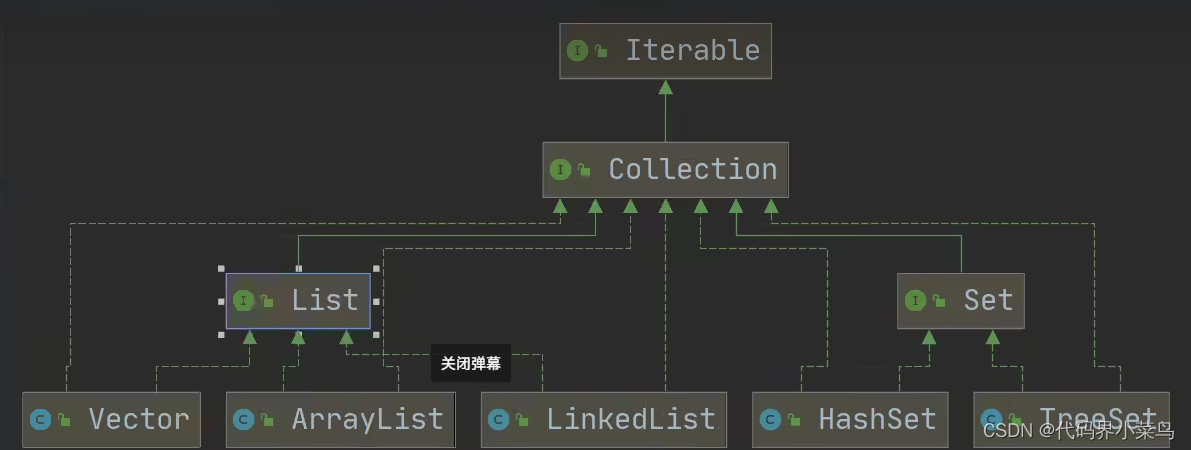
一、Collection
(1)常用方法以ArrayList为例:
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
//add():添加单个元素
list.add("你好");
list.add(10);
list.add(true);
//remove():删除指定元素
// list.remove(0);//删除第一个元素
// list.remove(true);//删除某个元素
//contains():判断一个元素是否存在
boolean contains = list.contains(10);
System.out.println(contains);
//size():获取一个元素的个数
System.out.println(list.size());
//isEmpty():判断一个元素是否为空
System.out.println(list.isEmpty());
//clear():清空
list.clear();
//addAll():添加多个继承Collection元素
list.addAll(list);
//containsAll():判断多个元素是否存在
System.out.println(list.containsAll(list));
//removeAll():删除多个元素
list.removeAll(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
}(2)iterator迭代器遍历:
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection cl = new ArrayList();
cl.add(new Book("三国演义","罗贯中"));
cl.add(new Book("雄安里飞到","韩顺平"));
cl.add(new Book("蛤蟆非全","里蛤蟆"));
Iterator iterator = cl.iterator();
//ctrl+j生成方法快捷键 itit生成Interator迭代器
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Object obj = iterator.next();
System.out.println(obj);
}
//这个时候指针已经到最后面了需要重置指针,就可以重新遍历了
iterator = cl.iterator();
}
}
class Book{
private String name;
private String author;
public Book(String name, String author) {
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + ''' +
", author='" + author + ''' +
'}';
}
}(3)使用增强for循环:
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection cl = new ArrayList();
cl.add(new Book("三国演义", "罗贯中"));
cl.add(new Book("雄安里飞到", "韩顺平"));
cl.add(new Book("蛤蟆非全", "里蛤蟆"));
//可以用在数组,也可以用在集合 快捷键 I
for (Object obj : cl) {
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
}
class Book {
private String name;
private String author;
public Book(String name, String author) {
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + ''' +
", author='" + author + ''' +
'}';
}
}案例:创建3个Dog对象name,age放到ArrayList中。使用for增强和迭代器循环
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection cl = new ArrayList();
cl.add(new Dog("小黑", 1));
cl.add(new Dog("小黄", 2));
cl.add(new Dog("小白", 3));
//使用增强for循环遍历
for (Object obj : cl) {
System.out.println(obj);
}
System.out.println("");
//使用迭代器遍历
Iterator iterator = cl.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
class Dog {
private String name;
private int age;
public Dog(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "name='" + name + ", age=" + age;
}
}二、List
实现的集合有:ArrayList、 Vector、LinkedList 可重复添加、有序
(1)ArrayList:
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.List集合类中元素有序(即添加顺序和取出顺序一致)、且可重复
List list = new ArrayList();
//插入一个值第一个值可以为索引
list.add("jack");
list.add(1,"贾宝玉");
list.addAll(list);//一次加入一个数组
System.out.println(list.indexOf("jack"));//返回字符第一次出现的位置
