目录
- 需求
- 原理简单介绍
- 流程
- 电路要求
- 软件编写简要说明
- 1、编写 ram BootLoader
- 2、编写 SWD接口驱动
- 3、编写从机用户程序代码
- 4、编写下载从机程序的代码
需求
在实际项目中使用MCU+蓝牙芯片的方式给产品添加蓝牙功能,由于蓝牙芯片要跑协议栈和一些用户代码,MCU也要跑应用代码,这样一来软件升级就成了一个棘手的问题,分别给蓝牙芯片和主控MCU做软件升级显然对量产十分不友好。
例如:笔者在一个腕表产品的项目中使用了GD32F450+NRF52832的方案,而生产时给蓝牙芯片升级软件非常繁琐,需要在电路板上预留的swd测试焊盘上焊接下载线,然后在电脑上使用jlink下载软件,再拆除swd下载线。
本文介绍一种使用swd接口实现主控MCU给NRF52832芯片做程序升级的方法,用于解决以上问题,此方法不需要更改蓝牙芯片的代码,不需要修改蓝牙芯片的BootLoader程序。并且理论上此方法支持任何支持SWD调试接口的单片机。
原理简单介绍
SWD接口是ARM cortex-M 内核单片机选配的调试接口,内部连接到 CoreSight 调试组件,CoreSight 可以直接访问单片机内部所有可寻址空间,并且可以修改所有内核寄存器,使用这两个特性就可以实现软件编程,keil和jlink下载程序就是使用这个原理。
流程
以下把主控MCU称为主机,NRF52832称为从机,以简化描述。
主机初始化SWD接口->主机把从机的ram BootLoader 搬运到其内存区域->从机执行初始化代码(主机等待从机初始化完成)->主机发送擦除flash命令并等待从机擦除完成(从机擦除flash)->主机循环发送程序数据到从机并等待flash写入结束(从机进行flash写入)->主机发送结束命令(从机重启)->软件升级完成
电路要求
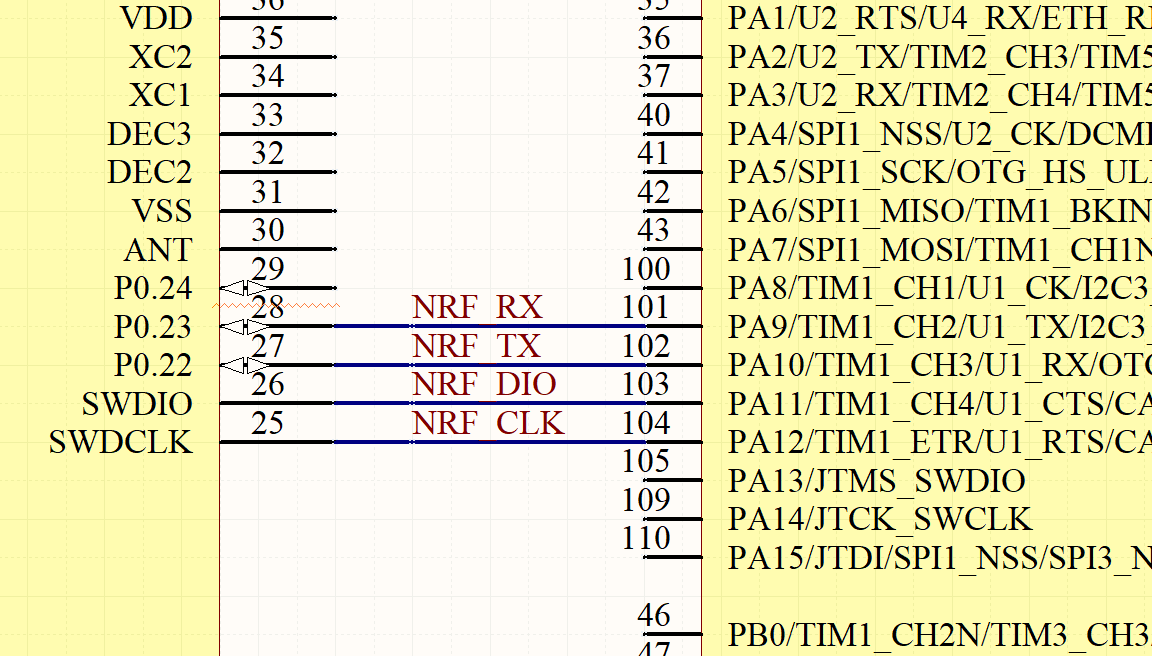
假设nrf52832蓝牙芯片使用串口与主控单片机通信,则至少需要进行如下连接(假设P0.23配置为RX,P0.22配置为TX),从机的swd接口则可以与主机的任意GPIO连接,下图以连接到PA11、PA12为例:
软件编写简要说明
1、编写 ram BootLoader
此部分软件的功能是进行数据搬运,接收主机的数据写入flash,擦除flash等。
对于nrf52832,编写代码如下:
#include "nrf_nvmc.h"
#define TYPE_NONE 0x00000000
#define TYPE_INIT 0x00000001
#define TYPE_ERASE 0x00000002
#define TYPE_START 0x00000003
#define TYPE_DONE 0x00000004
#define TYPE_END 0x00000005
// 尺寸,以字为单位
typedef struct{
volatile uint32_t type;
volatile uint32_t all_size;
volatile uint32_t mem_base;
volatile uint32_t mem_size;
volatile uint32_t data[4096/4];
}info_struct;
// 限制结构体到指定地址,主控要访问这段内存
static info_struct g_sram __attribute__((at(0x20009000)));
int main(void)
{
//初始化,初始化完成之后把状态设置为初始化
g_sram.type=TYPE_INIT;
while(1)
{
if(g_sram.type==TYPE_ERASE)
{
//接收到擦除命令
int num=g_sram.all_size/1024+1;
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
{
nrf_nvmc_page_erase(i*4096);
}
g_sram.type=TYPE_DONE;
}
else if(g_sram.type==TYPE_START)
{
//接收到开始写入命令
nrf_nvmc_write_words(g_sram.mem_base,(const uint32_t *)g_sram.data,g_sram.mem_size);
g_sram.type=TYPE_DONE;
}
else if(g_sram.type==TYPE_END)
{
//接收到结束命令,重启
NVIC_SystemReset();
}
}
}
2、编写 SWD接口驱动
编写 swd.h 文件如下:
#ifndef SWD_H__
#define SWD_H__
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
//命令字定义
#define SWD_REG_DP 0x00
#define SWD_REG_AP 0x02
#define SWD_READ 0x04
#define SWD_WRITE 0x00
//DP寄存器
#define SWD_REG_IDCODE (0x00<<1)//只读
#define SWD_REG_ABORT (0x00<<1)//只写
#define SWD_REG_CTRL_STAT (0x04<<1)//读写
#define SWD_REG_RESEND (0x08<<1)//只读
#define SWD_REG_SELECT (0x08<<1)//只写
#define SWD_REG_RDBUFF (0x0c<<1)//只读
//AP寄存器
#define SWD_REG_CSW (0x00<<1)
#define SWD_REG_TAR (0x04<<1)
#define SWD_REG_BASE (0x08<<1)
#define SWD_REG_DRW (0x0c<<1)
#define SWD_REG_IDR (0x0c<<1)
//通信错误类型
#define SWD_ERR_OK (0x01)
#define SWD_ERR_WAIT (0x02)
#define SWD_ERR_FAIL (0x04)
#define SWD_ERR_OTHER (0x07)
// Cortex M3 Debug Registers (AHB addresses)
#define CM3_DDFSR 0xE000ED30 // Debug Fault StatusRegister
