4 位二进制计数器
构建一个 4 位二进制计数器,从 0 到 15(含)计数,周期为 16。复位输入是同步的,应将计数器复位为 0。

Module Declaration
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset, // Synchronous active-high reset
output [3:0] q);
答案:
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset, // Synchronous active-high reset
output [3:0] q);
always @ (posedge clk)begin
if(reset==1)begin
q <= 0;
end
else begin
q <= q + 1;
end
end
endmodule
十进制计数器
构建一个十进制计数器,从 0 到 9(含)计数,周期为 10。复位输入是同步的,应将计数器复位为 0。
Module Declaration
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset, // Synchronous active-high reset
output [3:0] q);
答案:
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset, // Synchronous active-high reset
output [3:0] q);
always @ (posedge clk)begin
if(reset==1)begin
q <= 0;
end
else if(q==9)begin
q <= 0;
end
else begin
q <= q + 1;
end
end
endmodule
十进制计数器1
制作一个从 1 到 10(包括 1 到 10)计数的十年计数器。复位输入是同步的,应将计数器复位为 1。

Module Declaration
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset, // Synchronous active-high reset
output [3:0] q);
答案:
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset, // Synchronous active-high reset
output [3:0] q);
always @ (posedge clk)begin
if(reset==1)begin
q <= 1;
end
else if(q==10)begin
q <= 1;
end
else begin
q <= q + 1;
end
end
endmodule
慢计数
构建一个从 0 到 9 计数的十进制计数器,周期为 10。重置输入是同步的,应该将计数器重置为 0。我们希望能够暂停计数器而不是每个时钟周期总是递增,所以slowena输入指示计数器何时应该增加。

