写在前面
有关于本文目的的说明和一些代码的链接已经放在系列1中,可以进我的主页进行查看。
废话不多说,开淦。
欢迎来到卡拉自动驾驶汽车教程系列的第二部分。在本教程中,我们将向你介绍Carla的Python API。
首先,在Carla中有几种类型的对象。首先,你当然有“世界”。这是你的环境。然后,你有这个世界的演员。演员是你的车,你车上的传感器,行人,等等。最后,我们有了蓝图。蓝图是参与者的属性。
有了这些信息,让我们开始编写一些实际的代码。首先,让我们做一辆车,生成并简单地向前行驶,然后我们想要看到信息从一个常规RGB摄像头,我们将放置在汽车的引擎盖。
在前几行代码中,我将复制并粘贴示例目录中的其他脚本,我也将在示例目录中编写这段代码。
import glob
import os
import sys
try:
sys.path.append(glob.glob('../carla/dist/carla-*%d.%d-%s.egg' % (
sys.version_info.major,
sys.version_info.minor,
'win-amd64' if os.name == 'nt' else 'linux-x86_64'))[0])
except IndexError:
pass
import carla
上面的代码非常简单,除了try/except部分。这里要做的就是找到卡拉蛋文件,这就是我们用来制作卡拉包的文件。为了导入carla,我们需要找到它,这也是为什么我们现在把文件放到example目录中。您还可以通过Python站点包移动所需的Carla文件并以这种方式导入。
接下来,我们将做更多的导入:
import random
import time
import numpy as np
import cv2
如果你需要,你可以安装numpy和cv2:
pip install opencv-python
pip install numpy
我们要立即处理的第一件事是actor列表,并在完成时清理它们。回想一下,我们同时拥有客户机和服务器。当我们开始在服务器上运行客户机时,我们在服务器上创建actor。如果我们只是退出,而不清理,我们的actors仍将在服务器上。
actor_list = []
try:
finally:
print('destroying actors')
for actor in actor_list:
actor.destroy()
print('done.')
在这里,我们将在try/finally中封装主要代码块。我们将把所有的逻辑和角色创建放在try中,然后最后一点将为我们清理它。
接下来,回忆一下我们在卡拉有三个主要的“东西”:世界、蓝图和演员。首先,我们将连接到服务器,获取世界,然后访问蓝图。
actor_list = []
try:
client = carla.Client('localhost', 2000)
client.set_timeout(2.0)
world = client.get_world()
blueprint_library = world.get_blueprint_library()
注意,您需要运行carla (shell或.exe)才能进行连接。
现在我们有了蓝图,我们可以过滤一些东西。例如:
bp = blueprint_library.filter('model3')[0]
这将为我们提供特斯拉model 3的默认蓝图。现在我们有了蓝图,我们可以造出这辆车,但是在哪里呢?卡拉拥有大约200个衍生点,所以我们可以随机选择其中一个:
spawn_point = random.choice(world.get_map().get_spawn_points())
现在我们可以衍生汽车:
vehicle = world.spawn_actor(bp, spawn_point)
我们还可以通过以下方式控制汽车:
vehicle.apply_control(carla.VehicleControl(throttle=1.0, steer=0.0))
最后,让我们不要忘记将这个车辆添加到我们需要跟踪和清理的角色列表中:
actor_list.append(vehicle)
很好,我们有一辆车,我们可以开着它跑。让我们运行5秒钟,然后清理:
time.sleep(5)
所以完整的代码到这一点:
import glob
import os
import sys
try:
sys.path.append(glob.glob('../carla/dist/carla-*%d.%d-%s.egg' % (
sys.version_info.major,
sys.version_info.minor,
'win-amd64' if os.name == 'nt' else 'linux-x86_64'))[0])
except IndexError:
pass
import carla
import random
import time
import numpy as np
import cv2
im_width = 640
im_height = 480
def process_img(image):
i = np.array(image.raw_data)
i2 = i.reshape((im_height, im_width, 4))
i3 = i2[:, :, :3]
cv2.imshow("", i3)
cv2.waitKey(1)
return i3/255.0
actor_list = []
try:
client = carla.Client('localhost', 2000)
client.set_timeout(2.0)
world = client.get_world()
blueprint_library = world.get_blueprint_library()
bp = blueprint_library.filter('model3')[0]
print(bp)
spawn_point = random.choice(world.get_map().get_spawn_points())
vehicle = world.spawn_actor(bp, spawn_point)
vehicle.apply_control(carla.VehicleControl(throttle=1.0, steer=0.0))
actor_list.append(vehicle)
# sleep for 5 seconds, then finish:
time.sleep(5)
finally:
print('destroying actors')
for actor in actor_list:
actor.destroy()
print('done.')
