Apollo的planning模块,有很多值得学习和借鉴的地方。
但是整个模块非常庞大,只有理清框架之后,才便于对场景(决策)和规划算法进行逐个击破。
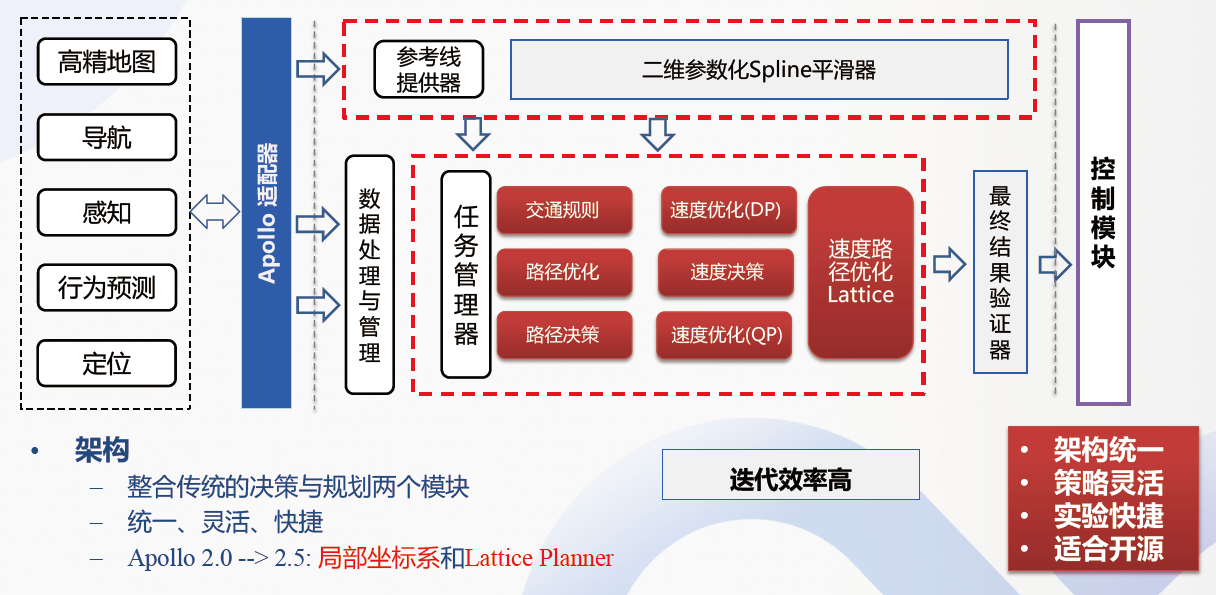
一些非常好的总结:
dig-into-apollo/modules/planning at main · daohu527/dig-into-apollo · GitHub
Planning-Apollo 6.0 Planning模块pipeline_Schulz King的博客-CSDN博客
Planning-Apollo6.0 planning module protobuf定义_Schulz King的博客-CSDN博客
Apollo代码库结构简介:
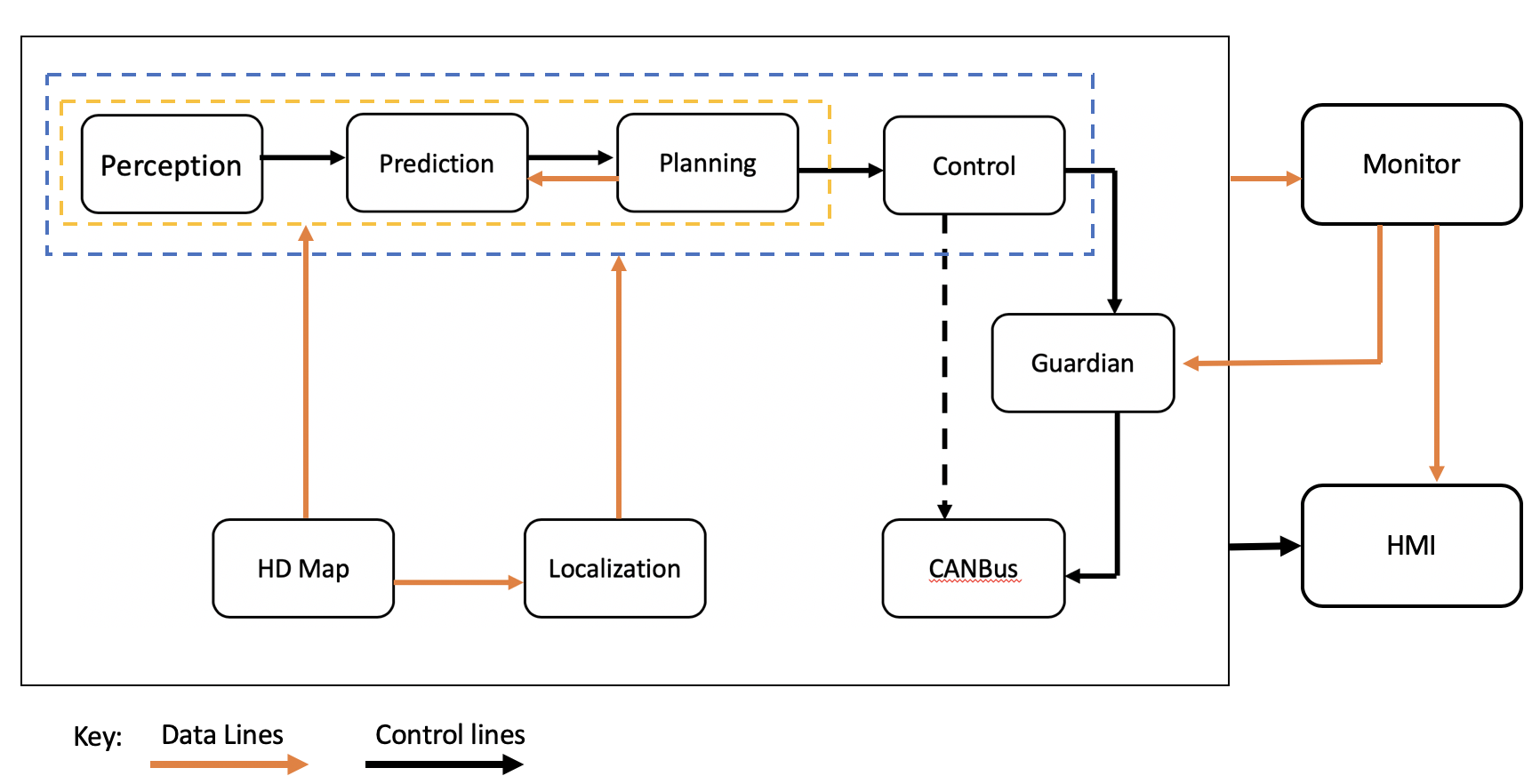
Planning module是自动驾驶的决策模块,会收集其他模块的所有信息进行综合决策。
Planning模块
Planning模块数据输入
为了计算最终的输出路径,Planning模块需要统一的规划多个输入数据。Planning模块的输入数据包括:
- Routing
- 感知和预测
- 车辆状态和定位
- 高清地图
(1)Routing定义了概念性问题“我想去哪儿”,消息定义在routing.proto文件中。RoutingResponse包含了RoadSegment,RoadSegment指明了车辆到达目的地应该遵循的路线。
(2)关于概念性问题“我周围有什么”的消息定义在perception_obstacles.proto和traffic_light_detection.proto中。perception_obstacles.proto定义了表示车辆周围的障碍物的数据,车辆周围障碍物的数据由感知模块提供。traffic_light_detection定义了信号灯状态的数据。除了已被感知的障碍物外,动态障碍物的路径预测对Planning模块也是非常重要的数据,因此prediction.proto封装了perception_obstacle消息来表示预测路径。
每个预测的路径都有其单独的可能性,而且每个动态障碍物可能有多个预测路径。
(3)另外一个重要的概念性问题是“我在哪”。关于该问题的数据通过高清地图和定位模块获得。定位信息和车辆车架信息被封装在VehicleState消息中,该消息定义在vehicle_state.proto
Planning会订阅感知,预测,地图,导航,定位,底盘,HMI(Pad),Storytelling模块发布的消息.