Module Declaration
module top_module (
input clk,
input slowena,
input reset,
output [3:0] q);
答案:
module top_module (
input clk,
input slowena,
input reset,
output [3:0] q);
always @(posedge clk)begin
if(reset == 1)begin
q <= 0;
end
else if(slowena ==1)begin
if(q==9)begin
q <= 0;
end
else begin
q <= q + 1;
end
end
end
endmodule
1-12计数
设计一个具有以下输入和输出的 1-12 计数器:
Reset : 同步高电平有效复位,强制计数器为 1
Enable : 使计数器运行设置为高
Clk : 正边沿触发时钟输入
Q[3:0] : 计数器的输出
c_enable, c_load, c_d[3:0] : 进入提供的 4 位计数器的控制信号,因此可以验证正确的操作。
您可以使用以下组件:
下面的 4 位二进制计数器 ( count4 ),它具有使能和同步并行加载输入(加载的优先级高于使能)。该count4模块提供给你。在您的电路中实例化它。
module count4(
input clk,
input enable,
input load,
input [3:0] d,
output reg [3:0] Q
);
c_enable、c_load 和 c_d 输出分别是进入内部计数器的启用、加载和 d 输入的信号。 它们的目的是允许检查这些信号的正确性。
Module Declaration
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset,
input enable,
output [3:0] Q,
output c_enable,
output c_load,
output [3:0] c_d
);
答案:
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset,
input enable,
output [3:0] Q,
output c_enable,
output c_load,
output [3:0] c_d
); //
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(reset == 1)begin
Q <= 1;
end
else if(enable == 1)begin
if(Q==12)begin
Q<=1;
end
else begin
Q <= Q + 1;
end
end
end
assign c_enable = enable;
assign c_load = (reset==1)|(Q==12&&enable);
assign c_d = (reset==1)|(Q==12) ;
count4 the_counter (clk, c_enable, c_load, c_d /*, ... */ );
endmodule
计数器1000
从 1000 Hz 时钟导出一个 1 Hz 信号,称为OneHertz,可用于驱动一组小时/分钟/秒计数器的启用信号以创建数字挂钟。由于我们希望时钟每秒计数一次,因此OneHertz信号必须每秒被断言恰好一个周期。使用模 10 (BCD) 计数器和尽可能少的其他门构建分频器。还从您使用的每个 BCD 计数器输出启用信号(c_enable[0] 表示最快的计数器,c_enable[2] 表示最慢的计数器)。
为您提供了以下 BCD 计数器。Enable必须为高电平才能运行计数器。复位是同步的并设置为高电平以强制计数器归零。电路中的所有计数器必须直接使用相同的 1000 Hz 信号。
module bcdcount (
input clk,
input reset,
input enable,
output reg [3:0] Q
);
Module Declaration
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset,
output OneHertz,
output [2:0] c_enable
);
答案:
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset,
output OneHertz,
output [2:0] c_enable
); //
wire [3:0] Q1,Q2,Q3;
assign c_enable[0] = 1;
assign c_enable[1] =(Q1==9);
assign c_enable[2] =(Q2==9 && Q1==9);
assign OneHertz =(Q1==9 && Q2==9 && Q3==9);
bcdcount counter0 (clk, reset, c_enable[0],Q1);
bcdcount counter1 (clk, reset, c_enable[1],Q2);
bcdcount counter2 (clk, reset, c_enable[2],Q3);
endmodule
4 位 BCD计数器
构建一个 4 位 BCD(二进制编码的十进制)计数器。每个十进制数字使用 4 位编码:q[3:0] 是个位,q[7:4] 是十位等。对于数字 [3:1],还输出一个使能信号,指示每个上面的三位数字应该递增。
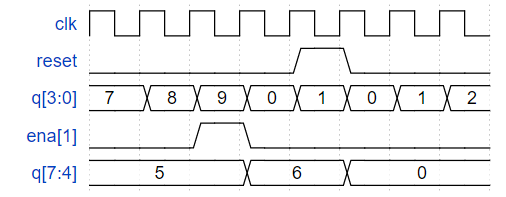
Module Declaration
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset, // Synchronous active-high reset
output [3:1] ena,
output [15:0] q);
答案:
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset, // Synchronous active-high reset
output [3:1] ena,
output [15:0] q);
assign ena[1] =(q[3:0]==9) ;
assign ena[2] =(q[3:0]==9&&q[7:4]==9) ;
assign ena[3] =(q[3:0]==9&&q[7:4]==9&&q[11:8]==9) ;
bcd bcd0(clk,reset,1,q[3:0]);
bcd bcd1(clk,reset,ena[1],q[7:4]);
bcd bcd2(clk,reset,ena[2],q[11:8]);
bcd bcd3(clk,reset,ena[3],q[15:12]);
endmodule
module bcd (
input clk,
input reset,// Synchronous active-high reset
input ena,
output [3:0] q);
always @ (posedge clk)begin
if(reset==1)begin
q <= 0;
end
else if (ena==1)begin
if(q==9)begin
q <= 0;
end
else begin
q <= q + 1;
end
end
else begin
q<=q;
end
end
endmodule
Count clock
创建一组适合用作 12 小时制的计数器(带有 am/pm 指示器)。您的计数器由快速运行的clk计时,每当您的时钟应增加(即每秒一次)时,就会在ena上发出脉冲。
reset将时钟重置为 12:00 AM。pm是 0 代表上午,1 代表下午。hh、mm和ss是两个BCD(二进制编码的十进制)数字,每个数字表示小时 (01-12)、分钟 (00-59) 和秒 (00-59)。复位的优先级高于使能,即使未使能也可能发生。
以下时序图显示了从上午 11:59:59到下午 12:00:00的翻转行为以及同步复位和启用行为。