System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf("jack"));//返回字符最后一次出现的位置
list.remove(0);//删除索引的元素
list.set(1,"marry");//设置索引为1的值为marry。一定要存在
list.subList(0,2);//返回0-2的集合0<=x<2 前闭后开
System.out.println("list="+list);
//2.List集合中的每个元素都有对其对应的顺序索引,即支持索引
// 索引是从0开始
System.out.println(list.get(3)); //获取元素
}
}案例:添加10个以上的元素,在2号位插入一个元素,韩顺平教育,获得第5个元素,删除第6元素,修改第7个元素,使用迭代器遍历,ArrayList
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List ls = new ArrayList();
ls.add("hello1");
ls.add("hello2");
ls.add("hello3");
ls.add("hello4");
ls.add("hello5");
ls.addAll(ls);
ls.add(1,"韩顺平教育");
System.out.println(ls);
System.out.println(ls.get(4));
ls.remove(5);
ls.set(6,"你好");
System.out.println(ls);
}
}案例:新建Book对象Arraylist存储,冒泡排序,遍历
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
al.add(new Book("红楼梦","曹雪芹",100));
al.add(new Book("水浒传","施耐庵",80));
al.add(new Book("西游记","吴承恩",90));
for (int i = 0; i < al.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < al.size()-i-1; j++) {
Book book1 =(Book) al.get(j);
Book book2 =(Book) al.get(j+1);
if (book1.getPrice()>book2.getPrice()){
al.set(j,book2);
al.set(j+1,book1);
}
}
}
for (Object o :al) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
}
class Book {
private String name;
private String author;
private double price;
public Book(String name, String author, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name + "tt" + author + "tt" + price;
}
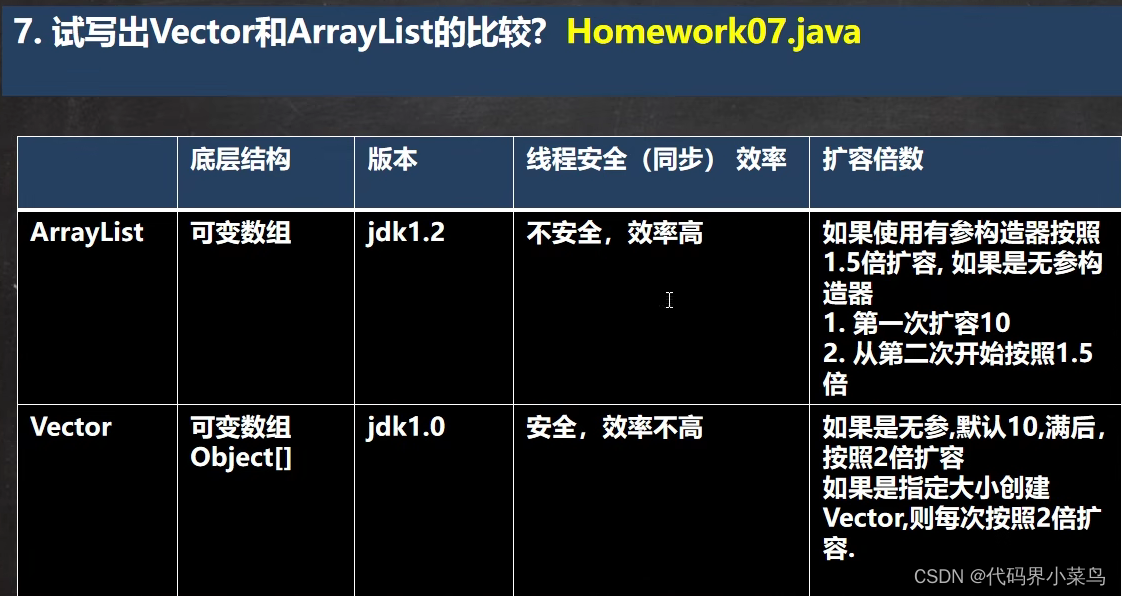
}(2)Vector:
- 底层也是一个对象
- Vector线程安全,线程同步
- 开发中需要线程安全就使用Vector
- 方法同ArrayList方法一样
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector vector = new Vector();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
vector.add(i);
}
System.out.println(vector);
}
}(3)LinkedList
- LinkedList底层实现了双向列表和双向列表特点
- 可以添加任意元素(元素可以重复),包括null
- 线程不安全,没有实现同步
1.双向链表的底层原理
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//模拟一个简单的双向列表
Node jack = new Node("jack");
Node tom = new Node("tom");
Node hsp = new Node("韩顺平");
//连接三个节点,形成双链表
//jack->tom->hsp
jack.next = tom;
tom.next = hsp;
//hsp->tom->jack
tom.pre=jack;
hsp.pre = tom;
Node first = jack;//让first引用指向jack,就是双向链表的头
Node last = hsp; //让last引用指向jack,就是双向链表的尾
System.out.println("演示从头到尾遍历");
while (true){
if (first == null){
break;
}
System.out.println(first);
first = first.next;
}
//演示插入一个节点 smith
Node smith = new Node("smith");
smith.pre = jack;
smith.next = tom;
jack.next = smith;
tom.pre = smith;
System.out.println("演示从尾到头遍历");
while (true){
if (last == null){
break;
}
System.out.println(last);
last = last.pre;
}
}
}
//定义一个Node类,Node 对象 的表示双向列表的一个节点
class Node{
public Object item; //真正存放数据
public Node next; //下一个
public Node pre; //上一个
public Node(Object name) {
