一、赛题理解
赛题以预测心电图心跳信号类别为任务,其中每个样本的信号序列采样频次一致,长度相等,并抽取10万条作为训练集,2万条作为测试机A,2万条作为测试集B。
字段表
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| id | 为心跳信号分配的唯一标识 |
| heartbeat_signals | 心跳信号序列 |
| label | 心跳信号类别(0、1、2、3) |
模型的评测标准
针对某一个信号,若真实值为[y1,y2,y3,y4],模型预测概率值为[a1,a2,a3,a4],那么该模型的平均指标abs-sum为
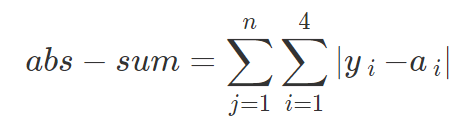
结果提交
提交文件的格式为csv,其内容格式如下:
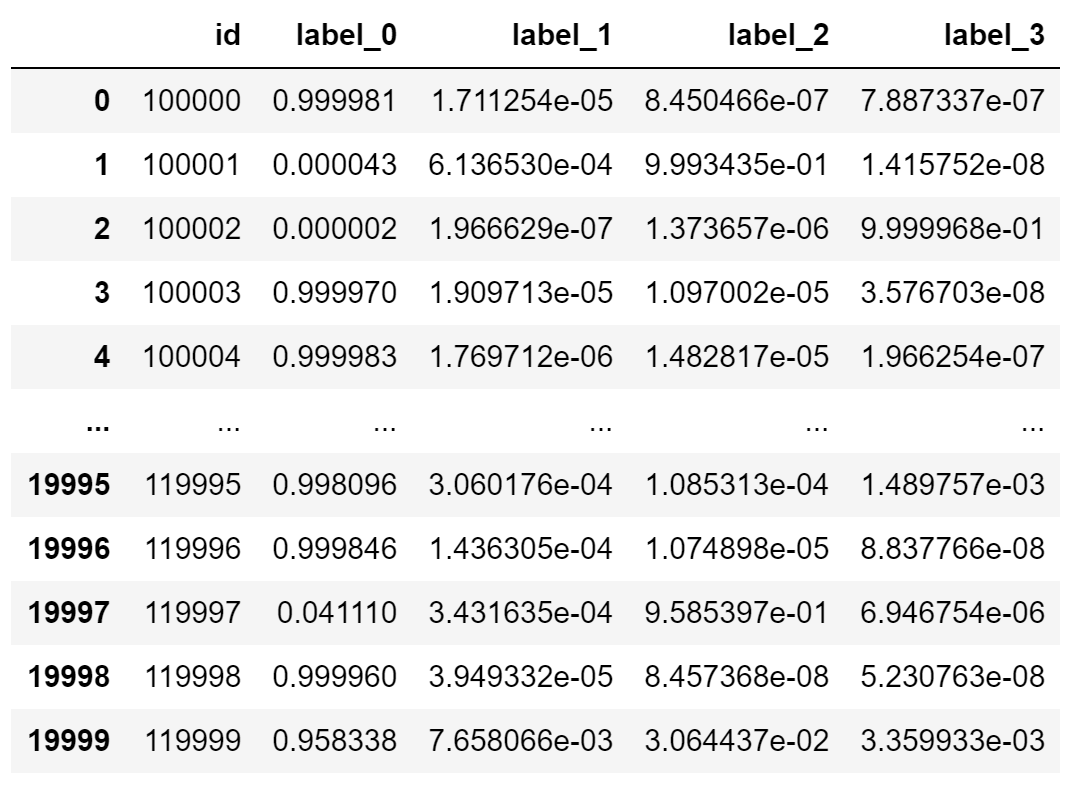
| id | label_0 | label_1 | label_2 | label_3 |
|---|
二、baseline学习
数据预处理
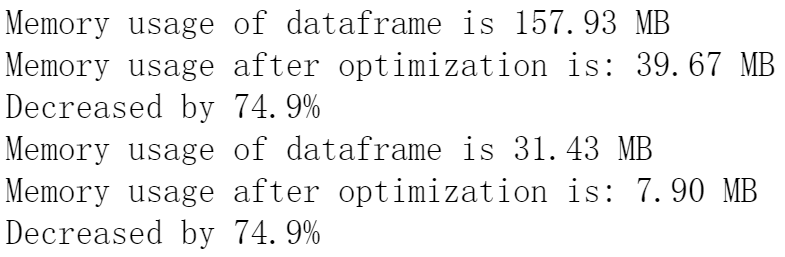
通过简单函数处理原始训练集及测试集数据,并通过reduce_mem_usage()函数降低数据集所占用的内存。
def reduce_mem_usage(df):
start_mem = df.memory_usage().sum() / 1024**2
print('Memory usage of dataframe is {:.2f} MB'.format(start_mem))
for col in df.columns:
col_type = df[col].dtype
if col_type != object:
c_min = df[col].min()
c_max = df[col].max()
if str(col_type)[:3] == 'int':
if c_min > np.iinfo(np.int8).min and c_max < np.iinfo(np.int8).max:
df[col] = df[col].astype(np.int8)
elif c_min > np.iinfo(np.int16).min and c_max < np.iinfo(np.int16).max:
df[col] = df[col].astype(np.int16)
elif c_min > np.iinfo(np.int32).min and c_max < np.iinfo(np.int32).max:
df[col] = df[col].astype(np.int32)
elif c_min > np.iinfo(np.int64).min and c_max < np.iinfo(np.int64).max:
df[col] = df[col].astype(np.int64)
else:
if c_min > np.finfo(np.float16).min and c_max < np.finfo(np.float16).max:
df[col] = df[col].astype(np.float16)
elif c_min > np.finfo(np.float32).min and c_max < np.finfo(np.float32).max:
df[col] = df[col].astype(np.float32)
else:
df[col] = df[col].astype(np.float64)
else:
df[col] = df[col].astype('category')
end_mem = df.memory_usage().sum() / 1024**2
print('Memory usage after optimization is: {:.2f} MB'.format(end_mem))
print('Decreased by {:.1f}%'.format(100 * (start_mem - end_mem) / start_mem))
return df
训练数据/测试数据准备
基于drop()函数,将训练集中的心跳数据及标签数据分别提取出来,同时得到测试集的心跳数据
模型训练
def cv_model(clf, train_x, train_y, test_x, clf_name):
folds = 5
seed = 2021
kf = KFold(n_splits=folds, shuffle=True, random_state=seed)
test = np.zeros((test_x.shape[0],4))
cv_scores = []
onehot_encoder = OneHotEncoder(sparse=False)
for i, (train_index, valid_index) in enumerate(kf.split(train_x, train_y)):
print('************************************ {} ************************************'.format(str(i+1)))
trn_x, trn_y, val_x, val_y = train_x.iloc[train_index], train_y[train_index], train_x.iloc[valid_index], train_y[valid_index]
if clf_name == "lgb":
train_matrix = clf.Dataset(trn_x, label=trn_y)
valid_matrix = clf.Dataset(val_x, label=val_y)
params = {
'boosting_type': 'gbdt',
'objective': 'multiclass',