#define CM3_DHCSR 0xE000EDF0 // Debug Halting Control and Status Register
#define CM3_DCRSR 0xE000EDF4 // Debug Core Register Selector Register
#define CM3_DCRDR 0xE000EDF8 // Debug Core Register Data Register
#define CM3_DEMCR 0xE000EDFC // Debug Exception and Monitor Control Register
#define CM3_AIRCR 0xE000ED0C // The Application Interrupt and Reset Control Register
//读写内核寄存器
#define CM3_REG_READ 0x00000000
#define CM3_REG_WRITE 0x00010000
//内核寄存器选址
#define CM3_REG_R0 0x0000
#define CM3_REG_R1 0x0001
#define CM3_REG_R2 0x0002
#define CM3_REG_R3 0x0003
#define CM3_REG_R4 0x0004
#define CM3_REG_R5 0x0005
#define CM3_REG_R6 0x0006
#define CM3_REG_R7 0x0007
#define CM3_REG_R8 0x0008
#define CM3_REG_R9 0x0009
#define CM3_REG_R10 0x000a
#define CM3_REG_R11 0x000b
#define CM3_REG_R12 0x000c
#define CM3_REG_R13 0x000d
#define CM3_REG_SP 0x000d
#define CM3_REG_R14 0x000e
#define CM3_REG_LR 0x000e
#define CM3_REG_R15 0x000f
#define CM3_REG_PC 0x000f
#define CM3_REG_xPSR 0x0010
#define CM3_REG_MSP 0x0011
#define CM3_REG_PSP 0x0012
//初始化
void SWD_Init (void);
//总线复位
void SWD_LineReset (void);
//读取寄存器
u32 SWD_ReadReg (u8 cmd,u8 *err);
//写入寄存器
void SWD_WriteReg (u8 cmd,u8 *err,u32 data);
//向内存写入数据,成功返回设备id
u32 SWD_WriteSram (u32 addr,u32 *data,u32 len);
//向内存读取数据,成功返回设备id
u32 SWD_ReadSram (u32 addr,u32 *data,u32 len);
//暂停或者启动内核1,暂停,0,启动
u32 SWD_Cm3Halt (u8 value);
//向内核寄存器写入数据
u32 SWD_WriteCm3Reg (u16 reg_select,u32 data);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif
编写 swd.c 文件如下:
#include "sys.h"
#include "swd.h"
// 本文以 stm32f103 的GPIO PB6、PB7 为例
#define SWD_CLK PBout(6)
#define SWD_DIO_OUT PBout(7)
#define SWD_DIO_IN PBin(7)
//用寄存器方式设置PB7为上拉输入模式
#define SWD_DIN() {u32 temp=GPIOB->CRL&0x0fffffff;
GPIOB->CRL=temp|(0x8<<(4*(7)));
GPIOB->BSRR=1<<7;}
//用寄存器方式设置PB7为推挽输出模式
#define SWD_DOUT() {u32 temp=GPIOB->CRL&0x0fffffff;
GPIOB->CRL=temp|(0x3<<(4*(7)));}
void SWD_Init (void)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOB, ENABLE);
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd( RCC_APB2Periph_AFIO, ENABLE );//PORTB时钟使能
GPIO_PinRemapConfig(GPIO_Remap_SWJ_JTAGDisable,ENABLE);
//使用GPIO来模拟SWD接口
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_6|GPIO_Pin_7; //PB6、PB7
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_Out_PP; //推挽输出
GPIO_Init(GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStructure);
SWD_CLK=0;
SWD_DIO_OUT=1;
}
//低位在前,高位在后
//上升沿刷新,下降沿锁存
void SWD_SendByte (u8 byte)
{
SWD_DOUT();
for (u8 i=0;i<8;i++)
{
SWD_DIO_OUT=byte>>i;
SWD_CLK=1;
SWD_CLK=0;
}
}
u8 SWD_RecvByte (void)
{
u8 byte=0;
SWD_DIN();
for (u8 i=0;i<8;i++)
{
byte>>=1;
byte|=(SWD_DIO_IN<<7);
SWD_CLK=1;
SWD_CLK=0;
}
return byte;
}
void SWD_Turn (void)
{
SWD_CLK=1;
SWD_CLK=0;
}
u8 SWD_Ask (void)
{
u8 ask=0;
SWD_DIN();