| channel | message | module | content |
|---|---|---|---|
| "/apollo/prediction" | PredictionObstacles | Predicition | 障碍物信息 |
| "/apollo/perception/traffic_light" | TrafficLightDetection | Perception | 交通灯信息 |
| "/apollo/relative_map" | MapMsg | Map* | 地图信息 |
| "/apollo/routing_response" | RoutingResponse | Routing | 导航信息 |
| "/apollo/localization/pose" | LocalizationEstimate | Localization | 定位信息 |
| "/apollo/canbus/chassis" | Chassis | Canbus | 底盘信息 |
| "/apollo/planning/pad" | PadMessage | Pad* | Pad信息 |
| "/apollo/storytelling" | Stories | Storytelling* | -- |
注:以上消息均通过Proto定义
以预测信息为例,在处理动态障碍物时的必要信息modules/prediction/proto/prediction_obstacle.proto
syntax = "proto2";
package apollo.prediction;
import "modules/common/proto/error_code.proto";
import "modules/common/proto/header.proto";
import "modules/prediction/proto/scenario.proto";
import "modules/perception/proto/perception_obstacle.proto";
import "modules/prediction/proto/feature.proto";
// estimated obstacle intent 预测障碍物的行为/意图
message ObstacleIntent {
enum Type {
UNKNOWN = 0;
STOP = 1;
STATIONARY = 2;
MOVING = 3;
CHANGE_LANE = 4;
LOW_ACCELERATION = 5;
HIGH_ACCELERATION = 6;
LOW_DECELERATION = 7;
HIGH_DECELERATION = 8;
}
optional Type type = 1 [default = UNKNOWN];
}
// self driving car intent
自车的驾驶意图
message Intent {
enum Type {
UNKNOWN = 0;
STOP = 1;
CRUISE = 2;
CHANGE_LANE = 3;
}
optional Type type = 1 [default = UNKNOWN];
}
message PredictionObstacle {
optional apollo.perception.PerceptionObstacle perception_obstacle = 1;
// 障碍物信息
optional double timestamp = 2;
// GPS time in seconds 时间戳
// the length of the time for this prediction (e.g. 10s)
optional double predicted_period = 3;
// 预测周期
// can have multiple trajectories per obstacle
repeated Trajectory trajectory = 4;
// 障碍物的预测轨迹,一个障碍物可能有多条预测轨迹,每条轨迹有概率值
// estimated obstacle intent
optional ObstacleIntent intent = 5;
// 障碍物的意图
optional ObstaclePriority priority = 6; // 预测给出的障碍物的处理的等级: caution/normal/ignore
optional bool is_static = 7 [default = false];
// 是否是静态障碍物
// Feature history latest -> earliest sequence
repeated Feature feature = 8;
// 用于做预测的特征信息, PNC模块不用关心,是prediction使用的
}
message PredictionObstacles {
// timestamp is included in header
optional apollo.common.Header header = 1;
// make prediction for multiple obstacles
repeated PredictionObstacle prediction_obstacle = 2;
// perception error code
optional apollo.common.ErrorCode perception_error_code = 3;
// start timestamp
optional double start_timestamp = 4;
// end timestamp
optional double end_timestamp = 5;
// self driving car intent
optional Intent intent = 6;
// Scenario
optional Scenario scenario = 7; // 场景信息, prediction模块使用的,PNC不用关心, Planning有自己的scenario,且二者定义不同
}地图信息分为HD Map(UTM坐标系)和Relative Map(相对坐标系),两者地图数据格式相同.
目前Apollo并未对Storytelling信息做响应或者处理.
Planning模块会向控制模块广播ADCTrajectory,向导航模块广播重规划消息,并广播用于planning模块机器学习所需的数据.
Planning模块数据输出:
Planning模块的输出数据类型定义在planning.proto
syntax = "proto2";
package apollo.planning;
import "modules/canbus/proto/chassis.proto";
import "modules/common/proto/drive_state.proto";
import "modules/common/proto/geometry.proto";
import "modules/common/proto/header.proto";
import "modules/common/proto/pnc_point.proto";
import "modules/map/proto/map_id.proto";
import "modules/planning/proto/decision.proto";
import "modules/planning/proto/planning_internal.proto";
message EStop {
// is_estop == true when emergency stop is required
optional bool is_estop = 1;
// 是否紧急刹车
optional string reason = 2;
// 紧急刹车原因
}
message TaskStats {
optional string name = 1;
optional double time_ms = 2;
}
message LatencyStats {
optional double total_time_ms = 1;
repeated TaskStats task_stats = 2;
optional double init_frame_time_ms = 3;
}
message RSSInfo {
optional bool is_rss_safe = 1;
optional double cur_dist_lon = 2;
optional double rss_safe_dist_lon = 3;
optional double acc_lon_range_minimum = 4;
optional double acc_lon_range_maximum = 5;
optional double acc_lat_left_range_minimum = 6;
optional double acc_lat_left_range_maximum = 7;
optional double acc_lat_right_range_minimum = 8;
optional double acc_lat_right_range_maximum = 9;
}
// next id: 24
message ADCTrajectory {
optional apollo.common.Header header = 1;
optional double total_path_length = 2;
// in meters, 规划轨迹的长度
optional double total_path_time = 3;
// in seconds, 规划轨迹的时间
// path data + speed data
repeated apollo.common.TrajectoryPoint trajectory_point = 12; // 轨迹
optional EStop estop = 6; // 紧急刹车
// path point without speed info
repeated apollo.common.PathPoint path_point = 13; // 规划的路径信息(没有速度信息)
// is_replan == true mean replan triggered
optional bool is_replan = 9 [default = false];
// 是否是重规划的轨迹
optional string replan_reason = 22;
// 重规划的原因
// Specify trajectory gear
optional apollo.canbus.Chassis.GearPosition gear = 10;
// 档位信息
optional apollo.planning.DecisionResult decision = 14;
//决策信息:任务决策(停车换道等),障碍物决策,灯光信息(转向信号等)
optional LatencyStats latency_stats = 15;
// Planning的运算时间造成的延迟
// the routing used for current planning result
optional apollo.common.Header routing_header = 16;
// 导航信息的时间戳
optional apollo.planning_internal.Debug debug = 8;
// planning的debug信息
enum RightOfWayStatus { // adc右侧道路的状态:有保护,无保护
UNPROTECTED = 0;
PROTECTED = 1;
}
optional RightOfWayStatus right_of_way_status = 17;
// lane id along current reference line
repeated apollo.hdmap.Id lane_id = 18; // 当前车道id
// set the engage advice for based on current planning result.
