sptr)
{
double iIncpid=0;
sptr->iError=iError; // 计算当前误差
sptr->iError=iError;
//积分分离处理
if(fabs(sptr->iError)> 40) sptr->index=0;
else sptr->index=1;
sptr->Error_sum+=sptr->iError;
iIncpid=sptr->Proportion * sptr->iError // P
+sptr->Integral * sptr->Error_sum // I
+sptr->Derivative * (sptr->iError-sptr->Error1); // D
iIncpid=PID_OutputLimit(iIncpid);//限幅处理
sptr->Error1=sptr->iError; // 存储误差,用于下次计算
return(iIncpid); // 返回计算值
}
//下面是主要编写S函数的部分
#define S_FUNCTION_NAME test //修改s函数名称,此处为test
#define S_FUNCTION_LEVEL 2 //不需要改使用LEVEL 2,可以提供更过API函数
#define SAMPLE_TIME 0.01 //自己设置的采样时间
#include "simstruc.h"//必须包含的头文件
//**输出函数:**
static void mdlInitializeSizes(SimStruct *S)
{
ssSetNumSFcnParams(S, 3); /*设置参数个数,这里为3,分别设置PID的三个参数分别是P I D */
if (ssGetNumSFcnParams(S) != ssGetSFcnParamsCount(S)) /*判断参数个数,这里为3 ,在S-Function的对话框里面设置3个*/
{
return;
}
ssSetNumContStates(S, 0);//设置连续状态的个数,缺省为0;
ssSetNumDiscStates(S, 0);//设置离散状态的个数,缺省为0;
if (!ssSetNumInputPorts(S, 1)) return;//设置输入变量的个数,这里为1
ssSetInputPortWidth(S, 0, 1);//指定输入端口的宽度。0号,1维
ssSetInputPortRequiredContiguous(S, 0, true); //指定进入端口的信号元素必须是连续的。
//连续指的是:指定端口的信号元素必须占用内存的连续区域。以便于访问信号指针即可访问信号的元素,可以使用ssGetInputPortSignal访问。
//指定进入指定端口的信号元素必须占用内存的连续区域。以便于访问信号指针即可访问信号的元素ssGetInputPortSignal
//端口的输入用于mdlOutputs或mdlGetTimeOfNextVarHit函数。设置直接馈通标志(1=yes,0=no)
ssSetInputPortDirectFeedThrough(S, 0, 1);
if (!ssSetNumOutputPorts(S, 1)) return;设置输出变量的个数
ssSetOutputPortWidth(S, 0, 1);//指定输入端口的宽度。0号,1维
ssSetNumSampleTimes(S, 1);//设定的样本采样次数,此处为1次
ssSetNumRWork(S, 0);//用于mdlInitializeSizes将real_T工作向量元素的数量指定为0,
ssSetNumIWork(S, 0);//可以不用管,一些清零操作
ssSetNumPWork(S, 0);//可以不用管,一些清零操作
ssSetNumModes(S, 0);//可以不用管,一些清零操作
//如果该选项设置为使用默认SIM状态,并且S函数不使用PWorks,则Simulink将S函数视为内置块。
ssSetNumNonsampledZCs(S, 0);
ssSetOptions(S, 0);//有许多选项,使用or连接,采取默认值
}
//指定采样时间函数
static void mdlInitializeSampleTimes(SimStruct *S)
{
ssSetSampleTime(S, 0, SAMPLE_TIME);//指定采样时间SAMPLE_TIME也就是0.01 秒,索引从0开始的采样时间段
ssSetOffsetTime(S, 0, 0.0);//使用此宏mdlInitializeSizes指定从0开始的采样时间的偏移量。
}
#define MDL_INITIALIZE_CONDITIONS /* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_INITIALIZE_CONDITIONS)
/* Function: mdlInitializeConditions ========================================
* Abstract:
* In this function, you should initialize the continuous and discrete
* states for your S-function block. The initial states are placed
* in the state vector, ssGetContStates(S) or ssGetRealDiscStates(S).
