- 1、一些想说的
- 2、简介
- 3、环境配置
- 4、数据集配置
- 5、训练(以PPYOLO为例)
- 6、模型导出
- 7、模型预测
1、一些想说的
对PaddlePaddle框架的使用做一下记录。
最近有一些任务,要求使用paddlepaddle框架去做一个目标检测的项目,刚拿到这个任务的时候我的内心也是有一点排斥的,这么好用的pytorch不香吗?
基于任务的要求我还是去开始做了,看了PaddleDection之后感觉还是比较齐全的,而且也是很简单去调用的,且各个trick很容易就可以组合起来。
总结起来
优点:
1.用起来确实蛮方便,
2.模块丰富
3.数据增强、组网、训练、压缩、部署端到端打通,支持云端/边缘端多架构、多设备部署
不足:
1.会存在一些难以解决的BUG
2.拿paddle去部署的资料还是不够丰富
国产框架还有一段的路要走,希望做大做强
2、简介
PaddleDetection飞桨目标检测开发套件,旨在帮助开发者更快更好地完成检测模型的组建、训练、优化及部署等全开发流程。
PaddleDetection模块化地实现了多种主流目标检测算法,提供了丰富的数据增强策略、网络模块组件(如骨干网络)、损失函数等,并集成了模型压缩和跨平台高性能部署能力。
经过长时间产业实践打磨,PaddleDetection已拥有顺畅、卓越的使用体验,被工业质检、遥感图像检测、无人巡检、新零售、互联网、科研等十多个行业的开发者广泛应用。
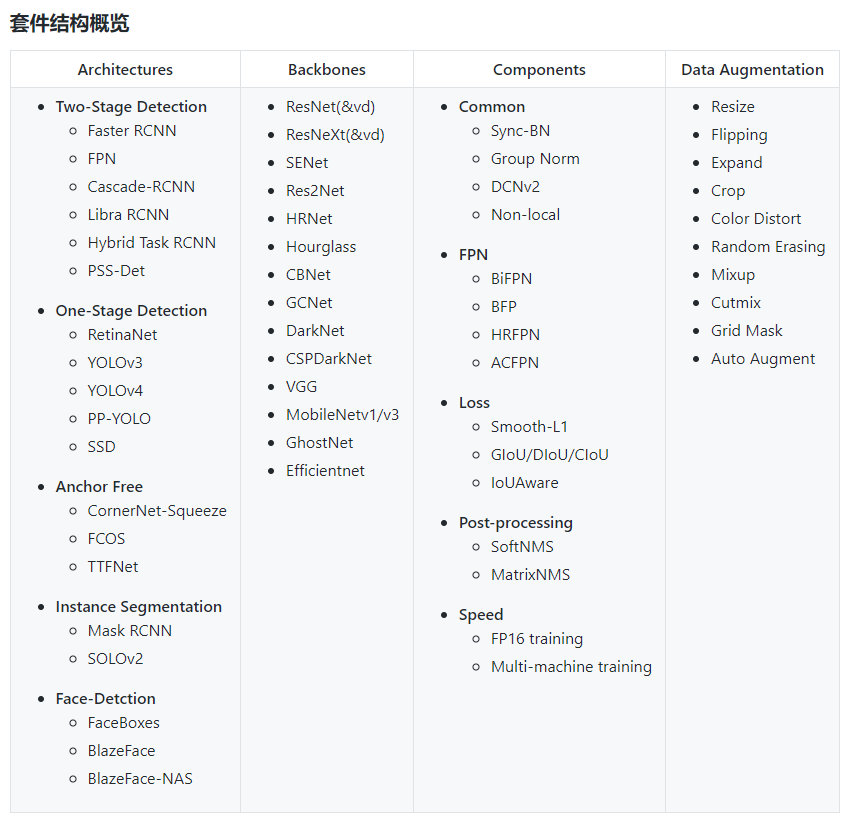
包含套件的总览图,用起来十分方便,直接调用就OK
3、环境配置
可以从网上找很多资料,这一点还是比较方便的。
4、数据集配置
可以选择的数据集格式有很多,包括COCO,VOC
我用的是VOC格式的数据集
关于VOC数据集的介绍:
https://blog.csdn.net/u013832707/article/details/800603272.
