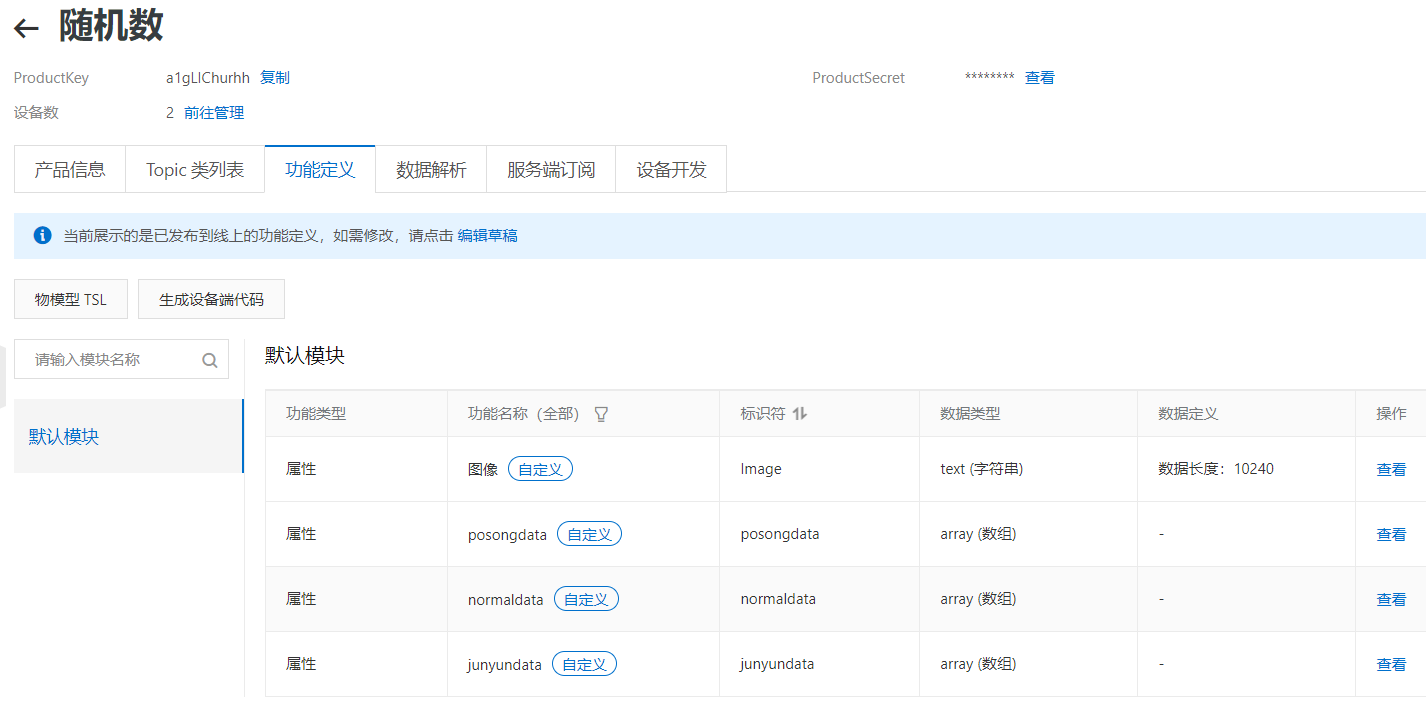
- 注册阿里云账户,然后在阿里云的物联网平台(iot.console.aliyun.com/lk/summary/new)中创建:产品、设备和规则引擎;
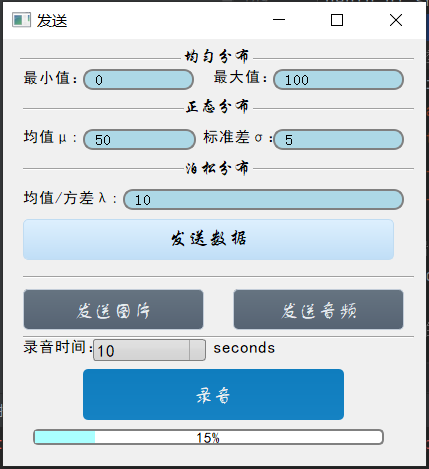
- 在PC机上,按一定的规则(比如随机数、正态分布、泊松分布等)产生一批数据,或者绘制一个图片文件。
- 将上述数据传输到阿里云。
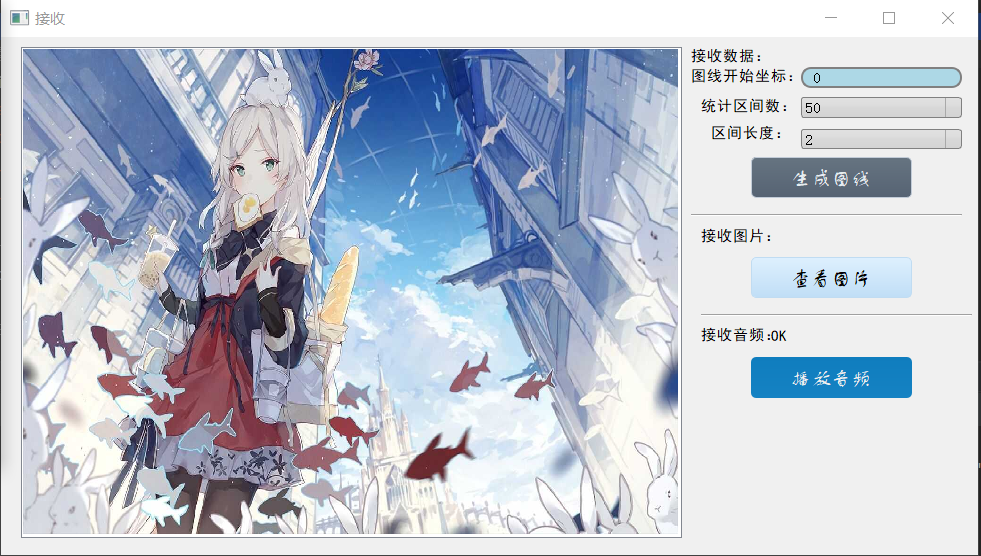
- 从阿里云将数据回传到PC上,由应用程序接收数据并进行图形化显示。
- 设计一个图形用户界面,来实现文本数据或二进制数据(比如图像文件或者音频文件等)的双向传输。
编译环境:PyCharm
运行结果演示:
1. 配置阿里云
创建产品:设定功能模块
设备:
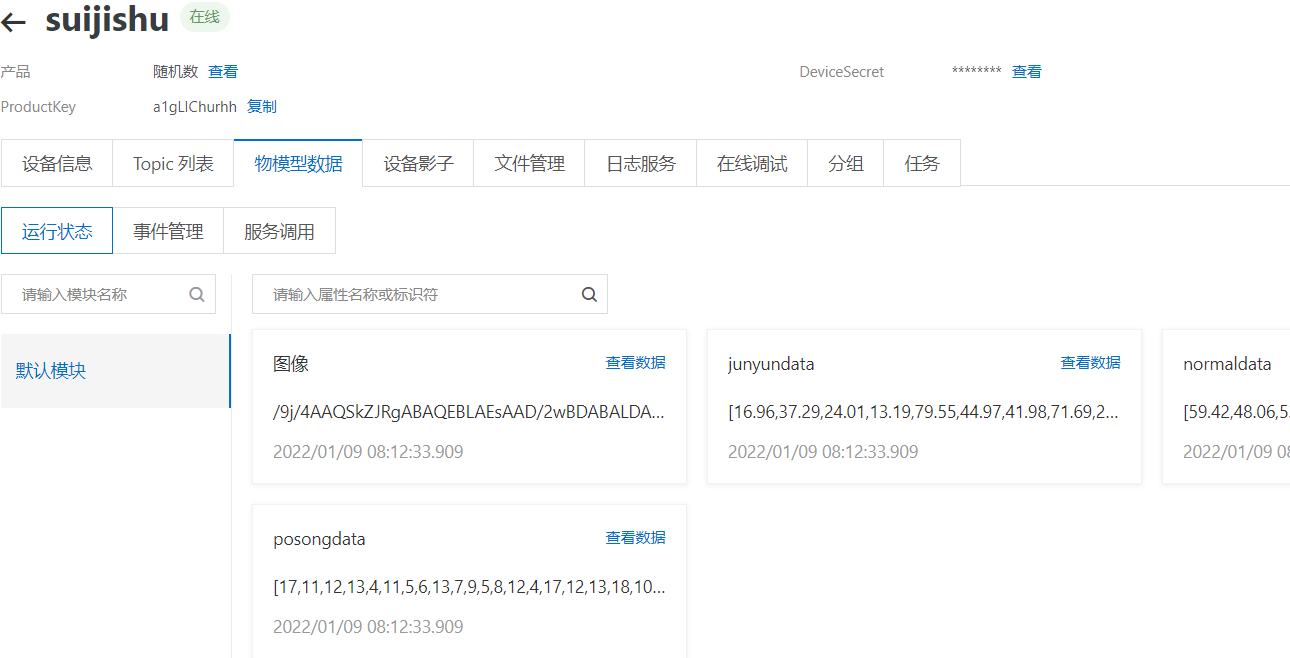 配置规则引擎:
配置规则引擎:
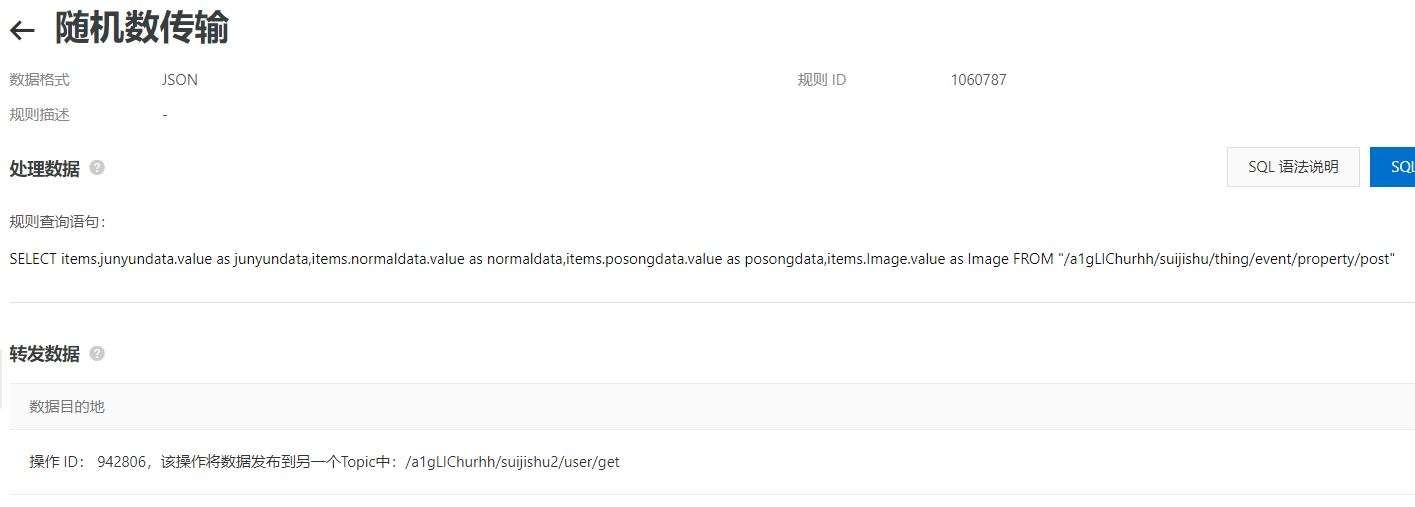
2 . 发送数据代码
主程序——发送数据.py:
import base64
# 图片/音频转base64流
import threading
import time
import numpy as np
# 随机数生成
from PySide2.QtCore import QFile
from PySide2.QtUiTools import QUiLoader
from PySide2.QtWidgets import QApplication, QFileDialog, QMainWindow
import aliyun
# 自己定义
import 录音
# 随机数信息初始化,全局变量
data_random = [0]
data_normal = [0]
data_posong = [0]
class UI:
def __init__(self):
# 从文件中加载UI定义
qfile_Server = QFile("send.ui")
qfile_Server.open(QFile.ReadOnly)
qfile_Server.close()
# 从 UI 定义中动态 创建一个相应的窗口对象
self.ui = QUiLoader().load(qfile_Server)
self.ui.senddata.clicked.connect(self.senddata)
self.ui.sendpicture.clicked.connect(self.sendpicture)
self.ui.luying.clicked.connect(self.luying_thread)
self.ui.music.clicked.connect(self.sendmusic)
