使用Thread.join(long million)方法,参数是毫秒
代码&解析如下:
解析:原本有t1和t2两个线程,根据实例化new Task()时t1传入了4,t2传入了2,分别相当于t1需要执行4次,t2需要执行2次,但是在run方法中使用了Thread.sleep(1000),所以t1执行4次就等于是执行4秒,t2同理。在t1.start启动后,调用了join方法设置了两秒的参数,相当于在t1执行两秒后就超时了,后面就是t1超时后的设置,
1、t1.interrupt()表示打断t1线程必须写,否则超时后还会继续执行。
2、run方法catch代码块中的return方法也是必须写的,否则t1线程也还会继续执行。
总结:Thread.join(long million)、nterrupt()、return三个地方需要同时书写,否则就会出现问题。
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Task task1 = new Task("one", 4);
Task task2 = new Task("two", 2);
Thread t1 = new Thread(task1);
Thread t2 = new Thread(task2);
t1.start();
try {
t1.join(2000); // 在主线程中等待t1执行2秒
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("t1 interrupted when waiting join");
e.printStackTrace();
}
t1.interrupt(); // 这里很重要,一定要打断t1,因为它已经执行了2秒。
t2.start();
try {
t2.join(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("t2 interrupted when waiting join");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class Task implements Runnable {
public String name;
private int time;
public Task(String s, int t) {
name = s;
time = t;
}
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < time; ++i) {
System.out.println("task " + name + " " + (i + 1) + " round");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(name
+ "is interrupted when calculating, will stop...");
return; // 注意这里如果不return的话,线程还会继续执行,所以任务超时后在这里处理结果然后返回
}
}
}
}
t1超时后正确处理方式的打印结果:
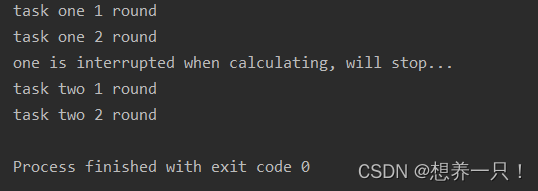
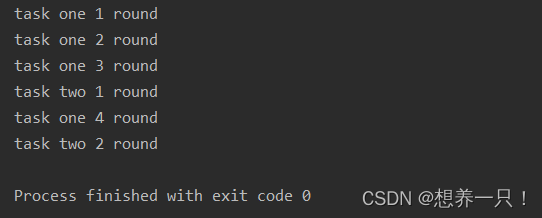
如果调用过join()后没有书写interrupt()和return就会是以下错误打印:
因为设置了两秒后t1任务需要停止,所以正确的时候是不需要打印task one 3 round和task one 4 round的
Future.get(long million, TimeUnit unit) 配合Future.cancle(true)
f1.get(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)就是设置两秒后超时,超时后会这个方法本身会抛出一个TimeoutException 异常,有TimeoutException 这个异常时设置f1.cancel(true);,同样在call方法中也要进行return,不然超时后线程还依然会执行。
public class Test1 {
static class Task implements Callable<Boolean> {
public String name;
private int time;
public Task(String s, int t) {
name = s;
time = t;
}
@Override
public Boolean call() throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < time; ++i) {
System.out.println("task " + name + " round " + (i + 1));
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(name
+ " is interrupted when calculating, will stop...");
return false; // 注意这里如果不return的话,线程还会继续执行,所以任务超时后在这里处理结果然后返回
}
}
return true;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Task task1 = new Task("one", 5);
Future<Boolean> f1 = executor.submit(task1);
try {
if (f1.get(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) { // future将在2秒之后取结果
System.out.println("one complete successfully");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("future在睡着时被打断");
executor.shutdownNow();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
System.out.println("future在尝试取得任务结果时出错");
executor.shutdownNow();
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
System.out.println("future时间超时");
f1.cancel(true);
// executor.shutdownNow();
// executor.shutdown();
} finally {
executor.shutdownNow();
}
}
}
设置2秒后超时的运行结果:
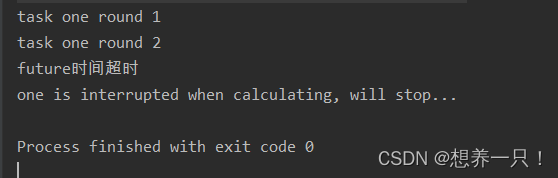
ExecutorService.awaitTermination(long million, TimeUnit unit)
这个方法会一直等待所有的任务都结束,或者超时时间到立即返回,若所有任务都完成则返回true,否则返回false
代码如下:
public class Test1 {
static class Task implements Runnable {
public String name;
private int time;
public Task(String s, int t) {
name = s;
time = t;
}
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < time; ++i) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(name
+ " is interrupted when calculating, will stop...");
return; // 注意这里如果不return的话,线程还会继续执行,所以任务超时后在这里处理结果然后返回
}
System.out.println("task " + name + " " + (i + 1) + " round");
}
System.out.println("task " + name + " finished successfully");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Task task = new Task("one", 5);
Task task2 = new Task("two", 2);
Future<?> future = executor.submit(task);
Future<?> future2 = executor.submit(task2);
List<Future<?>> futures = new ArrayList<Future<?>>();
futures.add(future);
futures.add(future2);
try {
if (executor.awaitTermination(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
System.out.println("task finished");
} else {
System.out.println("task time out,will terminate");
for (Future<?> f : futures) {
if (!f.isDone()) {
f.cancel(true);
}
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("executor is interrupted");
} finally {
executor.shutdown();
}
}
}
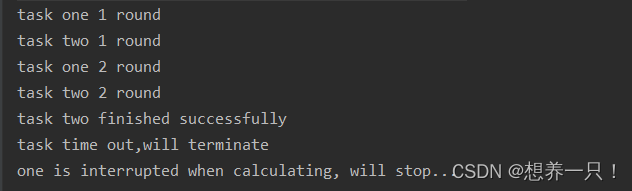
设置3秒超时,task2线程总共运行2秒,不存在超时情况,所以会返回task two finished successfully,task线程总共运行5秒,在第三秒超时,所以task超时后的结果都不会打印,而是提示task time out,will terminate。
设置一个守护线程,守护线程先sleep一段定时时间(睡眠时长就是超时时长),睡醒后打断它所监视的线程
public class Test1 {
static class Task implements Runnable {
private String name;
private int time;
public Task(String s, int t) {
name = s;
time = t;
}
public int getTime() {
return time;
}
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < time; ++i) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(name
+ " is interrupted when calculating, will stop...");
return; // 注意这里如果不return的话,线程还会继续执行,所以任务超时后在这里处理结果然后返回
}
System.out.println("task " + name + " " + (i + 1) + " round");
}
System.out.println("task " + name + " finished successfully");
}
}
static class Daemon implements Runnable {
List<Runnable> tasks = new ArrayList<Runnable>();
private Thread thread;
private int time;
public Daemon(Thread r, int t) {
thread = r;
time = t;
}
public void addTask(Runnable r) {
tasks.add(r);
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(time * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
thread.interrupt();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Task task1 = new Task("one", 5);
Thread t1 = new Thread(task1);
Daemon daemon = new Daemon(t1, 4);
Thread daemoThread = new Thread(daemon);
daemoThread.setDaemon(true);
t1.start();
daemoThread.start();
}
}
设置4秒醒来,从而打断所监视的目标线程。运行结果:
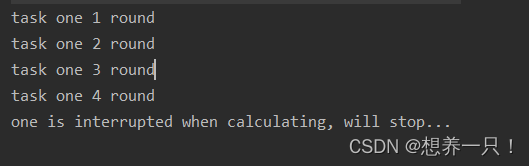
最后
以上就是美满导师最近收集整理的关于多线程任务超时的处理机制的全部内容,更多相关多线程任务超时内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。

![[转] 解决socket端口被占用的问题](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg5.png)






发表评论 取消回复