optional apollo.common.EngageAdvice engage_advice = 19;
// the region where planning cares most
message CriticalRegion {
repeated apollo.common.Polygon region = 1;
}
// critical region will be empty when planning is NOT sure which region is
// critical
// critical regions may or may not overlap
optional CriticalRegion critical_region = 20;
//
enum TrajectoryType {
UNKNOWN = 0;
NORMAL = 1;
// 规划求解成功
PATH_FALLBACK = 2;
// 路径规划求解失败,fallback
SPEED_FALLBACK = 3; // 速度规划求解失败,fallback
PATH_REUSED = 4;
// 复用上一帧路路径
}
optional TrajectoryType trajectory_type = 21 [default = UNKNOWN];
// lane id along target reference line
repeated apollo.hdmap.Id target_lane_id = 23; // 目标车道ID
// output related to RSS
optional RSSInfo rss_info = 100;
}| channel | message | module | content |
|---|---|---|---|
| "/apollo/planning" | ADCTrajectory | Control | 规划信息 |
| "/apollo/routing_request" | RoutingRequest | Routing | 导航更新信息 |
| "/apollo/planning/learning_data" | PlanningLearningData | Planning | Planning机器学习数据 |
在proto数据的定义中,输出数据包括总时间、总长度和确切的路径信息,输出数据由控制单元解析执行,输出数据结构定义在repeated apollo.common.TrajectoryPointtrajectory_point。
trajectory point类继承自path_point类,并新增了speed、acceleration和timing属性。 定义在pnc_point.proto中的trajectory_point包含了路径的详细属性。
除了路径信息,Planning模块输出了多种注释信息。主要的注释数据包括:
- Estop
- DecisionResult
- 调试信息
Estop是标示了错误和异常的指令。例如,当自动驾驶的车辆碰到了障碍物或者无法遵守交通规则时将发送estop信号。DecisionResult主要用于展示模拟的输出结果以方便开发者更好的了解Planning模块的计算结果。更多详细的中间值结果会被保存并输出作为调试信息供后续的调试使用。
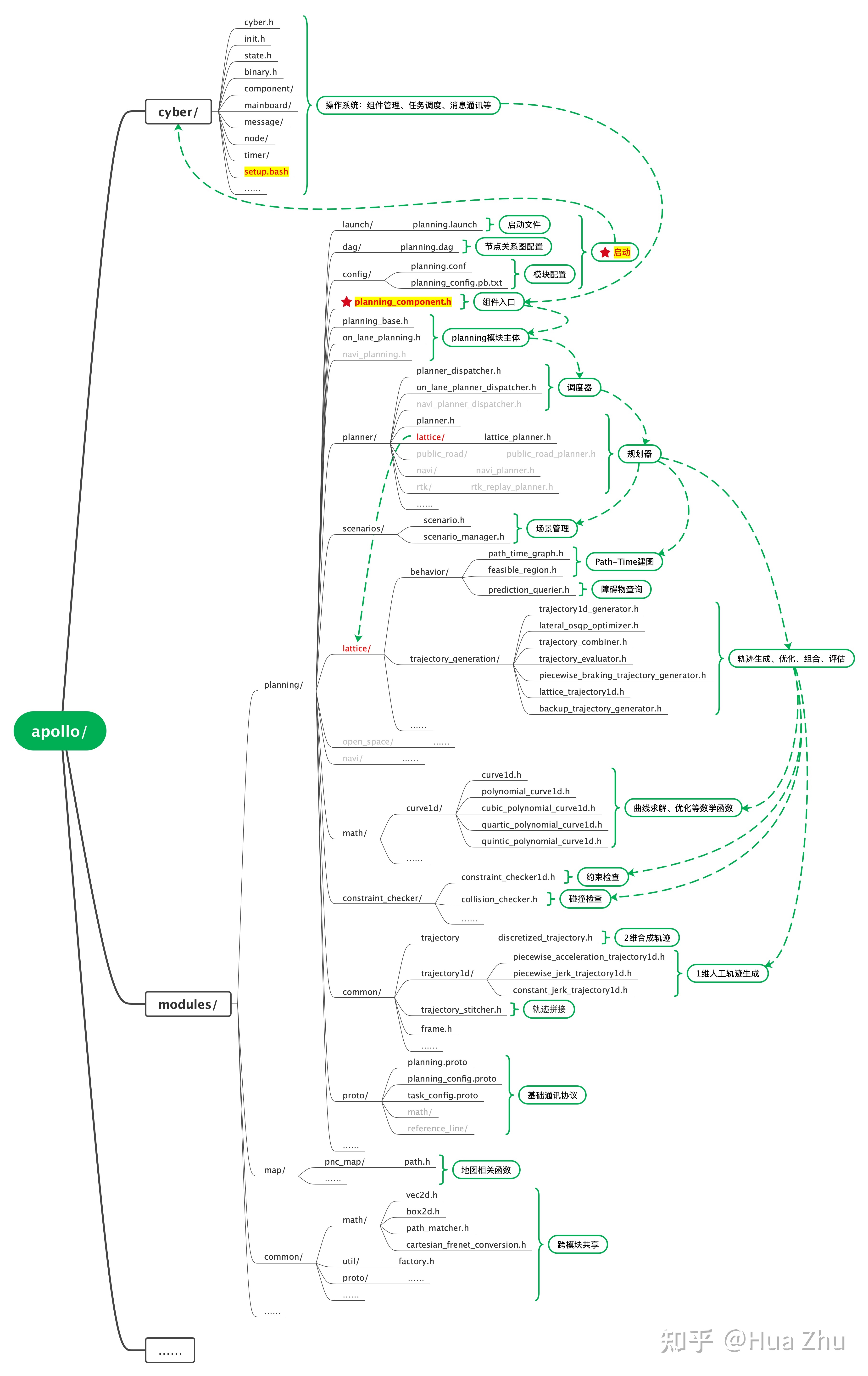
Planning模块代码结构和类层次:
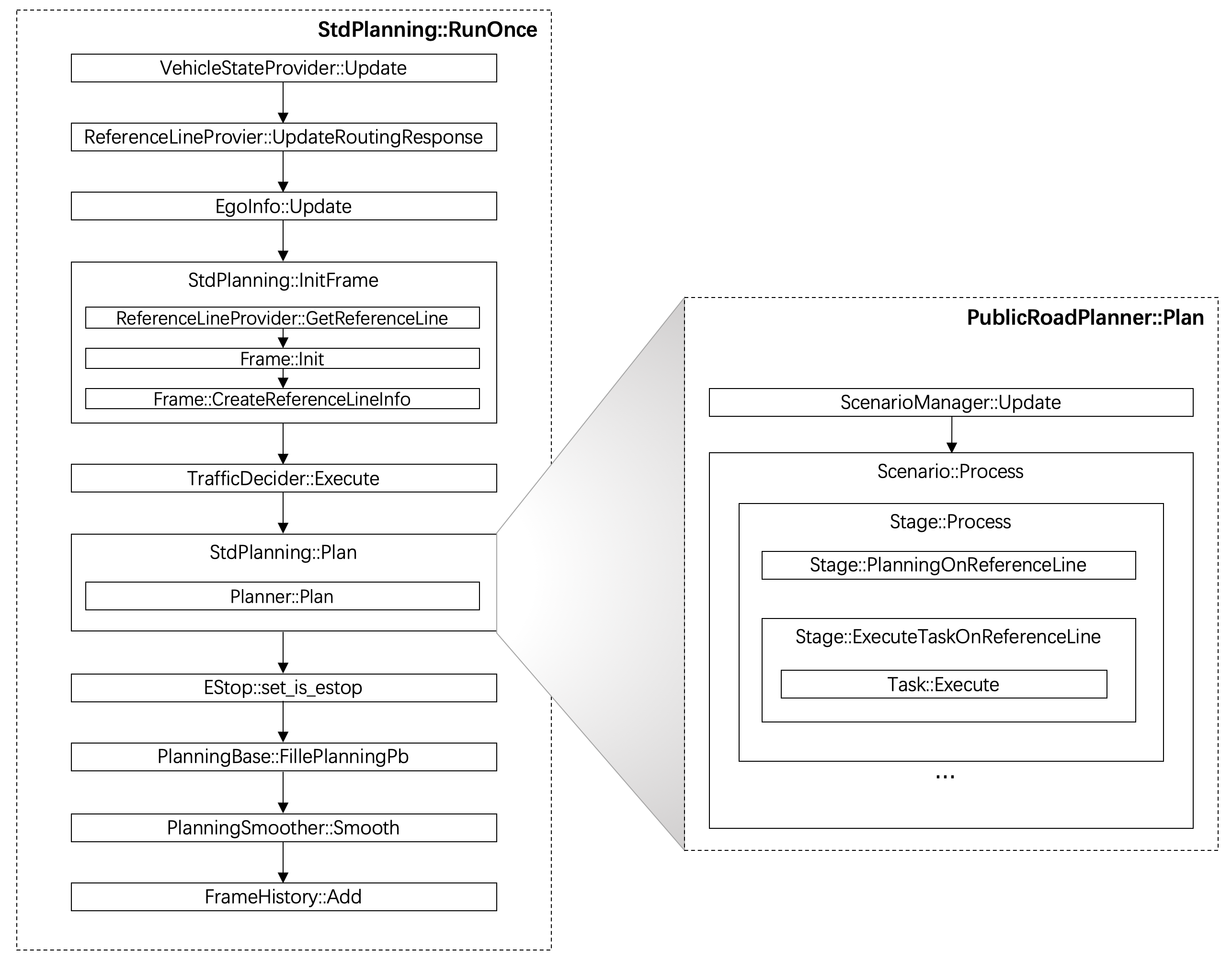
代码组织方式如下图所示:Planning模块的入口是planning.cc。在Planning模块内部,重要的类在下图中展示。
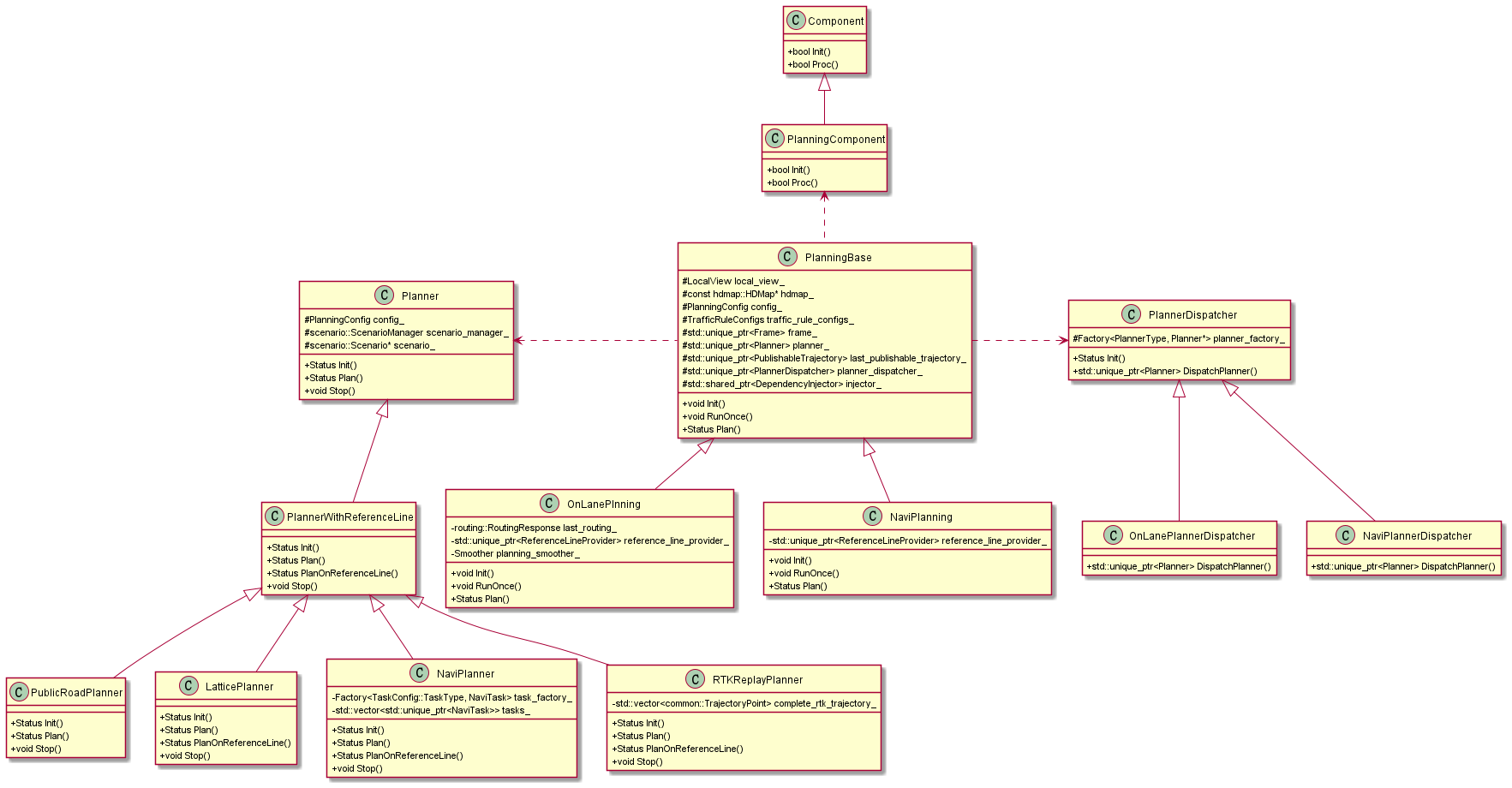
Planning模块运行流程:
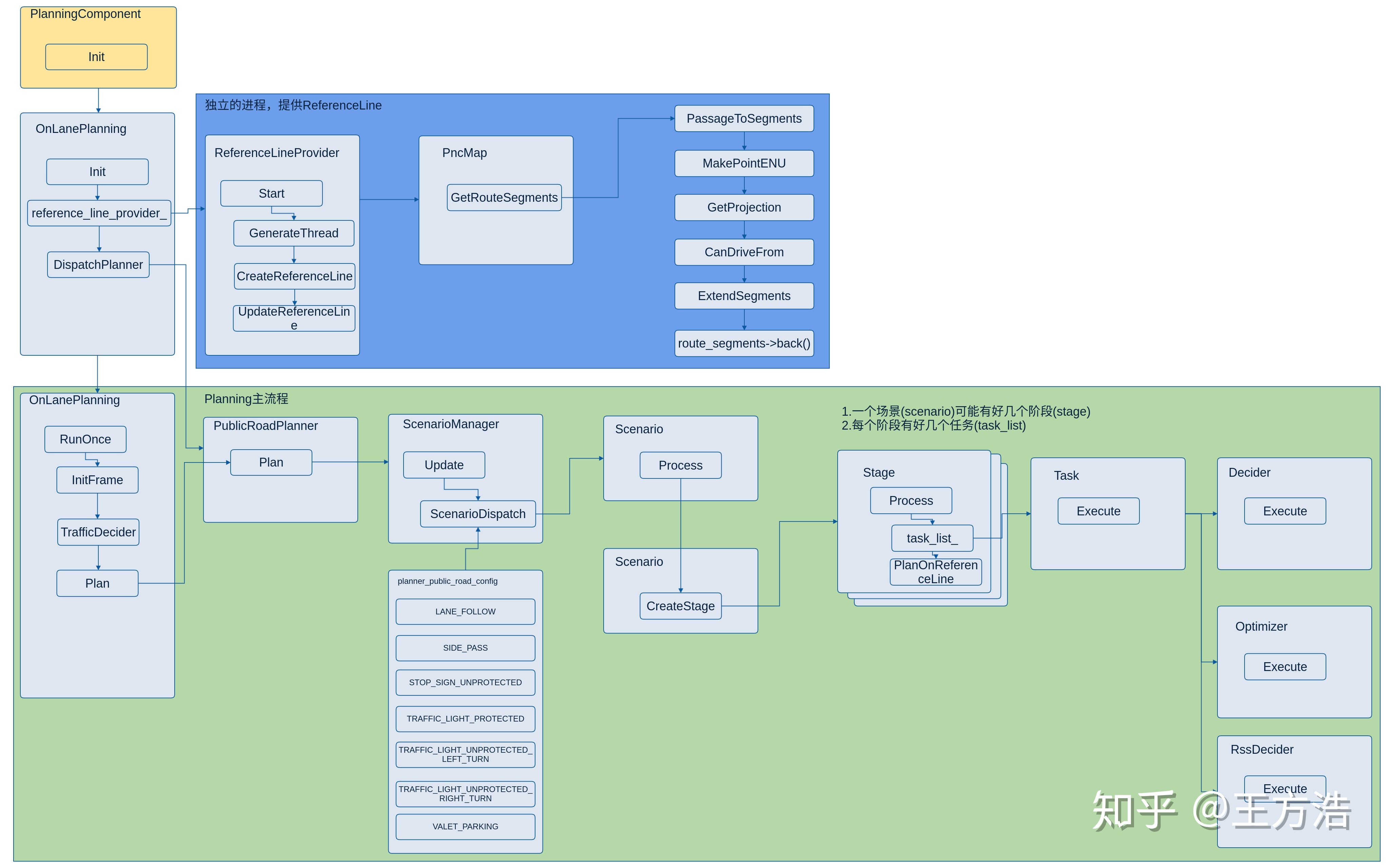
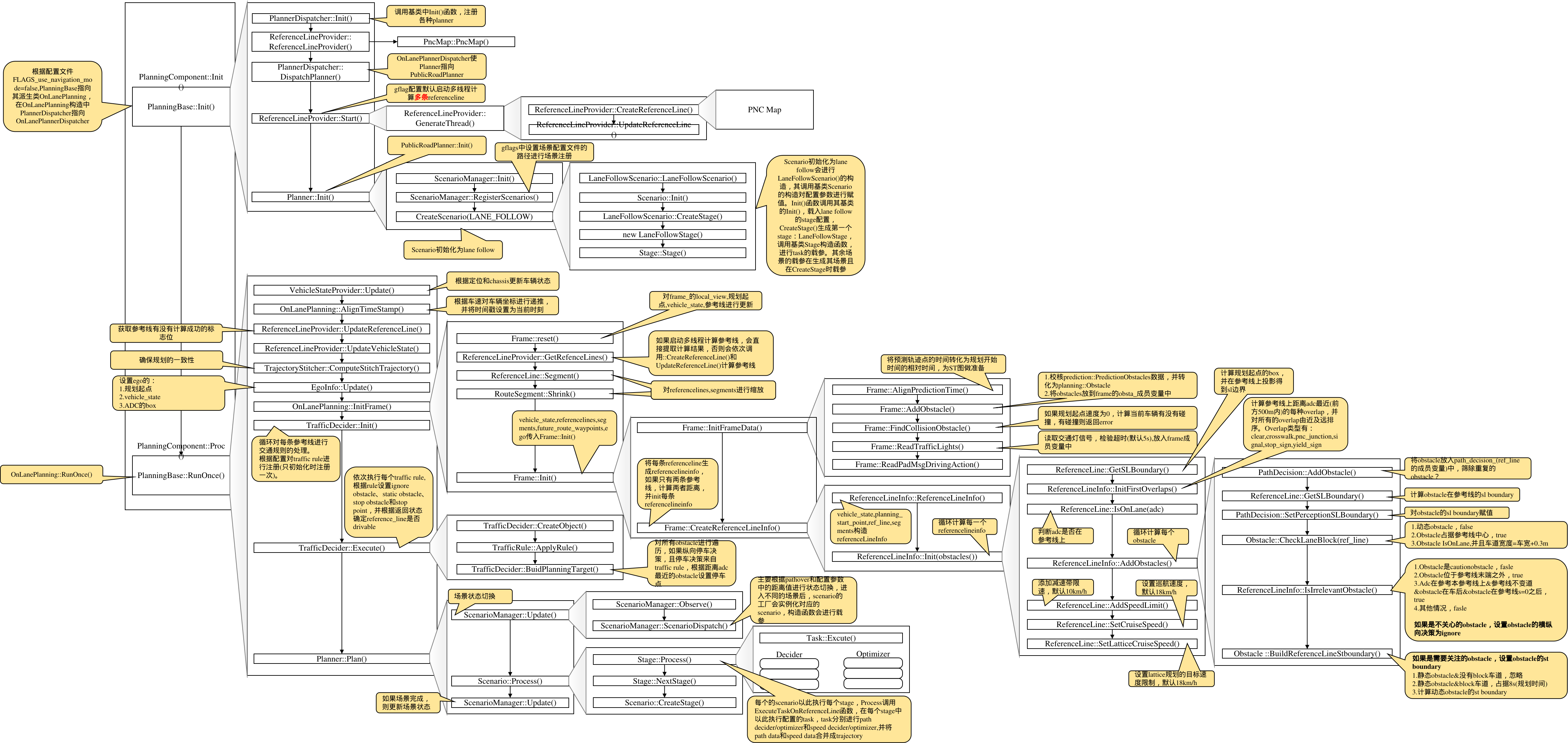
Planning主流程示意图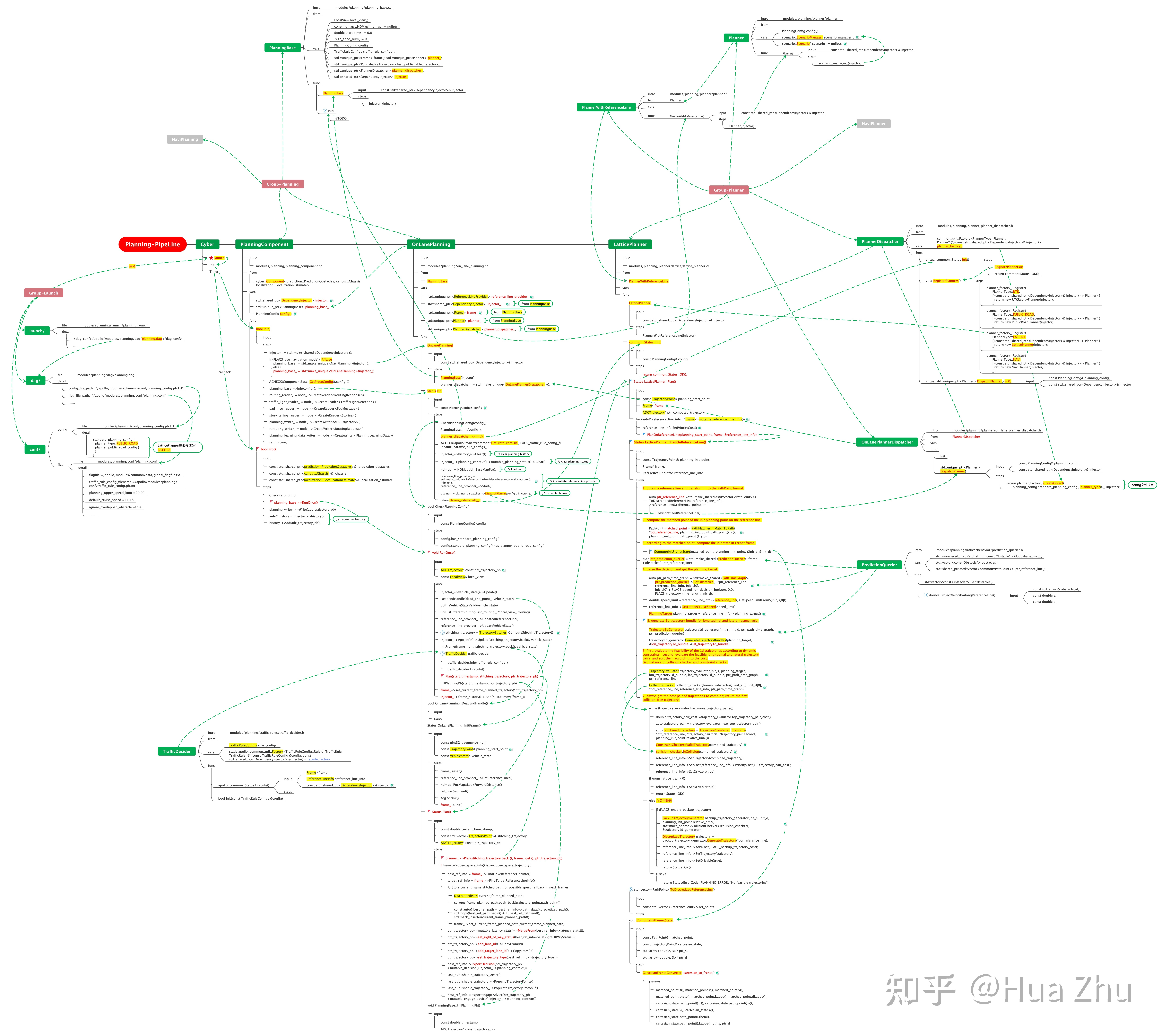
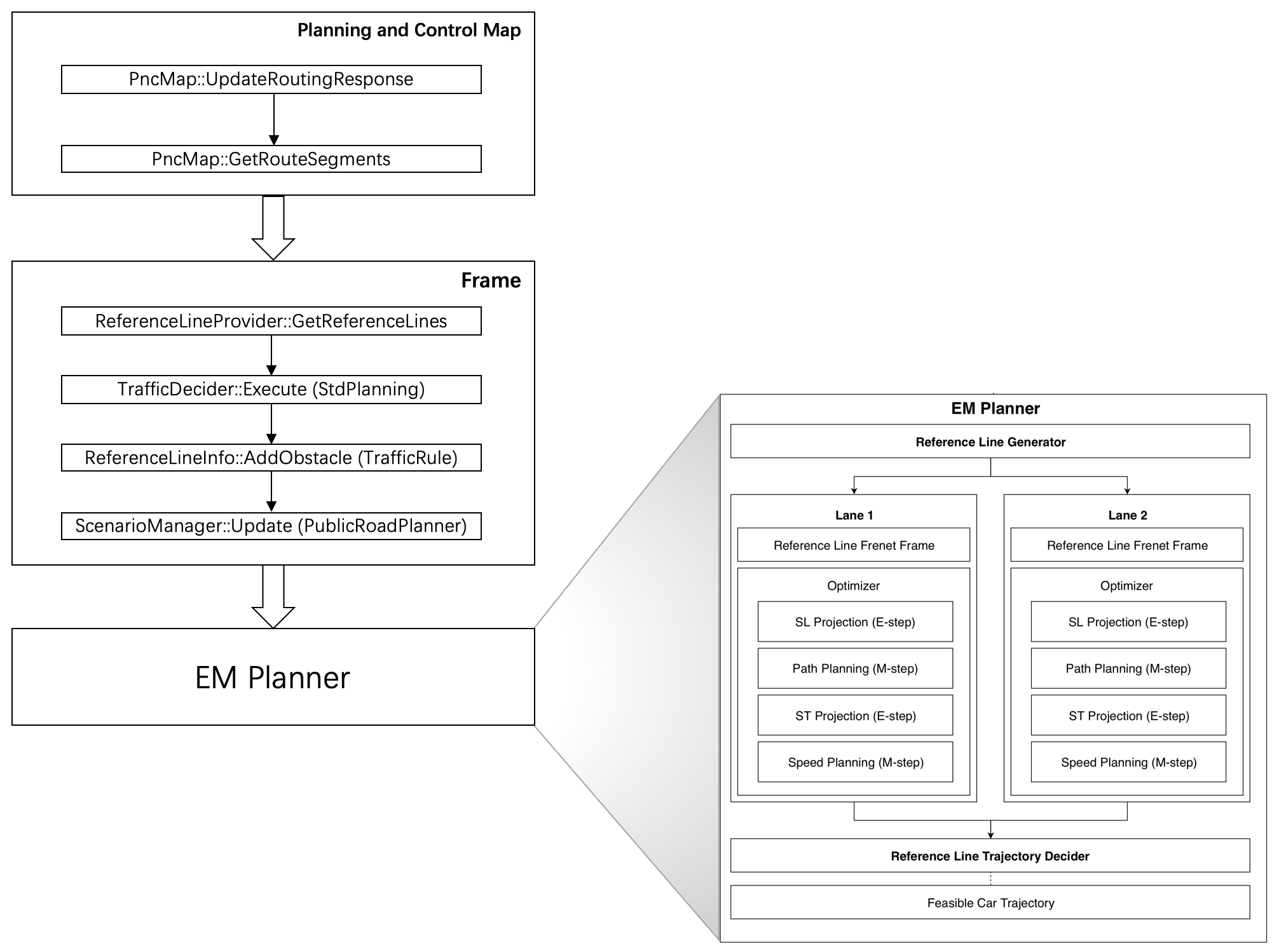
这里有三个主要部分需要说明:
PncMap:全称是Planning and Control Map。这个部分的实现并不在Planning内部,而是位于/modules/map/pnc_map/目录下。但是由于该实现与Planning模块紧密相关,因此这里放在一起讨论。该模块的主要作用是:根据Routing提供的数据,生成Planning模块需要的路径信息。Frame:Frame中包含了Planning一次计算循环中需要的所有数据。例如:地图,车辆状态,参考线,障碍物信息等等。ReferenceLine是车辆行驶的参考线,TrafficDecider与交通规则相关,这两个都是Planning中比较重要的子模块,因此会在下文中专门讲解。EM Planner:下文中我们会看到,Apollo系统中内置了好几个Planner,但目前默认使用的是EM Planner(现已改为Piece wise Jerk),这也是专门为开放道路设计的。该模块的实现可以说是整个Planning模块的灵魂所在。