# 开启录音线程
def luying_thread(self):
thread = threading.Thread(target=self.luying)
thread.setDaemon(True)
thread.start()
# 进行录音,并发送至阿里云
def luying(self):
self.ui.luying.setEnabled(False)
timeluying = self.ui.time.currentText()
thread = threading.Thread(target=lambda: 录音.luying(self, int(timeluying)))
thread.setDaemon(True)
thread.start()
time.sleep(int(timeluying)+1)
f = open('luying.mp3', 'rb')
# base64编码
base64_data = base64.b64encode(f.read())
f.close()
'''注意编码类型问题,byte->string '''
base64_data = base64_data.decode()
aliyun.senddata(data_random, data_normal, data_posong, '', base64_data)
self.ui.luying.setEnabled(True)
# 向阿里云发送随机数数据
def senddata(self):
# 获取UI界面数据
junyunmin = self.ui.min.text()
junyunmax = self.ui.max.text()
zhentaijunzhi = self.ui.zhentaijunzhi.text()
zhentaibiaozhuncha = self.ui.zhentaibiaozhuncha.text()
posong = self.ui.posong.text()
# 生成随机数
global data_random
global data_normal
global data_posong
data_random = [round(np.random.uniform(float(junyunmin), float(junyunmax)), 2) for i in range(512)]
# 均匀分布
data_normal = [round(np.random.normal(float(zhentaijunzhi), float(zhentaibiaozhuncha)), 2) for i in range(512)]
# 正态分布
data_posong = [round(np.random.poisson(float(posong)), 2) for i in range(512)]
