前言
上篇作业1
本篇继续更新作业2相关。
作业2相关链接
games的作业2链接
我的源码
作业2简述
- 在作业1的基础上栅格化一个三角形
- 判断点是否在三角形内
- (提高)使用Supersampling抗锯齿
作业2相关知识笔记
- 光栅化算法:如何构建一个三角形的BoundingBox
- Depth buffer(Z-Buffering)
- Antialising Supersampling(SSAA、MSAA)
作业2思路
注意:后面有代码展示,一定要自己先做一遍再看,而且我的设计不一定正确规范高效。
-
构建三角形BoundingBox
-
根据BoundingBox,遍历其中所有点判断是否在三角形内
-
若在点内,更新该点的Depth buffer
static bool insideTriangle(int x, int y, const Vector3f* _v) { // TODO : Implement this function to check if the point (x, y) is inside the triangle represented by _v[0], _v[1], _v[2] Eigen::Vector3f a1 = {_v[0].x()-_v[1].x(),_v[0].y()-_v[1].y(),0}; Eigen::Vector3f a2 = {_v[1].x()-_v[2].x(),_v[1].y()-_v[2].y(),0}; Eigen::Vector3f a3 = {_v[2].x()-_v[0].x(),_v[2].y()-_v[0].y(),0}; Eigen::Vector3f b1 = {x-_v[1].x(),y-_v[1].y(),0}; Eigen::Vector3f b2 = {x-_v[2].x(),y-_v[2].y(),0}; Eigen::Vector3f b3 = {x-_v[0].x(),y-_v[0].y(),0}; float c1,c2,c3; c1=a1.cross(b1).z(); c2=a2.cross(b2).z(); c3=a3.cross(b3).z(); if( (c1>=0 && c2>=0 && c3>=0) || (c1<0&&c2<0&&c3<0) )return true; else return false; }
对应三角形栅格化
void rst::rasterizer::rasterize_triangle(const Triangle& t) {
auto v = t.toVector4();
int x_max,x_min,y_max,y_min,index;
x_min=MIN(floor(v[0].x()),MIN(floor(v[1].x()),floor(v[2].x())));
x_max=MAX(ceil(v[0].x()),MAX(ceil(v[1].x()),ceil(v[2].x())));
y_min=MIN(floor(v[0].y()),MIN(floor(v[1].y()),floor(v[2].y())));
y_max=MAX(ceil(v[0].y()),MAX(ceil(v[1].y()),ceil(v[2].y())));
// TODO : Find out the bounding box of current triangle.
// iterate through the pixel and find if the current pixel is inside the triangle
for(int x=x_min;x<=x_max;x++){
for(int y=y_min;y<=y_max;y++){
if(insideTriangle(x+0.5,y+0.5,t.v)){
// If so, use the following code to get the interpolated z value.
auto[alpha, beta, gamma] = computeBarycentric2D(x, y, t.v);
float w_reciprocal = 1.0/(alpha / v[0].w() + beta / v[1].w() + gamma / v[2].w());
float z_interpolated = alpha * v[0].z() / v[0].w() + beta * v[1].z() / v[1].w() + gamma * v[2].z() / v[2].w();
z_interpolated *= w_reciprocal;
// TODO : set the current pixel (use the set_pixel function) to the color of the triangle (use getColor function) if it should be painted.