Planning模块基础数据结构
Planning模块是一个比较大的模块,因此这其中有很多的数据结构需要在内部实现中流转。
这些数据结构集中定义在两个地方:
proto目录:该目录下都是通过Protocol Buffers格式定义的结构。这些结构会在编译时生成C++需要的文件。这些结构没有业务逻辑,就是专门用来存储数据的。(实际上不只是Planning,几乎每个大的模块都会有自己的proto文件夹。)common目录:这里是C++定义的数据结构。很显然,通过C++定义数据结构的好处是这些类的实现中可以包含一定的处理逻辑。
proto相关
Commen相关
common目录下的头文件如下:
apollo/modules/planning/common/
├── decision_data.h
├── dependency_injector.h
├── ego_info.h
├── feature_output.h
├── frame.h
├── history.h
├── indexed_list.h
├── indexed_queue.h
├── learning_based_data.h
├── local_view.h
├── message_process.h
├── obstacle.h
├── obstacle_blocking_analyzer.h
├── open_space_info.h
├── path
│ ├── discretized_path.h
│ ├── frenet_frame_path.h
│ └── path_data.h
├── path_boundary.h
├── path_decision.h
├── planning_context.h
├── planning_gflags.h
├── reference_line_info.h
├── smothers
│ └── smother.h
├── speed
│ ├── speed_data.h
│ ├── st_boundary.h
│ └── st_point.h
├── speed_limit.h
├── speed_profile_generator.h
├── st_graph_data.h
├── trajectory
│ ├── discretized_trajectory.h
│ └── publishable_trajectory.h
├── trajectory1d
│ ├── constant_deceleration_trajectory1d.h
│ ├── constant_jerk_trajectory1d.h
│ ├── piecewise_acceleration_trajectory1d.h
│ ├── piecewise_jerk_trajectory1d.h
│ ├── piecewise_trajectory1d.h
│ └── standing_still_trajectory1d.h
├── trajectory_evaluator.h
├── trajectory_stitcher.h
└── util
├── common.h
├── math_util.h
└── util.h这里有如下一些结构值得我们注意:
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
EgoInfo类 | 包含了自车信息,例如:当前位置点,车辆状态,外围Box等。 |
Frame类 | 包含了一次Planning计算循环中的所有信息。障碍物&参考线&交通规则融合器 |
FrameManager类 | Frame的管理器,每个Frame会有一个整数型id。 |
LocalView类 | Planning计算需要的输入,下文将看到其定义。 |
Obstacle类 | 描述一个特定的障碍物。障碍物会有一个唯一的id来区分。 |
PlanningContext类 | Planning全局相关的信息,例如:是否正在变道。这是一个单例。 |
ReferenceLineInfo类 | 车辆行驶的参考线,下文会专门讲解。 |
path文件夹 | 描述车辆路线信息。包含:PathData,DiscretizedPath,FrenetFramePath三个类。 |
speed文件夹 | 描述车辆速度信息。包含SpeedData,STPoint,StBoundary三个类。 |
trajectory文件夹 | 描述车辆轨迹信息。包含DiscretizedTrajectory,PublishableTrajectory,TrajectoryStitcher三个类。 |
planning_gflags.h | 定义了模块需要的许多常量,例如各个配置文件的路径。 |