# 泊松分布
# 向阿里云发送数据
aliyun.senddata(data_random, data_normal, data_posong, '', '')
# 向阿里云发送图片
def sendpicture(self):
FileDirectory = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(QMainWindow(), "选择文件")
f = open(FileDirectory[0], 'rb')
# base64编码
base64_data = base64.b64encode(f.read())
f.close()
'''注意编码类型问题,byte->string '''
base64_data = base64_data.decode()
aliyun.senddata(data_random, data_normal, data_posong, base64_data, '')
# 向阿里云发送音频
def sendmusic(self):
FileDirectory = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(QMainWindow(), "选择文件")
f = open(FileDirectory[0], 'rb')
# base64编码
base64_data = base64.b64encode(f.read())
f.close()
'''注意编码类型问题,byte->string '''
base64_data = base64_data.decode()
aliyun.senddata(data_random, data_normal, data_posong, '', base64_data)
# 登陆界面
class Denlu:
def __init__(self):
# 从文件中加载UI定义
qfile = QFile("denlu.ui")
qfile.open(QFile.ReadOnly)
qfile.close()
# 从 UI 定义中动态 创建一个相应的窗口对象
self.ui = QUiLoader().load(qfile)
self.ui.acknowledge.clicked.connect(self.acknowledge)
self.ui.delete_2.clicked.connect(self.ui.close)
# 确认按钮程序
def acknowledge(self):
name = self.ui.name.text()
password = self.ui.password.text()
if name == '2537148609' and password == '12345678':
self.state = UI()
self.state.ui.show()