* You can also perform any other initialization activities that your
* S-function may require. Note, this routine will be called at the
* start of simulation and if it is present in an enabled subsystem
* configured to reset states, it will be call when the enabled subsystem
* restarts execution to reset the states.
*/
//初始化连续和离散状态,此处不使用,使用ssGetContStates(S) or ssGetRealDiscStates(S).访问状态
//例如 real_T *xdisc = ssGetRealDiscStates(S);
static void mdlInitializeConditions(SimStruct *S)
{
}
#endif /* MDL_INITIALIZE_CONDITIONS */
#define MDL_START /* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_START)
//此函数在模型执行开始时调用一次。自己需要初始化的函数可以放在这里面。*/
static void mdlStart(SimStruct *S)
{
PID_Init(sptr_increase);//PID参数初始化
}
#endif /* MDL_START */
//用于计算S函数的输出,算法一般是在这里实现的。
static void mdlOutputs(SimStruct *S, int_T tid)
{
real_T *para1 = mxGetPr(ssGetSFcnParam(S, 0)); //获得参数1,P
real_T *para2 = mxGetPr(ssGetSFcnParam(S, 1)); //获得参数2,I
real_T *para3 = mxGetPr(ssGetSFcnParam(S, 2)); //获得参数2,D
const real_T *u1 = (const real_T*) ssGetInputPortSignal(S,0); //获得输入u1
real_T *y1 = ssGetOutputPortSignal(S,0); //输出y1
sptr_increase->Proportion=(double)*para1;
sptr_increase->Integral=(double)*para2;
sptr_increase->Derivative=(double)*para3;
Error=(int)*u1;
*y1=(double)PID_increase(Error,sptr_increase);//PID输出
}
#define MDL_UPDATE /* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_UPDATE)
/* Function: mdlUpdate ======================================================
* Abstract:
* This function is called once for every major integration time step.
* Discrete states are typically updated here, but this function is useful
* for performing any tasks that should only take place once per
* integration step.
*/
//离散状态通常在此更新,做任何任务都应该更新一次,需要k'kssSetNumDiscStates宏指定它具有离散状态。
static void mdlUpdate(SimStruct *S, int_T tid)
{
}
#endif /* MDL_UPDATE */
#define MDL_DERIVATIVES /* Change to #undef to remove function */
#if defined(MDL_DERIVATIVES)
/* Function: mdlDerivatives =================================================
* Abstract:
* In this function, you compute the S-function block's derivatives.
* The derivatives are placed in the derivative vector, ssGetdX(S).
*/
//计算S函数块的导数。
//*导数被放置在导数向量ssGetdX(S)中
static void mdlDerivatives(SimStruct *S)
{
}
#endif /* MDL_DERIVATIVES */
/* Function: mdlTerminate =====================================================
* Abstract:
* In this function, you should perform any actions that are necessary
* at the termination of a simulation. For example, if memory was
* allocated in mdlStart, this is the place to free it.