index=get_index(x,y);
if(z_interpolated<depth_buf[index]){
depth_buf[index]=z_interpolated;
set_pixel(Vector3f(x,y,1),t.getColor());
}
}
}
}
}
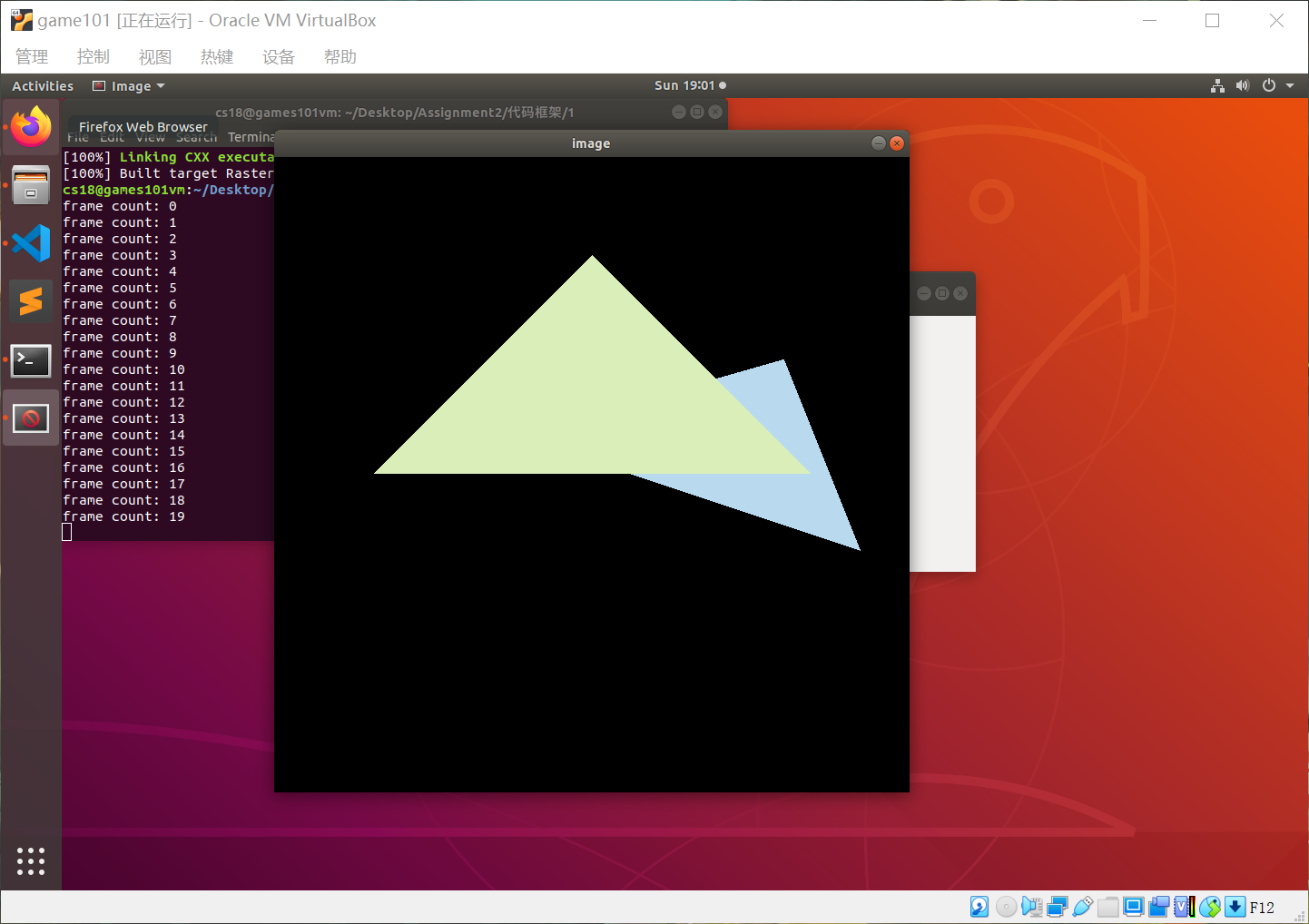
提高部分
采用Supersampling可以改善抗锯齿,注意对应的头文件也要进行对应函数参数修改。
这里我采用的是4xSSAA。观察锯齿变化需要将图像放大到像素级别。
注意SSAA的定义,本质上是扩大采样点,所以需要扩展depth-buffer和frame-buffer,然后再进行下采样。所以这里要维护新的sample-list。
void rst::rasterizer::rasterize_triangle(const Triangle& t) {
auto v = t.toVector4();
int x_max,x_min,y_max,y_min,index;
x_min=MIN(floor(v[0].x()),MIN(floor(v[1].x()),floor(v[2].x())));
x_max=MAX(ceil(v[0].x()),MAX(ceil(v[1].x()),ceil(v[2].x())));
y_min=MIN(floor(v[0].y()),MIN(floor(v[1].y()),floor(v[2].y())));
y_max=MAX(ceil(v[0].y()),MAX(ceil(v[1].y()),ceil(v[2].y())));
// TODO : Find out the bounding box of current triangle.
