文章目录
- 向量 Vectors
- 矩阵
- 变换
向量 Vectors
- Dot product
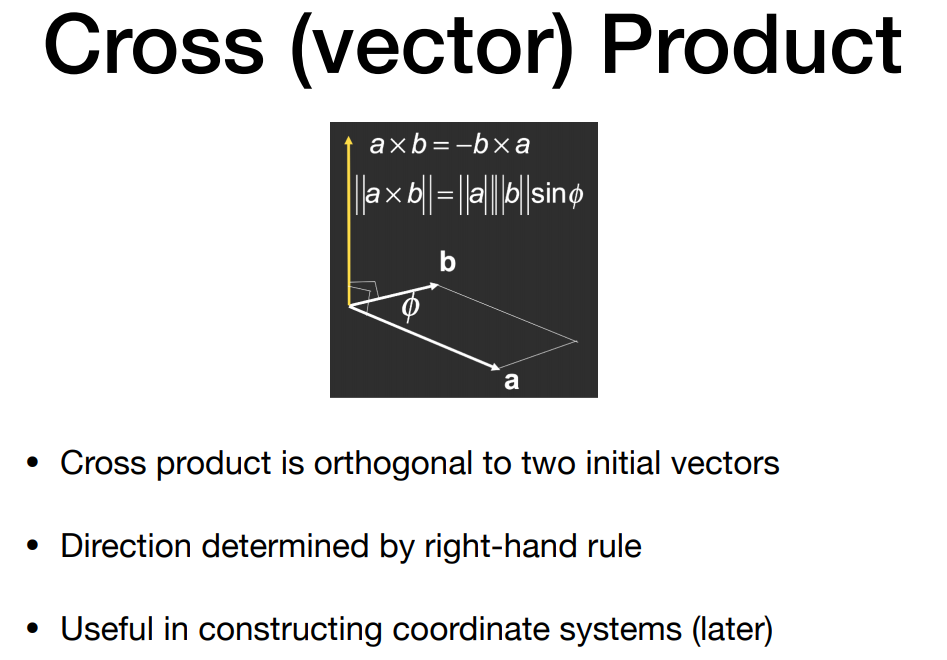
- Cross product
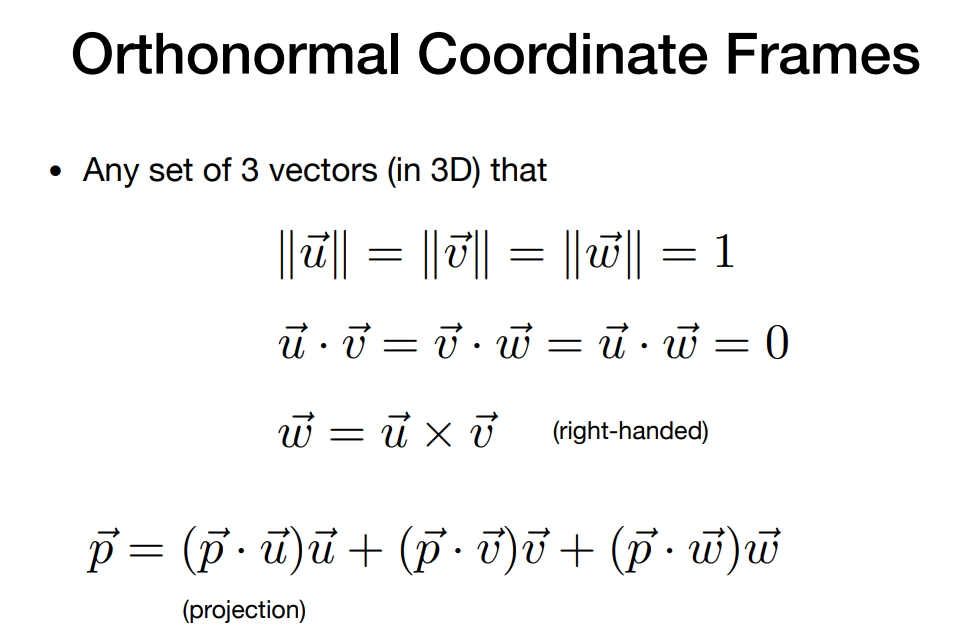
- Orthonormal bases and coordinate frames
- Dot product
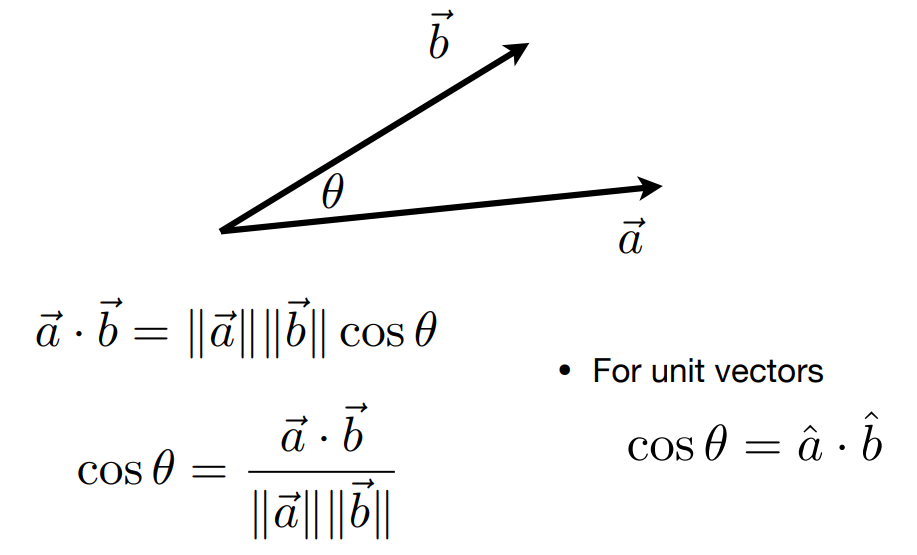
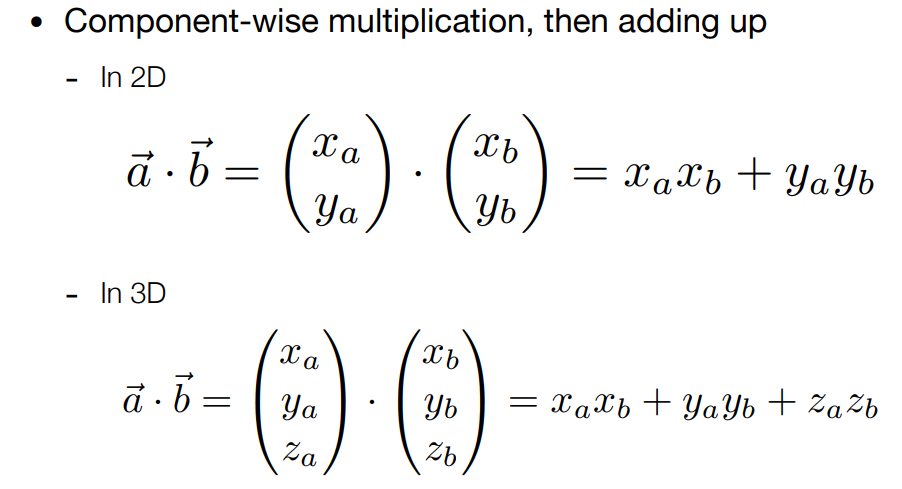
Dot Product in Graphics
- Find angle between two vectors (e.g. cosine of angle between light source and surface)
- Finding projection of one vector on another
