帮助文档
crossvalind交叉验证
Generate cross-validation indices 生成交叉验证索引
Syntax语法
Indices = crossvalind('Kfold', N, K) K折交叉
[Train, Test] = crossvalind('HoldOut', N, P)
[Train, Test] = crossvalind('LeaveMOut', N, M)留M法交叉验证,默认M为1,留一法交叉验证
[Train, Test] = crossvalind('Resubstitution', N, [P,Q])
[...] = crossvalind(Method, Group, ...)
[...] = crossvalind(Method, Group, ..., 'Classes', C)
[...] = crossvalind(Method, Group, ..., 'Min', MinValue)
Description描述
Indices = crossvalind('Kfold', N, K) returns randomly generated indices for a K-fold cross-validation ofN observations.Indices contains equal (or approximately equal) proportions of the
integers1 throughK that define a partition of the N observations intoK disjoint subsets. Repeated calls return different randomly generated partitions.K defaults to5 when omitted. In K-fold cross-validation,
K-1 folds are used for training and the last fold is used for evaluation. This process is repeatedK times, leaving one different fold for evaluation each time.
[Train, Test] = crossvalind('HoldOut', N, P) returns logical index vectors for cross-validation ofN observations by randomly selectingP*N (approximately) observations to hold out for the evaluation set.P
must be a scalar between0 and 1. P defaults to 0.5 when omitted, corresponding to holding50% out. Using holdout cross-validation within a loop is similar to K-fold cross-validation one time outside the loop, except that
non-disjointed subsets are assigned to each evaluation.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
LeaveMOut
[Train, Test] = crossvalind('LeaveMOut', N, M), where M is an integer, returns logical index vectors for cross-validation ofN observations by randomly selectingM of the observations to hold out for the evaluation set.M
defaults to1 when omitted. Using 'LeaveMOut' cross-validation within a loop does not guarantee disjointed evaluation sets. To guarantee disjointed evaluation sets, use'Kfold' instead.
M是整数,返回交叉索引逻辑索引向量,其中N个观测值,从N个观测值中随机选取M个观测值保留作为验证集,其余作为训练集。省略时,M默认为1,即留一法交叉验证。
在一个循环中使用LeaveMOut交叉验证不保证不连贯的验证集.为保证非连贯的验证集,使用K-fold方法替换。
Approximate a leave-one-out prediction error estimate. 拟合一个留一法交叉验证预测误差估计
load carbig
x = Displacement; y = Acceleration;
% x为轿车形状的大小,y为轿车轿车速度从0到60公里所用时间
N = length(x);
% N为x长度=406
sse = 0;
for i = 1:100
[train,test] = crossvalind('LeaveMOut',N,1);
yhat = polyval(polyfit(x(train),y(train),2),x(test));
sse = sse + sum((yhat - y(test)).^2);
end
CVerr = sse / 100
% sse=353.10 CVerr交叉验证误差为sse/100=3.5310
CVerr =
4.9750
polyfit(x(train),y(train),2) x为横坐标,y为纵坐标,拟合2次多项式
polyfit 输出是一个多项式系数的行向量,从左到右表示从高次到低次的多项式系数。2 1 0次
y = polyval(p,x)
返回n次多项式在x处的值。输入变量p是一个长度为n+1的向量,其元素为按降幂排列的多项式系数。
y=p1*x^n+p2*x^(n-1)+...+pn*x+p(n+1)
x可以是一个矩阵或者一个向量,在这两种情况下,polyval计算在X中任意元素处的多项式p的估值。
计算均方误差(估值减去观测值的平方)之和。
进行了100次交叉验证,除以总次数100,为单次均方误差。
模型的均方误差越小,拟合的越好。
其中carbig.mat是一个各国轿车的统计数据,总计406辆轿车。
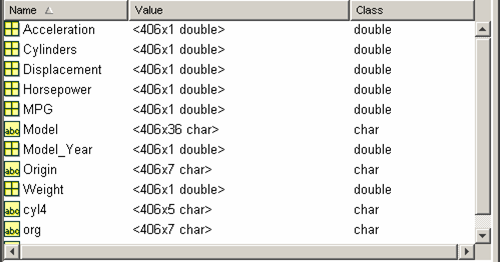
这里:
Accelaration: 轿车速度从0到60公里所用时间
Cylinders: 轿车的汽缸数
Displacement:轿车形状的大小
Horsepower:轿车的马力
MPG: 每加仑汽油行驶的里程
Model: 轿车的型号
Model_year:那一年代的模型
Origin: 轿车产自那里
Weight: 轿车的重量
其中有些是数据型变量,有些是字符型变量。
>> x=1:10
x =
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
>> y=sin(x)
y =
Columns 1 through 8
0.8415 0.9093 0.1411 -0.7568 -0.9589 -0.2794 0.6570 0.9894
Columns 9 through 10
0.4121 -0.5440
>> [train,test]=crossvalind('LeaveMOut',10,1);
>> train
train =
1
1
1
1
0
1
1
1
1
1
>> test
test =
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
>> [train,test]=crossvalind('LeaveMOut',10,2);
>> train
train =
1
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
>> test
test =
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
[Train, Test] = crossvalind('Resubstitution', N, [P,Q]) returns logical index vectors of indices for cross-validation ofN observations by randomly selectingP*N observations for the evaluation set andQ*N
observations for training. Sets are selected in order to minimize the number of observations that are used in both sets.P andQ are scalars between
0 and 1. Q=1-P corresponds to holding out(100*P)%, whileP=Q=1 corresponds to full resubstitution.[P,Q] defaults to
[1,1] when omitted.