this.item = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node name" + item;
}
}2.linkedList的演示
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.add(1);
list.add(1);
list.remove(0);
list.set(0,"hsp");
System.out.println(list.get(0));
}
}(4)ArrayList与LinkedList的选取:
- 如果我们改查的操作多,选择ArrayList
- 如果我们增删的操作多,选择LinkeList
- 一般来说,在项目中,80%~90%都是查询因此大部分情况下回选择ArrayList
- 在一个项目中,根据业务灵活选择,也可能这样,一个模块使用的是ArrayList,另外一个模块是LinkedList
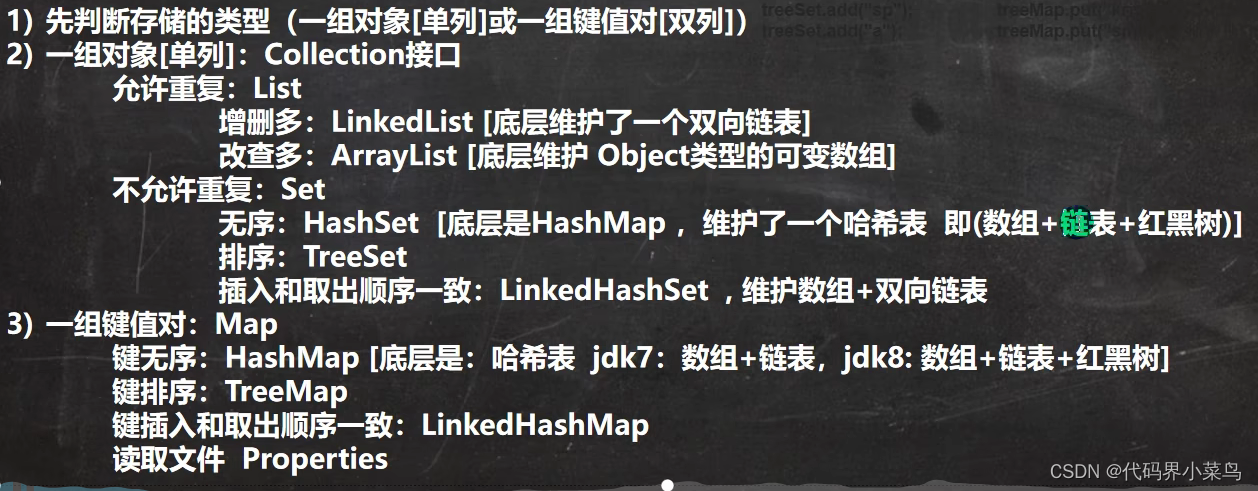
三、Set
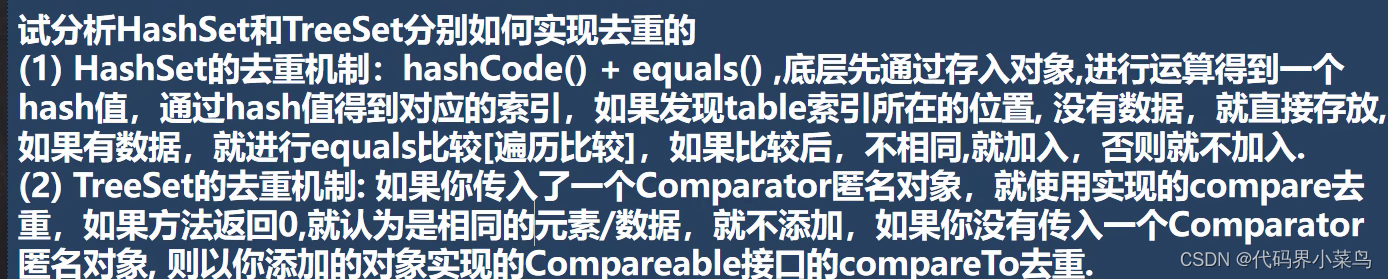
定义:无序(添加和取出的顺序不一致),没有索引,不允许重复元素,所以最多包含一个null,实现的类有TreeSet、HashSet、LinkedHashSet
常用方法和Collection一样因为也是继承与他。
(1)Set接口方法:
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.以Set 接口的实现类 HashSet 来讲解Set接口方法
Set set = new HashSet(); //没有get方法,不能使用for循环索引来获取
set.add("john"); //添加
set.add("lucy");
set.add("john");
set.add("mary");//无序:添加顺序,与取出的顺序不同,取出的顺序是一样的,而且不能重复
System.out.println(set); //[mary, john, lucy]
//遍历 使用迭代器
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next =iterator.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
for (Object o :set) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
}(2)HashSet:
数据不能重复,取出与存入的顺序不同,是否重复比较的是地址值
案例:定义一个Employee类,private属性name,age要求创建3个Employee放入HashSet中,名字和年龄相同时表示重复
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set = new HashSet();
set.add(new Employee("张三",14));
set.add(new Employee("张三",14));
set.add(new Employee("张三",15));
System.out.println(set);
}
}
class Employee{
private String name;
private int age;
public Employee(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Employee employee = (Employee) o;
return age == employee.age && Objects.equals(name, employee.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"name='" + name + ''' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}案例2:定义一个Employee类,该类包含:private成员属性name,sal,birthday(MyDate类·型),其中 birthday 为 MyDate类型(属性包括:year, month, day),要求:1.创建3个Employee放入 HashSet中2.当name和birthday的值相同时,认为是相同员工,不能添加到HashSet集合中
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set = new HashSet();
set.add(new Employee("张三",14,new MyDate(1,1,1)));
set.add(new Employee("张三",14,new MyDate(1,1,1)));
set.add(new Employee("张三",15,new MyDate(1,1,1)));
System.out.println(set);
}
}
class Employee{
private String name;
private int age;
private MyDate date;
public Employee(String name, int age, MyDate date) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.date = date;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Employee employee = (Employee) o;
return age == employee.age && Objects.equals(name, employee.name) && Objects.equals(date, employee.date);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age, date);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"name='" + name + ''' +