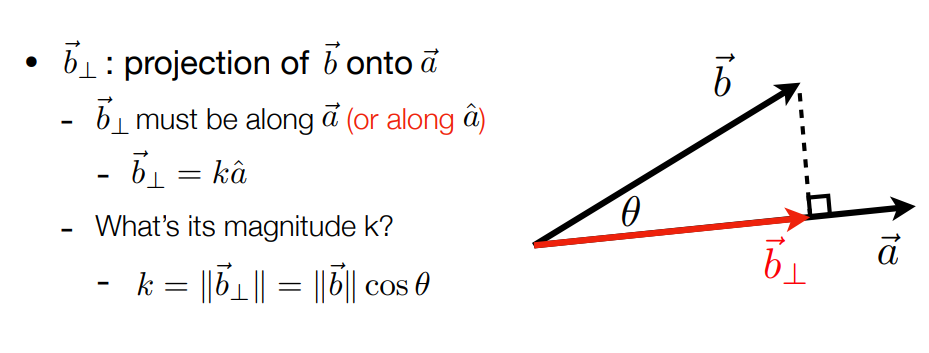
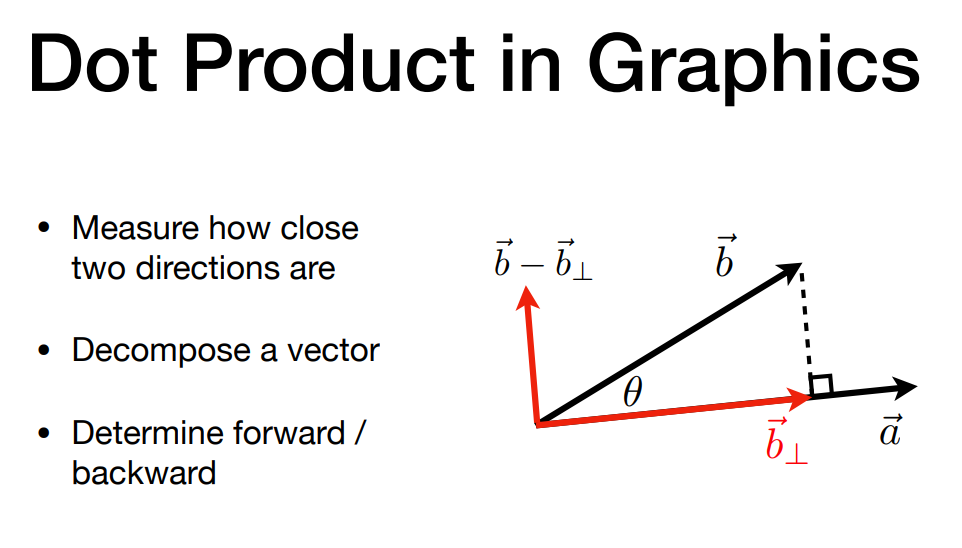
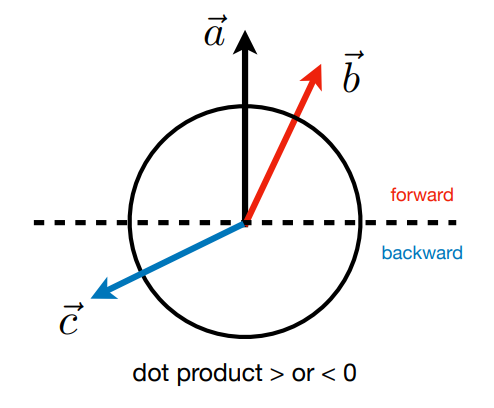
1.向量的点乘可以告诉我们方向性(基本一致、基本相反、基本垂直)
2.两个向量在方向上有多接近
- Cross product
右手螺旋定则,拇指方向即两向量叉乘后结果的方向。(也就意味着叉积不满足交换律)
如果在一个坐标系中,向量x叉乘向量y得到向量z,就假设这是右手系。
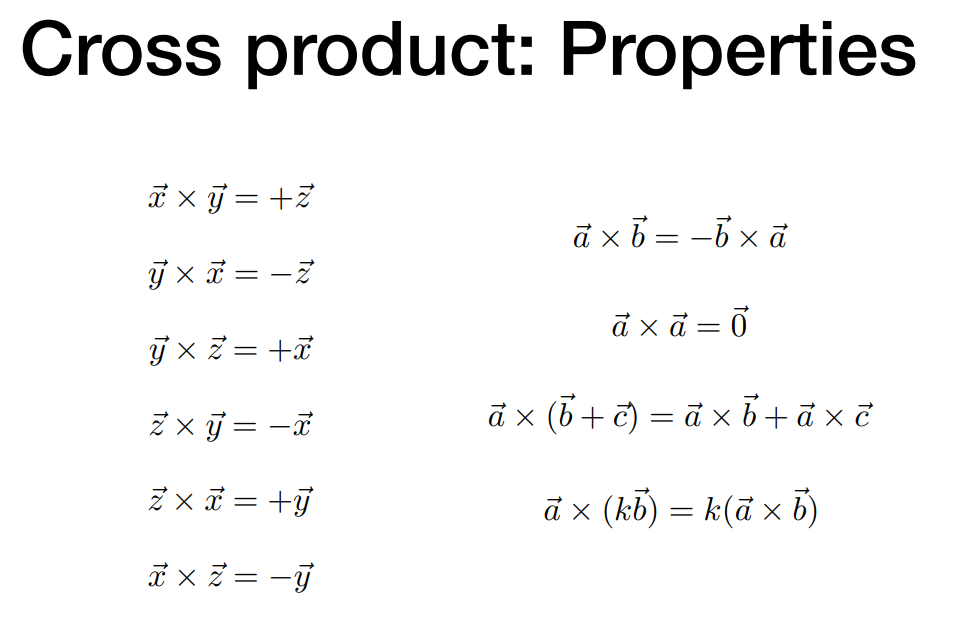
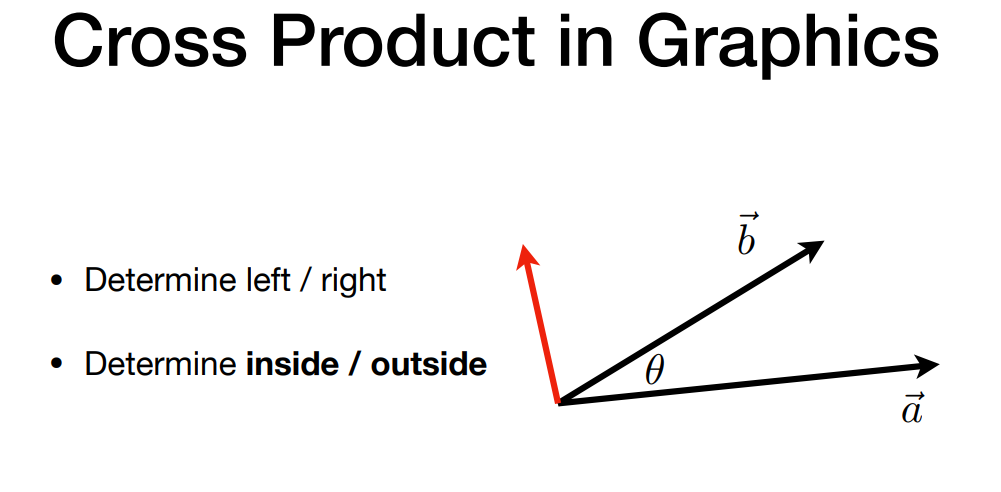
a叉乘b,右手螺旋定则可得到z为正,即b在a左侧;即a在b右侧。
判断p点是否在三角形内部?
