了解opencv里面的函数,第一步必须是看官网上给出的文档。下面给出Rect类的c++使用。
class Rect_
Template class for 2D rectangles, described by the following parameters:
- Coordinates of the top-left corner. This is a default interpretation of Rect_::x and Rect_::y in OpenCV. Though, in your algorithms you may count x and y from the bottom-left corner.
- Rectangle width and height.
OpenCV typically assumes that the top and left boundary of the rectangle are inclusive, while the right and bottom boundaries are not. For example, the method Rect_::contains returns true if
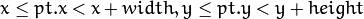
Virtually every loop over an image ROI in OpenCV (where ROI is specified by Rect_<int> ) is implemented as:
In addition to the class members, the following operations on rectangles are implemented:
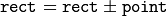 (shifting a rectangle by a certain offset)
(shifting a rectangle by a certain offset)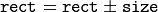 (expanding or shrinking a rectangle by a certain amount)
(expanding or shrinking a rectangle by a certain amount)- rect += point, rect -= point, rect += size, rect -= size (augmenting operations)
- rect = rect1 & rect2 (rectangle intersection)
- rect = rect1 | rect2 (minimum area rectangle containing rect2 and rect3 )
- rect &= rect1, rect |= rect1 (and the corresponding augmenting operations)
- rect == rect1, rect != rect1 (rectangle comparison)
This is an example how the partial ordering on rectangles can be established (rect1  rect2):
rect2):
For your convenience, the Rect_<> alias is available:
最后
以上就是自由招牌最近收集整理的关于Rect函数的全部内容,更多相关Rect函数内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复