'num_class': 4,
'num_leaves': 2 ** 5,
'feature_fraction': 0.8,
'bagging_fraction': 0.8,
'bagging_freq': 4,
'learning_rate': 0.1,
'seed': seed,
'nthread': 28,
'n_jobs':24,
'verbose': -1,
}
model = clf.train(params,
train_set=train_matrix,
valid_sets=valid_matrix,
num_boost_round=2000,
verbose_eval=100,
early_stopping_rounds=200)
val_pred = model.predict(val_x, num_iteration=model.best_iteration)
test_pred = model.predict(test_x, num_iteration=model.best_iteration)
val_y=np.array(val_y).reshape(-1, 1)
val_y = onehot_encoder.fit_transform(val_y)
print('预测的概率矩阵为:')
print(test_pred)
test += test_pred
score=abs_sum(val_y, val_pred)
cv_scores.append(score)
print(cv_scores)
print("%s_scotrainre_list:" % clf_name, cv_scores)
print("%s_score_mean:" % clf_name, np.mean(cv_scores))
print("%s_score_std:" % clf_name, np.std(cv_scores))
test=test/kf.n_splits
return test
def lgb_model(x_train, y_train, x_test):
lgb_test = cv_model(lgb, x_train, y_train, x_test, "lgb")
return lgb_test
lgb_test = lgb_model(x_train, y_train, x_test)
函数的输出结果
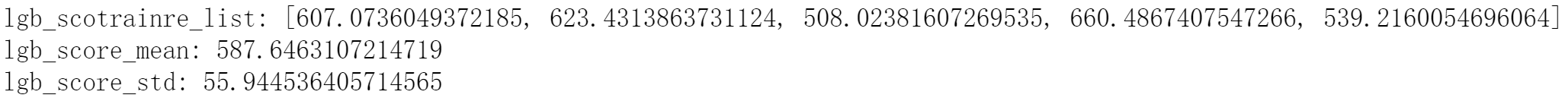
天池提交成绩
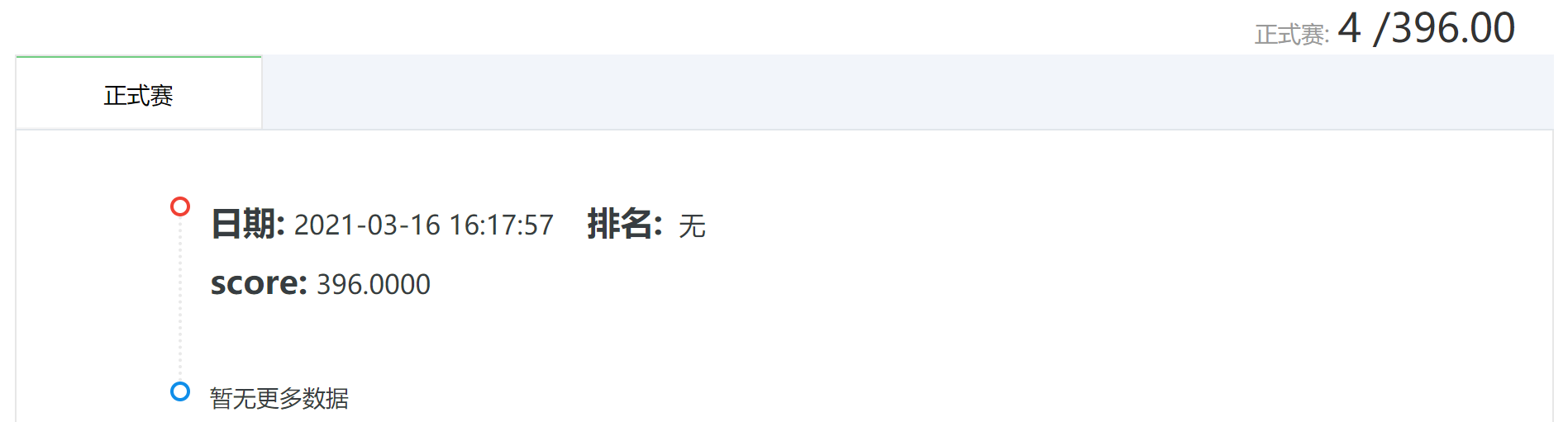
最后
以上就是时尚路人最近收集整理的关于天池数据挖掘比赛-心跳信号分类01-赛题理解及baseline学习的全部内容,更多相关天池数据挖掘比赛-心跳信号分类01-赛题理解及baseline学习内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复