AB叉乘AP,得到的结果向外,即p点在AB左侧,同理得到P点在BC左侧,也在CA左侧。
对于任何三角形(不管输入为逆时针或顺时针),P点一直在三条边的左边(或三条边的右边),那么P点就在三角形内部。
定义一个坐标系:
矩阵
Matrices
Matrix-Matrix Multiplication
- Properties
Non-commutative(AB and BA are different in general)
Associative and distributive
-(AB)C=A(BC)
-A(B+C) = AB + AC
-(A+B)C = AC + BC
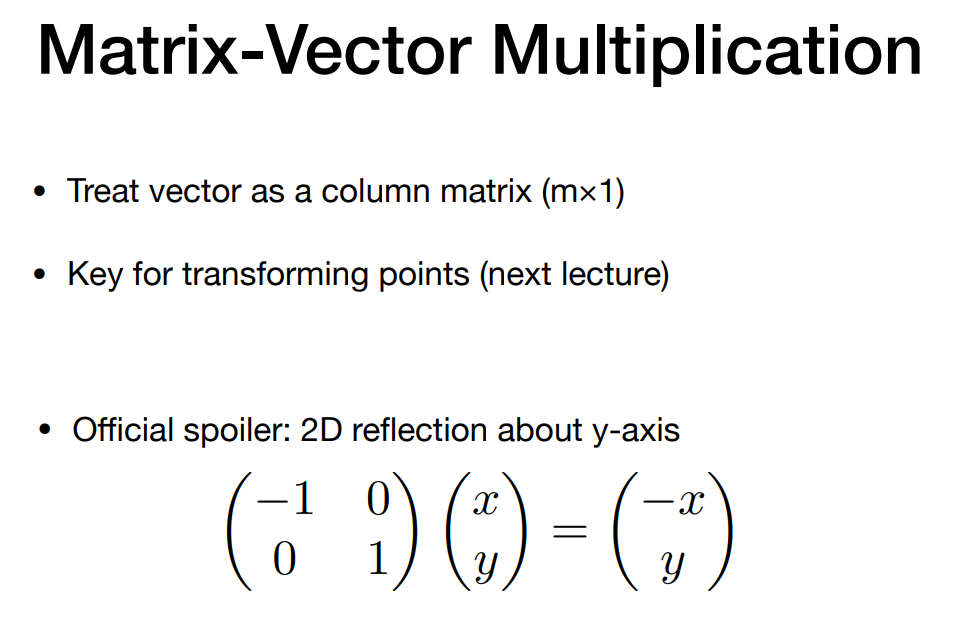
把一个向量看成列向量,矩阵在左,向量在右
- Transpose of a Matrix
- Identity Matrix and Inverses
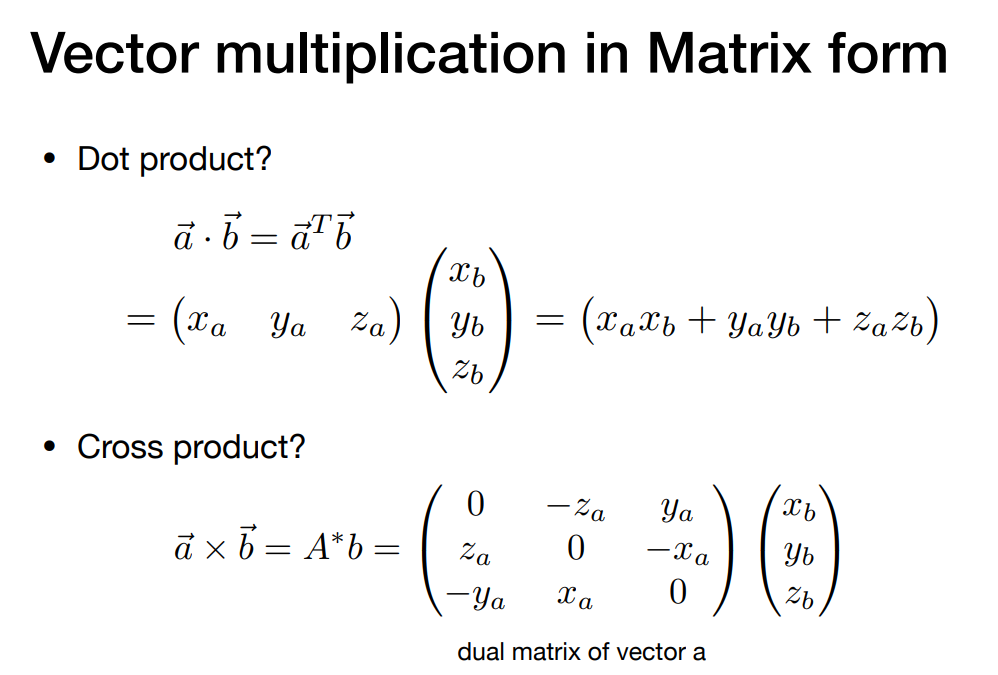