整体的结构图

划分数据集相关代码
import os
import random
train_precent=0.7
xml="./Annotations"
save="./ImageSets/Main"
total_xml=os.listdir(xml)
num=len(total_xml)
tr=int(num*train_precent)
train=range(0,tr)
ftrain=open("./ImageSets/Main/train.txt","w")
ftest=open("./ImageSets/Main/test.txt","w")
for i in range(num):
name=total_xml[i][:-4]+"n"
if i in train:
ftrain.write(name)
else:
ftest.write(name)
ftrain.close()
ftest.close()
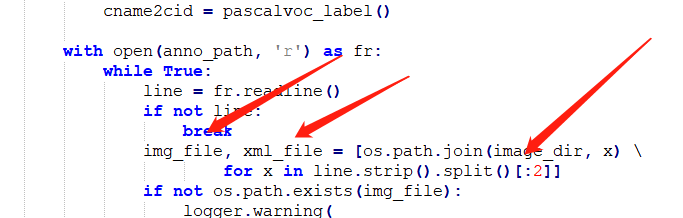
这里需要注意的点是:在Main文件夹中生成的train.txt文件和val.txt文件是对数据集的划分,还需要进一步的利用如下代码(create_list.py,该代码paddle提供,但是我看现在提供的有点问题参考的这位老哥好大哥)生成含有路径信息以及图像和xml文件一一对应的文件。
处理完之后应该是这种格式。

原因如下:
#############################create_list.py######################################
import os
import os.path as osp
import re
import random
devkit_dir = './'
years = ['2007', '2012']
def get_dir(devkit_dir, type):
return osp.join(devkit_dir, type)
def walk_dir(devkit_dir):
filelist_dir = get_dir(devkit_dir, 'ImageSets/Main')
annotation_dir = get_dir(devkit_dir, 'Annotations')
img_dir = get_dir(devkit_dir, 'JPEGImages')
trainval_list = []
test_list = []
added = set()
for _, _, files in os.walk(filelist_dir):
for fname in files:
img_ann_list = []
if re.match('train.txt', fname):
img_ann_list = trainval_list
elif re.match('val.txt', fname):
img_ann_list = test_list
else:
continue
fpath = osp.join(filelist_dir, fname)
for line in open(fpath):
name_prefix = line.strip().split()[0]
if name_prefix in added:
continue
added.add(name_prefix)
ann_path = osp.join(annotation_dir, name_prefix + '.xml')
img_path = osp.join(img_dir, name_prefix + '.jpg')
assert os.path.isfile(ann_path), 'file %s not found.' % ann_path
assert os.path.isfile(img_path), 'file %s not found.' % img_path
img_ann_list.append((img_path, ann_path))
return trainval_list, test_list
def prepare_filelist(devkit_dir, output_dir):
trainval_list = []
test_list = []
trainval, test = walk_dir(devkit_dir)
trainval_list.extend(trainval)
test_list.extend(test)
random.shuffle(trainval_list)
with open(osp.join(output_dir, 'train.txt'), 'w') as ftrainval:
for item in trainval_list:
ftrainval.write(item[0] + ' ' + item[1] + 'n')
with open(osp.join(output_dir, 'val.txt'), 'w') as ftest:
for item in test_list:
ftest.write(item[0] + ' ' + item[1] + 'n')
if __name__ == '__main__':
prepare_filelist(devkit_dir, '.')