self.ui.close()
elif name == '' or password == '':
self.ui.Error.setText('Error! Do not enter a user name or password')
else:
self.ui.Error.setText('Error! Incorrect user name or password')
app = QApplication([])
denlu = Denlu()
denlu.ui.show()
# 循环执行
app.exec_()辅程序——aliyun.py:
import paho.mqtt.client as mqtt
# mqtt阿里云
import time
# 延时库
import hashlib
# 哈希计算
import hmac
# 密钥认证
# 把我们自己对应的三元组填进去即可
options = {
'productKey': 'productKey',
'deviceName': 'deviceName',
'deviceSecret': 'deviceSecret',
'regionId': 'cn-shanghai'
}
HOST = options['productKey'] + '.iot-as-mqtt.'+options['regionId']+'.aliyuncs.com'
PORT = 1883
PUB_TOPIC = "/sys/" + options['productKey'] + "/" + options['deviceName'] + "/thing/event/property/post"
# The callback for when a PUBLISH message is received from the server.
def on_message(client, userdata, msg):
print(msg.topic+" "+str(msg.payload))
def hmacsha1(key, msg):
return hmac.new(key.encode(), msg.encode(), hashlib.sha1).hexdigest()
def getAliyunIoTClient():
timestamp = str(int(time.time()))
CLIENT_ID = "paho.py|securemode=3,signmethod=hmacsha1,timestamp="+timestamp+"|"
CONTENT_STR_FORMAT = "clientIdpaho.pydeviceName"+options['deviceName']+"productKey"+options['productKey']+"timestamp"+timestamp