- Vector multiplication in Matrix form
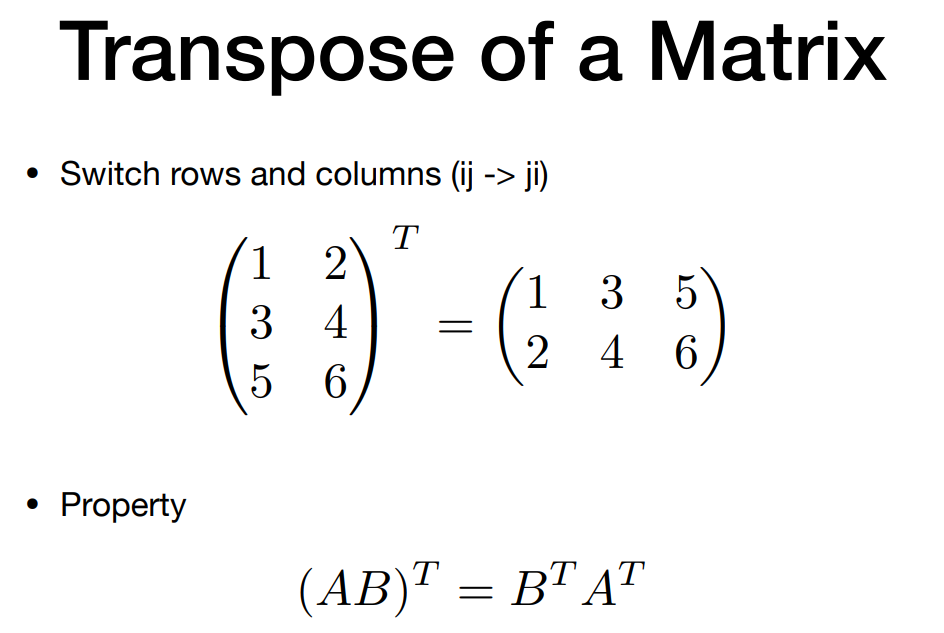
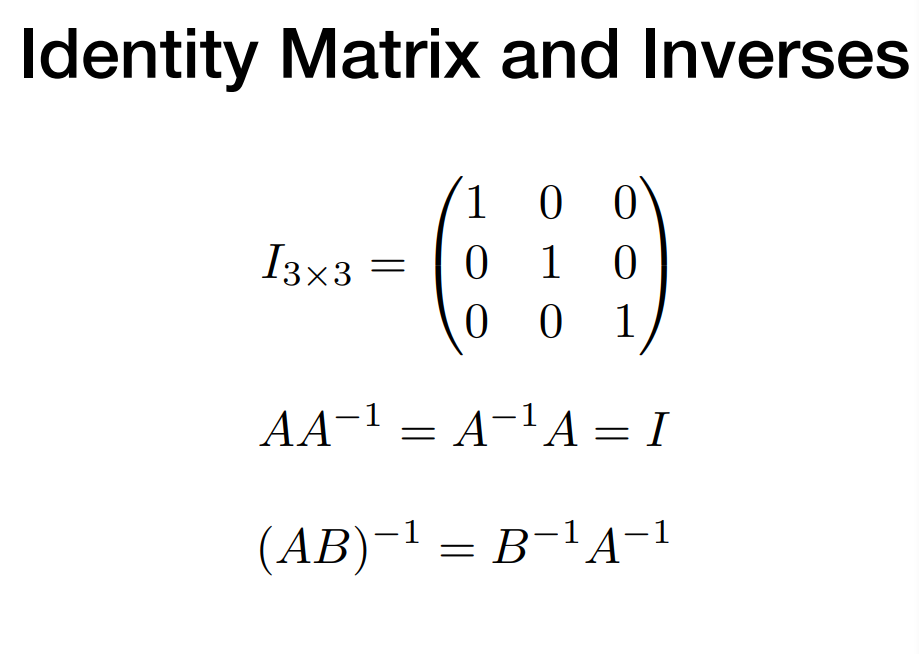
变换
transformation
- Modeling
- Viewing
2D transformations
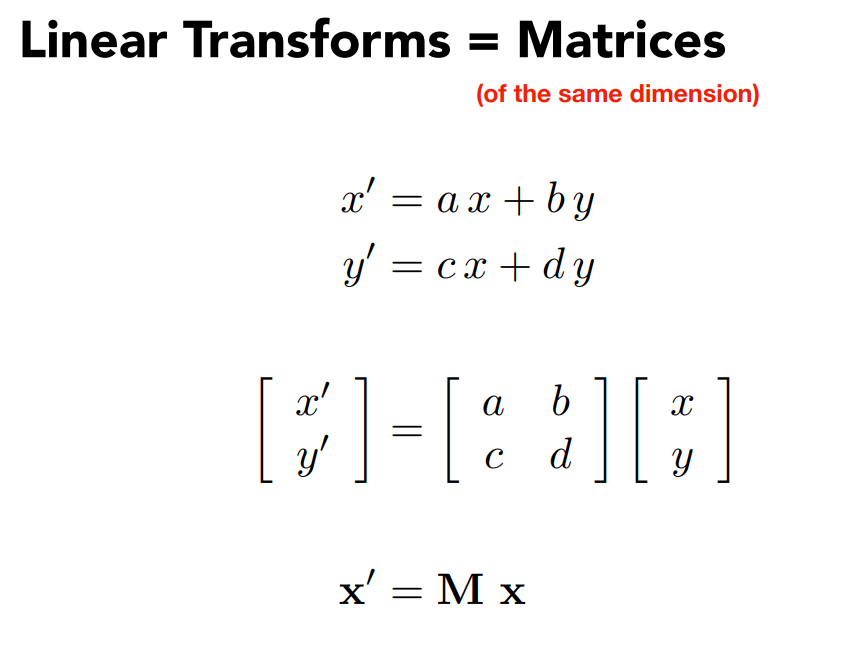
- Representing transformations using matrices
- Rotation, scale, shear
Homogeneous coordinates
- Why homogeneous coordinates
- Affine transformation
2D:
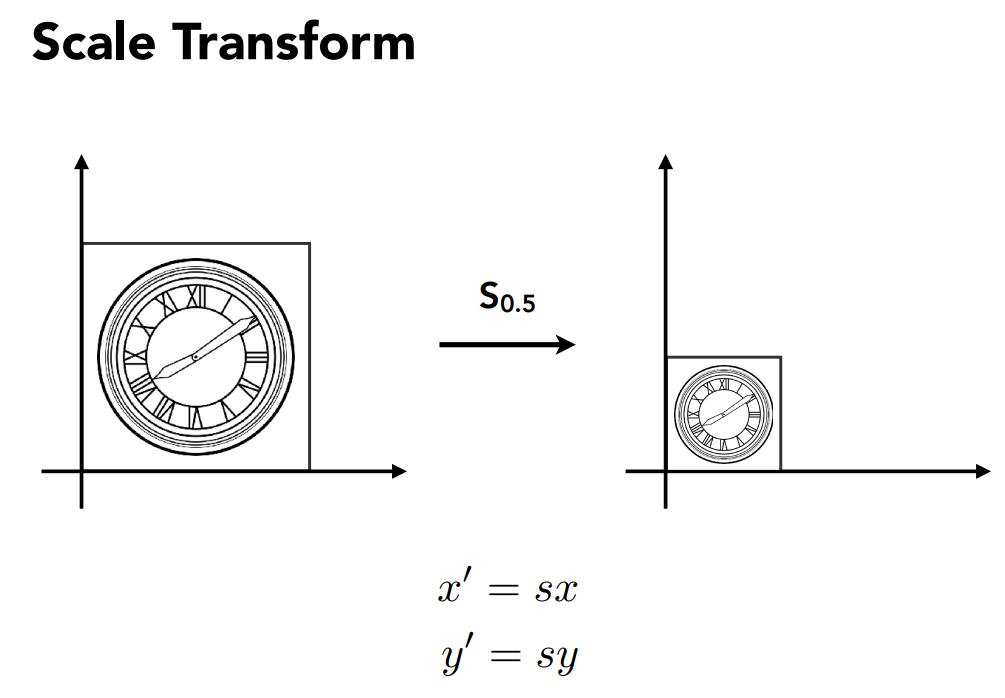
