% QPSK.m
%
% Simulation program to realise QPSK transmission (Modulation and Demodulation)
%
% Programmed by KY, 2021.3.2
clc
clear all
close all
%******************** Preparation part **********************
Ndata=1000; % Symbols Number
Ts=0.001; % Symbol period
sr=1/Ts; % Symbol rate
L=48; % Bit Number in one Symbol
Tb=Ts/L; % Bit period
fs=1/Tb; % Bit rate
fc=12e3; % Carrier freq
M=4; % Modulation size--8psk
modetype='psk';
dataenc='nondiff';
ebn=-10:1:10; % Transmitting SNR
%******************** Produce data **********************
data=randi([0 M-1],Ndata,1);
Transmit=data;
%******************* M-psk Modulation *******************
s=pskmod(data,M,pi/4,'gray');
%******************* Pulse shaping *******************
alpha=0.9;
span=100; % Truncation Numbers
sps=L; % Bit Number in one Symbol
rh = rcosdesign(alpha,span,sps)';
xb=conv(upsample(s,L),rh);
%******************* Modulation (Carrier) *******************
t=(0:length(xb)-1)'*Tb;
xT=real(exp(1i*2*pi*fc*t).*xb);
%******************* Calculate signal energy *******************
ebn0=10.^(ebn/10); % bit snr
k=log2(M);
esn0=k*ebn0; % Symbol snr
signal_power=sum(abs(xT).^2)/length(xT); % mean power of signal
es=signal_power*Ts; % power of one Symbol
no=es./esn0; % power of noise in one Symbol
noise_power=no/Tb; % mean power of noise
std=sqrt(noise_power);
%******************* Channel and Receiver *******************
for i_ebn=1:length(ebn)
t=(1/fs:1/fs:length(xT)/fs)';
n=std(i_ebn)/sqrt(2)*(randn(size(xT))).*cos(2*pi.*fc.*t)+std(i_ebn)/sqrt(2)*(randn(size(xT))).*sin(2*pi*fc.*t);
xR=xT+n;
% Bandpass filter for receiver
w = [2*11/48 2*13/48]; % fc=12e3, which results in w=[11e3/(fs/2) 13e3/(fs/2)]
fil_ord=128;
b = fir1(fil_ord,w);
b = b/sqrt(sum(b.^2));
xR = conv(b,xR);
xR= xR(fil_ord/2+1:end-fil_ord/2);
% Demodulation and Filter
t=(0:length(xb)-1)'*Tb;
xR=2*exp(-1i*2*pi*fc*t).*xR;
w=[1/10000 1/10]; % This coefficients is designed according to the bandwidth of the baseband signal "xb"
h=fir1(fil_ord,w);
xR = conv(h,xR);
xR=xR(fil_ord/2+1:end-fil_ord/2);
% Filter-(Pulse shaping)
xR=conv(xR,rh);
xR=xR(length(rh)-1+1:L:end-length(rh)-1);
Receive=pskdemod(xR,M,pi/4,'gray');
[number(i_ebn),ber(i_ebn)]=biterr(Receive,Transmit);
[numser(i_ebn),ser(i_ebn)]=symerr(Receive,Transmit);
end
%******************* Plot *******************
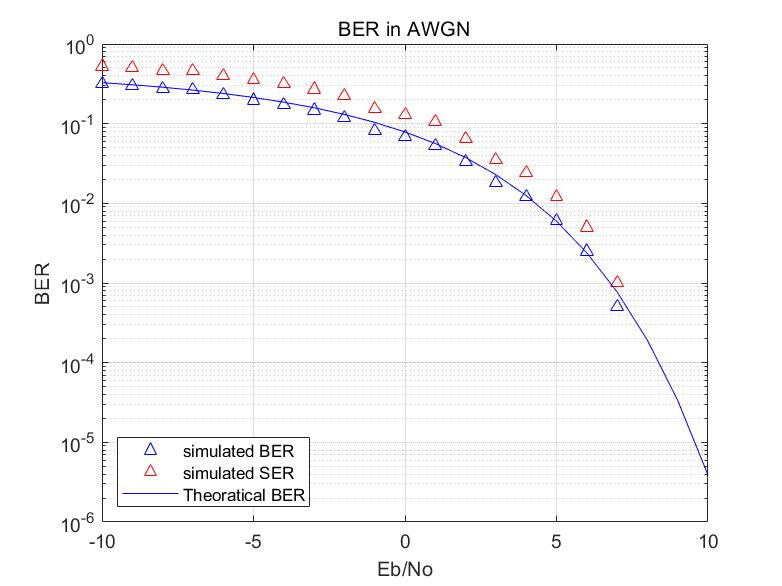
figure;
semilogy(ebn,ber,'b^');
hold on;
grid on;
semilogy(ebn,ser, 'r^');
% calculate the theoratical ber
ber = berawgn(ebn, modetype, M, dataenc);
semilogy(ebn,ber,'b');
title('BER in AWGN');
xlabel('Eb/No');
ylabel('BER');
legend('simulated BER','simulated SER', 'Theoratical BER','location', 'SouthWest');
最后
以上就是鲜艳奇异果最近收集整理的关于QPSK调制解调(具备脉冲成形+载波调制,计算误码率并与理论值相比较)的全部内容,更多相关QPSK调制解调(具备脉冲成形+载波调制内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复