一.什么是Socket
1.Socket起源于Unix,而Unix/Linux基本思想之一就是“一切皆文件”,也称为文件描述符
2.既然一切都是文件,那么就可以把对Socket的操作就是对“open—write/read—close”模式的一种实现
3.Socket是对TCP/IP协议的封装,Socket本身不是协议,通过Socket才能使用TCP/IP协议
二.Java四种IO模型
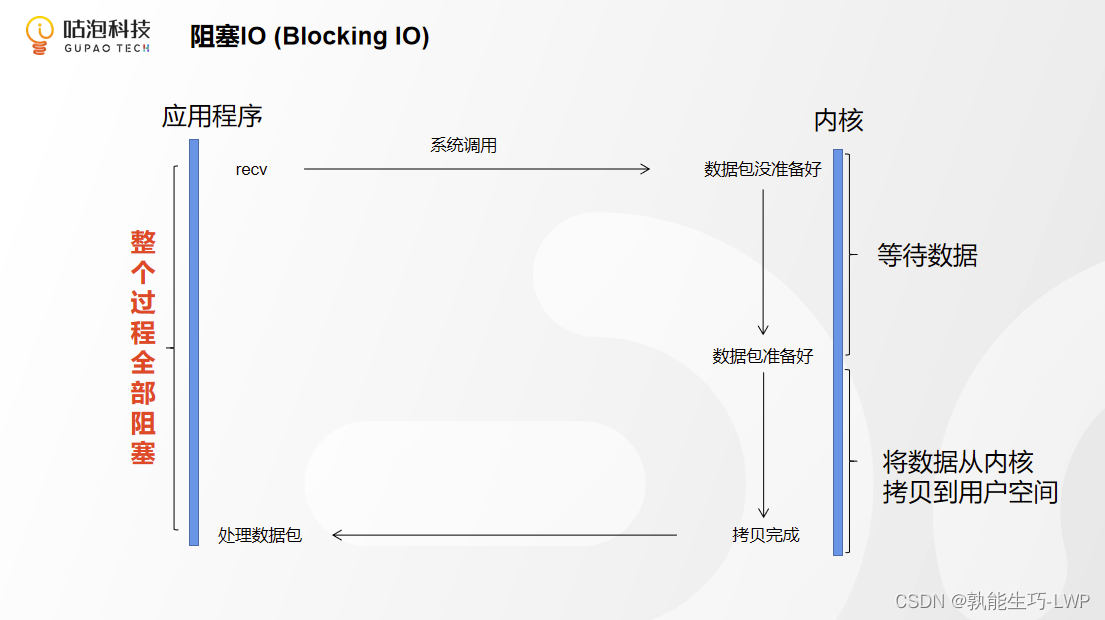
1.BIO(阻塞IO)
package com.lx.netty.bio;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class BlockingServer {
final static ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 监听端口
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
// 等待客户端的连接过来,如果没有连接过来,就会阻塞
while (true){
// 阻塞IO中一个线程只能处理一个连接
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
exec.execute(() ->{
// 获取数据
String line = null;
try {
// 获取Socket中的输入流
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
line = bufferedReader.readLine();
System.out.println("客户端的数据:"+ line);
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
bufferedWriter.write("okn");
bufferedWriter.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package com.lx.netty.bio;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
public class BlockingClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 建立连接
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost",8080);
// 向服务端写数据
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
bufferedWriter.write("我是客户端,收到请回答!!n");
bufferedWriter.flush();
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String line = bufferedReader.readLine();
System.out.println(line);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
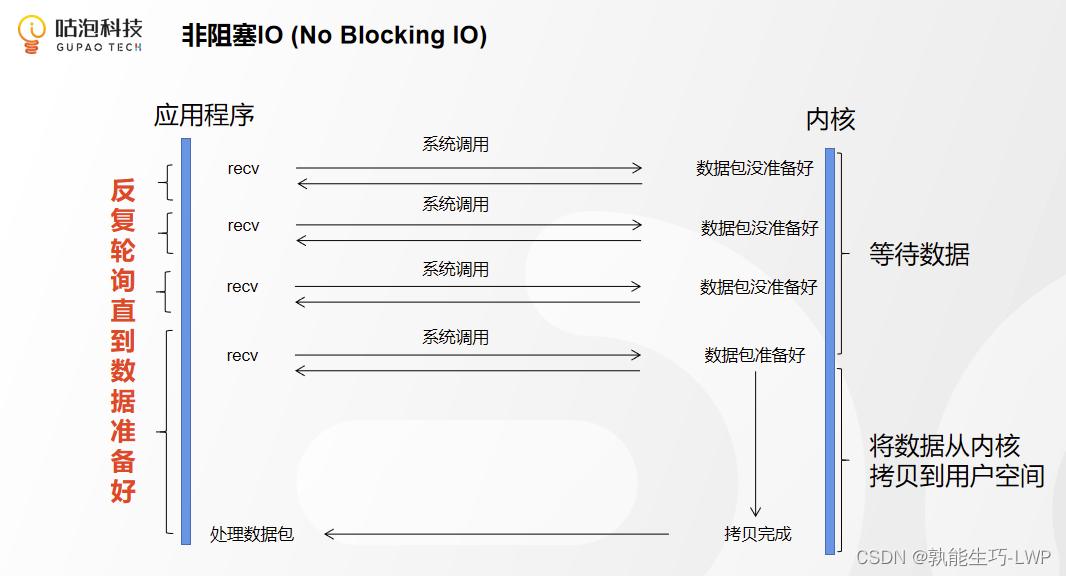
2.Non Blocking IO(非阻塞)
package com.lx.netty.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class NoBlockingServer {
public static List<SocketChannel> channelList = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 相当于serverSocket
// 1.支持非阻塞 2.数据总是写入buffer,读取也是从buffer中去读 3.可以同时读写
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
while (true){
// 这里将不再阻塞
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
if(socketChannel != null){
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
channelList.add(socketChannel);
}else {
System.out.println("没有请求过来!!!");
}
for (SocketChannel client : channelList){
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 也不阻塞