ReferenceLineInfo对ReferenceLine类进行了封装,为Planning模块提供了平滑的指令执行序列。 Frame包含了所有的数据依赖关系,例如包含了预测路径信息的障碍物,自动驾驶车辆的状态等。 HD-Map在Planning模块内作为封装了多个数据的库使用,提供不同特点的地图数据查询需求。
Planner
Planning与Planner、PlanningCycle
modules/palnning/on_line_planning 中的RunOnce函数
/**
* @brief main logic of the planning module, runs periodically triggered by
* timer.
*/
void RunOnce(const LocalView& local_view,
ADCTrajectory* const ptr_trajectory_pb) override;这是Planning模块的主体逻辑,会被timer以固定的间隔调用。每次调用就是一个规划周期。
Planner配置
Planner的配置文件路径 modules/planning/planner/on_lane_planner_dispatcher_test.cc
class OnLanePlannerDispatcherTest : public ::testing::Test {
public:
virtual void SetUp() {}
protected:
std::unique_ptr<PlannerDispatcher> pd_;
};
TEST_F(OnLanePlannerDispatcherTest, Simple) {
auto injector = std::make_shared<DependencyInjector>();
pd_.reset(new OnLanePlannerDispatcher());
pd_->Init();
const std::string planning_config_file =
"/apollo/modules/planning/conf/planning_config.pb.txt";
PlanningConfig planning_config;
apollo::cyber::common::GetProtoFromFile(planning_config_file,
&planning_config);
auto planner = pd_->DispatchPlanner(planning_config, injector);
EXPECT_EQ(planner->Name(), "PUBLIC_ROAD");
}planning/conf/planning_config.pb.txt
topic_config {
chassis_topic: "/apollo/canbus/chassis"
hmi_status_topic: "/apollo/hmi/status"
localization_topic: "/apollo/localization/pose"
planning_pad_topic: "/apollo/planning/pad"
planning_trajectory_topic: "/apollo/planning"
prediction_topic: "/apollo/prediction"
relative_map_topic: "/apollo/relative_map"
routing_request_topic: "/apollo/routing_request"
routing_response_topic: "/apollo/routing_response"
story_telling_topic: "/apollo/storytelling"
traffic_light_detection_topic: "/apollo/perception/traffic_light"
}
standard_planning_config {
planner_type: PUBLIC_ROAD
planner_public_road_config {
}
}PublicRoadPlanner
PublicRoadPlanner是目前默认的Planner
Planner的算法实现依赖于两个输入:
- 车辆自身状态:通过
TrajectoryPoint描述。该结构中包含了车辆的位置,速度,加速度,方向等信息。 - 当前环境信息:通过
Frame描述。前面我们已经提到,Frame中包含了一次Planning计算循环中的所有信息。
在Frame中有一个数据结构值得我们重点关于一下,那就是LocalView。这个类在前面我们也已经提到过。它的定义如下:
struct LocalView {
std::shared_ptr<prediction::PredictionObstacles> prediction_obstacles;
std::shared_ptr<canbus::Chassis> chassis;