# set username/password.
USER_NAME = options['deviceName']+"&"+options['productKey']
PWD = hmacsha1(options['deviceSecret'], CONTENT_STR_FORMAT)
client = mqtt.Client(client_id=CLIENT_ID, clean_session=False)
client.username_pw_set(USER_NAME, PWD)
return client
# 发送数据
def senddata(data_random, data_normal, data_posong, dase64_data, music):
client = getAliyunIoTClient()
client.on_message = on_message
client.connect(HOST, 1883, 300)
# 以json结构发送数据
payload_json = {
'id': int(time.time()),
'params': {
'junyundata': data_random,
'normaldata': data_normal,
'posongdata': data_posong,
'Image': dase64_data,
'music': music,
},
'method': "thing.event.property.post"
}
client.publish(PUB_TOPIC, payload=str(payload_json), qos=1)
client.loop_start()
time.sleep(1)辅程序——录音.py:
import pyaudio
import wave
from pydub import AudioSegment
from tqdm import tqdm
# 启动录音
def record_audio(self, wave_out_path, record_second):
CHUNK = 1024
FORMAT = pyaudio.paInt16
CHANNELS = 2
RATE = 44100
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
stream = p.open(format=FORMAT,
channels=CHANNELS,
rate=RATE,
input=True,
frames_per_buffer=CHUNK)
wf = wave.open(wave_out_path, 'wb')
wf.setnchannels(CHANNELS)
wf.setsampwidth(p.get_sample_size(FORMAT))
wf.setframerate(RATE)
print("* recording")
for i in tqdm(range(0, int(RATE / CHUNK * record_second))):
self.ui.jindutiao.setValue(round(float(i)/int(RATE / CHUNK * record_second)*100, 0))
data = stream.read(CHUNK)
wf.writeframes(data)
print("* done recording")
self.ui.jindutiao.setValue(0)
stream.stop_stream()
stream.close()
p.terminate()
wf.close()
# 录音wav转MP3
def luying(self,time):
AudioSegment.converter ='D://ffmpeg-4.4.1-essentials_build//bin//ffmpeg.exe'
record_audio(self, "luying.wav", record_second=time)
song = AudioSegment.from_wav("luying.wav")
song.export("luying.mp3")3. 接收数据代码
主程序——接收数据.py:
import base64
# 图片/音频转base64流
import threading
# 多线程
from PySide2.QtCore import QFile
from PySide2.QtGui import QPixmap
# 加载图像
from PySide2.QtUiTools import QUiLoader
from PySide2.QtWidgets import QApplication, QGraphicsScene, QGraphicsPixmapItem
# 加载图像
from linkkit import linkkit
# 阿里云aliyun-iot-linkkit库
import time
# python延时库
import json
# 发送json数据
import 折线图
# 自己定义
from selenium import webdriver
# 用浏览器打开html
import os
# 三元组信息
ProductKey = "ProductKey"
# 阿里云物联网ProductKey
DeviceName = "DeviceName"
# 阿里云物联网DeviceName
DeviceSecret = "DeviceSecret"
# 阿里云物联网DeviceSecret
# 随机数信息初始化,全局变量
data_random = [0]
data_normal = [0]
data_posong = [0]
class UI:
def __init__(self):
# 从文件中加载UI定义
qfile_Server = QFile("receive.ui")
qfile_Server.open(QFile.ReadOnly)
qfile_Server.close()
# 从 UI 定义中动态 创建一个相应的窗口对象
self.ui = QUiLoader().load(qfile_Server)
self.ui.tuxian.clicked.connect(lambda: self.receivedata(data_random, data_normal, data_posong))
self.ui.picture.clicked.connect(self.showImage)
self.ui.music.clicked.connect(self.openmusic)
