LMI例子,考虑下面的问题,找到满足P>I的对称矩阵P,使得
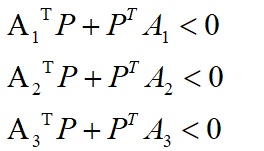
其中
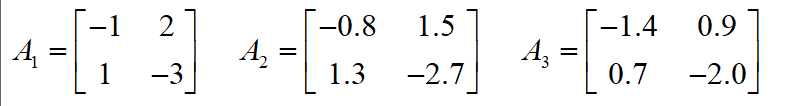
%这个问题是二次稳定性问题中提取出来的,首先确定已知的LMI,再调用函数feasp
%常数
A1 = [-1 2;1 -3];
A2 = [-0.8 1.5;1.3 -2.7];
A3 = [-1.4 0.9;0.7 -2.0];
%初始化LMI
setlmis([]);
% 定义变量
P = lmivar(1,[2,1]);
% 添加项
lmiterm([1 1 1 P],1,A1,‘s’);
lmiterm([2 1 1 P],1,A2,‘s’);
lmiterm([3 1 1 P],1,A3,‘s’);
lmiterm([-4 1 1 P],1,1);%注意还有一个I<P
lmiterm([4 1 1 0],1);
% 获取LMI系统描述
lmisys = getlmis;
[tmin,xfeas] = feasp(lmisys) %options 参数可以自己设置,也可以默认
运行结果如下:
Solver for LMI feasibility problems L(x) < R(x)
This solver minimizes t subject to L(x) < R(x) + t*I
The best value of t should be negative for feasibility
Iteration : Best value of t so far
1
0.972718
2
0.870460
3
-3.136305
Result: best value of t: -3.136305
f-radius saturation: 0.000% of R = 1.00e+09
tmin =
-3.1363
xfeas =
270.8553
126.3999
155.1336
从运行结果看tmin<0,表明LMI系统是可行的。下面使用dec2mat来得到可行矩阵变量的值:
pmat = dec2mat(lmisys,xfeas,P)
运行结果如下:
pmat =
270.8553
126.3999
126.3999
155.1336
最后
以上就是疯狂树叶最近收集整理的关于matlab中LMI工具箱函数feasp的用法的全部内容,更多相关matlab中LMI工具箱函数feasp内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复