例14.模为60的BCD码加法计数器
module count60(
input [7:0] data,
input clk,
input reset,
input cin,//计数使能
output [7:0] qout,
output cout
);
always@( posedge clk)begin
if(reset)
qout <= 0;
else if(load)
qout <= data;
else if(cin) begin
if(qout[3:0] == 4'd9)begin
qout[3:0] <= 4'd0
if(qout[7:4] == 4'd5)
qout[7:4] <= 4'd0;
else
qout[7:4] <= qout[7:4] +4'd1;
else
qout[3:0] <= qout[3:0] + 4'd1;
end
end
assign cout = (qout == 8'h59 & cin)?1:0;
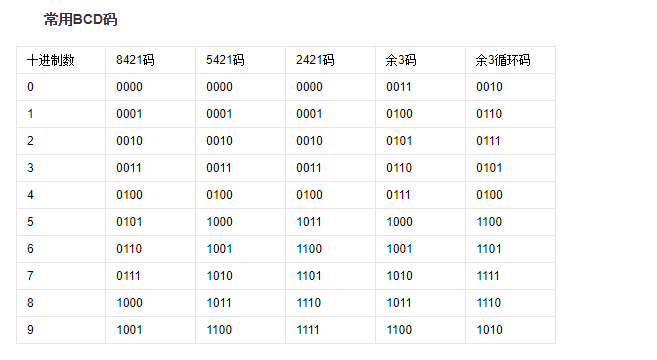
endmoduleBCD码(Binary-Coded Decimal)亦称二进码十进数或二-十进制代码。用4位二进制数来表示1位十进制数中的0~9这10个数码。是一种二进制的数字编码形式,用二进制编码的十进制代码。BCD码这种编码形式利用了四个位元来储存一个十进制的数码,使二进制和十进制之间的转换得以快捷的进行。
例15.用casez描述的数据选择器
module mux_casez(
input a,
input b,
input c,
input d,
input [3:0]select,
output reg out
);
always@(select or a or b or c or d)begin
casez(select)
4'b???1: out = a;
4'b??1?: out = b;
4'b?1??: out = c;
4'b1???: out = d;
default: out = 0;
endcase
end
endmodulecase、casez和casex的介绍请见博客文章。https://blog.csdn.net/zpc0212/article/details/88210915
例16. 隐含锁存器举例
module buried_ff(
input a,
input b,
output reg c
);
always @(a or b)begin
if((b == 1) && ( a== 1)) c = a&b;
end
endmoudle例18.使用for语句描述七人投票表决器
module Voter7(
input [6:0] voter;
output reg pass
);
reg [2:0] sum;
integer i;
always@(vote)begin
sum = 0;
for(i = 0;i <= 6;i = i + 1)
if(vote[i])
sum = sum + 1;
else
sum = sum
if(sum[2])
pass = 1;
else
pass = 0;
end
endmoudleinteger与reg的用法请见博客。https://blog.csdn.net/zpc0212/article/details/88206226
例19.用for语句实现2个8位数相乘
module mult_for(
input [8:1] a,
input [8:1] b,
output reg [16:1] outcome
);
integer i;
always@(a or b)begin
outcome = 0;
for(i = 1;i <= size;i = i+1)
if(b[i]) outcome = outcome + (a << (i - 1)); //b为1的时候进行移位相加
end
endmoudle
例20.使用repeat实现8位二进制数的乘法
module mult_repeat(outcome,a,b);
patameter size = 8;
input [size:1] a,b;
output[2*size:1] outcome;
reg [2*size:1] temp_a,outcome;
reg [size:1] temp_b;
always@(a or b)begin
outcome = 0;
temp_a = a;
temp_b = b;
repeat(size)begin
if(temp_b[1])
outcome = outcome + temp_a;
temp_a = temp_a << 1;
temp_b = temp_b >> 1;
end
end
endmodule例20.同一循环的不同实现方式
module loop1{};
integer i;
initial
begin
for(i = 0;i < 4;i = i + 1)
$display("i = %h",i);
end
endmodule
module loop2{};
integer i;
initial
begin
i = 0;
while(i < 4)
begin
$display("i = %h",i);
i = i + 1;
end
end
endmodule
module loop3{};
integer i;
initial
begin
repeat(4)
begin
$display("i = %h",i);
i = i+1;
end
end
endmodule
三种循环方式。for,while,repeat。
最后
以上就是聪明鞋垫最近收集整理的关于经典设计实例_整理加解释(14-20)的全部内容,更多相关经典设计实例_整理加解释(14-20)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复