# 播放音乐
def openmusic(self):
self.ui.isOK1.setText('')
thread = threading.Thread(target=lambda: os.system('yuying.mp3'))
thread.setDaemon(True)
thread.start()
# 接收随机数数据并生成折线图
def receivedata(self, data_random, data_normal, data_posong):
self.ui.isOK2.setText('')
self.ui.music.setEnabled(False)
print(data_random, data_normal, data_posong, sep='n')
start = self.ui.start.text()
number_of_interval = self.ui.number_of_interval.currentText()
length = self.ui.length.currentText()
折线图.getzhexian(data_random, data_normal, data_posong, float(start), int(number_of_interval), int(length))
# 设置数据守护线程
thread1 = threading.Thread(target=self.keepdriver)
thread1.setDaemon(True)
thread1.start()
# 使html在游览器上循环出现
def keepdriver(self):
driver = webdriver.Edge()
while (True):
driver.get('file://C://Users//hp//Desktop//Python//云接入课设//Lib//zhexian.html')
driver.maximize_window()
time.sleep(1000)
# 展示图片
def showImage(self):
self.ui.isOK.setText('')
self.ui.music.setEnabled(False)
# 将词云图加载到UI.ui界面
self.ui.GraphView.scene_img = QGraphicsScene()
self.imgShow = QPixmap()
self.imgShow.load('mypicture.png')
self.imgShowItem = QGraphicsPixmapItem()
self.imgShowItem.setPixmap(QPixmap(self.imgShow))
self.ui.GraphView.scene_img.addItem(self.imgShowItem)
self.ui.GraphView.setScene(self.ui.GraphView.scene_img)
self.ui.GraphView.fitInView(QGraphicsPixmapItem(QPixmap(self.imgShow)))
# 接收阿里云的数据
def on_topic_message(self, topic, payload, qos, userdata):
# 拿到接收来的数据
data = str(payload)[2:-1]
dataDict = json.loads(data)
global data_random
global data_normal
global data_posong
# 多层解析
data_random = dataDict["junyundata"]
data_normal = dataDict["normaldata"]
data_posong = dataDict["posongdata"]
base64_data = dataDict['Image']
base64_data1 = dataDict['music']
self.ui.music.setEnabled(True)
if base64_data != '':
# 进行base64解码工作 base64->数组
image_decode = base64.b64decode(base64_data)
with open('mypicture.png', 'wb') as f:
f.write(image_decode)
self.ui.isOK.setText('OK')
elif base64_data1 != '':
# 进行base64解码工作 base64->数组
image_decode1 = base64.b64decode(base64_data1)
with open('yuying.mp3', 'wb') as f:
f.write(image_decode1)
self.ui.isOK1.setText('OK')
else:
self.ui.isOK2.setText('OK')
print("OK")
# 订阅Topic
def on_subscribe_topic(mid, granted_qos, userdata):
# 订阅topic
print("on_subscribe_topic mid:%d, granted_qos:%s" %
(mid, str(','.join('%s' % it for it in granted_qos))))
# 登陆界面
class Denlu:
def __init__(self):
# 从文件中加载UI定义
qfile = QFile("denlu.ui")
qfile.open(QFile.ReadOnly)
qfile.close()
# 从 UI 定义中动态 创建一个相应的窗口对象
self.ui = QUiLoader().load(qfile)
self.ui.acknowledge.clicked.connect(self.acknowledge)
self.ui.delete_2.clicked.connect(self.ui.close)
# 确认按钮程序
def acknowledge(self):
name = self.ui.name.text()
password = self.ui.password.text()
if name == '2537148609' and password == '12345678':
self.state = UI()
self.state.ui.show()