", age=" + age +
", date=" + date +
'}';
}
}
class MyDate{
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
public MyDate(int year, int month, int day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
MyDate myDate = (MyDate) o;
return year == myDate.year && month == myDate.month && day == myDate.day;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(year, month, day);
}
}(3)LinkedHashSet:
定义:是HashSet的子类,所以方法也是一样的,但是啊是按顺序添加与取出
案例:Car类(name:price),如果name和price一样则认为是相同,就不能添加
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashSet linkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet();
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("马自达",15));
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("马自达",15));
linkedHashSet.add(new Car("宝马",19));
System.out.println(linkedHashSet);
}
}
class Car{
private String name;
private double price;
public Car(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Car)) return false;
Car car = (Car) o;
return Double.compare(car.price, price) == 0 && Objects.equals(name, car.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, price);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"name='" + name + ''' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
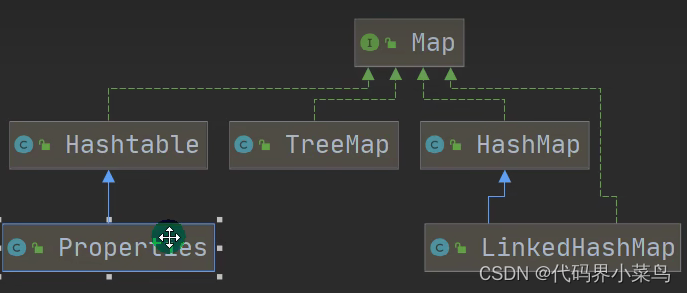
}四、Map
(1)map的常用方法:
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("邓超","孙俪");
map.put("王宝强","马蓉");
map.put("宋喆","马蓉");
map.put("hsp","韩顺平");
map.put(null,"空");
map.put("空",null); //添加
map.remove(null);//删除
System.out.println(map.get("空"));
System.out.println(map.size()); //返回有几对
// map.clear();//清空
System.out.println(map.isEmpty()); //判断map是否为空
System.out.println(map.containsKey("hsp")); //判断某个是否存在
System.out.println(map);
}
}(2)map的循环: keySet 、map.values() 、entryMap
@SuppressWarnings({"all"}) //取消文件警告
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("邓超","孙俪");
map.put("王宝强","马蓉");
map.put("宋喆","马蓉");
map.put("hsp","韩顺平");
map.put(null,"空");
map.put("空",null);
//map接口的遍历
//第一组取出所有的key
Set keySet = map.keySet();
//增强for循环,迭代器,
for (Object key :keySet) {
System.out.println(keySet+"====="+map.get(key));
}
//第二组取出所有value
Collection values = map.values();
//增强for,迭代器
System.out.println("----取出所有Value-----");
for (Object val :values) {
System.out.println(val);
}
//第三组:通过entrySet获取key-value
Set entrySet = map.entrySet(); //EntrySet<Map.Entry<K,V>>
//增强for,迭代器
for (Object entry : entrySet) {
//将entry转成mapEntry
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry) entry;
System.out.println(m.getKey()+"====="+m.getValue());
}
}
}(3)hashMap:
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