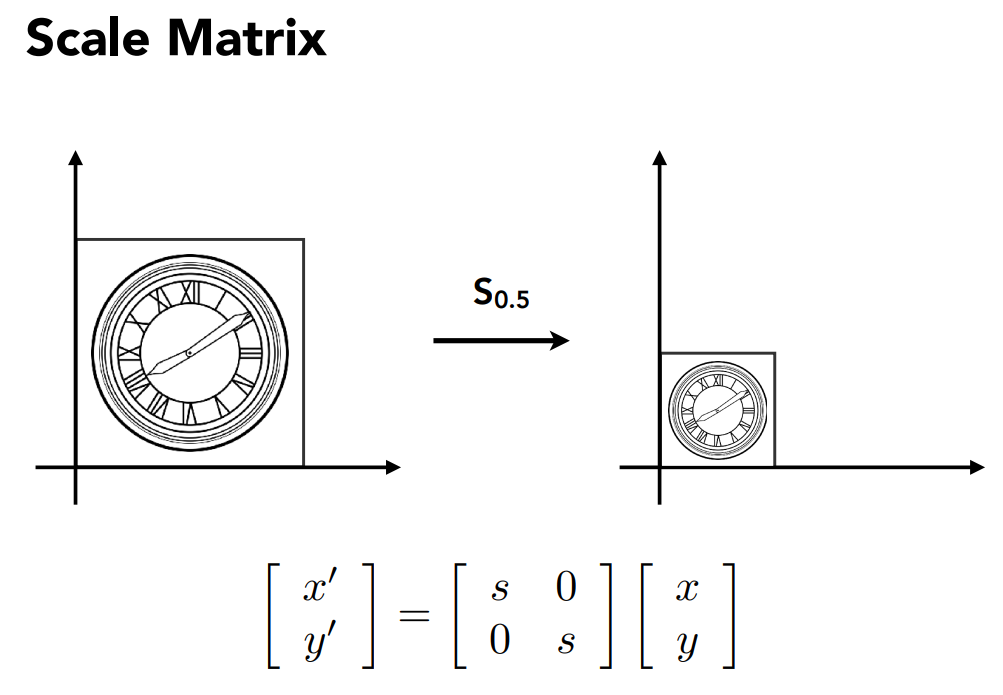
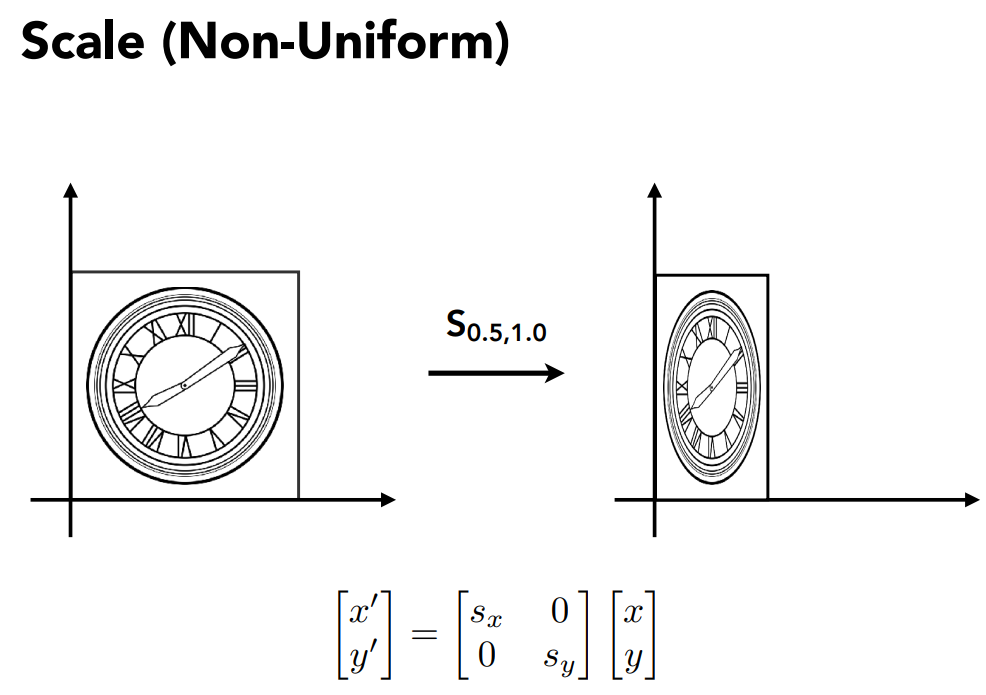
缩放:
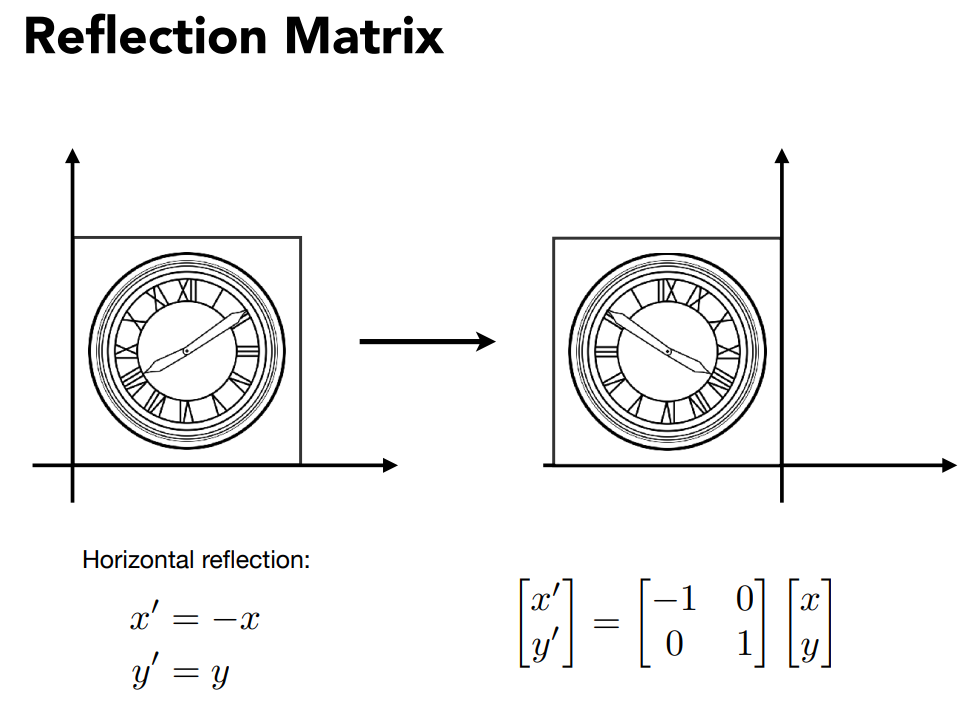
镜像
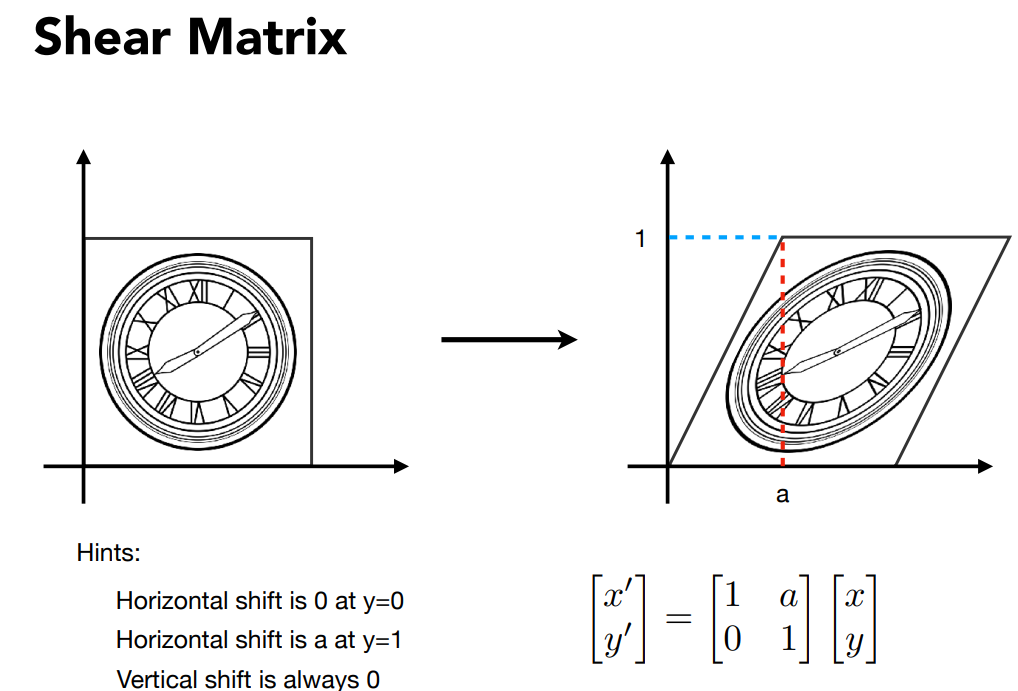
切变:
比如在二分之一a处,水平方向的移动是二分之一乘以a,即a乘以y,可得任何x在水平方向上的移动都是a乘以y
旋转矩阵:
Rotate (about the origin (0, 0), CCW by default)
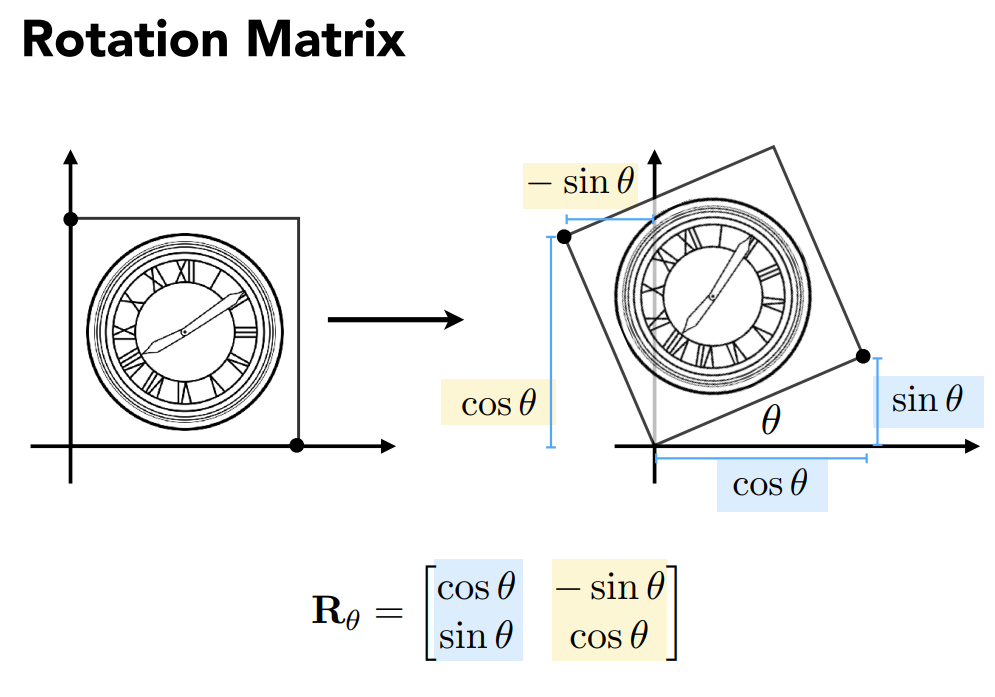
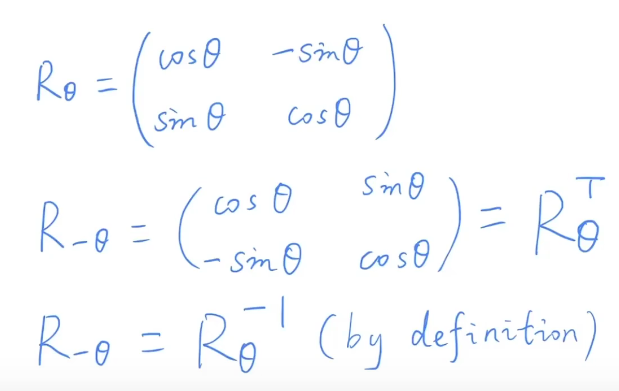
注:一个矩阵的逆等于它的转置,即为正交矩阵
通过两个特殊点推出旋转公式
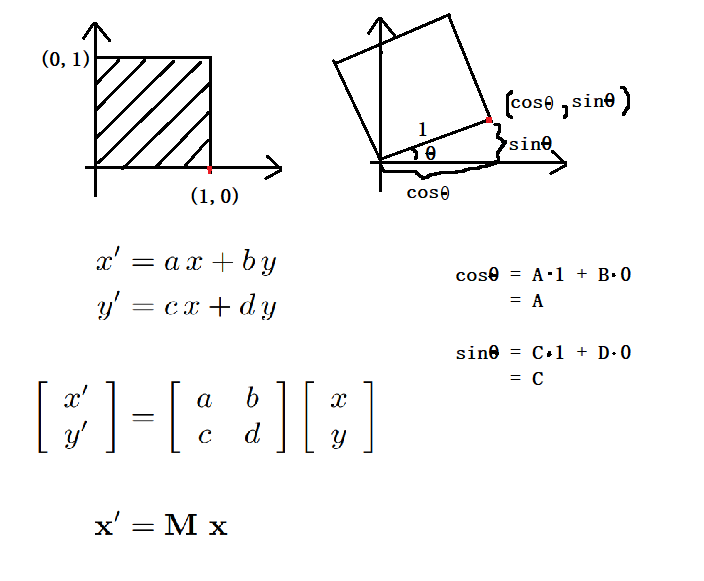