// iterate through the pixel and find if the current pixel is inside the triangle
for(int x=x_min;x<=x_max;x++){
for(int y=y_min;y<=y_max;y++){
float d[] = {0.0f,0.5f};
int inside_num = 0;
Eigen::Vector3f sample_list = {0,0,0};
for (int i=0;i<2;i++){
for (int j=0;j<2;j++){
float x1 = x + d[i];
float y1 = y + d[j];
if(insideTriangle(x1+0.25f,y1+0.25f,t.v)){
sample_list += t.getColor();
// If so, use the following code to get the interpolated z value.
auto[alpha, beta, gamma] = computeBarycentric2D(x1+0.25f, y1+0.25f, t.v);
float w_reciprocal = 1.0/(alpha / v[0].w() + beta / v[1].w() + gamma / v[2].w());
float z_interpolated = alpha * v[0].z() / v[0].w() + beta * v[1].z() / v[1].w() + gamma * v[2].z() / v[2].w();
z_interpolated *= w_reciprocal;
// TODO : set the current pixel (use the set_pixel function) to the color of the triangle (use getColor function) if it should be painted.
index=get_index(x,y,i,j);
if(z_interpolated<depth_buf[index]){
depth_buf[index]=z_interpolated;
inside_num++;
}
}
}
}
if(inside_num>0)
set_pixel(Vector3f(x,y,1),sample_list/4);
}
}
}
rst::rasterizer::rasterizer(int w, int h) : width(w), height(h)
{
frame_buf.resize(4* w *h);
depth_buf.resize(4* w *h);
}
static bool insideTriangle(float x, float y, const Vector3f* _v)
{
// TODO : Implement this function to check if the point (x, y) is inside the triangle represented by _v[0], _v[1], _v[2]
