当前位置:操作系统 > 安卓/Android >>
Android模拟器学framework和driver之传感器篇3(Android HAL)
前面,带着大家一起写了一个temperature sensor的驱动,已经一个测试tool来测试这个驱动,基本功能已经ok,若还有问题的可以参考前面2篇文章,在这里我们要在HAL层中添加我们的设备,来跟framework中的代码连接起来。
在开始摆代码之前我觉得有必要啰嗦几句,HAL层我个人觉得是个比较重要的东西,虽然这边现在还不是很成熟,还不是很规范,但是google还是做了很大力气针对HAL的。
首先来介绍一下android HAL 层,
Android的硬件抽象层,简单来说,就是对Linux内核驱动程序的封装,向上提供接口,屏蔽低层的实现细节。也就是说,把对硬件的支持分成了两层,一层放在用户空间(User Space),一层放在内核空间(Kernel Space),其中,硬件抽象层运行在用户空间,而Linux内核驱动程序运行在内核空间。
下图为整个android 架构:
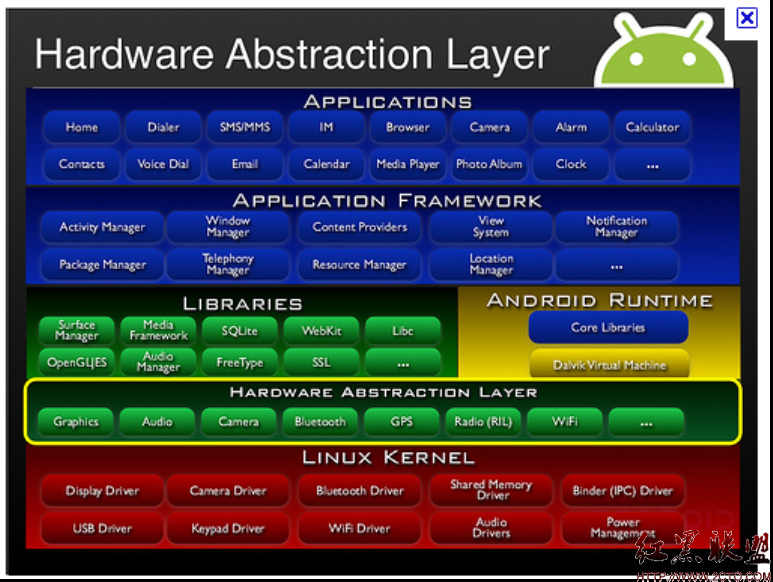
这个是google定义的android整个系统的架构,大家可以看到HAL层起了一个承上启下的作用,HAL层主要是针对一些传感器和一些个硬件而存在的,其实也可以绕过HAL层直接使用JNI来实现从驱动到framework这个过程,但是我们这里主要是讲android中的sensor,针对标准的android而言,sensor都是在HAL中添加的,个人理解还是呼应硬件厂商的建议吧,毕竟这部分代码还可以不开源的。
好了,开源不开源什么的,我是不去关心,对我影响不大,我们还是接着看HAL。
Android硬件抽象层,从下到上涉及到了Android系统的硬件驱动层、硬件抽象层、运行时库和应用程序框架层等等,下图描述了硬件抽象层在Android系统中的位置,以及它和其它层的关系:
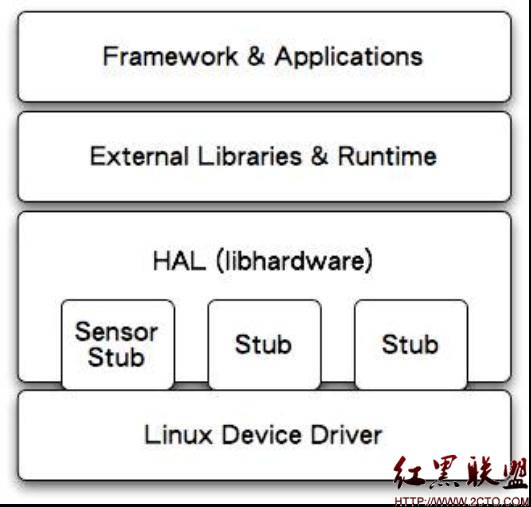
现在的libhardware 作法,使用了stub的概念。stub 虽然仍是以*.so 檔的形式存在,但HAL 已经将*.so 档隐藏起来了。Stub 向HAL提供操作函数(operations),而runtime 则是向HAL 取得特定模块(stub)的operations,再callback 这些操作函数。
HAL的实现主要在hardware.c和hardware.h文件中。实质也是通过加载*.so 库。从而呼叫*.so 里的符号(symbol)实现。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
到此,都是些理论的东西,实在是不想讲这些条条杠杠的,从小语文就不好的我,最讨厌的就是这些理论的东西了,实践才是真理呢。。。
好了接下来轮到我们的sensor的HAL层了,这里先列出来主要用到的代码:
。。。。。。
讲漏了,这边sensor的HAL层代码我参考的是freescale的BSP,因为个人感觉比较容易懂,哈哈。
先给下载链接,不然大家看不到完整的代码。
http://download.csdn.net/detail/zhangjie201412/4039312
代码目录如下:
sensor/
├──AccelSensor.cpp
├──AccelSensor.h
├──Android.mk
├──InputEventReader.cpp
├──InputEventReader.h
├──LightSensor.cpp
├──LightSensor.h
├──SensorBase.cpp
├──SensorBase.h
├──sensors.cpp
├──sensors.h
├──TemperatureSensor.cpp
└──TemperatureSensor.h
这里我们要修改以及添加的是三个文件:
sensor.cpp TemperatureSensor.cpp TemperatureSensor.h
好了,接下来就带大家分析下android sensor的HAL层!!!
先看一下/hardware/libhareware/hardware.c和/hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/hardware.h
这2个文件是android hal层最重要的两个文件,其中定义了hal层主要要实现的3个结构体,
struct hw_module_t;
struct hw_module_methods_t;
struct hw_device_t;
/**
* Every hardware module must have a data structure named HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM
* and the fields of this data structure must begin with hw_module_t
* followed by module specific information.
*/
typedef struct hw_module_t {