线性变换(写成矩阵形式)
Homogeneous coordinates 齐次坐标
如下平移操作:
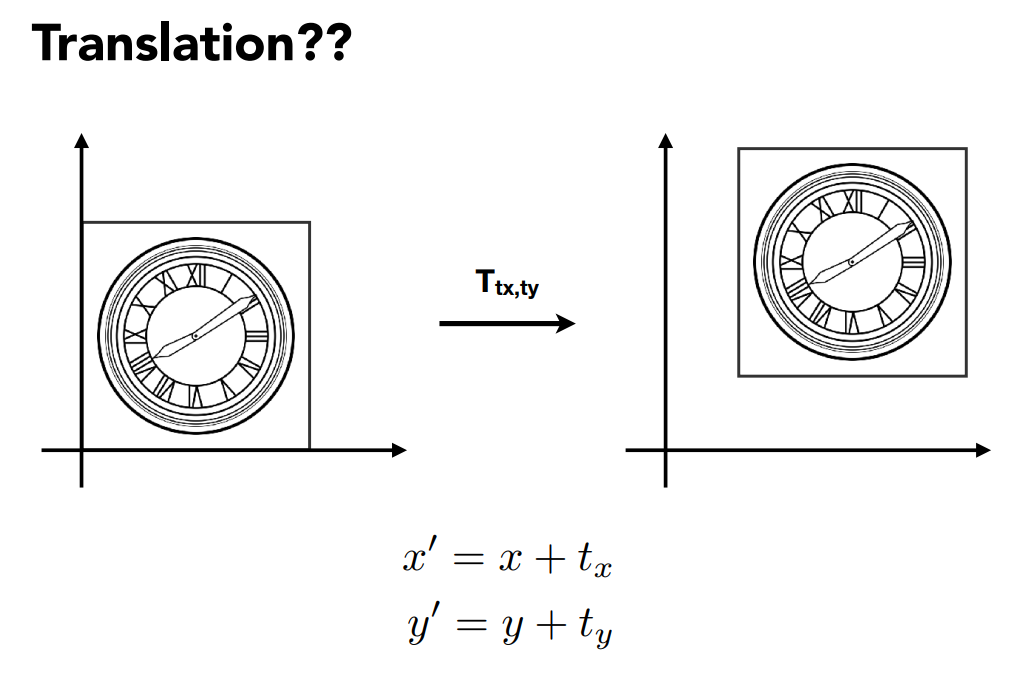
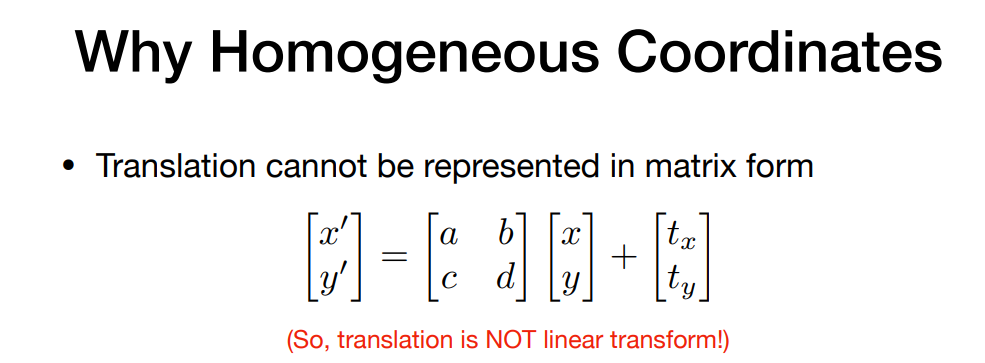
这就不是线性变换了,但我们不想让平移成为一个特例,于是引入了齐次坐标。
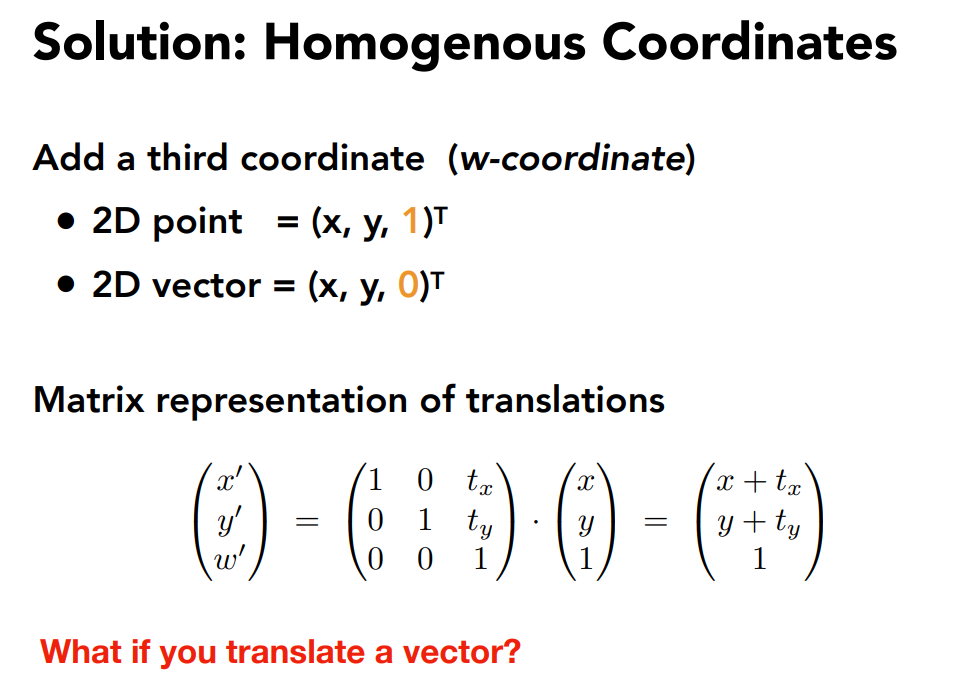 向量具有平移不变性,向量的最后一个维度增加一个0,目的是让平移后不变,并且让以下操作正确:
向量具有平移不变性,向量的最后一个维度增加一个0,目的是让平移后不变,并且让以下操作正确:
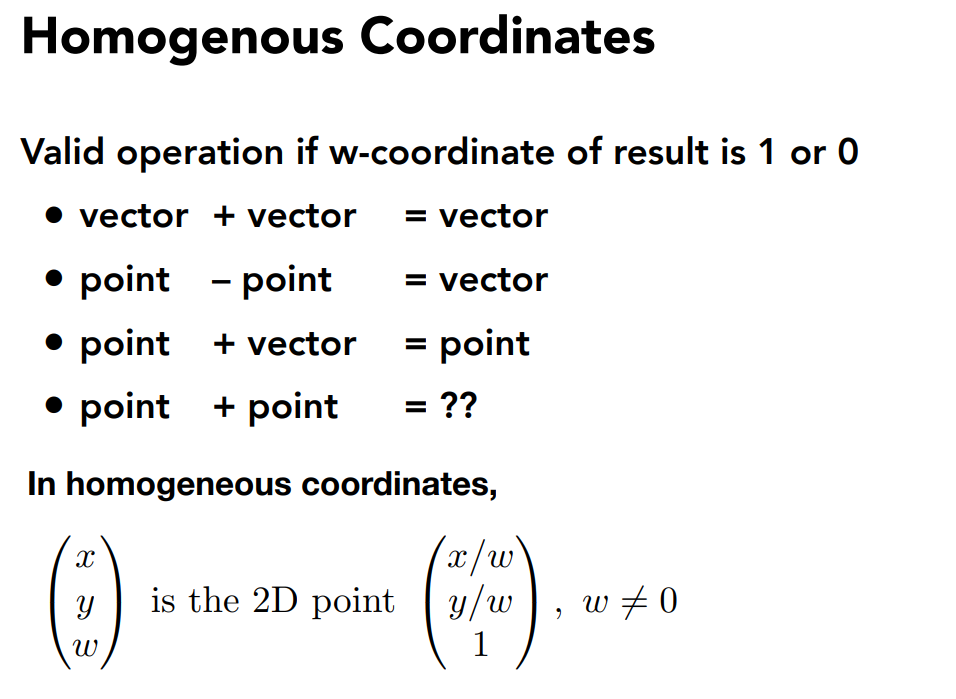 注:在齐次坐标的表示下,两个点相加表示这两个点的中点。
注:在齐次坐标的表示下,两个点相加表示这两个点的中点。
仿射变换可以用齐次坐标表示