for (u8 i=0;i<3;i++)
{
ask>>=1;
ask|=(SWD_DIO_IN<<2);
SWD_CLK=1;
SWD_CLK=0;
}
return ask;
}
u8 SWD_Praity (void)
{
u8 par=0;
SWD_DIN();
par=SWD_DIO_IN;
SWD_CLK=1;
SWD_CLK=0;
return par;
}
void SWD_SendPraity (u8 pra)
{
SWD_DOUT();
SWD_DIO_OUT=pra;
SWD_CLK=1;
SWD_CLK=0;
}
void SWD_LineReset (void)
{
for (u8 i=0;i<7;i++)
{
SWD_SendByte(0xff);
}
SWD_SendByte(0x9e);//低字节在前
SWD_SendByte(0xe7);
for (u8 i=0;i<7;i++)
{
SWD_SendByte(0xff);
}
SWD_SendByte(0xb6);//低字节在前
SWD_SendByte(0xed);
for (u8 i=0;i<7;i++)
{
SWD_SendByte(0xff);
}
SWD_SendByte(0x00);//低字节在前
SWD_SendByte(0x00);
}
u32 SWD_ReadReg (u8 cmd,u8 *err)
{
cmd|=0x81|SWD_READ;
u8 _1num=0;
for (u8 i=0;i<4;i++)
{
if (cmd&(1<<(i+1)))
{
_1num++;
}
}
if (_1num%2) cmd|=1<<5;
u8 ask=0;
do
{
SWD_SendByte(cmd);
SWD_Turn();
ask=SWD_Ask();
}while (ask==SWD_ERR_WAIT);
*err=ask;
u32 data=0;
u8 praity=0;
data|=SWD_RecvByte();
data|=SWD_RecvByte()<<8;
data|=SWD_RecvByte()<<16;
data|=SWD_RecvByte()<<24;
praity=SWD_Praity();
SWD_SendByte(0);
//SWD_Turn();
_1num=0;
for (u8 i=0;i<32;i++)
{
if (data&(1<<i))
{
_1num++;
}
}
//delay_us(170);
if ((_1num%2)==(praity&1))//校验成功
{
return data;
}
else
{
*err=0x07;
return 0;
}
}
void SWD_WriteReg (u8 cmd,u8 *err,u32 data)
{
cmd|=0x81|SWD_WRITE;
u8 _1num=0;
for (u8 i=0;i<4;i++)
{
if (cmd&(1<<(i+1)))
{
_1num++;
}
}
if (_1num%2) cmd|=1<<5;
u8 ask=0;
do
{
SWD_SendByte(cmd);
SWD_Turn();
ask=SWD_Ask();
SWD_Turn();
}while (ask==SWD_ERR_WAIT);
*err=ask;
_1num=0;
for (u8 i=0;i<32;i++)
{
if (data&(1<<i))
{
_1num++;
}
}
SWD_SendByte(data&0xff);
SWD_SendByte(data>>8);
SWD_SendByte(data>>16);
SWD_SendByte(data>>24);
//SWD_SendPraity(_1num%2);
SWD_SendByte(_1num%2);
//delay_us(170);
}
//向内存写入数据,成功返回设备id
u32 SWD_WriteSram (u32 addr,u32 *data,u32 len)
{
u8 err=0;
u32 id=0;
//SWD_LineReset();
id=SWD_ReadReg(SWD_REG_DP|SWD_REG_IDCODE,&err);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_DP|SWD_REG_ABORT,&err,0x1e);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_DP|SWD_REG_CTRL_STAT,&err,0x50000000);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_DP|SWD_REG_SELECT,&err,0x00);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_CSW,&err,0x23000012);//地址自动递增
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_TAR,&err,addr);//在这个地址的内存空间写数据
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
while (len--)
{
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_DRW,&err,*data);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
data++;
}
return id;
}
//向内存读取数据,成功返回设备id
u32 SWD_ReadSram (u32 addr,u32 *data,u32 len)
{
u8 err=0;
u32 id=0;
//SWD_LineReset();
id=SWD_ReadReg(SWD_REG_DP|SWD_REG_IDCODE,&err);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_DP|SWD_REG_ABORT,&err,0x1e);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_DP|SWD_REG_CTRL_STAT,&err,0x50000000);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_DP|SWD_REG_SELECT,&err,0x00);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_CSW,&err,0x23000012);//地址自动递增