Employee a1 = new Employee("张三", 20000, 1);
Employee a2 = new Employee("王五", 19000, 2);
Employee a3 = new Employee("李四", 10000, 3);
map.put(a1.getId(), a1);
map.put(a2.getId(), a2);
map.put(a3.getId(), a3);
Set keySet = map.keySet();
for (Object key : keySet) {
Employee employee = (Employee) map.get(key);
if (employee.getSalary() > 18000) System.out.println(key + "======" + employee);
}
}
}
class Employee {
private String name;
private double salary;
private int id;
public Employee(String name, double salary, int id) {
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
this.id = id;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"name='" + name + ''' +
", salary=" + salary +
", id=" + id +
'}';
}
}(4)Hashtable:不允许空值null
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable();
hashtable.put("john", 100);
// hashtable.put(null, 100); //报错
// hashtable.put(100, null); //报错
System.out.println(hashtable);
}
}(5)Properties:一般用读取配置文件
继承了HashTable所有键和值不能为空,后面会说读取properties文件很重要
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("123",123);
properties.put("三","四");
properties.remove("123");
properties.setProperty("三","五");
System.out.println(properties.get("三"));
}
}(6)技术选型:
四、TreeSet
@SuppressWarnings({"all"}) //取消文件警告
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* 当我们使用无参构造器,创建TreeSet时,任是无序的
* 当我们希望添加元素,按照字符串大小排序
* 使用treeSet,提供的构造器,可以传入一个比较值
* */
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return ((String) o2 ).compareTo((String) o1);
}
});
treeSet.add("jack");
treeSet.add("tom");
treeSet.add("a");
treeSet.add("sp");
System.out.println(treeSet);
}
}五、TreeMap
@SuppressWarnings({"all"}) //取消文件警告
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//无参构造器,没有排序按字母排序
//有参传个比较器
TreeMap map = new TreeMap(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
//按字符的降序
// return ((String) o2).compareTo((String) o1);
return ((String) o2).length() - ((String) o1).length(); //打印一个
}
});
map.put("a","A");
map.put("b","B");
map.put("c","C");
map.put("d","D");
System.out.println(map);
}
}六、Collections工具类
@SuppressWarnings({"all"}) //取消文件警告
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("tom");
list.add("jack");
list.add("smith");
list.add("marry");
//reserve(list) 反转List中元素的顺序
Collections.reverse(list);
System.out.println(list);
//shuffle(list) 对数组进行随机排序
Collections.shuffle(list);
System.out.println(list);
//sort(list) 对元素进行升序 自然排序 abcdefg
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
//需要自己定义排序 sort(lis,comparaor)
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator() { //按字符串长度排序
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return ((String) o1).length() - ((String) o2).length();
}
});
System.out.println(list);
