gPTP(Generalized PTP )由IEEE 802.1AS规范定义;
其与PTP之间的主要联系和区别见下表:
IEEE 1588-2008 被称为PTPV2
IEEE 1588-2019 被称为PTPV2.1
目前PTPV2用的比较广泛;
gPTP主要是IEEE TSN(时间敏感网络)工作组定义的规范族中的一个组成部分;
TSN工作组是原先的AVB(Audio-Video Bridging)工作组;
| Features | IEEE 1588-2002 | IEEE 1588-2008 (v2) | IEEE 802.1AS-2011 | IEEE 802.1AS-2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residence time correction | No transparent clocks – e.g. switches are not time-aware | Transparent clocks – switch adjusts packet timestamps with residence time | ||
| Hardware timestamping | one step only | one and two-step | two-step only | one and two-step |
| Delay calculation mechanism | path delay | peer delay or path delay | peer delay | |
| Bridge compatibility | time-aware and non-time-aware | time-aware only | ||
| Protocols supported | layer 2-4, IPv4 multicast only | layer 2-4, IPv4 or IPv6, multicast or unicast | layer 2 only | |
| GM time transmit interval | up to 1/s | up to 10/s | ||
| Grandmaster redundancy | Multiple domains supported simultaneously (different subnets) | Single domain (single active grandmaster) | Redundant GMs in “hot-Standby” | |
| Syntonization | optional | logically required | ||
| Asymmetry correction | none | optional | ||
| Conformance | not specified | specified | ||
| Min End to End Sync Accuracy | < 1 us | < 1 us for <= 7 hops | <1 us for <= 7 hops FFO +/- 100 ppm; RR: +/-0.1 ppm Jitter <2ns/60s; Granularity: <40ns | |