int num = client.read(byteBuffer);
if(num>0){
System.out.println("客户端端口:"+ client.socket().getPort()+",客户端收据:"+new String(byteBuffer.array()));
}else {
System.out.println("等待客户端写数据");
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3.NIO
package com.lx.netty.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class NewIOServer {
static Selector selector;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
// 需要把serverSocketChannel注册到多路复用器上
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true) {
// 阻塞
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
handlerAccept(key);
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
handlerRead(key);
}else if(key.isWritable()){
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void handlerRead(SelectionKey key) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
try {
socketChannel.read(allocate);
System.out.println("server msg:" + new String(allocate.array()));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void handlerAccept(SelectionKey key) {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
// 不阻塞
try {
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("I am wentai,is shuai".getBytes()));
// 读取客户端的数据
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package com.lx.netty.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class NewIOClient {
static Selector selector;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
selector = Selector.open();
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
// 需要把socketChannel注册到多路复用器上
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
while (true) {
// 阻塞
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
if (key.isConnectable()) {
handlerConnect(key);
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
handlerRead(key);
} else if (key.isWritable()) {
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void handlerRead(SelectionKey key) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
try {
socketChannel.read(allocate);
System.out.println("client msg:" + new String(allocate.array()));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void handlerConnect(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
if (socketChannel.isConnectionPending()) {
socketChannel.finishConnect();
}
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("client I am wentai,is shuai".getBytes()));
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
}
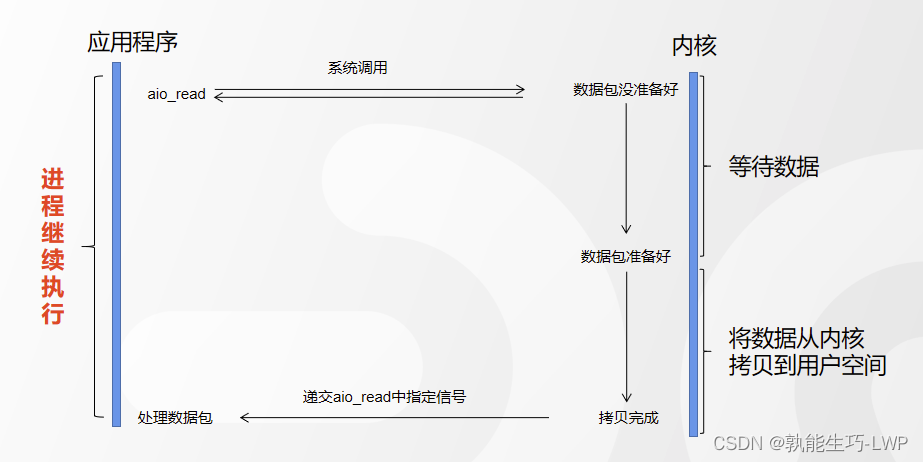
4.AIO(异步IO)
package com.lx.netty.aio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
// 服务端
public class AIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 创建一个SocketChannel并绑定了8080端口
final AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverChannel =
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
serverChannel.accept(null, new CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, Object>() {
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel, Object attachment) {
try {
// 打印线程的名字
System.out.println("2--"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println(socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// socketChannel异步的读取数据到buffer中
socketChannel.read(buffer, buffer, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer buffer) {
// 打印线程的名字
System.out.println("3--"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
buffer.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buffer.array(), 0, result));
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("HelloClient".getBytes()));
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer buffer) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
System.out.println("1--"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
}
package com.lx.netty.aio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
public class AIOClient {
private final AsynchronousSocketChannel client;
public AIOClient() throws IOException {
client = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new AIOClient().connect("localhost",8080);
}
public void connect(String host, int port) throws Exception {
// 客户端向服务端发起连接
client.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host, port), null, new CompletionHandler<Void, Object>() {
@Override
public void completed(Void result, Object attachment) {
try {
client.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("这是一条测试数据".getBytes())).get();