std::shared_ptr<localization::LocalizationEstimate> localization_estimate;
std::shared_ptr<perception::TrafficLightDetection> traffic_light;
std::shared_ptr<routing::RoutingResponse> routing;
std::shared_ptr<relative_map::MapMsg> relative_map;
std::shared_ptr<PadMessage> pad_msg;
std::shared_ptr<storytelling::Stories> stories;
};从这个定义中可以看到,这个结构中包含了这些信息:
- 障碍物的预测信息
- 车辆底盘信息
- 大致定位信息
- 交通灯信息
- 导航路由信息
- 相对地图信息
对于每个Planner来说,其主要的逻辑都实现在Plan方法中。PublicRoadPlanner::Plan方法的实现逻辑如下:
palnning/palnner/public_rode/public_rode_palnner.cc
Status PublicRoadPlanner::Plan(const TrajectoryPoint& planning_start_point,
Frame* frame,
ADCTrajectory* ptr_computed_trajectory) {
//确定当前的场景:因为Frame中包含了当前状态的所有信息,所以通过它就可以确定目前是处于哪一个场景下。
scenario_manager_.Update(planning_start_point, *frame);
//获取当前Scenario。
scenario_ = scenario_manager_.mutable_scenario();
//针对当前场景,进行处理
auto result = scenario_->Process(planning_start_point, frame);
if (FLAGS_enable_record_debug) {
auto scenario_debug = ptr_computed_trajectory->mutable_debug()
->mutable_planning_data()
->mutable_scenario();
scenario_debug->set_scenario_type(scenario_->scenario_type());
scenario_debug->set_stage_type(scenario_->GetStage());
scenario_debug->set_msg(scenario_->GetMsg());
}
if (result == scenario::Scenario::STATUS_DONE) {
// only updates scenario manager when previous scenario's status is
// STATUS_DONE
// 如果处理成功,则再次通过ScenarioManager更新。
scenario_manager_.Update(planning_start_point, *frame);
} else if (result == scenario::Scenario::STATUS_UNKNOWN) {
return Status(common::PLANNING_ERROR, "scenario returned unknown");
}
return Status::OK();
}这段代码的几个关键步骤是:
- 确定当前Scenario:因为Frame中包含了当前状态的所有信息,所以通过它就可以确定目前是处于哪一个场景下。
- 获取当前Scenario。
- 通过Scenario进行具体的处理。
- 如果处理成功,则再次通过ScenarioManager更新。
Scenario
Frenet坐标系
ReferenceLine
ReferenceLineProvider
ReferenceLineProvider是一个很庞大的类
创建ReferenceLine
ReferenceLine是在OnLanePlanning::InitFrame函数中生成的,相关代码如下:
Status OnLanePlanning::InitFrame(const uint32_t sequence_num,
const TrajectoryPoint& planning_start_point,
const VehicleState& vehicle_state) {
frame_.reset(new Frame(sequence_num, local_view_, planning_start_point,
vehicle_state, reference_line_provider_.get()));