[...] = crossvalind(Method, Group, ...) takes the group structure of the data into account.Group is a grouping vector that defines the class for each observation.Group can be a numeric vector, a string array,
or a cell array of strings. The partition of the groups depends on the type of cross-validation: For K-fold, each group is divided intoK subsets, approximately equal in size. For all others, approximately equal numbers of observations from each group
are selected for the evaluation set. In both cases the training set contains at least one observation from each group.
[...] = crossvalind(Method, Group, ..., 'Classes', C) restricts the observations to only those values specified inC.C can be a numeric vector, a string array, or a cell array of strings, but it is of the
same form asGroup. If one output argument is specified, it contains the value0 for observations belonging to excluded classes. If two output arguments are specified, both will contain the logical value false for observations belonging to
excluded classes.
[...] = crossvalind(Method, Group, ..., 'Min', MinValue) sets the minimum number of observations that each group has in the training set.Min defaults to1. Setting a large value for
Min can help to balance the training groups, but adds partial resubstitution when there are not enough observations. You cannot setMin when using K-fold cross-validation.
Examples
Create a 10-fold cross-validation to compute classification error.
load fisheriris
indices = crossvalind('Kfold',species,10);
cp = classperf(species);
for i = 1:10
test = (indices == i); train = ~test;
class = classify(meas(test,:),meas(train,:),species(train,:));
classperf(cp,class,test)
end
cp.ErrorRate
Divide cancer data 60/40 without using the 'Benign' observations. Assume groups are the true labels of the observations.
labels = {'Cancer','Benign','Control'};
groups = labels(ceil(rand(100,1)*3));
[train,test] = crossvalind('holdout',groups,0.6,'classes',...
{'Control','Cancer'});
sum(test) % Total groups allocated for testing
ans =
35
sum(train) % Total groups allocated for training
ans =
26
函数原型
function [tInd,eInd] = crossvalind(method,N,varargin)
%CROSSVALIND generates cross-validation indices 按比例取出每次交叉验证的索引
% each time.
%
% [TRAIN,TEST] = CROSSVALIND('HoldOut',N,P) returns logical index vectors 返回逻辑索引向量
%
% [TRAIN,TEST] = CROSSVALIND('LeaveMOut',N,M), where M is an integer,
% returns logical index vectors for cross-validation of N observations by
% randomly selecting M of the observations to hold out for the evaluation
% set. M defaults to 1 when omitted. Using LeaveMOut cross-validation
% within a loop does not guarantee disjointed evaluation sets. Use K-fold
% instead.
% M是整数,返回交叉索引逻辑索引向量,其中N个观测值,随机选取M个观测值保留作为验证集,其余作为训练集
% 省略时,M默认为1,即留一法交叉验证。
% 在一个循环中使用LeaveMOut交叉验证不保证不连贯的验证集.使用K-fold方法替换
% [TRAIN,TEST] = CROSSVALIND('Resubstitution',N,[P,Q]) returns logical
% index vectors of indices for cross-validation of N observations by
% randomly selecting P*N observations for the evaluation set and Q*N
% observations for training. Sets are selected in order to minimize the
% number of observations that are used in both sets. P and Q are scalars
% between 0 and 1. Q=1-P corresponds to holding out (100*P)%, while P=Q=1
% corresponds to full resubstitution. [P,Q] defaults to [1,1] when omitted.
%
% [...] = CROSSVALIND(METHOD,GROUP,...) takes the group structure of the
% data into account. GROUP is a grouping vector that defines the class for
% each observation. GROUP can be a numeric vector, a string array, or a
% cell array of strings. The partition of the groups depends on the type
% of cross-validation: For K-fold, each group is divided into K subsets,
% approximately equal in size. For all others, approximately equal
% numbers of observations from each group are selected for the evaluation
% set. In both cases the training set will contain at least one
% observation from each group.