由于PTPv2定义了太多的特性选项,那么多个设备之间的互操作性变的较差;gPTP对PTPv2进行了简化,固定了特性选项的选择,相当于PTPv2的一个特定profile。
gPTP 消息不再支持在UDPoverIPv4/IPV6的等L3/L4的承载,只支持在Mac层的承载。
gPTP还可以用于无线网络。
PTP和gPTP的网络结构如下:
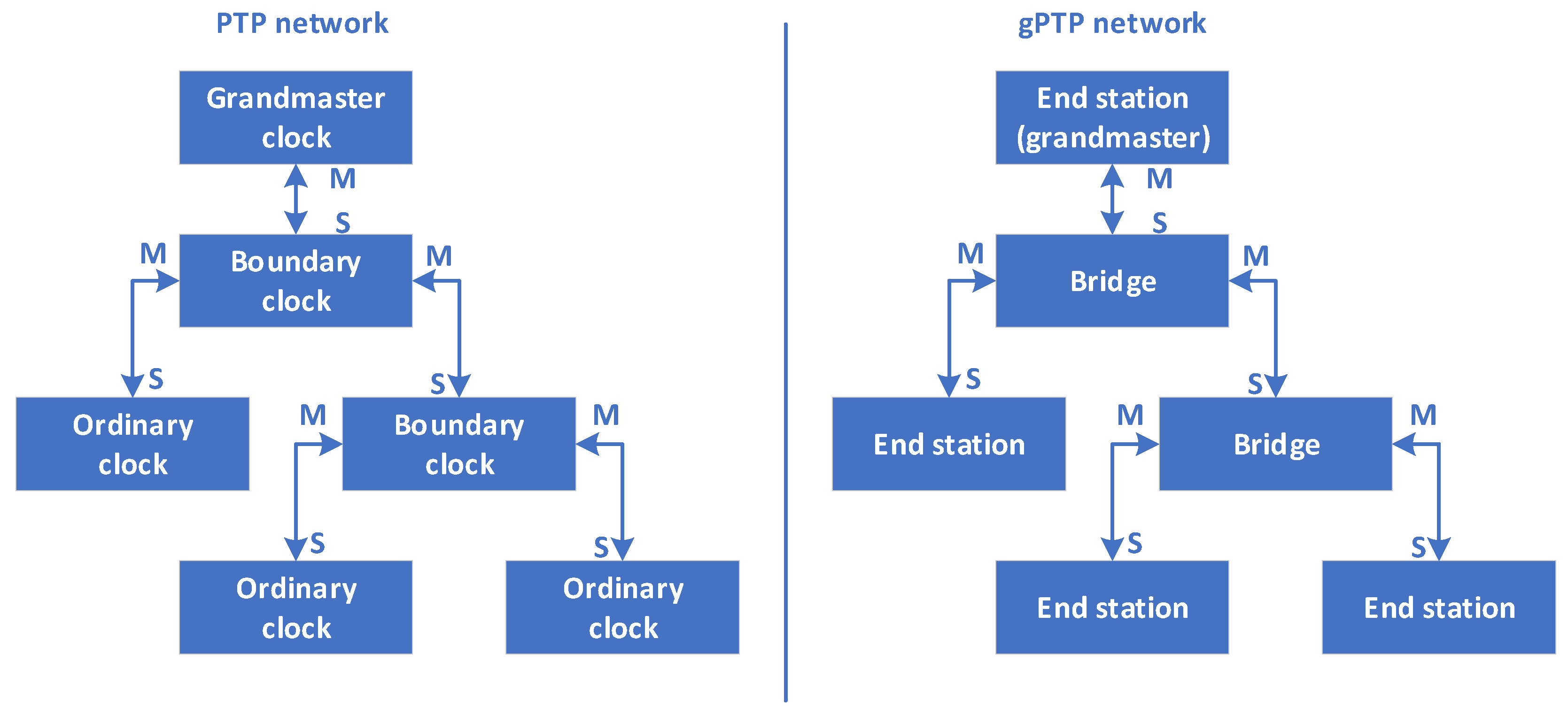
gPTP只支持两种节点类型:PTP End Instances(End station) 和 PTP Relay Instances(Bridge)
PTP支持Ordinary clock,Boundary Clock,end-to-end Transparent Clocks, 和 P2P Transparent Clocks;
PTP End Instances相当于PTP的Ordinary clock;
PTP Relay Instances相当于PTP的Boundary Clock,或P2P Transparent Clocks(就同步方式而言)
gPTP的instances之间采用PeertoPeer的方式测量delay:
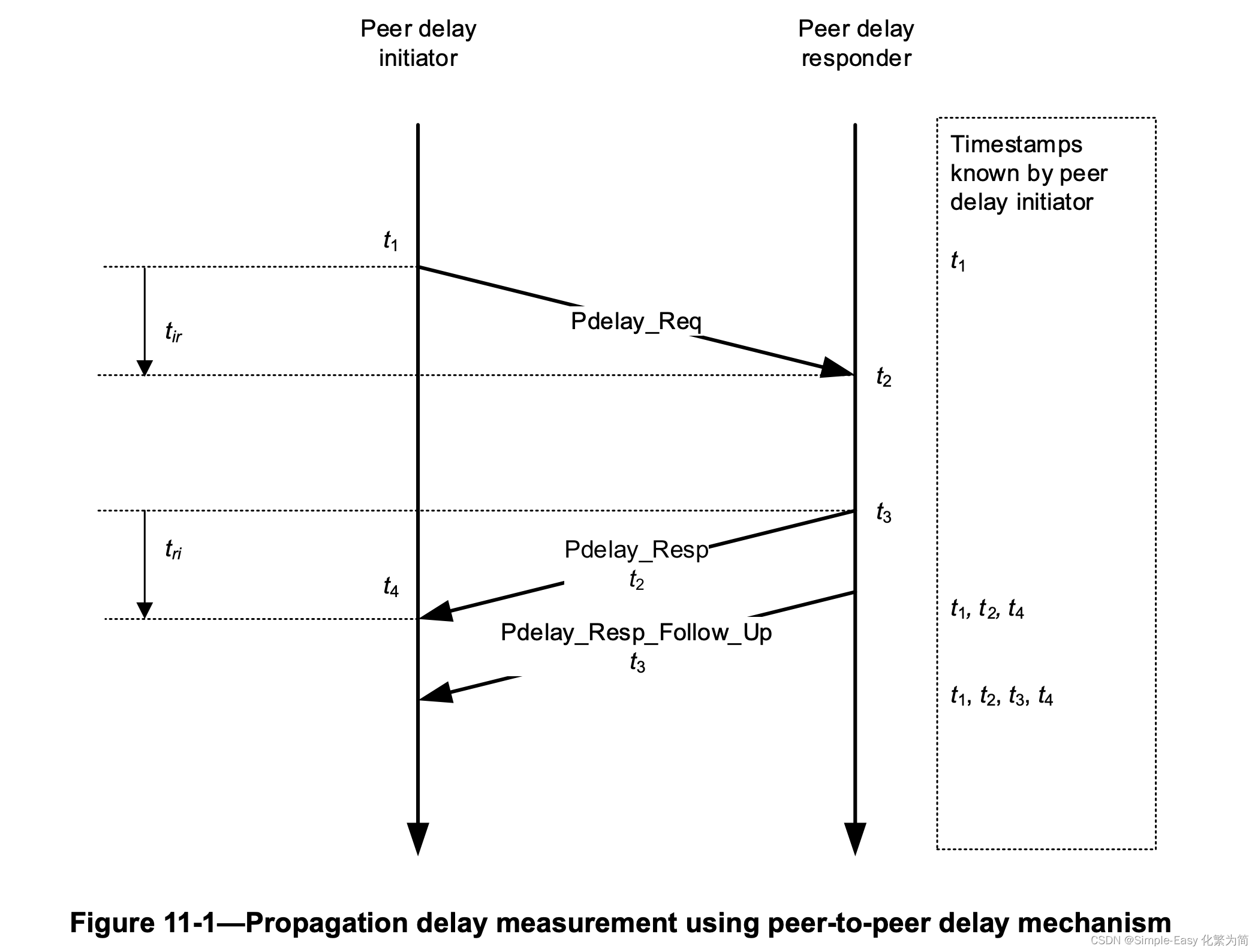
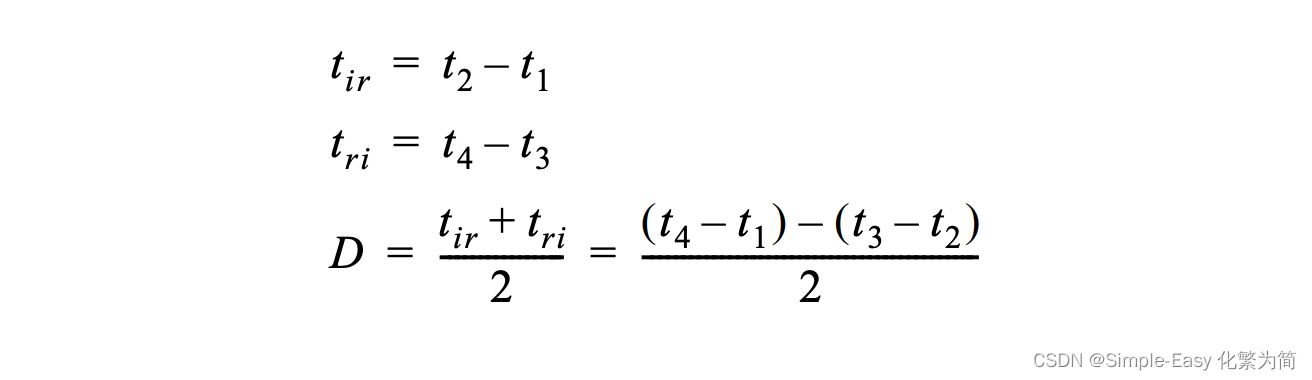
D是计算的平均路径时延;假设两个方向的时延相等;