/** tag must be initialized to HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG */
uint32_t tag;
/** major version number for the module */
uint16_t version_major;
/** minor version number of the module */
uint16_t version_minor;
/** Identifier of module */
const char *id;
/** Name of this module */
const char *name;
/** Author/owner/implementor of the module */
const char *author;
/** Modules methods */
struct hw_module_methods_t* methods;
/** module's dso */
void* dso;
/** padding to 128 bytes, reserved for future use */
uint32_t reserved[32-7];
} hw_module_t;
typedef struct hw_module_methods_t {
/** Open a specific device */
int (*open)(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* id,
struct hw_device_t** device);
} hw_module_methods_t;
/**
* Every device data structure must begin with hw_device_t
* followed by module specific public methods and attributes.
*/
typedef struct hw_device_t {
/** tag must be initialized to HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG */
uint32_t tag;
/** version number for hw_device_t */
uint32_t version;
/** reference to the module this device belongs to */
struct hw_module_t* module;
/** padding reserved for future use */
uint32_t reserved[12];
/** Close this device */
int (*close)(struct hw_device_t* device);
} hw_device_t;
struct hw_module_t;
struct hw_module_methods_t;
struct hw_device_t;
/**
* Every hardware module must have a data structure named HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM
* and the fields of this data structure must begin with hw_module_t
* followed by module specific information.
*/
typedef struct hw_module_t {
/** tag must be initialized to HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG */
uint32_t tag;
/** major version number for the module */
uint16_t version_major;
/** minor version number of the module */
uint16_t version_minor;
/** Identifier of module */
const char *id;
/** Name of this module */
const char *name;
/** Author/owner/implementor of the module */
const char *author;
/** Modules methods */
struct hw_module_methods_t* methods;
/** module's dso */
void* dso;
/** padding to 128 bytes, reserved for futu补充:移动开发 , Android ,
最后
以上就是长情薯片最近收集整理的关于android hal 光线传感器,Android模拟器学framework和driver之传感器篇3(Android HAL)的全部内容,更多相关android内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复