Eigen::Vector3f a1 = {_v[0].x()-_v[1].x(),_v[0].y()-_v[1].y(),0};
Eigen::Vector3f a2 = {_v[1].x()-_v[2].x(),_v[1].y()-_v[2].y(),0};
Eigen::Vector3f a3 = {_v[2].x()-_v[0].x(),_v[2].y()-_v[0].y(),0};
Eigen::Vector3f b1 = {x-_v[1].x(),y-_v[1].y(),0};
Eigen::Vector3f b2 = {x-_v[2].x(),y-_v[2].y(),0};
Eigen::Vector3f b3 = {x-_v[0].x(),y-_v[0].y(),0};
float c1,c2,c3;
c1=a1.cross(b1).z();
c2=a2.cross(b2).z();
c3=a3.cross(b3).z();
if( (c1>=0 && c2>=0 && c3>=0) || (c1<0&&c2<0&&c3<0) )return true;
else return false;
}
int rst::rasterizer::get_index(int x, int y, int i, int j)
{
return 4*((height-1-y)*width + x)+2*j+i;
}
对比一下效果
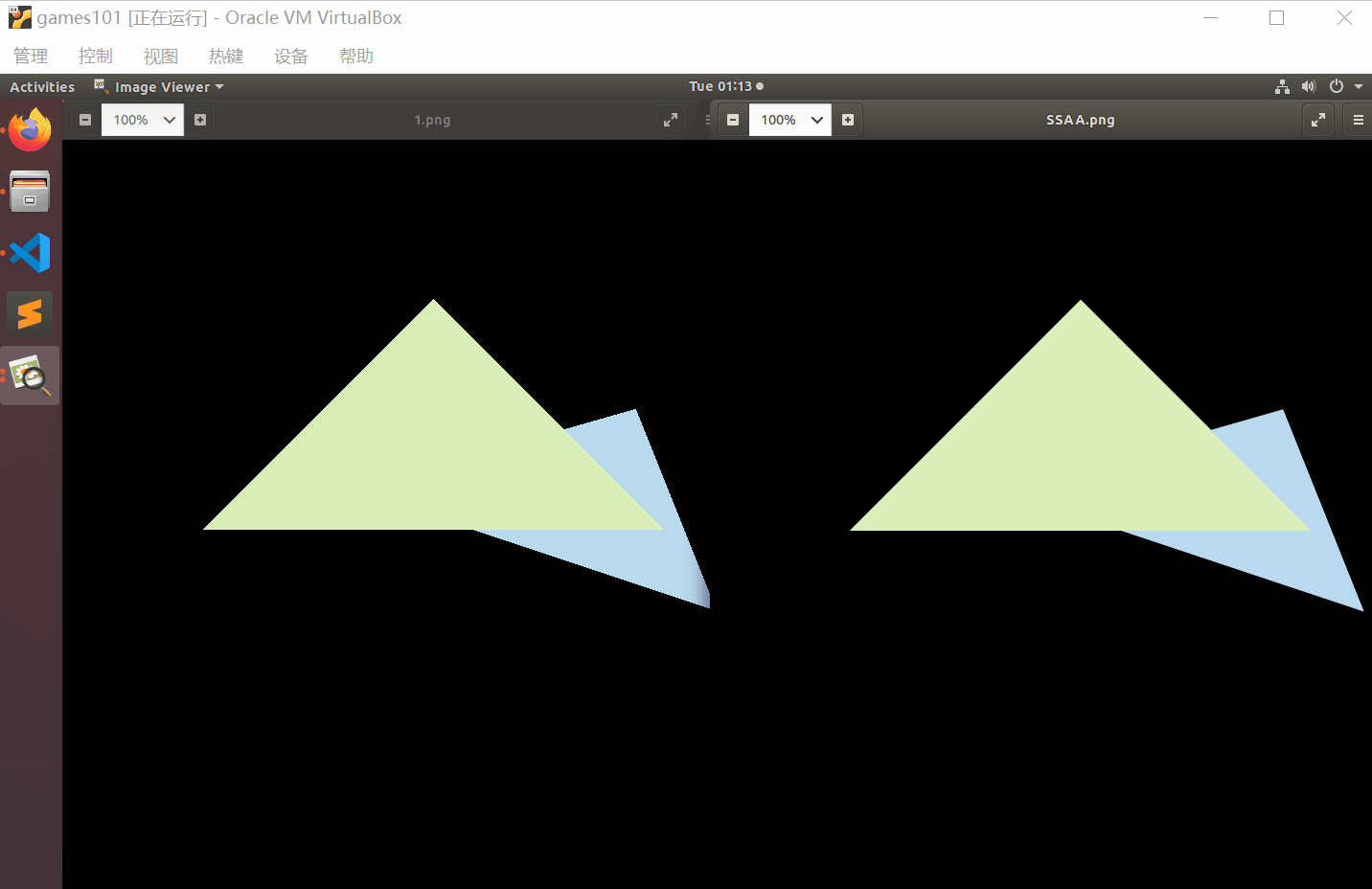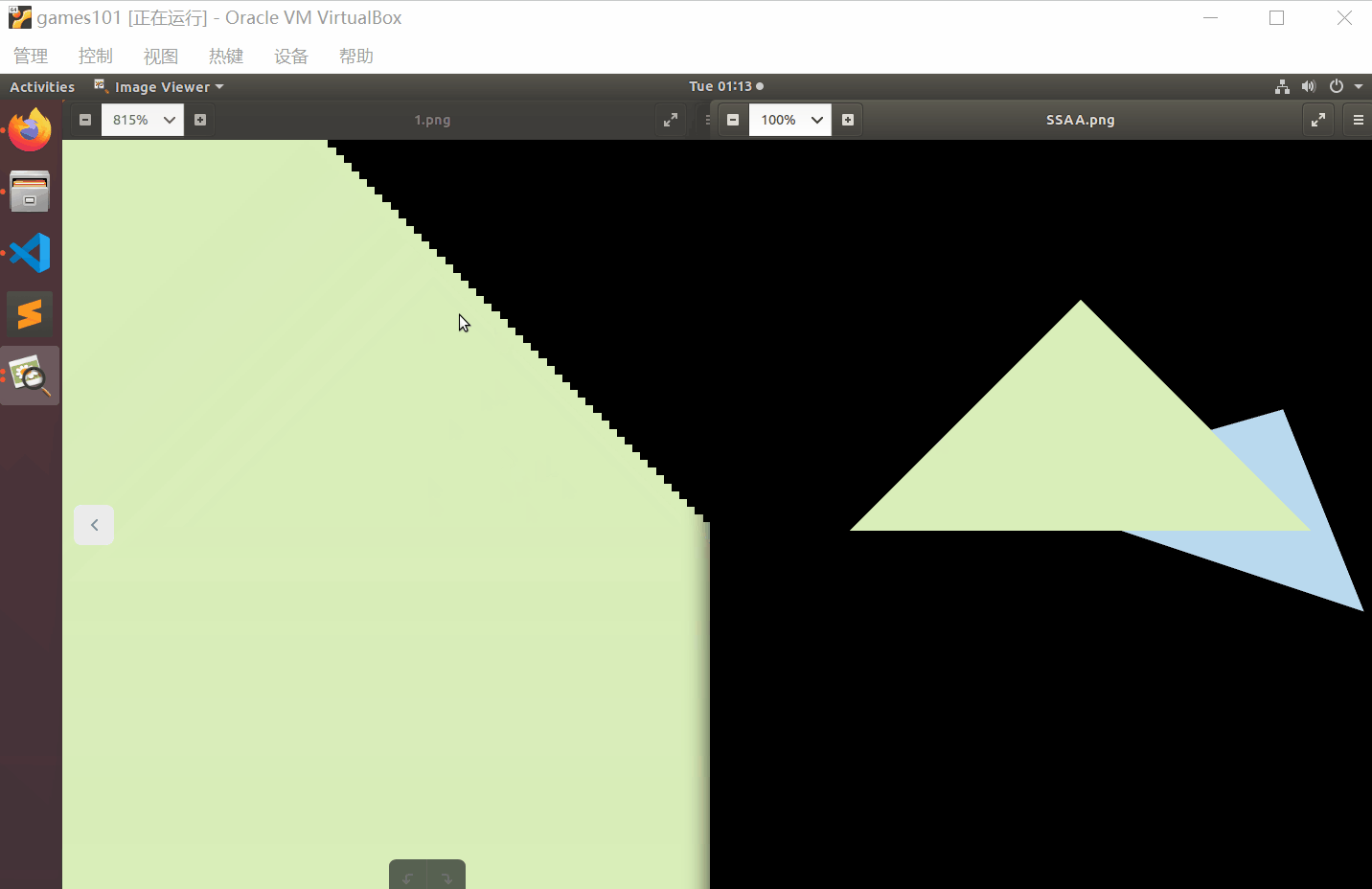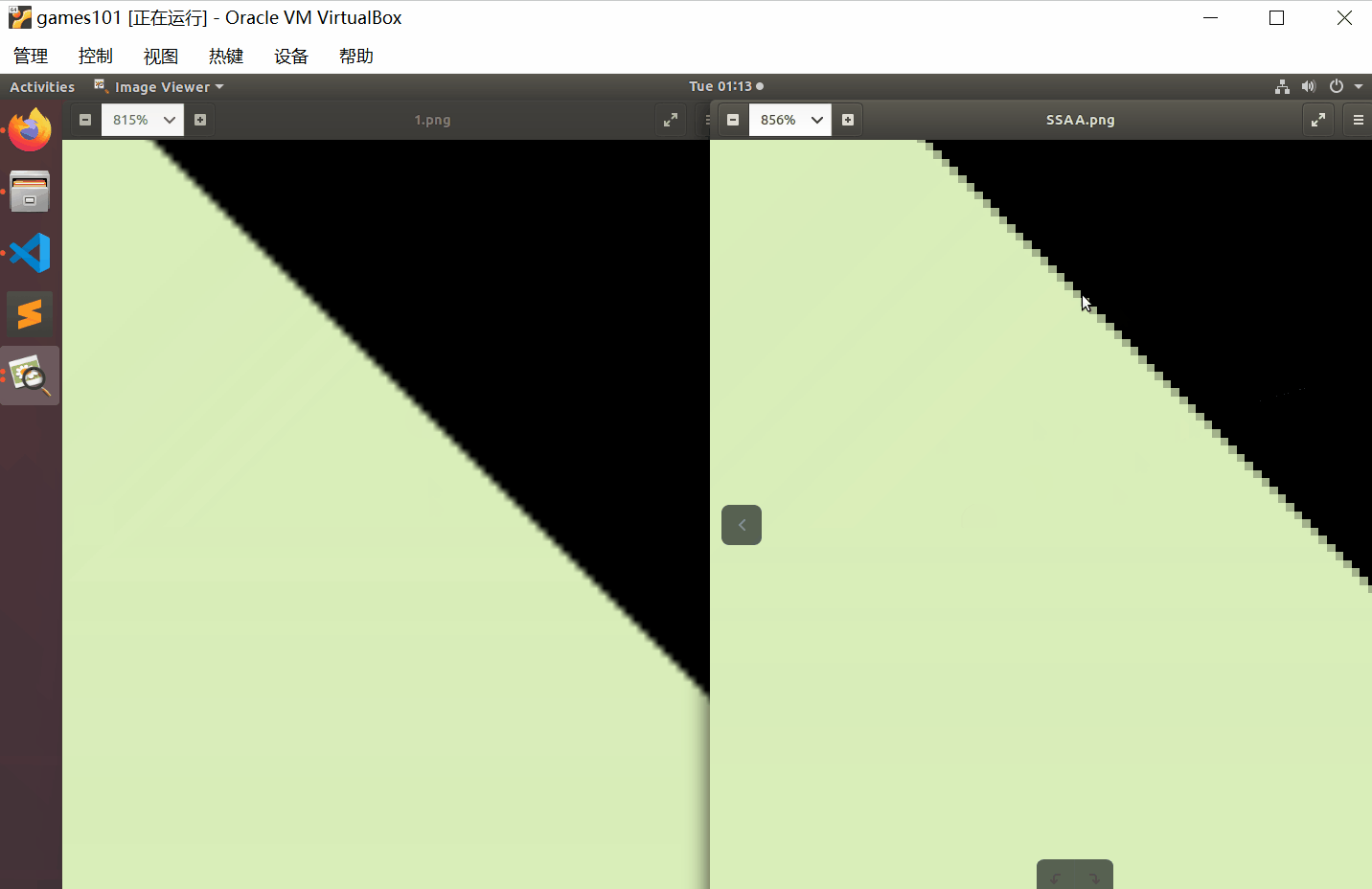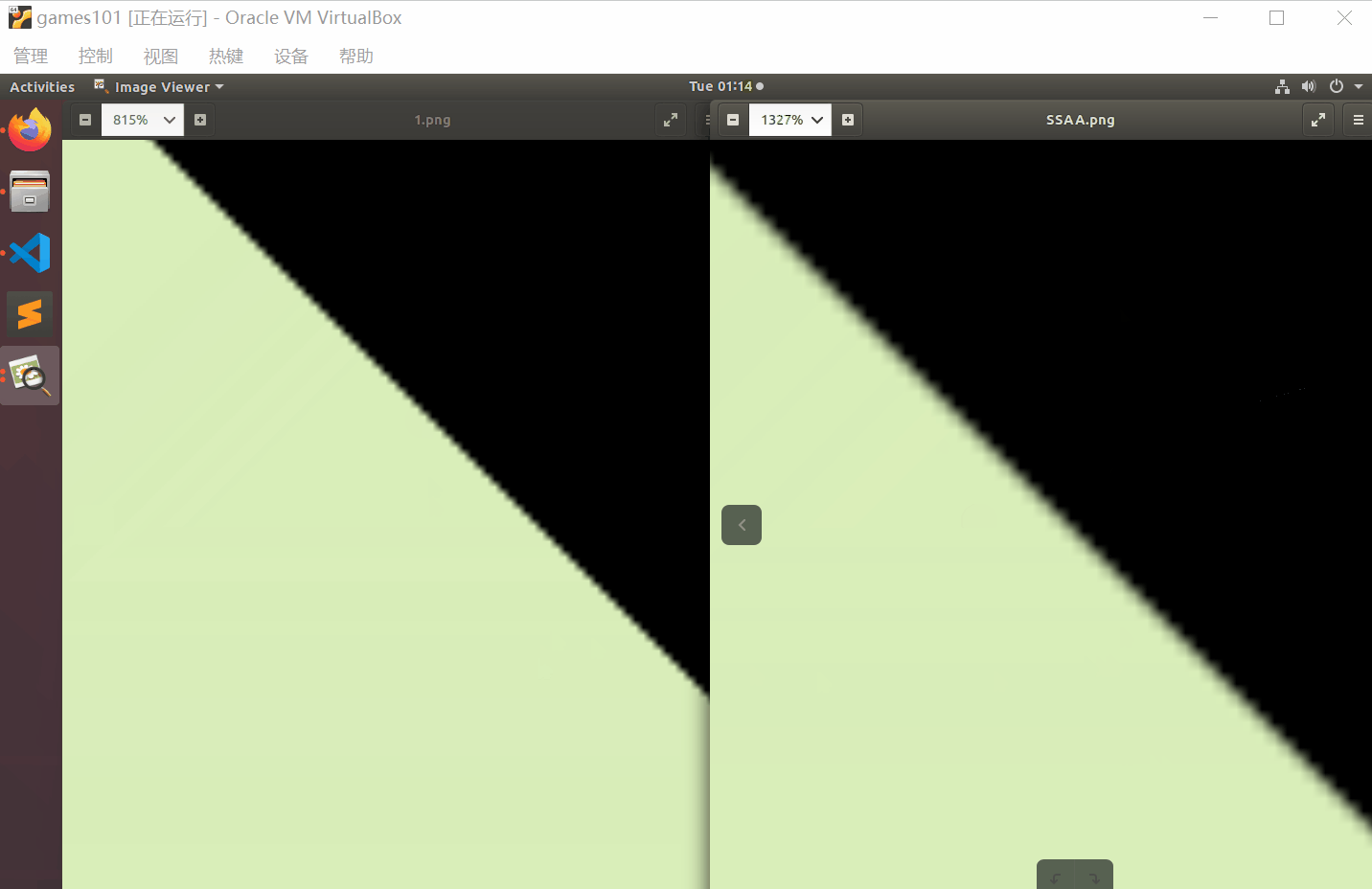
最后
以上就是温婉钢笔最近收集整理的关于GAMES101-现代计算机图形学学习笔记(3)作业2的全部内容,更多相关GAMES101-现代计算机图形学学习笔记(3)作业2内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复