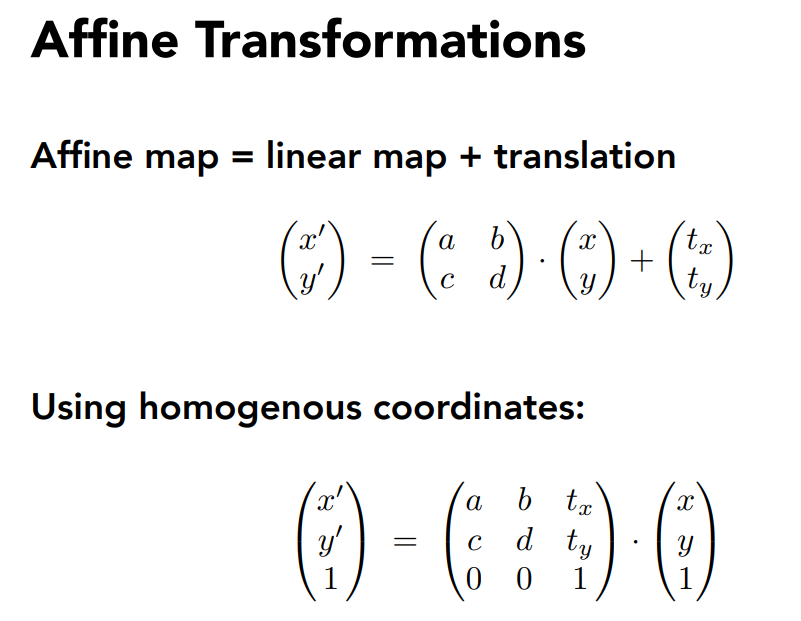
可以用齐次坐标把这些变换写成统一的形式:
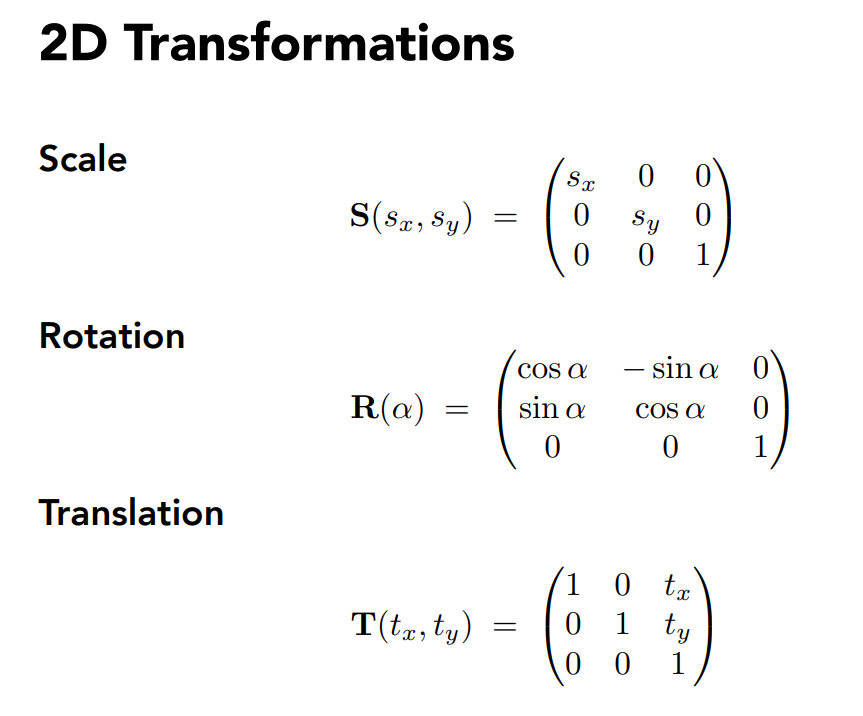
逆变换
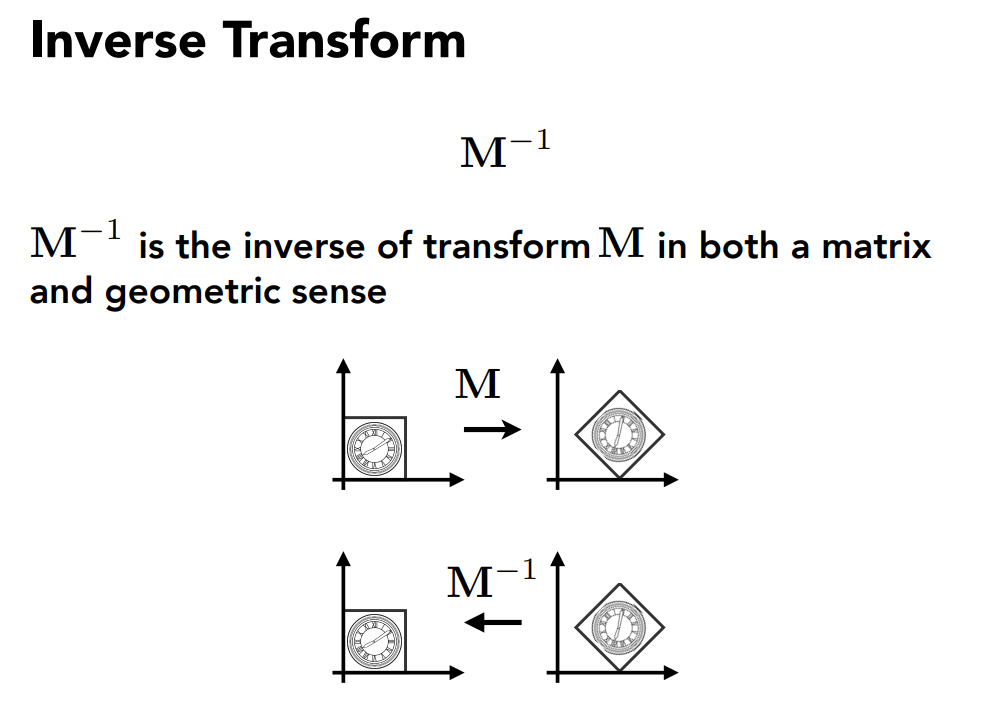
Composing Transforms组合变换
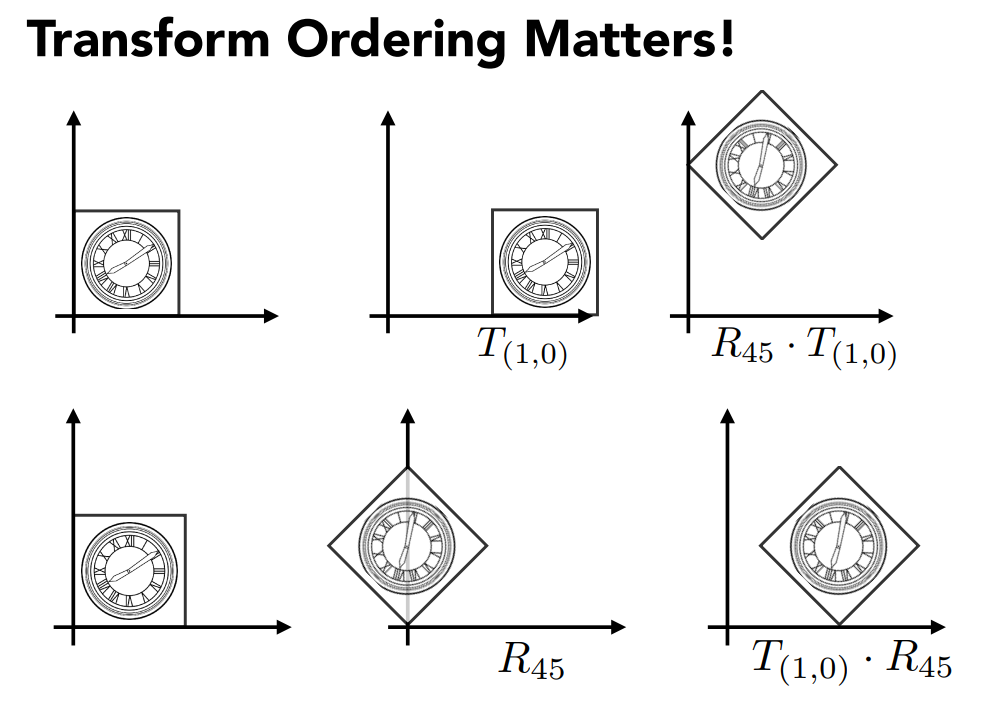 从右向左变换
从右向左变换
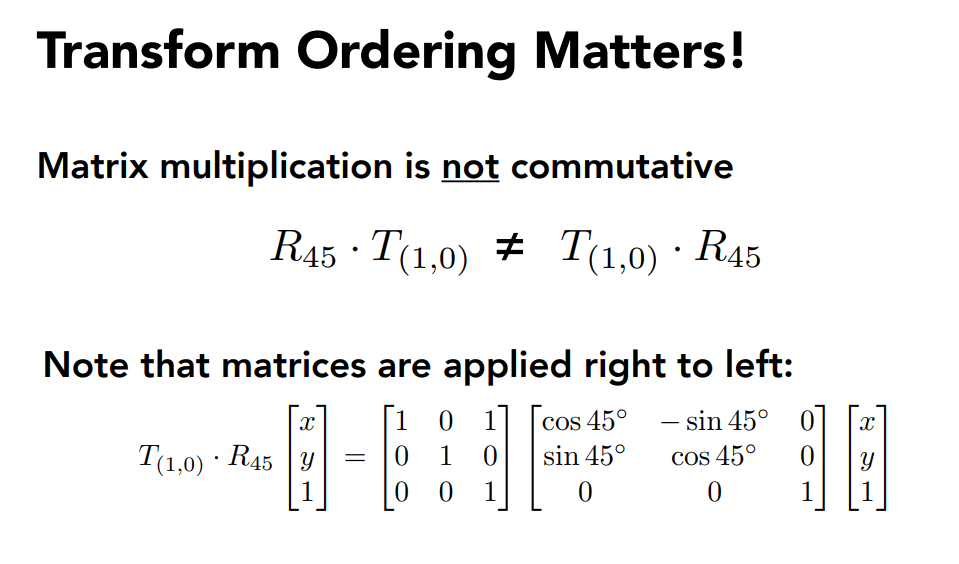
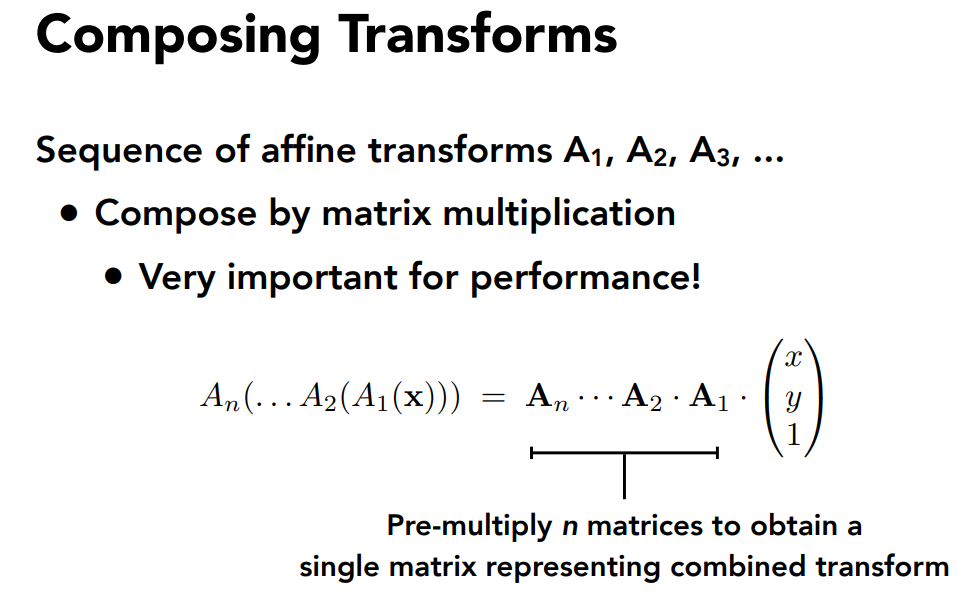
矩阵没有交换律,但有结合律,可以把矩阵相乘成一个矩阵,这个矩阵就表示了很多的变换。
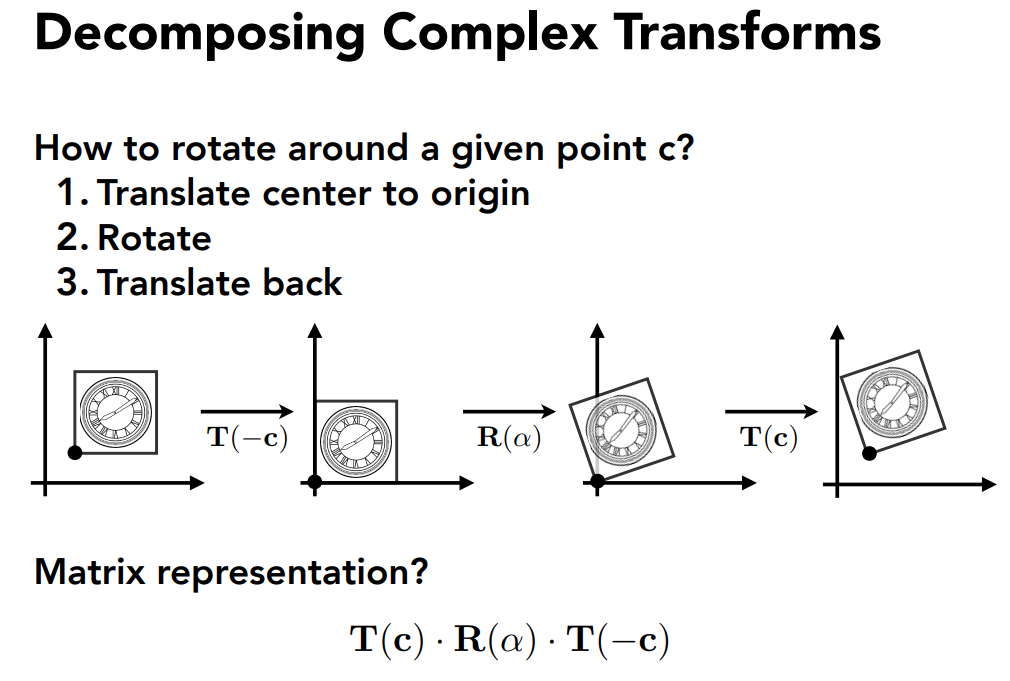
变换的分解:
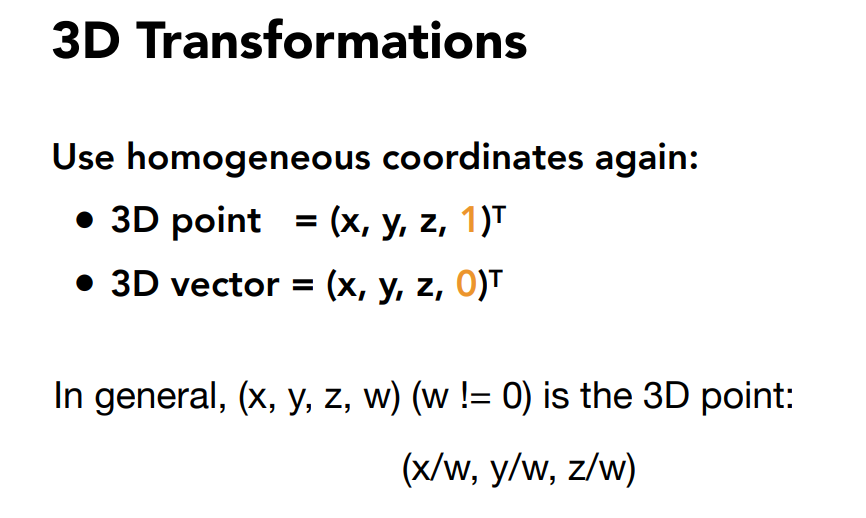
