UVM-FLM-FIFO
在基本TLM通信put示例中,producer和consumer在同一个进程当中,consumer仅在put()方法调用时才处于活动状态。
在许多情况下,可能需要不同速率的组件(components)独立运行,UVM提供了uvm_tlm_fifo通道以支持此类通信。
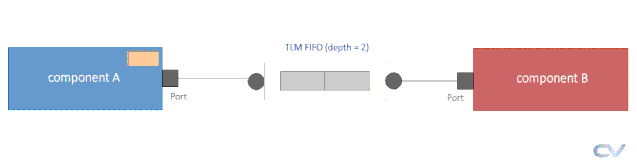
uvm_tlm_fifo,顾名思义就是具有所有TLM接口方法的FIFO,producer可以将transaction放入uvm_tlm_fifo,consumer独立地从fifo获取transaction
在上图中componentA将一个transaction放到fifo中(put操作,如果fifo满会被block),componentB从fifo中获取一个transaction(get操作,如果fifo空会被block)。
两次连续的get()操作会获得不同的transaction,而两次连续的peek()操作会获得相同的transaction,因为peek()操作只是复制fifo中的transaction,并不会移除从fifo中移除。
下面是一个uvm_tlm_fifo的实例
Packet (transaction)继承自uvm_object,其在组件之间传输
class Packet extends uvm_object;
randbit[7:0] addr;
randbit[7:0] data;
`uvm_object_utils_begin(Packet)
`uvm_field_int(addr, UVM_ALL_ON)
`uvm_field_int(data, UVM_ALL_ON)
`uvm_object_utils_end
function new(string name = "Packet");
super.new(name);
endfunction
endclass
然后创建componentA,定义put_port,实现transaction的生成、约束和发送
class componentA extends uvm_component;
`uvm_component_utils (componentA)
uvm_blocking_put_port #(Packet) m_put_port;
int m_num_tx = 2;
function new (string name = "componentA", uvm_component parent= null);
super.new (name, parent);
endfunction
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
m_put_port = new ("m_put_port", this);
endfunction
virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
phase.raise_objection(this);
repeat (m_num_tx) begin
Packet pkt = Packet::type_id::create ("pkt");
assert(pkt.randomize ());
#50;
//Print the packet to be displayed in log
`uvm_info ("COMPA", "Packetsent to CompB", UVM_LOW)
pkt.print (uvm_default_line_printer);
//Call the TLM put() method of put_port class and pass packet as argument
m_put_port.put(pkt);
end
phase.drop_objection(this);
endtask
endclass
然后创建componentB,定义get_port,实现transaction的接收。可以看出,uvm_tlm_fifo的两端都是export,都是put()和get()的实现端,而不是发起端。
class componentB extend suvm_component;
`uvm_component_utils (componentB)
//Create a get_port to request for data from componentA
uvm_blocking_get_port #(Packet) m_get_port;
int m_num_tx = 2;
function new (string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new (name, parent);
endfunction
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
m_get_port = new ("m_get_port", this);
endfunction
virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
Packet pkt;
phase.raise_objection(this);
repeat (m_num_tx) begin
#100;
m_get_port.get(pkt);
`uvm_info ("COMPB", "ComponentAjust gave me the packet", UVM_LOW)
pkt.print (uvm_default_line_printer);
end
phase.drop_objection(this);
endtask
endclass
最后在更高的测试平台层次中定义uvm_tlm_fifo,连接compA的put_port和tlm_fifo的put_export,以及compB的get_port和tlm_fifo的get_export

class my_test extendsuvm_env;
`uvm_component_utils (my_test)
componentA compA;
componentB compB;
int m_num_tx;
//Create the UVM TLM Fifo that can accept simple_packet
uvm_tlm_fifo #(Packet) m_tlm_fifo;
functionnew (string name = "my_test", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new (name, parent);
endfunction
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
//Create an object of both components
compA = componentA::type_id::create ("compA", this);
compB = componentB::type_id::create ("compB", this);
std::randomize(m_num_tx) with {m_num_tx inside {[4:10]}; };
compA.m_num_tx = m_num_tx;
compB.m_num_tx = m_num_tx;
//Create a FIFO with depth 2
m_tlm_fifo = new ("uvm_tlm_fifo", this, 2);
endfunction
//Connect the ports to the export of FIFO.
virtualfunctionvoid connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
compA.m_put_port.connect(m_tlm_fifo.put_export);
compB.m_get_port.connect(m_tlm_fifo.get_export);
endfunction
//Display a message when the FIFO is full
virtualtask run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
forever begin
#10;
if(m_tlm_fifo.is_full ())
`uvm_info ("UVM_TLM_FIFO", "Fifo isnow FULL !", UVM_MEDIUM)
end
endtask
endclass
仿真结果
# UVM_INFO tb_classes/componentA.sv(33) @50: uvm_test_top.compA [COMPA] Packet sent to CompB
# pkt: (Packet@543) { addr: 'h10 data: 'hcc }
# UVM_INFO tb_classes/componentB.sv(26) @100: uvm_test_top.compB [COMPB] ComponentA just gave me the packet
# pkt: (Packet@543) { addr: 'h10 data: 'hcc }
# UVM_INFO tb_classes/componentA.sv(33) @100: uvm_test_top.compA [COMPA] Packet sent to CompB
# pkt: (Packet@544) { addr: 'h3e data: 'h92 }
# UVM_INFO tb_classes/componentA.sv(33) @150: uvm_test_top.compA [COMPA] Packet sent to CompB
# pkt: (Packet@545) { addr: 'hde data: 'h65 }
# UVM_INFO tb_classes/my_test.sv(40) @ 150:uvm_test_top [UVM_TLM_FIFO] Fifo is now FULL !
# UVM_INFO tb_classes/my_test.sv(40) @ 160:uvm_test_top [UVM_TLM_FIFO] Fifo is now FULL !
# UVM_INFO tb_classes/my_test.sv(40) @ 170:uvm_test_top [UVM_TLM_FIFO] Fifo is now FULL !
# UVM_INFO tb_classes/my_test.sv(40) @ 180:uvm_test_top [UVM_TLM_FIFO] Fifo is now FULL !
# UVM_INFO tb_classes/my_test.sv(40) @ 190:uvm_test_top [UVM_TLM_FIFO] Fifo is now FULL !
# UVM_INFO tb_classes/componentB.sv(26) @200: uvm_test_top.compB [COMPB] ComponentA just gave me the packet
# pkt: (Packet@544) { addr: 'h3e data: 'h92 }
componentA每隔50ns往tlm_fifo写入一个transaction,componentB每隔100ns从tlm_fifo读出一个transaction。
转自微信公众号:数字芯片实验室
最后
以上就是还单身背包最近收集整理的关于UVM-FLM-FIFO的全部内容,更多相关UVM-FLM-FIFO内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。





![[UVM]UVM TLM FIFO使用方法總結 UVM TLM FIFO用法總結](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg7.png)


发表评论 取消回复