if (frame_ == nullptr) {
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, "Fail to init frame: nullptr.");
}
std::list<ReferenceLine> reference_lines;
std::list<hdmap::RouteSegments> segments;
if (!reference_line_provider_->GetReferenceLines(&reference_lines,
&segments)) {
const std::string msg = "Failed to create reference line";
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
......ReferenceLineInfo
在ReferenceLine之外,在common目录下还有一个结构:ReferenceLineInfo,这个结构才是各个模块实际用到数据结构,它其中包含了ReferenceLine,但还有其他更详细的数据。
从ReferenceLine到ReferenceLineInfo是在Frame::CreateReferenceLineInfo中完成的。
palnning/commen/frame.cc
bool Frame::CreateReferenceLineInfo(
const std::list<ReferenceLine> &reference_lines,
const std::list<hdmap::RouteSegments> &segments) {
reference_line_info_.clear();
auto ref_line_iter = reference_lines.begin();
auto segments_iter = segments.begin();
while (ref_line_iter != reference_lines.end()) {
if (segments_iter->StopForDestination()) {
is_near_destination_ = true;
}
reference_line_info_.emplace_back(vehicle_state_, planning_start_point_,
*ref_line_iter, *segments_iter);
++ref_line_iter;
++segments_iter;
}
......ReferenceLineInfo不仅仅包含了参考线信息,还包含了车辆状态,路径信息,速度信息,决策信息以及轨迹信息等。Planning模块中跟参考线有关的算法都是基于ReferenceLineInfo结构完成的。
palnning/scenarios/stage.cc 中的ExecuteTaskOnReferenceLine函数
bool Stage::ExecuteTaskOnReferenceLine(
const common::TrajectoryPoint& planning_start_point, Frame* frame) {
for (auto& reference_line_info : *frame->mutable_reference_line_info()) {
if (!reference_line_info.IsDrivable()) {
AERROR << "The generated path is not drivable";
return false;
}
for (auto* task : task_list_) {
const double start_timestamp = Clock::NowInSeconds();
const auto ret = task->Execute(frame, &reference_line_info);
const double end_timestamp = Clock::NowInSeconds();
const double time_diff_ms = (end_timestamp - start_timestamp) * 1000;
ADEBUG << "after task[" << task->Name()
<< "]: " << reference_line_info.PathSpeedDebugString();
ADEBUG << task->Name() << " time spend: " << time_diff_ms << " ms.";
RecordDebugInfo(&reference_line_info, task->Name(), time_diff_ms);
if (!ret.ok()) {
AERROR << "Failed to run tasks[" << task->Name()
<< "], Error message: " << ret.error_message();