最终生成如下所示的数据集格式如下,其中label_list.txt和Mian中的label_list.txt一致。train.txt文件和val.txt是新生成的图像-xml的名称路径对应文件。
5、训练(以PPYOLO为例)
训练前一些参数设置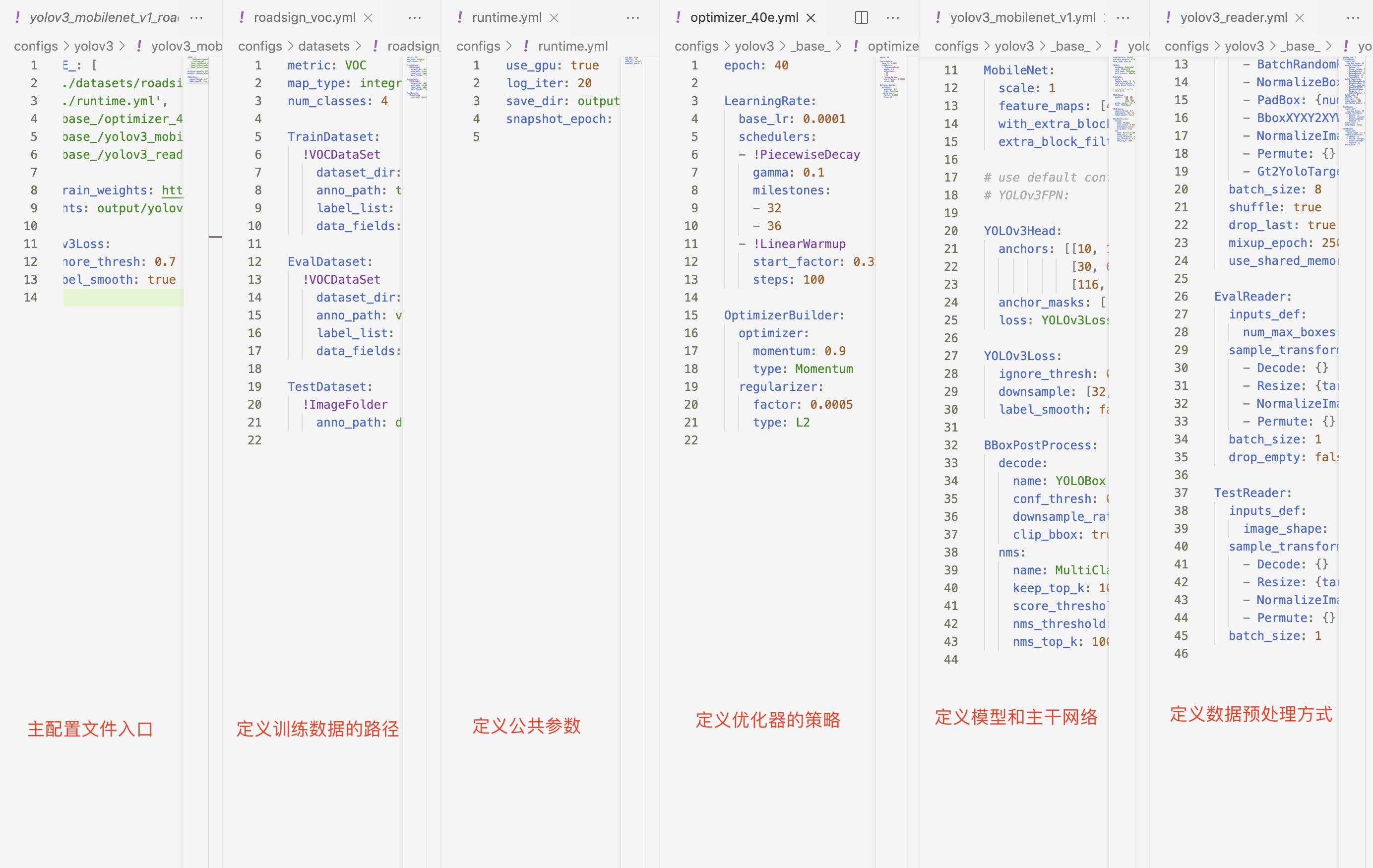
运行如下命令,即可开始训练
python -u tools/train.py configs/ppyolo/ppyolo_r18vd_coco.yml
评估结果
python -u tools/eval.py -c configs/ppyolo/ppyolo_r18vd_coco.yml -o weights=output/ppyolo_r18vd_coco/99.pdparam
也可以边训练便评估
python -u tools/train.py configs/ppyolo/ppyolo_r18vd_coco.yml --eval
关于训练命令的阐述:
-c configs/yolov3_mobilenet_v1_fruit.yml 用来指定配置文件
–use_tb 是否使用tb-paddle记录数据,进而在TensorBoard中显示,默认值是False
–tb_log_dir 指定 tb-paddle 记录数据的存储路径
–eval 是否边训练边测试
训练过程可视化
训练期间可以通过tensorboard实时观察loss和精度值,启动命令如下:
tensorboard --logdir tb_fruit_dir/scalar
6、模型导出
当我们训练完成后,在项目文件的output中可以看到我们生成的模型文件,由于我们使用 --eval参数进行边训练边测试,因此我们可以获得训练过程中最好的模型文件,我们将做好的模型进行导出