*/
//函数结束时执行的操作,例如释放内存等必要操作
static void mdlTerminate(SimStruct *S)
{
Error=0;
PID_Init(sptr_increase);
}
/*=============================*
* Required S-function trailer *
*=============================*/
#ifdef MATLAB_MEX_FILE /* Is this file being compiled as a MEX-file? */
#include "simulink.c" /* MEX-file interface mechanism */
#else
#include "cg_sfun.h" /* Code generation registration function */
#endif
编译成功:

填入模型和参数:
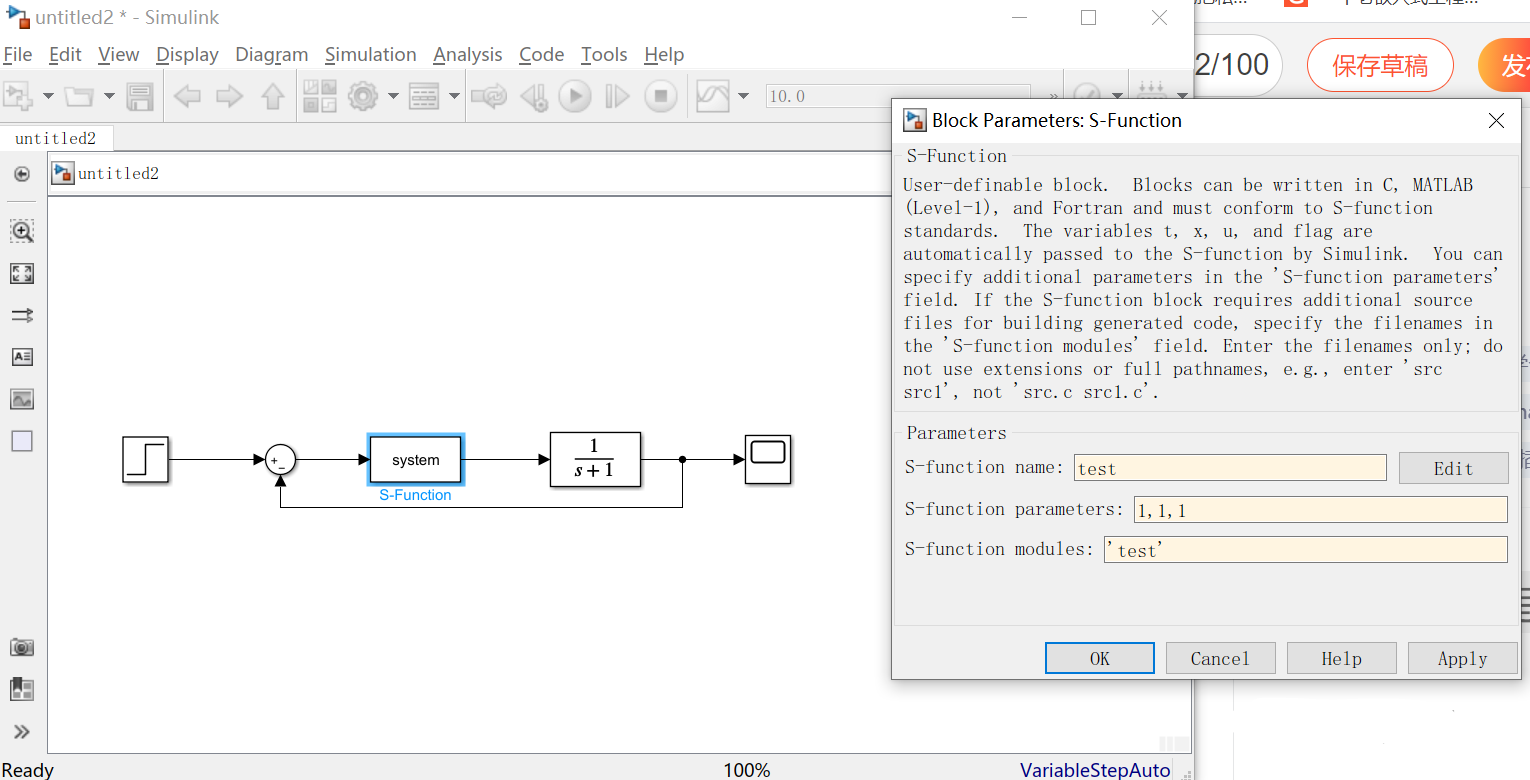
运行结果:
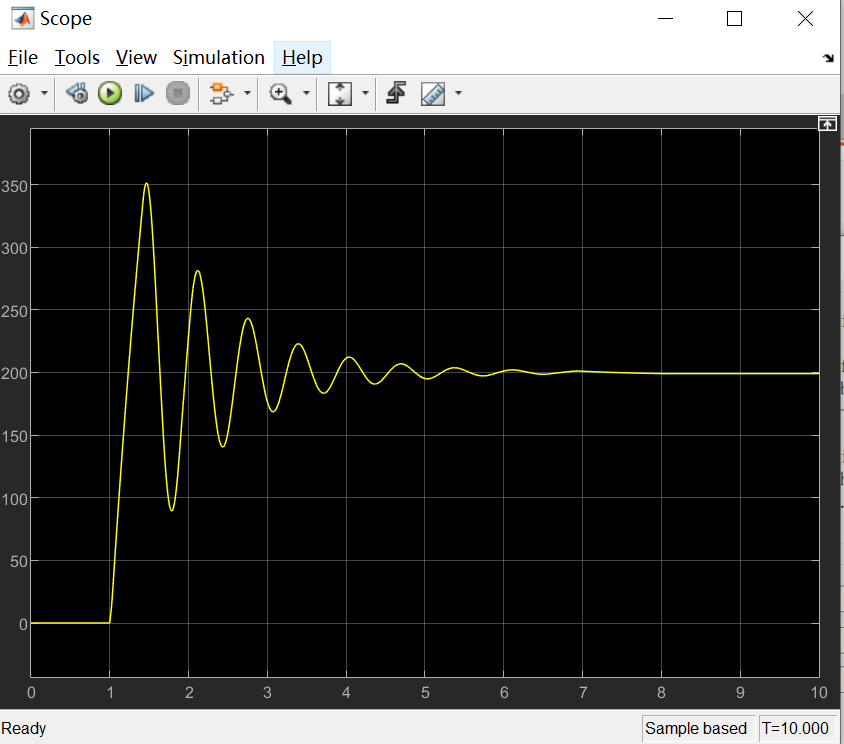
最后我们比较simulink的离散PID控制器和我们设计的控制器的区别:发现一个仿真曲线是一个不稳定,一个稳定。