break;
}
}
if (reference_line_info.speed_data().empty()) {
*reference_line_info.mutable_speed_data() =
SpeedProfileGenerator::GenerateFallbackSpeed(injector_->ego_info());
reference_line_info.AddCost(kSpeedOptimizationFallbackCost);
reference_line_info.set_trajectory_type(ADCTrajectory::SPEED_FALLBACK);
} else {
reference_line_info.set_trajectory_type(ADCTrajectory::NORMAL);
}
DiscretizedTrajectory trajectory;
if (!reference_line_info.CombinePathAndSpeedProfile(
planning_start_point.relative_time(),
planning_start_point.path_point().s(), &trajectory)) {
AERROR << "Fail to aggregate planning trajectory.";
return false;
}
reference_line_info.SetTrajectory(trajectory);
reference_line_info.SetDrivable(true);
return true;
}
return true;
}ReferenceLineSmooth
TrafficRule
- TrafficRule配置
- TrafficDecider
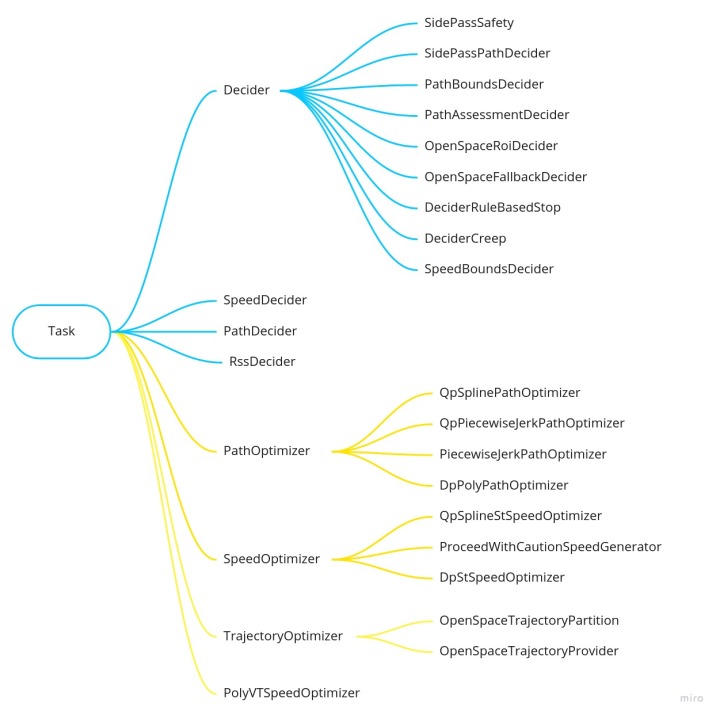
Task
- Task配置
- Task读取
- Task执行
总结:
main函数在Cyber/mainboard,加载动态链接库
PlanningComponent(PlanningBase)
Init()
proc() 定时触发改为消息触发
RunOnce()
InitFrame()
Plan()
Planer->Plan()
可执行程序层:Planning Dispatcher根据车辆的状态和其他信息,调用合适的Planner
app层:每种planner分成多个场景 Scenario(ScenarioManager),每个场景又分解成多个Stage
conf文件夹,Scenario配置文件
lib层:每个stage又分解成可执行的Task(包括不同的deciders,optimizers库),Task是一组实现决策任务和各种优化的无状态库。
参考链接:
Apollo_Planning模块架构和概述_WangN2的博客-CSDN博客_apollo planning
【开发者讲堂】学习笔记——Cyber工具使用示例_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
【开发者讲堂】算法部分_PlanningComponent__Init_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
Apollo Planning Frame_落羽归尘的博客-CSDN博客
【开发者讲堂】Parking与Public_road示例_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 18:40
apollo介绍之planning模块(四) - 知乎 王方浩
【机器人】无人车-运动规划-Apollo6.0-planning模块代码框架梳理(一)--整体结构 - 知乎
【机器人】无人车-运动规划-Apollo6.0-planning模块代码框架梳理(二)--PlanningComponent - 知乎
Baidu Apollo代码解析之Planning的结构与调用流程(1) - 知乎
Baidu Apollo代码解析之Planning的结构与调用流程(2) - 知乎
Apollo 3.5 各功能模块的启动过程解析_知行合一2018的博客-CSDN博客_apollo启动流程
Apollo Planning模块源代码分析_知行合一2018的博客-CSDN博客_apollo planning
保罗的酒吧,写了一系列精彩的文章:
最后
以上就是俭朴爆米花最近收集整理的关于Apollo 中 Planning 模块的框架Planning模块Planning模块基础数据结构PlannerScenarioFrenet坐标系ReferenceLineTrafficRuleTask参考链接:的全部内容,更多相关Apollo内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复