System.out.println("已发送到服务端");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
final ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 客户端接收服务端的数据,获取的数据写入到bb中
client.read(bb, null, new CompletionHandler<Integer, Object>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, Object attachment) {
// 服务端返回数据的长度result
System.out.println("I/O操作完成:" + result);
System.out.println("获取反馈结果:" + new String(bb.array()));
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
try {
Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
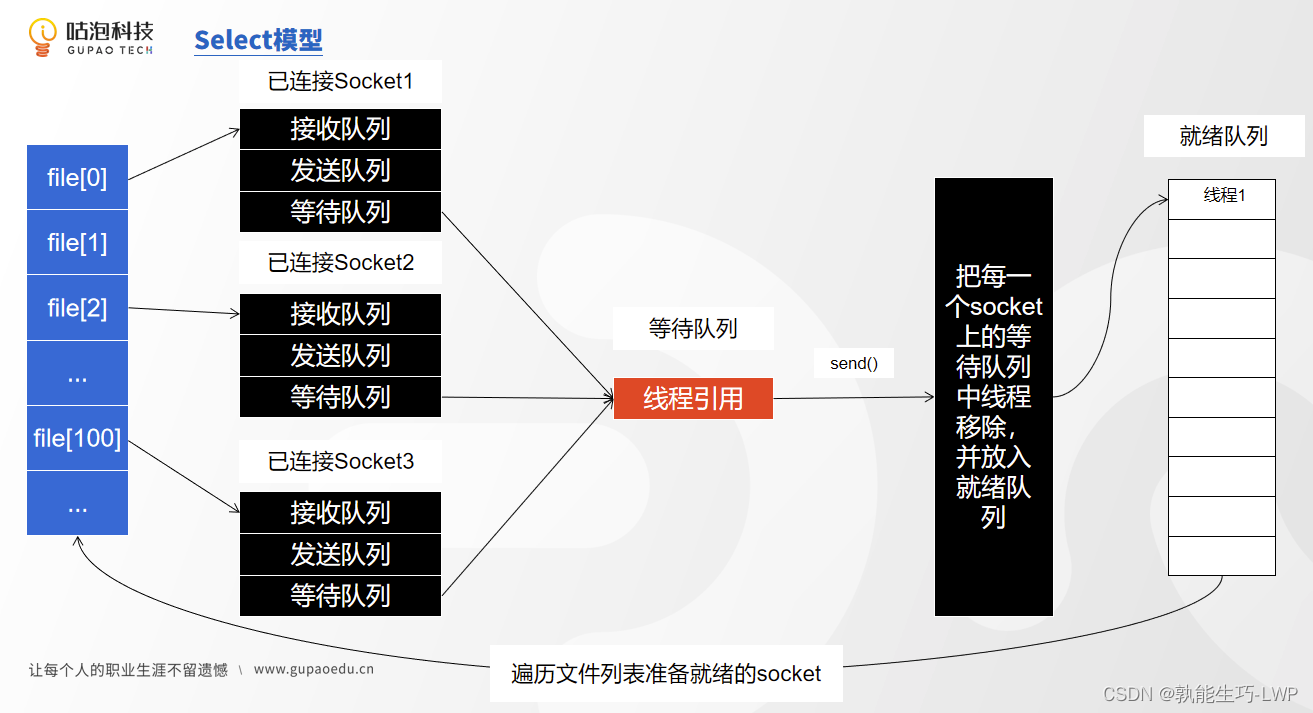
}5.多路复用IO:多路复用有三种模型,一种时select()模型,一种poll模型,还一种就是epoll模型。
6.select()模型: 在这个socket中,每个socket都是有接收队列,发送队列,等待队列组成,所以每次调 用selector.select()方法的时候,都会把线程的引用放入到所有socket中的等待队列中,当接收到客户端的数 据后,把每一个socket上的等待队列中的线程移除,并放入到就绪队列中,然后去遍历文件列表,找出所有 接收到数据的socket。
select()的缺点:
1. 每次调用select都需要将线程加入到所有socket对象的等待队列中,每次唤醒进程又要将线程从所有socket对象的等待队列中移除。这里涉及到对socket列表的两次遍历,而且每次都要将整个fds列表传 递给内核,有一定的开销。正因为遍历操作开销大,出于效率的考量,才会规定select的最大监视数 量,默认只能监视1024个socket(强行修改也是可以的);
2. 进程被唤醒后,程序并不知道socket列表中的那些socket上收到数据,因此在用户空间内需要对socket列表再做一次遍历。poll模型和select相似,只是对监听的socket没有限制。 我们发现其实select模型和poll模型其实每次都是 遍历所有的socket,有些socket其实没有事件,还是回去遍历,如果socket越多,那么遍历事件就越长,在高 并发的情况下,select模型的效率其实比较低,那么有没有一种模型,可以只返回有事件的socket呢,而不 需要遍历那么多的socket,答案就是epoll模型
7.epoll模型
其实epoll有两种工作方式,一种时LT,另外一种时ET。
LT模式意思就是通过是支持阻塞和非阻塞的socket,其实select和poll都是这种模式,我们今天主要谈的时ET模式,
ET模式只支持non-block socket,我们来看下epoll再ET模式下的工作原理。
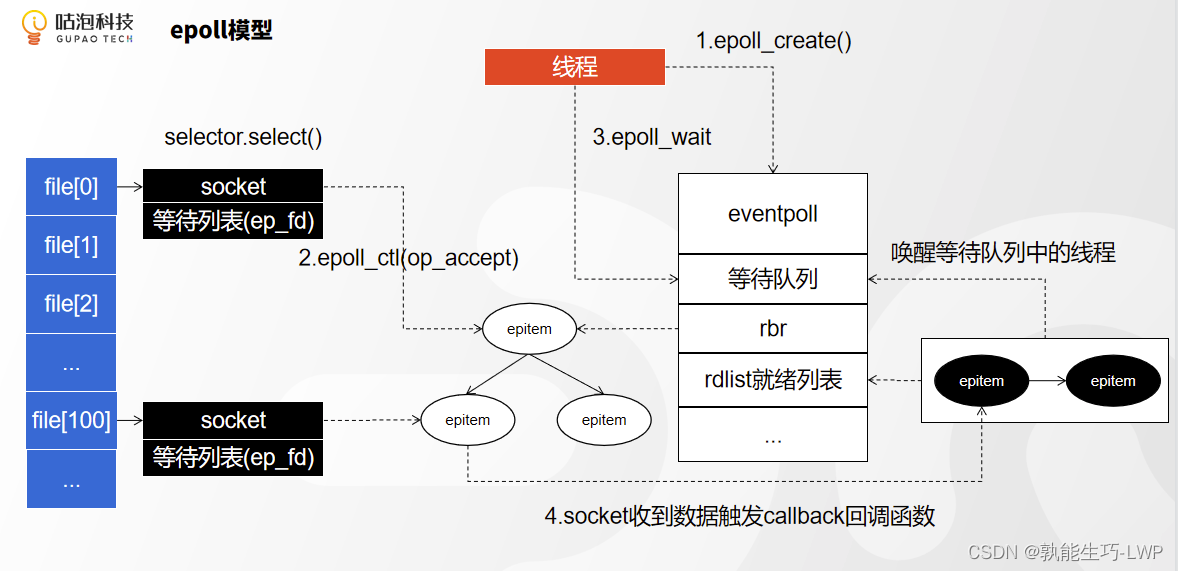
1.NIO中调用Selector.open()得到一个selector,实际上就是调用底层的epoll_create函数,创建一个 eventpoll的事件文件对象,假设为ep_fd
2.NIO中调用register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT),把需要注册的fd存储在jvm内存
3.循环调用selector.select(),底层触发epoll_ctl(ep_fd,add,fd,OP_ACCEPT),把需要注册的fd放到ep_fd对应 的红黑树上,注册OP_ACCEPT事件,并且对应到eventpoll文件对象中的rbr索引树中,然后调用epoll_wait()方法,然后把等待的线程的引用加入的eventpoll的等待队列中
4.一当接收到客户端的连接,那么将会触发socket上面的callback函数,并且把有数据处理的socket放入到eventpoll中的rdlist就序列表,同时唤醒等待队列中的线程,然后线程直接循环就绪列表中准备好的socket。
 所以epoll模型的优点是:
所以epoll模型的优点是:
1.支持一个进程打开很大数目的socket描述符
2.IO效率不随FD数目增加而线性下降
最后
以上就是淡定大地最近收集整理的关于Netty网络通信之Socket的全部内容,更多相关Netty网络通信之Socket内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复