%
% [...] = CROSSVALIND(METHOD,GROUP,...,'CLASSES',C) restricts the
% observations to only those values specified in C. C can be a numeric
% vector, a string array, or a cell array of strings, but it is of the
% same form as GROUP. If one output argument is specified, it will
% contain the value 0 for observations belonging to excluded classes. If
% two output arguments are specified, both will contain the logical value
% false for observations belonging to excluded classes.
%
% [...] = CROSSVALIND(METHOD,GROUP,...,'MIN',MIN) sets the minimum number
% of observations that each group has in the training set. MIN defaults
% to 1. Setting a large value for MIN can help to balance the training
% groups, but adds partial resubstitution when there are not enough
% observations. You cannot set MIN when using K-fold cross-validation.
%
% Examples:示例
%
% % Create a 10-fold cross-validation to compute classification error.十折交叉验证 计算分类误差
% 将样本打乱,然后均匀分成K份,轮流选择其中K-1份训练,剩余的一份做验证,计算预测误差平方和,
% 最后把K次的预测误差平方和再做平均作为选择最优模型结构的依据。这里取K=10
% 特别的K取N,就是留一法(leave one out)。
%
% load fisheriris
% indices = crossvalind('Kfold',species,10);
% cp = classperf(species);
% for i = 1:10
% test = (indices == i); train = ~test;
% class = classify(meas(test,:),meas(train,:),species(train,:));
% classperf(cp,class,test)
% end
% cp.ErrorRate
%
% % Approximate a leave-one-out prediction error estimate.
% load carbig
% x = Displacement; y = Acceleration;
% N = length(x);
% sse = 0;
% for i = 1:100
% [train,test] = crossvalind('LeaveMOut',N,1);
% yhat = polyval(polyfit(x(train),y(train),2),x(test));
% sse = sse + sum((yhat - y(test)).^2);
% end
% CVerr = sse / 100
%
% % Divide cancer data 60/40 without using the 'Benign' observations.
% % Assume groups are the true labels of the observations.
% labels = {'Cancer','Benign','Control'};
% groups = labels(ceil(rand(100,1)*3));
% [train,test] = crossvalind('holdout',groups,0.6,'classes',...
% {'Control','Cancer'});
% sum(test) % Total groups allocated for testing
% sum(train) % Total groups allocated for training
%
% See also CLASSPERF, CLASSIFY, GRP2IDX, KNNCLASSIFY, SVMCLASSIFY.
% References:
% [1] Hastie, T. Tibshirani, R, and Friedman, J. (2001) The Elements of
% Statistical Learning, Springer, pp. 214-216.
% [2] Theodoridis, S. and Koutroumbas, K. (1999) Pattern Recognition,
% Academic Press, pp. 341-342.
% Copyright 2003-2008 The MathWorks, Inc.
% $Revision: 1.1.10.5 $ $Date: 2008/06/16 16:32:40 $
% set defaults
classesProvided = false;
MG = 1; % default for minimum number of observations for every training group
P = 0.5; % default value for holdout
K = 5; % default value for Kfold
M = 1; % default value for leave-M-out
Q = [1 1];% default value for resubstitution
% get and validate the method (first input)
if ischar(method) && size(method,1)==1
validMethods = {'holdout','kfold','resubstitution','leavemout'};
method = strmatch(lower(method),validMethods);
if isempty(method)
error('Bioinfo:crossvalind:NotValidMethod',...
'Not a valid method.')
end
method = validMethods{method};
else
error('Bioinfo:crossvalind:NotValidTypeForMethod',...
'Valid methods are ''KFold'', ''HoldOut'', ''LeaveMOut'', or ''Resubstitution''.')
end
if nargout>1 && isequal(method,'kfold')
error('Bioinfo:crossvalind:TooManyOutputArgumentsForKfold',...
'To many output arguments for Kfold cross-validation.')
end
% take P,K,Q, or M if provided by the third input (first varargin) and
% validate it
if numel(varargin) && isnumeric(varargin{1})
S = varargin{1};
varargin(1)=[];
switch method
case 'holdout'
if numel(S)==1 && S>0 && S<1
P = S;
else
error('Bioinfo:crossvalind:InvalidThirdInputP',...
'For hold-out cross-validation, the third input must be a scalar between 0 and 1.');
end
case 'kfold'
if numel(S)==1 && S>=1
K = round(S);
else
error('Bioinfo:crossvalind:InvalidThirdInputK',...