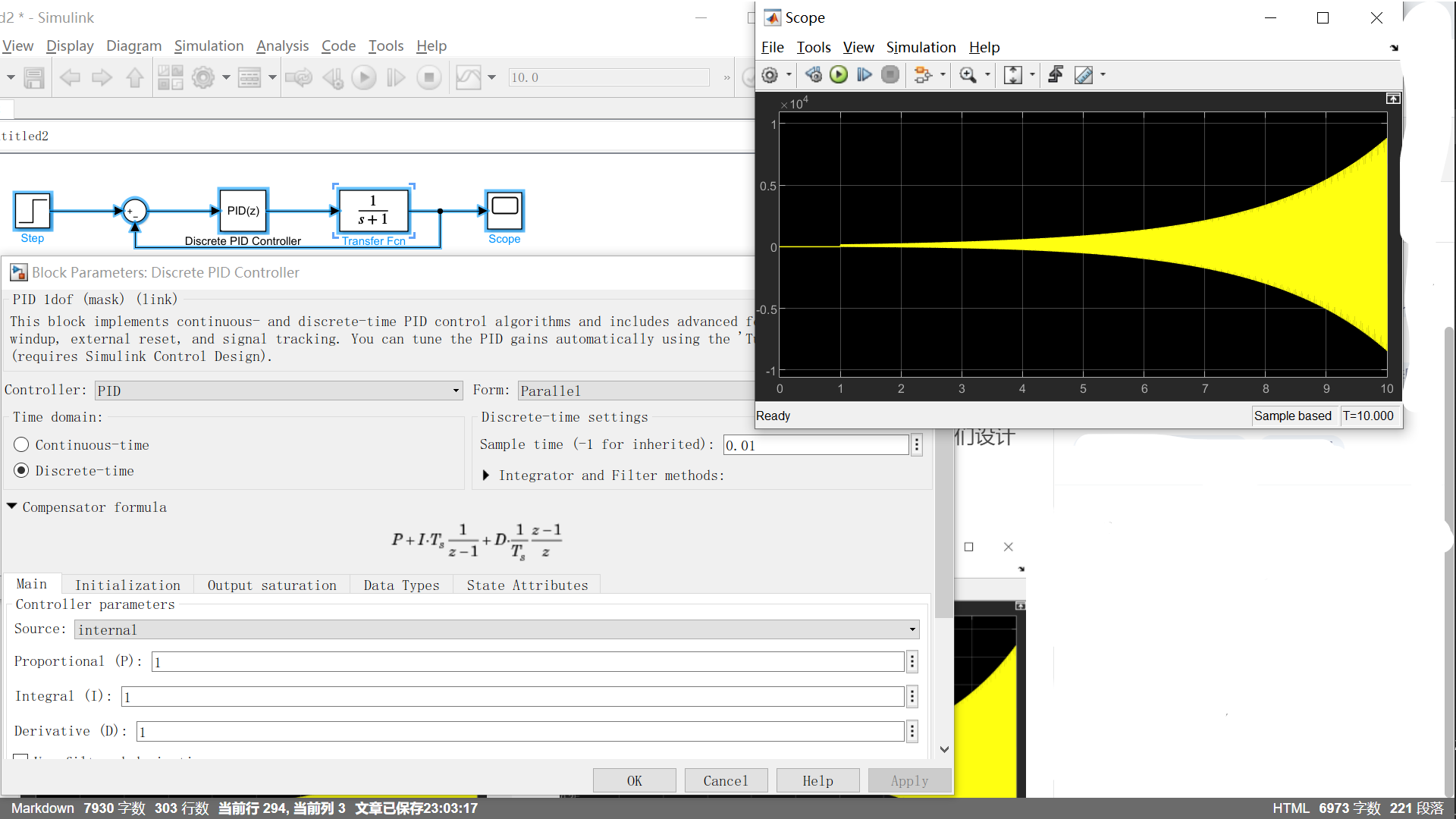
我们在看看C代码的区别,使用Embedded Coder查看C代码和查看它的simumlink模型。
这是标准离散PID控制器的部分C代码和simulink模型,可以看出,这个PID算法和我写的是不一样的。
simulink上的离散PID的公式:是标准的离散PID控制器
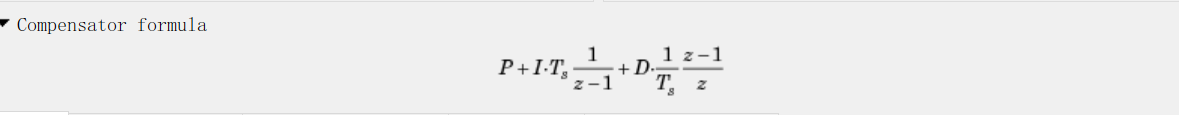
而文章使用的离散PID公式:是用矩形法数值积分近似代替积分,用一阶后向差分近似代替微分,最后可以得到离散的 PID 表达式为:
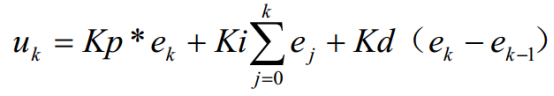
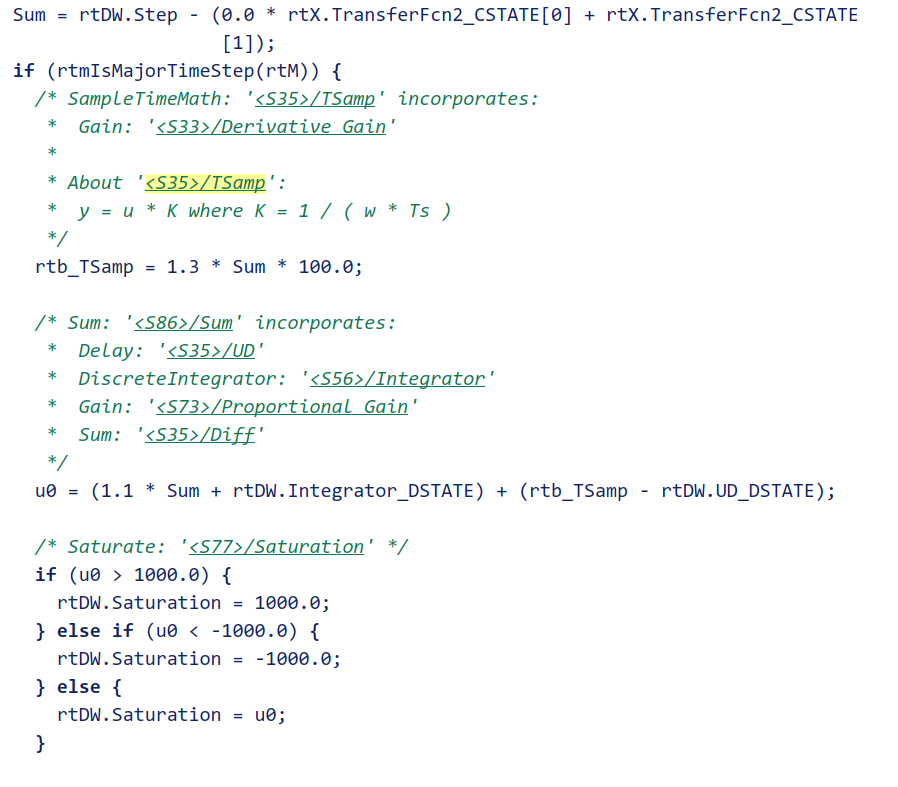
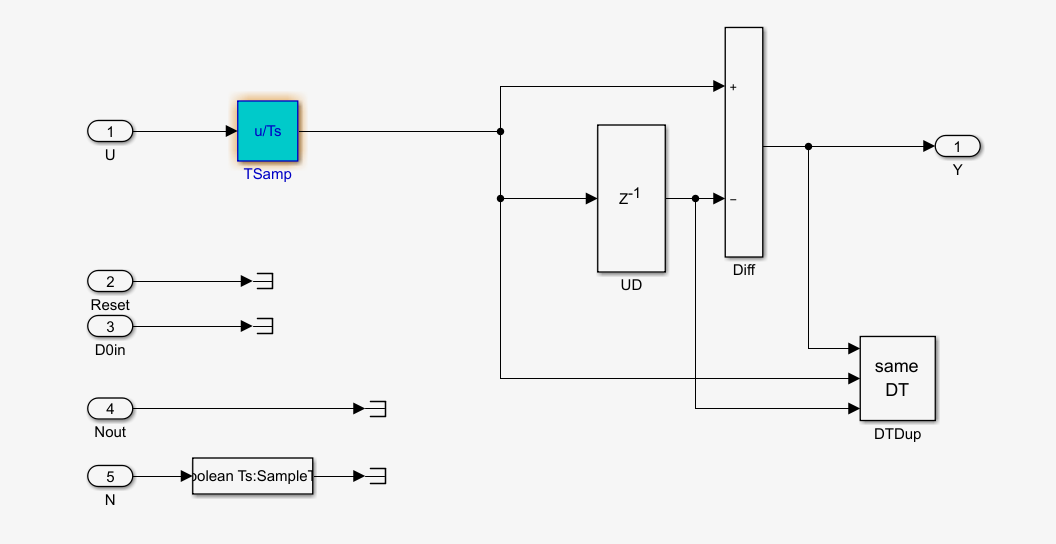
所以PID控制器还是有区别的。
最后
以上就是冷酷书包最近收集整理的关于用C语言编写S函数在simulink实现仿真的全部内容,更多相关用C语言编写S函数在simulink实现仿真内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复