D有两个可能的误差源:
1 t1和t4在initiator这一侧计算,是基于initiator本地时钟,而t2和t3在responder这一侧计算,是基于responder的本地时钟,两侧的时钟存在频率偏差,会导致计算误差;因此需要在一侧进行进行时钟偏差的计算校正。校准方法如下:
neighborRateRatio:在某个端口上的相连的邻居节点的时钟频率的比值和本地时钟频率的比值;
计算公式:
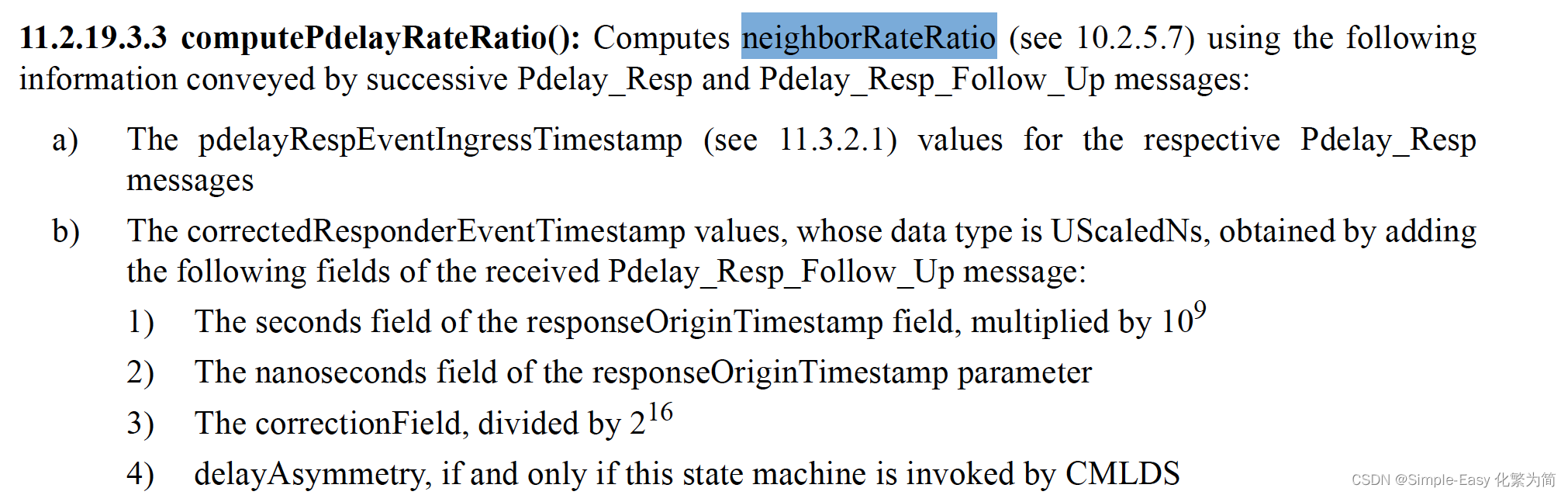
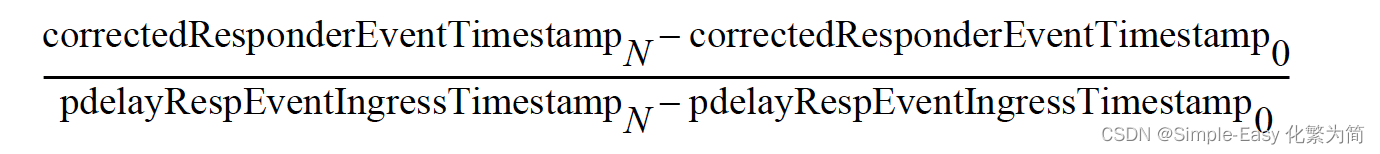
基本思想就是来自Resonder的t3的时间戳累积一段时间,本地的t4时间戳累积一段时间,然后两个时间比可以作为频率的比值的估计值;
meanLinkDelay:某个端口上的相连的邻居节点和本节点之间的路径时延(以邻居节点的时钟为基准表示);
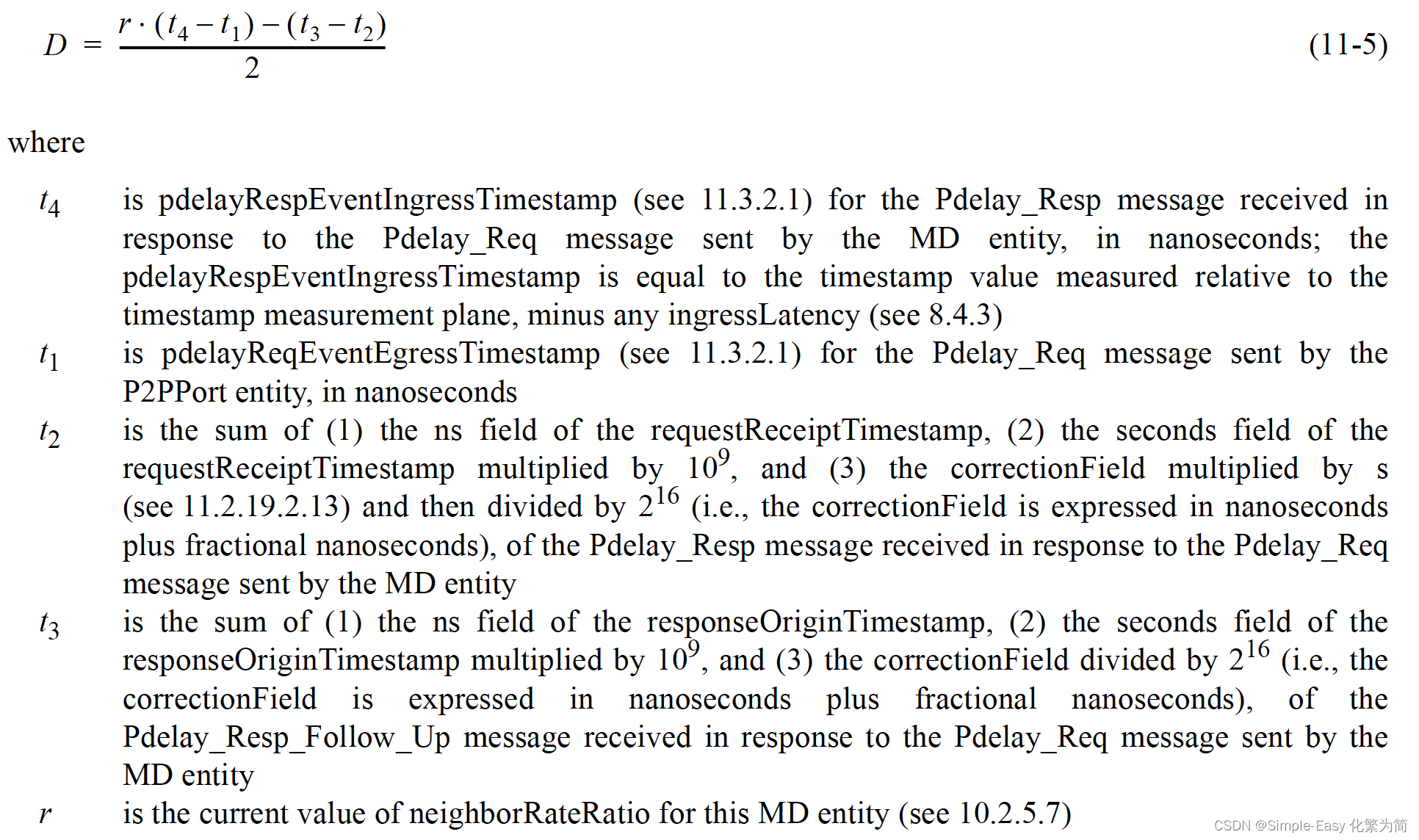
r是neighborRateRatio,所以 D的计算是按照responder的时钟频率为基准的。
2 t1/t2/t3/t4的测量分辨率带来的误差,比如时间戳的测量分辨率是40ns;这个误差可以通过多次测量结果的平均值来减小;具体方法如下:
前M次测量的计算公式:

M次以后的计算公式:


gPTP的时间同步信息的传输方式和PTP一样,都是通过Sync and Follow_Up消息来传递的;
也分为一步(右半边图)和两步(左半边图);