python tools/export_model.py -c configs/ppyolo/ppyolo_r18vd_coco.yml --output_dir=./inference_model -o weights=output/ppyolo_r18vd_coco/99
7、模型预测
不用导出也可以进行预测,导出模型只考虑模型的前向传播。
python -u tools/infer.py -c configs/ppyolo/ppyolo_r18vd_coco.yml -o weights=./inference_model/ppyolo_r18vd_coco --infer_img=demo/test/ --output_dir=infer_output
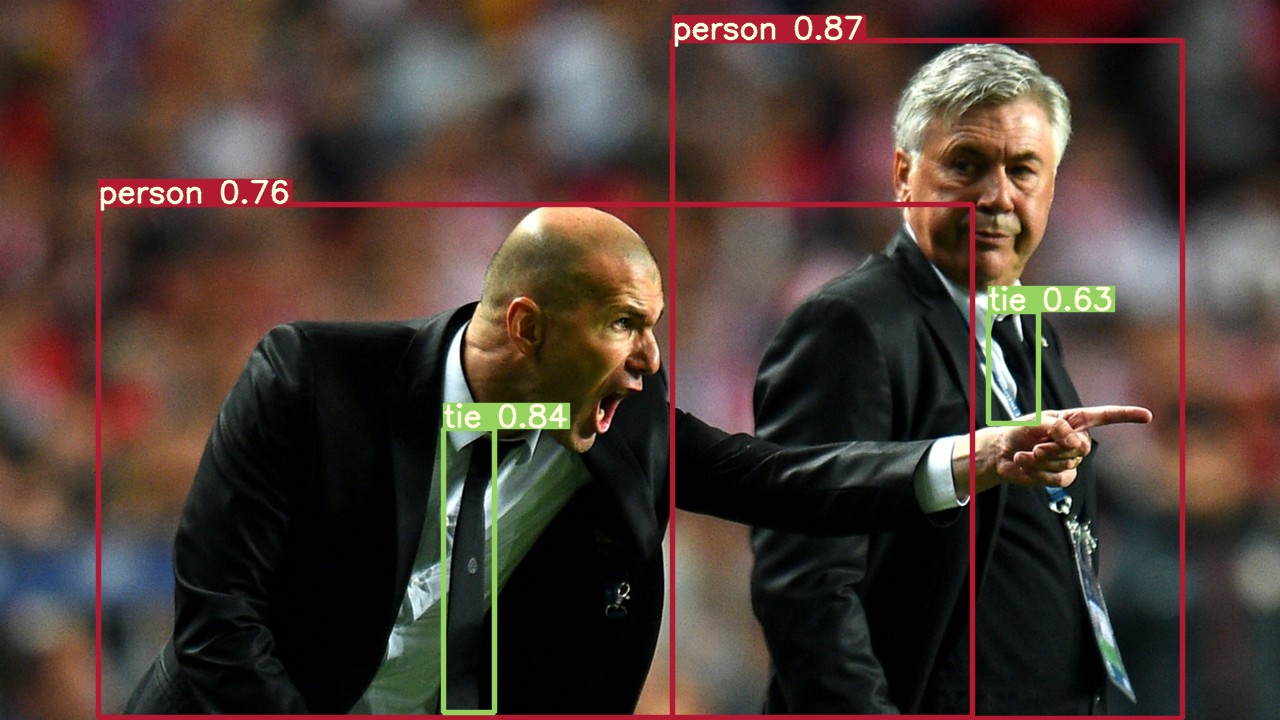


其实这个我用paddle框架训练出来的模型检测的图,不过paddl框架效果也很好
在训练中也有一些注意不到的地方,欢迎讨论~
参考:PaddleDetection的文档
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection.
https://blog.csdn.net/yzl819819/article/details/104336990.
https://blog.csdn.net/yzl819819/article/details/104336990.
最后
以上就是斯文大雁最近收集整理的关于如何使用PaddleDection复现YOLO/PPYOLO等网络1、一些想说的2、简介3、环境配置4、数据集配置5、训练(以PPYOLO为例)6、模型导出7、模型预测的全部内容,更多相关如何使用PaddleDection复现YOLO/PPYOLO等网络1、一些想说内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复