# 注册当接受到云端发送的数据的时候的方法
lk.on_topic_message = self.state.on_topic_message
self.ui.close()
elif name == '' or password == '':
self.ui.Error.setText('Error! Do not enter a user name or password')
else:
self.ui.Error.setText('Error! Incorrect user name or password')
app = QApplication([])
denlu = Denlu()
denlu.ui.show()
# 初始化连接参数,阿里云三码设置
lk = linkkit.LinkKit(
host_name="cn-shanghai",
# 当前设备服务器(上海-华东二)
product_key=ProductKey,
# 当前设备product_key
device_name=DeviceName,
# 当前设备device_name
device_secret=DeviceSecret)
# 当前设备device_secret
# //注册云端订阅的方法
lk.on_subscribe_topic = on_subscribe_topic
# 连接阿里云的函数(异步调用)
lk.connect_async()
time.sleep(1)
# 延时设置
# //订阅这个topic,不需要写prodect_key和device_name
rc, mid = lk.subscribe_topic(lk.to_full_topic("user/get"))
# 循环执行
app.exec_()辅程序——折线图.py:
import pyecharts.options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Line
# 折线图
# 用pyecharts生成图线html
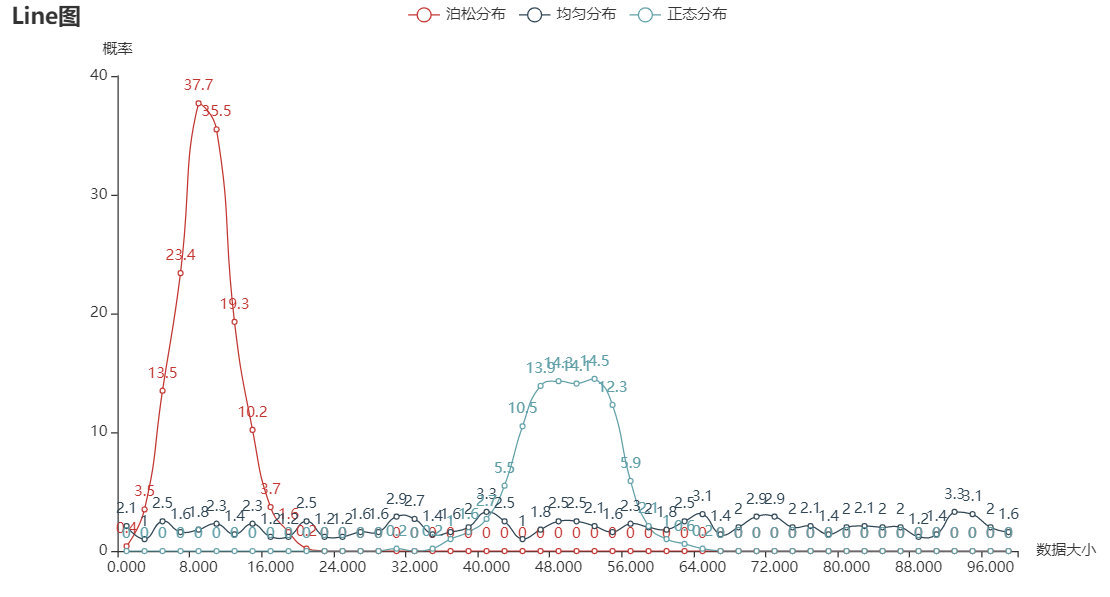
def zhexian(data_normal, data_random, data_posong):
x1=[];y1=[];y2=[];y3=[]
for i in data_normal:
[left, right] = i[0].split('~')
x1.append(left)
y1.append(round(i[1], 1))
for i in data_random:
y2.append(round(i[1], 1))
for i in data_posong:
y3.append(round(i[1], 1))
line = (
Line()
.add_xaxis(xaxis_data=x1)
.add_yaxis(series_name="泊松分布", y_axis=y3, is_smooth=True)
.add_yaxis(series_name="均匀分布", y_axis=y2, is_smooth=True)
.add_yaxis(series_name="正态分布", y_axis=y1, is_smooth=True)
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Line图"), yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name='概率'),
xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name='数据大小'))
).render('zhexian.html')
# 分区切片
def interval_statistics(data, intervals):
result = []
if len(data) == 0:
return
for num in data:
for interval in intervals:
lr = tuple(interval.split('~'))
left, right = float(lr[0]), float(lr[1])
if left <= num <= right:
intervals[interval] += 1
for key, value in intervals.items():
result.append([key, value * 100.000 / len(data)])
return result
# 数据分区切片,计算频率
def getzhexian(data_random, data_normal, data_posong, start, number_of_interval, length):
start = start
# 区间左端点
number_of_interval = number_of_interval
# 区间个数
length = length
# 区间长度
intervals = {'{:.3f}~{:.3f}'.format(length*x+start, length*(x+1)+start): 0 for x in range(number_of_interval)}
# 生成区间
data_random = interval_statistics(data_random, intervals)
intervals = {'{:.3f}~{:.3f}'.format(length * x + start, length * (x + 1) + start): 0 for x in range(number_of_interval)}
data_normal = interval_statistics(data_normal, intervals)
intervals = {'{:.3f}~{:.3f}'.format(length * x + start, length * (x + 1) + start): 0 for x in range(number_of_interval)}
data_posong = interval_statistics(data_posong, intervals)
zhexian(data_normal, data_random, data_posong)最后
以上就是英勇紫菜最近收集整理的关于Python_阿里云物联网_数据/图像/音频传输的全部内容,更多相关Python_阿里云物联网_数据/图像/音频传输内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复