现在,你可能很难在5秒内找到你的车,但你可以去服务器位可视化卡拉环境,用鼠标向下看,然后开始放大。你应该有一个俯瞰环境,像:
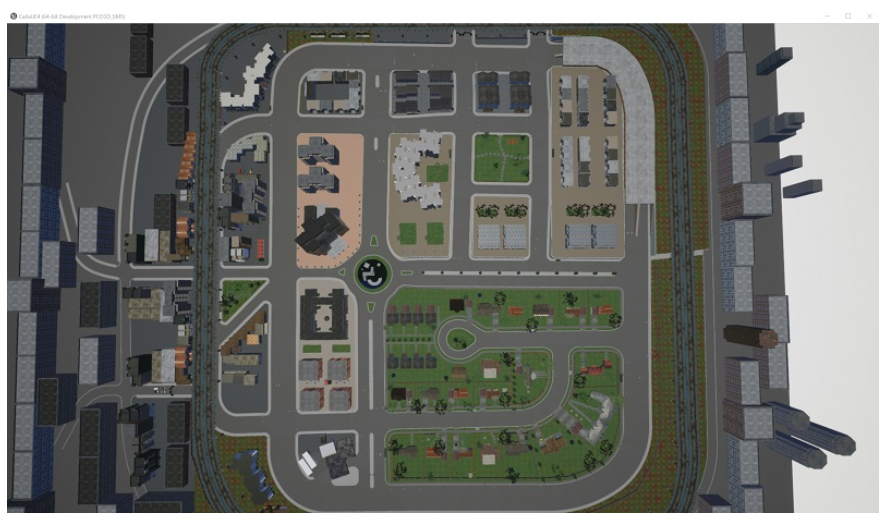
我们可以运行我们的脚本到目前为止,从上面看,我们可能可以看到它笔直地行驶:

很难看到,但当它移动时,就很容易被发现。注意,汽车可能会在隧道中产生。如果您没有看到您的车辆,只需再次运行该脚本。
很好,到目前为止一切正常。我们接下来想要的是在车上安装一个摄像头,然后弄清楚如何访问这些数据。这个引擎盖摄像头将理想地作为我们的主要传感器。我们可以稍后合并其他传感器也,但发动机罩摄像头似乎是一个好的开始。
您可以了解更多关于各种各样的传感器可用和如何与他们一起工作在这里:卡拉传感器。现在,我只展示如何与RGB相机:
在脚本的顶部,让我们设置几个常量:
IM_WIDTH = 640
IM_HEIGHT = 480
现在,我们为传感器加载蓝图并设置一些属性:
# https://carla.readthedocs.io/en/latest/cameras_and_sensors
# get the blueprint for this sensor
blueprint = blueprint_library.find('sensor.camera.rgb')
# change the dimensions of the image
blueprint.set_attribute('image_size_x', f'{IM_WIDTH}')
blueprint.set_attribute('image_size_y', f'{IM_HEIGHT}')
blueprint.set_attribute('fov', '110')
接下来,我们需要将其添加到汽车中。首先,我们将从一个相对位置调整传感器,然后我们将把它连接到我们的汽车上。假设传感器,从相对位置(车)出发,向前2.5向上7.7。我不知道这个单位是米还是什么。您可以根据您选择的车辆随意调整这些值,或者使用我的。
# Adjust sensor relative to vehicle
spawn_point = carla.Transform(carla.Location(x=2.5, z=0.7))
# spawn the sensor and attach to vehicle.
sensor = world.spawn_actor(blueprint, spawn_point, attach_to=vehicle)
现在我们想把这个传感器添加到我们的actor列表中:
# add sensor to list of actors
actor_list.append(sensor)
最后,我们想用这个传感器做点什么。我们想要从中获得图像,所以我们想要倾听。
为了处理我们从传感器获得的数据,我们可以使用lambda函数:
sensor.listen(lambda data: process_img(data))
在本例中,我们将从传感器获取数据,并将其通过一个名为process_img的函数传递。这还不存在,所以让我们做:
def process_img(image):
i = np.array(image.raw_data)
# convert to an array
i2 = i.reshape((IM_HEIGHT, IM_WIDTH, 4))
# was flattened, so we're going to shape it.
i3 = i2[:, :, :3]
# remove the alpha (basically, remove the 4th index
of every pixel. Converting RGBA to RGB)
cv2.imshow("", i3)