Note that 11:59:59 PM advances to 12:00:00 AM, and 12:59:59 PM advances to 01:00:00 PM. There is no 00:00:00.
Module Declaration
module top_module(
input clk,
input reset,
input ena,
output pm,
output [7:0] hh,
output [7:0] mm,
output [7:0] ss);
答案:
module top_module(
input clk,
input reset,
input ena,
output pm,
output [7:0] hh,
output [7:0] mm,
output [7:0] ss);
always @ (posedge clk)begin
if(reset==1)
pm <= 0;
else if(ss[3:0]==9 && ss[7:4]==5 && mm[3:0]==9 && mm[7:4]==5 && hh[3:0]==1 && hh[7:4]==1)
pm <= ~pm;
else
pm <= pm;
end
always @ (posedge clk)begin
if(reset==1)begin
hh[7:4] <= 1;
end
else if (ena==1)begin
if(ss[3:0]==9 && ss[7:4]==5 && mm[3:0]==9 && mm[7:4]==5 && hh[3:0]==2 && hh[7:4]==1)begin
hh[7:4]<= 0;
end
else if(ss[3:0]==9 && ss[7:4]==5 && mm[3:0]==9 && mm[7:4]==5 && hh[3:0]==9) begin
hh[7:4] <= hh[7:4] + 1;
end
end
else begin
hh[7:4]<=hh[7:4];
end
end
always @ (posedge clk)begin
if(reset==1)begin
hh[3:0] <= 2;
end
else if (ena==1)begin
if(ss[3:0]==9 && ss[7:4]==5 && mm[3:0]==9 && mm[7:4]==5 && hh[3:0]==2 && hh[7:4]==1)begin
hh[3:0]<= 1;
end
else if(hh[3:0]==9 && ss[3:0]==9 && ss[7:4]==5 && mm[3:0]==9 && mm[7:4]==5)begin
hh[3:0]<= 0;
end
else if(ss[3:0]==9 && ss[7:4]==5 && mm[3:0]==9 && mm[7:4]==5)begin
hh[3:0] <= hh[3:0] + 1;
end
end
else begin
hh[3:0]<=hh[3:0];
end
end
always @ (posedge clk)begin
if(reset==1)begin
mm[7:4] <= 0;
end
else if (ena==1)begin
if(mm[7:4]==5 && ss[3:0]==9 && ss[7:4]==5 && mm[3:0]==9)begin
mm[7:4]<= 0;
end
else if(mm[3:0]==9 && ss[3:0]==9 && ss[7:4]==5 ) begin
mm[7:4] <= mm[7:4] + 1;
end
end
else begin
mm[7:4]<=mm[7:4];
end
end
always @ (posedge clk)begin
if(reset==1)begin
mm[3:0] <= 0;
end
else if (ena==1)begin
if(mm[3:0]==9 && ss[3:0]==9 && ss[7:4]==5)begin
mm[3:0]<= 0;
end
else if( ss[3:0]==9 && ss[7:4]==5 )begin
mm[3:0] <= mm[3:0] + 1;
end
end
else begin
mm[3:0]<=mm[3:0];
end
end
always @ (posedge clk)begin
if(reset==1)begin
ss[7:4] <= 0;
end
else if (ena==1)begin
if(ss[7:4]==5 && ss[3:0]==9)begin
ss[7:4]<= 0;
end
else if(ss[3:0]==9) begin
ss[7:4] <= ss[7:4] + 1;
end
else begin
ss[7:4]<=ss[7:4];
end
end
else begin
ss[7:4]<=ss[7:4];
end
end
always @ (posedge clk)begin
if(reset==1)begin
ss[3:0] <= 0;
end
else if (ena==1)begin
if(ss[3:0]==9)begin
ss[3:0]<= 0;
end
else begin
ss[3:0] <= ss[3:0] + 1;
end
end
else begin
ss[3:0]<=ss[3:0];
end
end
endmodule
最后
以上就是快乐树叶最近收集整理的关于HDLBits练习汇总-11-时序逻辑设计测试--计数器4 位二进制计数器十进制计数器十进制计数器1慢计数1-12计数计数器10004 位 BCD计数器Count clock的全部内容,更多相关HDLBits练习汇总-11-时序逻辑设计测试--计数器4内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。


![[Craftor原创]关于一阶状态机跳转问题的研究与心得](https://file2.kaopuke.com:8081/files_image/reation/bcimg2.png)





发表评论 取消回复