前言
了解了在spinal HDL中如何利用scala语言进行状态机编写后,本文通过“1001”序列检测器的代码进行练习状态机的编写。
序列检测要求
检测1001序列,输入信号din依次输入1、0、0、1,当检测到完整序列后dout进行输出,使用mealy型状态机进行编写。
任务分析
对于使用Verilog的状态机编写,首先需要画状态转移图,然后根据状态转移图使用三段式状态机进行描述。
而对于spinal HDL来说,根据前文的讲述的语法规则,在完成状态转移图后,也需要根据状态转移图进行状态机描述。这里我根据三段式的思路,也大致分成三段:
- new 一个状态机 StateMachine 的val,new 需要的状态并指定状态机的入口。
- 根据spinal HDL的语法进行编写状态转移
- 根据实际需求,设计判断条件进行输出。
编写代码
为了对比spinal HDL的代码和Verilog代码的异同,首先给出一份手写的mealy型状态机的序列检测器。
module mealy_1001(clk,rst_n,din,dout,state_c,state_n
);
input clk ;
input rst_n ;
input din ;
output reg dout ;
output [2:0] state_c ;
output [2:0] state_n ;
reg [2:0] state_c ;//现态
reg [2:0] state_n ;//次态
//状态变量赋值
parameter S0 =3'b000,
S1 =3'b001,
S2 =3'b010,
S3 =3'b100;
//状态跳转
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(rst_n==1'b0)begin
state_c <=S0;
end
else begin
state_c <= state_n;
end
end
//状态转移条件判断
always@(*)begin
case(state_c)
S0:
if(din==1'b1)begin
state_n=S1;
end
else begin
state_n=S0;
end
S1:
if(din==1'b0)begin
state_n=S2;
end
else begin
state_n=S1;
end
S2:
if(din==1'b0)begin
state_n=S3;
end
else begin
state_n=S1;
end
S3:
if(din==1'b1)begin
state_n=S1;
end
else begin
state_n=S0;
end
default:state_n=S0;
endcase
end
//输出模块
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(rst_n==1'b0)begin
dout<=1'b0;
end
else if((state_c==S3)&&(din==1'b1))begin
dout<=1'b1;
end
else begin
dout<=1'b0;
end
end
endmodule
然后,根据硬件状态机的设计思路,编写spinal HDL的状态机代码。下面代码为mealy型状态机。相比Verilog的代码版本更像伪代码。这里按照上述的三段式的思路,编写序列检测功能。
import spinal.core._
import spinal.lib._
import spinal.lib.fsm._
case class mealy_1001() extends Component {
//定义一个输入输出的端口束
val io = new Bundle {
val din = in Bits (1 bit)
val dout = out Bits (1 bit)
}
//消除掉生成的代码前缀
noIoPrefix()
//1-创建一个状态机
val fsm = new StateMachine{
//定义状态,并指定状态机的入口
val S0 = new State with EntryPoint
val S1 = new State
val S2 = new State
val S3 = new State
//定义一个寄存器用于存储dout的值
val reg1: Bits = Reg(Bits(1 bit)).init(0)
//将输出的dout和寄存器reg1绑定一起
io.dout := reg1
//2-状态转移
S0.whenIsActive{
when(io.din === 1) {
goto(S1)
}.otherwise(goto(S0))
}
S1.whenIsActive {
when(io.din === 0) {
goto(S2)
}.otherwise(goto(S1))
}
S2.whenIsActive {
when(io.din === 0) {
goto(S3)
}.otherwise(goto(S1))
}
S3.whenIsActive {
when(io.din===1){
goto(S1)
}.otherwise{
goto(S0)
}
}
//3-输出段
when(io.din === 1&&isActive(S3)) {
reg1:= 1
}.otherwise(reg1:= 0)
}
}
//生成Verilog代码
object mealy_1001APP extends App{
SpinalConfig(
anonymSignalPrefix = "tmp"
).generateVerilog(mealy_1001())
}
运行代码可以生成spinal HDL自动生成的Verilog版本的代码。在intelliJ中运行可编译生成v代码。
生成V代码分析
相比手写版本的代码,使用spinal语法生成的代码多了fsm_wantStart,fsm_wantKill,这两部分是和对应一段状态机的开始和停止。因为对于自动生成的代码中开始的默认状态是BOOT,该状态没有用户设计的状态转移的功能。其余部分的代码对比手写版本的状态机,基本和手写的效果相当。
`define fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_type [2:0]
`define fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_BOOT 3'b000
`define fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S0 3'b001
`define fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S1 3'b010
`define fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S2 3'b011
`define fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S3 3'b100
module mealy_1001 (
input [0:0] din,
output [0:0] dout,
input clk,
input reset
);
wire fsm_wantExit;
reg fsm_wantStart;
wire fsm_wantKill;
reg [0:0] fsm_reg1;
wire when_fsm_01_l45;
reg `fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_type fsm_stateReg;
reg `fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_type fsm_stateNext;
wire when_fsm_01_l23;
wire when_fsm_01_l29;
wire when_fsm_01_l34;
wire when_fsm_01_l39;
`ifndef SYNTHESIS
reg [63:0] fsm_stateReg_string;
reg [63:0] fsm_stateNext_string;
`endif
`ifndef SYNTHESIS
always @(*) begin
case(fsm_stateReg)
`fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_BOOT : fsm_stateReg_string = "fsm_BOOT";
`fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S0 : fsm_stateReg_string = "fsm_S0 ";
`fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S1 : fsm_stateReg_string = "fsm_S1 ";
`fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S2 : fsm_stateReg_string = "fsm_S2 ";
`fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S3 : fsm_stateReg_string = "fsm_S3 ";
default : fsm_stateReg_string = "????????";
endcase
end
always @(*) begin
case(fsm_stateNext)
`fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_BOOT : fsm_stateNext_string = "fsm_BOOT";
`fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S0 : fsm_stateNext_string = "fsm_S0 ";
`fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S1 : fsm_stateNext_string = "fsm_S1 ";
`fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S2 : fsm_stateNext_string = "fsm_S2 ";
`fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S3 : fsm_stateNext_string = "fsm_S3 ";
default : fsm_stateNext_string = "????????";
endcase
end
`endif
assign fsm_wantExit = 1'b0;
always @(*) begin
fsm_wantStart = 1'b0;
case(fsm_stateReg)
`fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S0 : begin
end
`fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S1 : begin
end
`fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S2 : begin
end
`fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S3 : begin
end
default : begin
fsm_wantStart = 1'b1;
end
endcase
end
assign fsm_wantKill = 1'b0;
assign dout = fsm_reg1;
assign when_fsm_01_l45 = ((din == 1'b1) && (fsm_stateReg == `fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S3));
always @(*) begin
fsm_stateNext = fsm_stateReg;
case(fsm_stateReg)
`fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S0 : begin
if(when_fsm_01_l23) begin
fsm_stateNext = `fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S1;
end else begin
fsm_stateNext = `fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S0;
end
end
`fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S1 : begin
if(when_fsm_01_l29) begin
fsm_stateNext = `fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S2;
end else begin
fsm_stateNext = `fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S1;
end
end
`fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S2 : begin
if(when_fsm_01_l34) begin
fsm_stateNext = `fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S3;
end else begin
fsm_stateNext = `fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S1;
end
end
`fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S3 : begin
if(when_fsm_01_l39) begin
fsm_stateNext = `fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S1;
end else begin
fsm_stateNext = `fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S0;
end
end
default : begin
end
endcase
if(fsm_wantStart) begin
fsm_stateNext = `fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_S0;
end
if(fsm_wantKill) begin
fsm_stateNext = `fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_BOOT;
end
end
assign when_fsm_01_l23 = (din == 1'b1);
assign when_fsm_01_l29 = (din == 1'b0);
assign when_fsm_01_l34 = (din == 1'b0);
assign when_fsm_01_l39 = (din == 1'b1);
always @(posedge clk or posedge reset) begin
if(reset) begin
fsm_reg1 <= 1'b0;
fsm_stateReg <= `fsm_enumDefinition_binary_sequential_fsm_BOOT;
end else begin
if(when_fsm_01_l45) begin
fsm_reg1 <= 1'b1;
end else begin
fsm_reg1 <= 1'b0;
end
fsm_stateReg <= fsm_stateNext;
end
end
endmodule
仿真验证
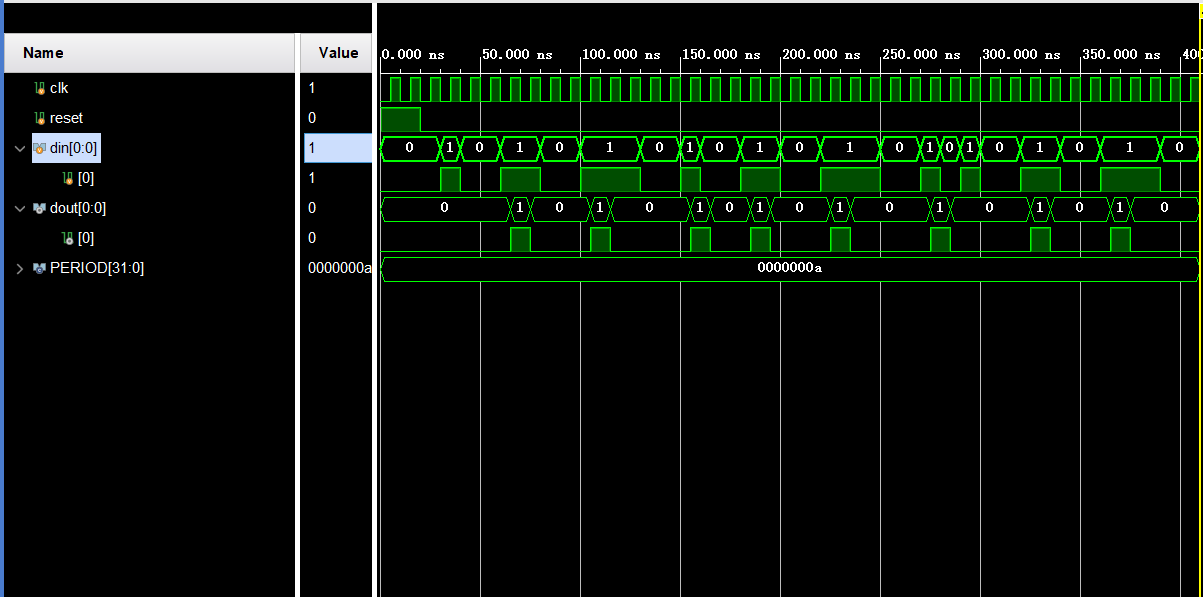
编写一个验证代码,输入序列,观察输出能正常输出序列检测到的指示信号,证明spinal HDL生成的代码功能正常。
小结
- 使用spinal HDL的生成代码虽然有部分自认为“冗余”的部分,但是完全不影响实际的阅读,几乎和手写的代码相当。
- 极大地减小了在手动编写Verilog中时的冗余工作量。
- 经过仿真验证,代码功能和手写一致。
最后
以上就是唠叨毛巾最近收集整理的关于spinal HDL - 11 - 使用状态机语法编写“1001“序列检测前言序列检测要求任务分析编写代码生成V代码分析仿真验证小结的全部内容,更多相关spinal内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复