# show it.
cv2.waitKey(1)
return i3/255.0
# normalize
完整的代码现在是:
import glob
import os
import sys
try:
sys.path.append(glob.glob('../carla/dist/carla-*%d.%d-%s.egg' % (
sys.version_info.major,
sys.version_info.minor,
'win-amd64' if os.name == 'nt' else 'linux-x86_64'))[0])
except IndexError:
pass
import carla
import random
import time
import numpy as np
import cv2
IM_WIDTH = 640
IM_HEIGHT = 480
def process_img(image):
i = np.array(image.raw_data)
i2 = i.reshape((IM_HEIGHT, IM_WIDTH, 4))
i3 = i2[:, :, :3]
cv2.imshow("", i3)
cv2.waitKey(1)
return i3/255.0
actor_list = []
try:
client = carla.Client('localhost', 2000)
client.set_timeout(2.0)
world = client.get_world()
blueprint_library = world.get_blueprint_library()
bp = blueprint_library.filter('model3')[0]
print(bp)
spawn_point = random.choice(world.get_map().get_spawn_points())
vehicle = world.spawn_actor(bp, spawn_point)
vehicle.apply_control(carla.VehicleControl(throttle=1.0, steer=0.0))
# vehicle.set_autopilot(True)
# if you just wanted some NPCs to drive.
actor_list.append(vehicle)
# https://carla.readthedocs.io/en/latest/cameras_and_sensors
# get the blueprint for this sensor
blueprint = blueprint_library.find('sensor.camera.rgb')
# change the dimensions of the image
blueprint.set_attribute('image_size_x', f'{IM_WIDTH}')
blueprint.set_attribute('image_size_y', f'{IM_HEIGHT}')
blueprint.set_attribute('fov', '110')
# Adjust sensor relative to vehicle
spawn_point = carla.Transform(carla.Location(x=2.5, z=0.7))
# spawn the sensor and attach to vehicle.
sensor = world.spawn_actor(blueprint, spawn_point, attach_to=vehicle)
# add sensor to list of actors
actor_list.append(sensor)
# do something with this sensor
sensor.listen(lambda data: process_img(data))
time.sleep(5)
finally:
print('destroying actors')
for actor in actor_list:
actor.destroy()
print('done.')
这应该会弹出一个新窗口来显示相机传感器:
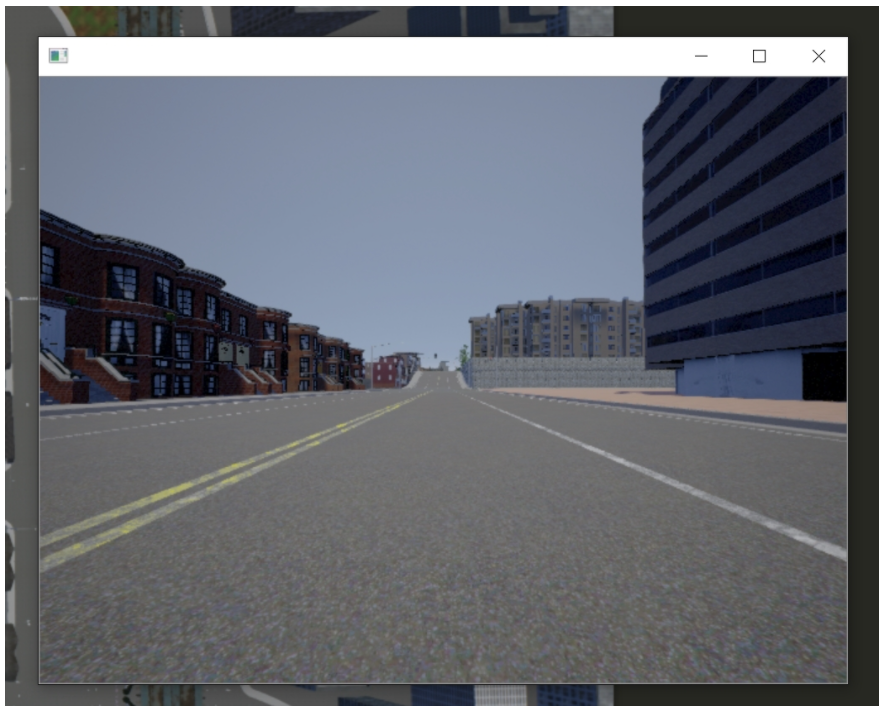
太棒了!现在,让我们在这里添加一些强化学习!应该很简单,对吧?
最后
以上就是缓慢冬天最近收集整理的关于基于carla和python的自动驾驶仿真系列2的全部内容,更多相关基于carla和python内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复