//swap(lis,i,j) 将list的指定元素 i j 处元素进行交换
Collections.swap(list,1,2);
System.out.println(list);
//返回自然排序list中最大值
System.out.println(Collections.max(list));
//根据自定义的比较返沪最大的
Object o = Collections.max(list, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return ((String) o1).length() - ((String) o2).length();
}
});
System.out.println(o);
//查抄集合中指定元素出现的次数
System.out.println(Collections.frequency(list,"tom"));
//copy复制list
}
}七、作业
@SuppressWarnings({"all"}) //取消文件警告
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
News news1 = new News("新冠确诊病例超千万,数百万印度教信徒赴恒河“圣浴”引民众担忧");
News news2 = new News("男子突然想起2个月前钓的鱼还在网兜里,捞起一看赶紧放生");
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(news1);
list.add(news2);
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return ((News) o2).getTitle().compareTo(((News) o1).getTitle());
}
});
for (Object news : list) {
System.out.println(news.toString().substring(0,15)+"...");
}
}
}
class News {
private String title;
public News(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return title;
}
}
@SuppressWarnings({"all"}) //取消文件警告
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
arrayList.add("123"); //添加一个元素
arrayList.remove("123");// 移除某个元素
System.out.println(arrayList.contains("123")); //判断某个元素是否存在
System.out.println(arrayList.size()); //获取元素大小
System.out.println(arrayList.isEmpty());//判断元素是否为空
arrayList.clear();//清空
ArrayList arrayList1 = new ArrayList();
arrayList1.add(new Car("宝马",190000));
arrayList1.add(new Car("宾利",500000));
arrayList.addAll(arrayList1);//i俺家多个元素
System.out.println(arrayList.containsAll(arrayList1));//判断多个元素是否存在
arrayList1.removeAll(arrayList);//移除多个元素
for (Object car : arrayList) {
System.out.println(car);
}
}
}
class Car{
private String name;
private double price;
public Car(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"name='" + name + ''' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
@SuppressWarnings({"all"}) //取消文件警告
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("jack", 650);
map.put("tom", 1200);
map.put("smith", 2900);
System.out.println("初始化后工资: " + map);
map.put("jack", 2600);
System.out.println("jack更新之后工资: " + map);
Set keySet = map.keySet();
for (Object o : keySet) {
map.put(o, (int) map.get(o) + 100);
}
System.out.println("所有员工加一百:"+map);
Set entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Object set : entrySet) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) set;
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"=====>"+entry.getValue());
}
}
}
最后
以上就是彩色小笼包最近收集整理的关于第十三章:集合 一、Collection二、List三、Set四、Map四、TreeSet五、TreeMap六、Collections工具类七、作业的全部内容,更多相关第十三章内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。









发表评论 取消回复