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_TAR,&err,addr);//在这个地址的内存空间数据
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
*data=SWD_ReadReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_DRW,&err);//读取一次无效数据
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
while (len--)
{
*data=SWD_ReadReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_DRW,&err);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
data++;
}
return id;
}
//暂停或者启动内核1,暂停,0,启动
u32 SWD_Cm3Halt (u8 value)
{
u8 err=0;
u32 id=0;
//SWD_LineReset();
id=SWD_ReadReg(SWD_REG_DP|SWD_REG_IDCODE,&err);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_DP|SWD_REG_ABORT,&err,0x1e);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_DP|SWD_REG_CTRL_STAT,&err,0x50000000);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_DP|SWD_REG_SELECT,&err,0x00);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_CSW,&err,0x23000002);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_TAR,&err,CM3_DHCSR);//暂停CM3内核
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
if (value)
{
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_DRW,&err,0xa05f0001);//写入钥匙,使能调试
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_TAR,&err,CM3_DEMCR);//使能复位后停止
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_DRW,&err,0x1);//
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_TAR,&err,CM3_AIRCR);//复位
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_DRW,&err,0x05fa0004);//
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
}
else
{
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_DRW,&err,0xa05f0000);//写入钥匙,使能调试
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
}
return id;
}
//向内核寄存器写入数据
u32 SWD_WriteCm3Reg (u16 reg_select,u32 data)
{
u8 err=0;
u32 id=0;
//SWD_LineReset();
id=SWD_ReadReg(SWD_REG_DP|SWD_REG_IDCODE,&err);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_DP|SWD_REG_ABORT,&err,0x1e);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_DP|SWD_REG_CTRL_STAT,&err,0x50000000);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_DP|SWD_REG_SELECT,&err,0x00);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_CSW,&err,0x23000002);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_TAR,&err,CM3_DCRDR);//内核数据寄存器
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_DRW,&err,data);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_TAR,&err,CM3_DCRSR);//选择内核寄存器
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_DRW,&err,reg_select|CM3_REG_WRITE);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
u32 dhcsr_data=0;
SWD_WriteReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_TAR,&err,CM3_DHCSR);//