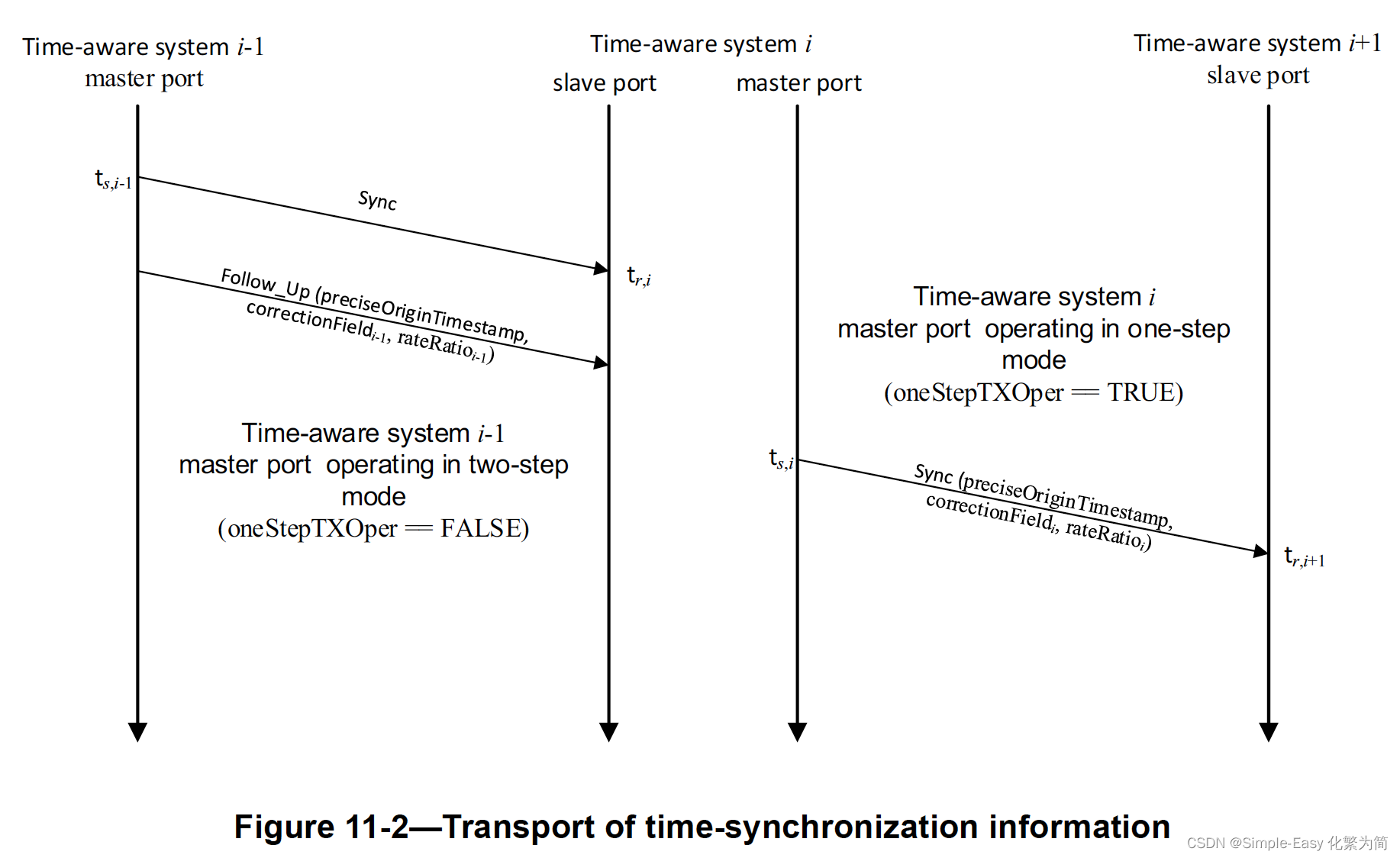
- 可以注意到preciseOrigin Timestamp在两级传递的过程中不变,这个值来自于grandmaster时钟,在穿越整个网络的时候保持不变;
会携带来自于grandmaster的preciseOrigin Timestamp和发送Sync时候的本地时间
的差值;
- 对于time-aware system i-1,把
和preciseOrigin Timestamp相加,可以得到发送sync消息的本地时间:
会携带grandmaster clock的freq和local clock的freq比值;方便下一级的节点把路径时延换算为以grandmaster clock为基准的值;
所以对于上图中的time-aware system i 这种bridge类型的设备,其行为和PTPv2中定义的PTP的透明时钟是在处理sync消息时候是等价的;都是在correctionField附加了路径时延和residence time,而且不改变Sync消息里面的preciseOrigin Timestamp。
注意:time-aware system i 在计算新的sync消息的correctionField的值时候,需要使用grandmaster时钟为基准的meanLinkDelay和residence time;
- time-aware system i 的meanLinkDelay是按照time-aware system i-1时钟为基准计算的值,所以可以乘以
得到以grandmaster时钟为基准的值;
- time-aware system i 的residence time同样是用
的值,再乘以
得到以grandmaster时钟为基准的值;
- meanLinkDelay+residence就是以grandmaster时钟为基准的correctionField;
- preciseOrigin Timestamp本身就是以grandmaster时钟为基准的;
所以gPTP网络可以理解为PTPv2的 Ordinary clock和 P2P Transparent Clocks组成,同时增强了一下,针对delay的两种误差源进行了修正;
A bridge or an end station that meets the requirements of IEEE 802.1AS is referred to as a time-sensitive system.
All nodes in the network (bridges and end stations) must be such time-sensitive systems.
gPTP is a so-called PTP profile
gPTP is also specified for wireless networks
最后
以上就是光亮月光最近收集整理的关于IEEE1588v2解析(7)gPTP协议和PTP的关系的全部内容,更多相关IEEE1588v2解析(7)gPTP协议和PTP内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复