'For Kfold cross-validation, the third input must be a positive integer.');
end
case 'leavemout'
if numel(S)==1 && S>=1
M = round(S);
else
error('Bioinfo:crossvalind:InvalidThirdInputM',...
'For leave-M-out cross-validation, the third input must be a positive integer.');
end
case 'resubstitution'
if numel(S)==2 && all(S>0) && all(S<=1)
Q = S(:);
else
error('Bioinfo:crossvalind:InvalidThirdInputQ',...
'For resubstitution cross-validation, the third input must be a 2x1 vector with values between 0 and 1.');
end
end %switch
end
% read optional paired input arguments in
if numel(varargin)
if rem(numel(varargin),2)
error('Bioinfo:crossvalind:IncorrectNumberOfArguments',...
'Incorrect number of arguments to %s.',mfilename);
end
okargs = {'classes','min'};
for j=1:2:numel(varargin)
pname = varargin{j};
pval = varargin{j+1};
k = find(strncmpi(pname, okargs,length(pname)));
if isempty(k)
error('Bioinfo:crossvalind:UnknownParameterName',...
'Unknown parameter name: %s.',pname);
elseif length(k)>1
error('Bioinfo:crossvalind:AmbiguousParameterName',...
'Ambiguous parameter name: %s.',pname);
else
switch(k)
case 1 % classes
classesProvided = true;
classes = pval;
case 2 % min
MG = round(pval(1));
if MG<0
error('Bioinfo:crossvalind:NotValidMIN',...
'MIN must be a positive scalar.')
end
end
end
end
end
if isscalar(N) && isnumeric(N)
if N<1 || N~=floor(N)
error('Bioinfo:crossvalind:NNotPositiveInteger',...
'The number of observations must be a positive integer.');
end
group = ones(N,1);
else
[group, groupNames] = grp2idx(N); % at this point group is numeric only
N = numel(group);
end
if classesProvided
orgN = N;
% change classes to same type as groups
[dummy,classes]=grp2idx(classes);
validGroups = intersect(classes,groupNames);
if isempty(validGroups)
error('bioinfo:crossvalind:EmptyValidGroups',...
'Could not find any valid group. Are CLASSES the same type as GROUP ?')
end
selectedGroups = ismember(groupNames(group),validGroups);
group = grp2idx(group(selectedGroups)); % group idxs are reduced to only the sel groups
N = numel(group); % the new size of the reduced vector
end
nS = accumarray(group(:),1);
if min(nS)
error('Bioinfo:crossvalind:MissingObservations',...
'All the groups must have at least least MIN obeservation(s).')
end
switch method
case {'leavemout','holdout','resubstitution'}
switch method
case 'leavemout'
% number of samples for holdout in every group
nSE = repmat(M,numel(nS),1);
% at least there is MG sample(s) for training in every group
nST = max(nS-nSE,MG);
case 'holdout'
% computes the number of samples for holdout in every group
nSE = floor(nS*P);
% at least there is MG sample(s) for training in every group
nST = max(nS-nSE,MG);
case 'resubstitution'
% computes the number of samples for training and evaluation
nSE = floor(nS*Q(1));
nST = floor(nS*Q(2));
% at least there is MG sample(s) for training in every group
nST = max(nST,MG);
end
% Initializing the outputs
tInd = false(N,1);
eInd = false(N,1);
% for every group select randomly the samples for both sets
for g = 1:numel(nS)
h = find(group==g);
randInd = randperm(nS(g));
tInd(h(randInd(1:nST(g))))=true;
eInd(h(randInd(end-nSE(g)+1:end)))=true;
end
case 'kfold'
tInd = zeros(N,1);
for g = 1:numel(nS)
h = find(group==g);
% compute fold id's for every observation in the group
q = ceil(K*(1:nS(g))/nS(g));
% and permute them to try to balance among all groups
pq = randperm(K);
% randomly assign the id's to the observations of this group
randInd = randperm(nS(g));
tInd(h(randInd))=pq(q);
end
end
if classesProvided
if isequal(method,'kfold')
temp = zeros(orgN,1);
temp(selectedGroups) = tInd;
tInd = temp;
else
temp = false(orgN,1);
temp(selectedGroups) = tInd;
tInd = temp;
temp = false(orgN,1);
temp(selectedGroups) = eInd;
eInd = temp;
end
end
最后
以上就是英俊小松鼠最近收集整理的关于在matlab采用交叉验证选择参数,使用matlab交叉验证 | 学步园的全部内容,更多相关在matlab采用交叉验证选择参数,使用matlab交叉验证内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复