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
dhcsr_data=SWD_ReadReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_DRW,&err);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
do
{
dhcsr_data=SWD_ReadReg(SWD_REG_AP|SWD_REG_DRW,&err);
if (err!=SWD_ERR_OK) return 0;
}while ((dhcsr_data&0x00010000)==0);
return id;
}
3、编写从机用户程序代码
本示例用户程序主要用于演示,则编写led闪烁的代码来表示实验结果,如果led如预期闪烁,则实验成功。
#include "nrf_gpio.h"
#include "nrf_radio.h"
int delay(int n)
{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<1000;j++);
return 0;
}
int main(void)
{
nrf_gpio_pin_set(17);
nrf_gpio_cfg_output(17);
nrf_gpio_pin_set(18);
nrf_gpio_cfg_output(18);
while(1)
{
nrf_gpio_pin_set(17);
nrf_gpio_pin_clear(18);
delay(5000);
nrf_gpio_pin_clear(17);
nrf_gpio_pin_set(18);
delay(5000);
}
}
4、编写下载从机程序的代码
// 定义 acloader 数据,数组内容是从机的 ram BootLoader 程序
#include "loader.c"
// 定义 acled 数组,数组内容是本示例的从机用户程序
#include "led.c"
#define TYPE_NONE 0x00000000
#define TYPE_INIT 0x00000001
#define TYPE_ERASE 0x00000002
#define TYPE_START 0x00000003
#define TYPE_DONE 0x00000004
#define TYPE_END 0x00000005
// 访问从机 0x20009000 地址的内存
#define TYPE_ADDR (0x20009000)
#define ALLSIZE_ADDR (0x20009004)
#define MEMBASE_ADDR (0x20009008)
#define MEMSIZE_ADDR (0x2000900c)
int main(void)
{
u8 err;
u32 id;
u32 data;
// 初始化swd接口,复位总线
SWD_Init();
SWD_LineReset();
// 写入从机 ram BootLoader 程序,等待从机初始化
data=TYPE_NONE;
SWD_WriteSram(TYPE_ADDR,&data,1);
id=SWD_Cm3Halt(1);
id=SWD_WriteSram(0x20000000,(uint32_t *)acloader,sizeof(acloader)/4+1);
id=SWD_WriteCm3Reg(CM3_REG_MSP,((uint32_t *)acloader)[0]);
id=SWD_WriteCm3Reg(CM3_REG_PC,((uint32_t *)acloader)[1]);
SWD_Cm3Halt(0);
while(SWD_ReadSram(TYPE_ADDR,&data,1),data!=TYPE_INIT);
uint32_t *sram=(uint32_t *)acled;
uint32_t all_size=sizeof(acled)/4+1;
uint32_t mem_size=0;
uint32_t mem_base=0;
uint32_t times=(all_size+1023)/1024;
// 擦除从机flash,等待擦除完毕
id=SWD_WriteSram(ALLSIZE_ADDR,&all_size,1);
data=TYPE_ERASE;
id=SWD_WriteSram(TYPE_ADDR,&data,1);
while(SWD_ReadSram(TYPE_ADDR,&data,1),data!=TYPE_DONE);
// 循环写入从机flash
for(int i=0;i<times;i++)
{
mem_size=1024;
if(mem_size>all_size) mem_size=all_size;
id=SWD_WriteSram(0x20009000+16,sram,mem_size);
id=SWD_WriteSram(MEMSIZE_ADDR,&mem_size,1);
id=SWD_WriteSram(MEMBASE_ADDR,&mem_base,1);
data=TYPE_START;
id=SWD_WriteSram(TYPE_ADDR,&data,1);
while(SWD_ReadSram(TYPE_ADDR,&data,1),data!=TYPE_DONE);
mem_base+=mem_size*4;
all_size-=mem_size;
}
// 从机重启
data=TYPE_END;
id=SWD_WriteSram(TYPE_ADDR,&data,1);
// 死循环,不做任何事
while(1)
{
id=SWD_ReadReg(SWD_REG_DP|SWD_REG_IDCODE,&err);
if(id)
{
memset(&id,0,sizeof(int));
}
}
}
最后
以上就是体贴母鸡最近收集整理的关于使用单片机给nrf52832蓝牙芯片软件升级需求原理简单介绍电路要求软件编写简要说明的全部内容,更多相关使用单片机给nrf52832蓝牙芯片软件升级需求原理简单介绍电路要求软件编写简要说明内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复