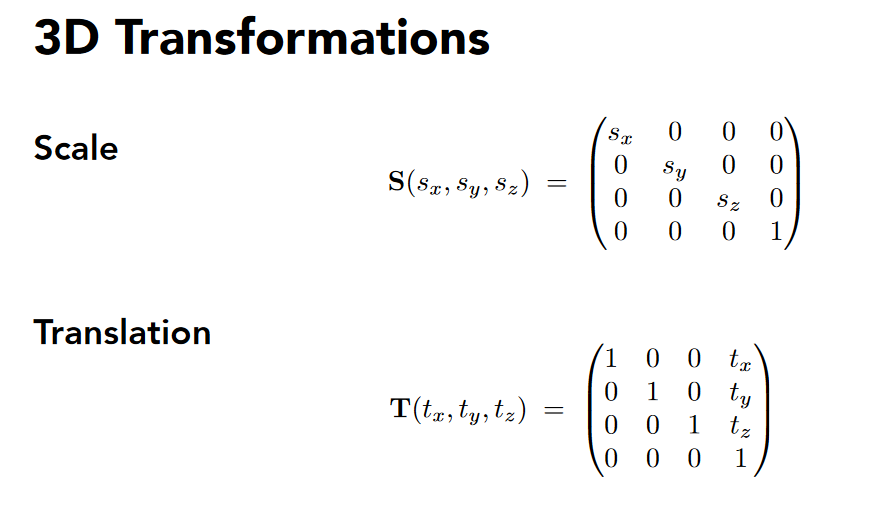
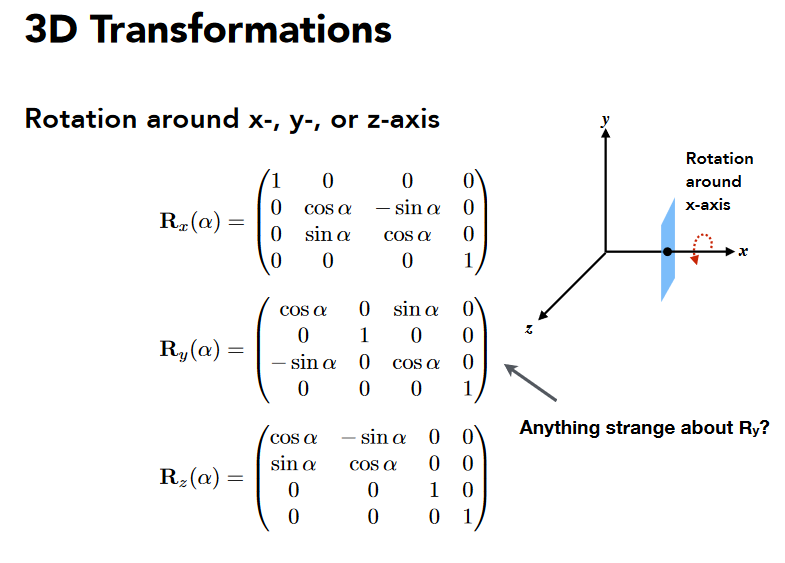
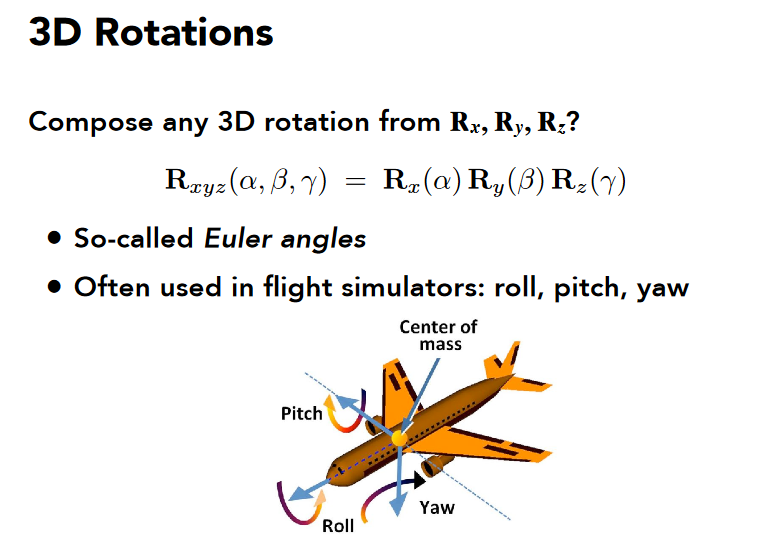
3D Transformations
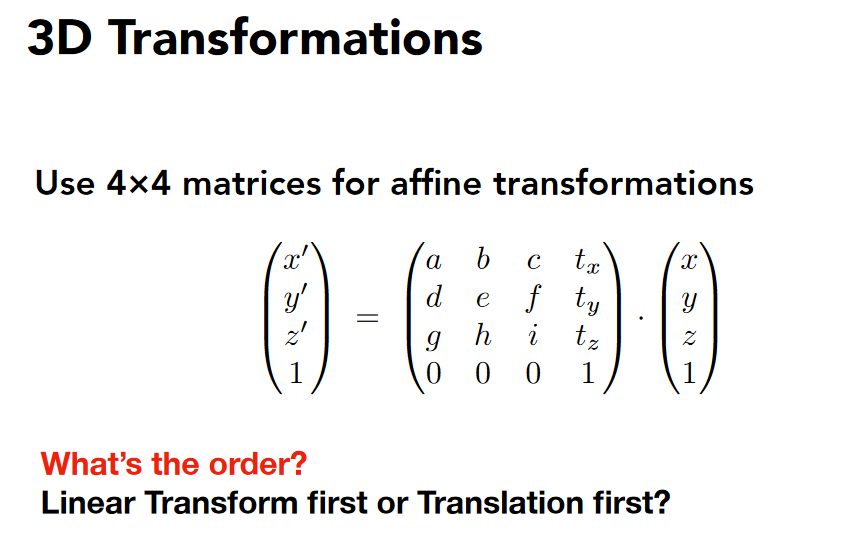 先线性变换再平移
先线性变换再平移
变换:
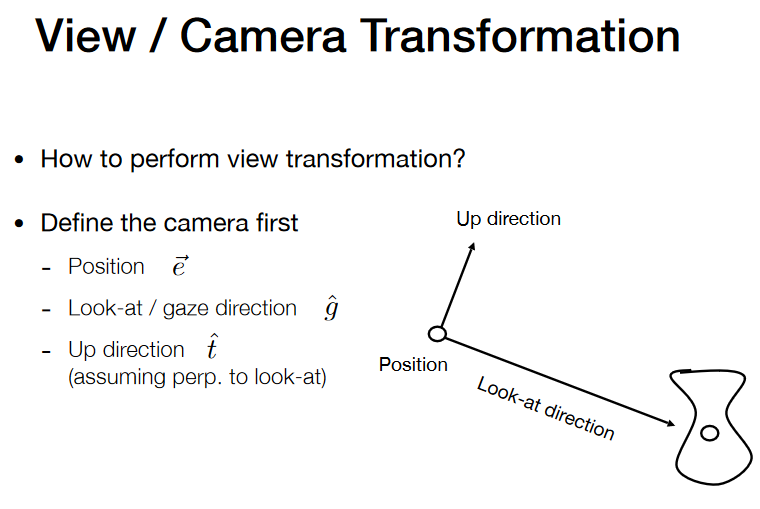
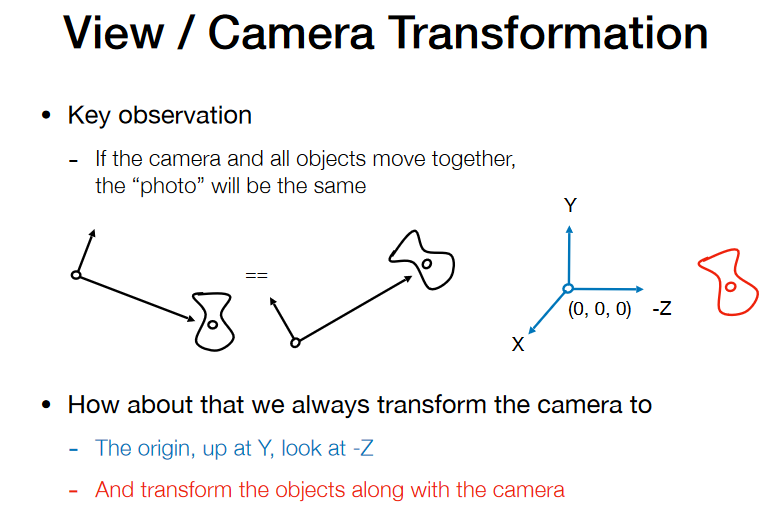
Viewing transformation
- View / Camera transformation
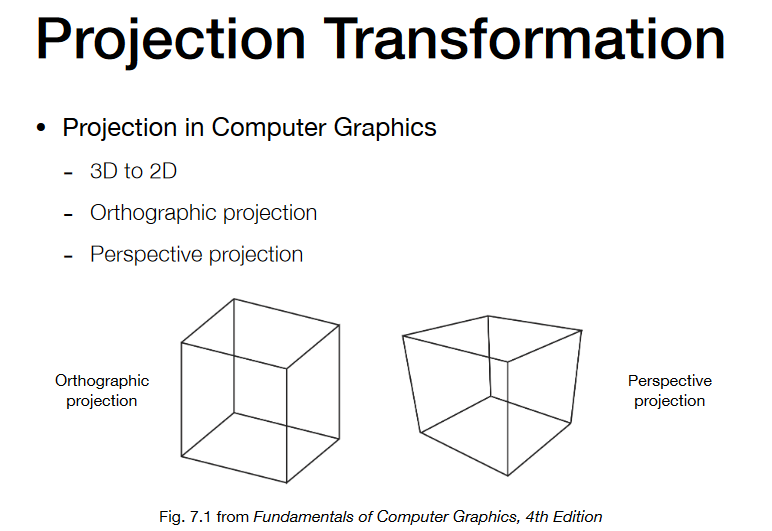
- Projection transformation
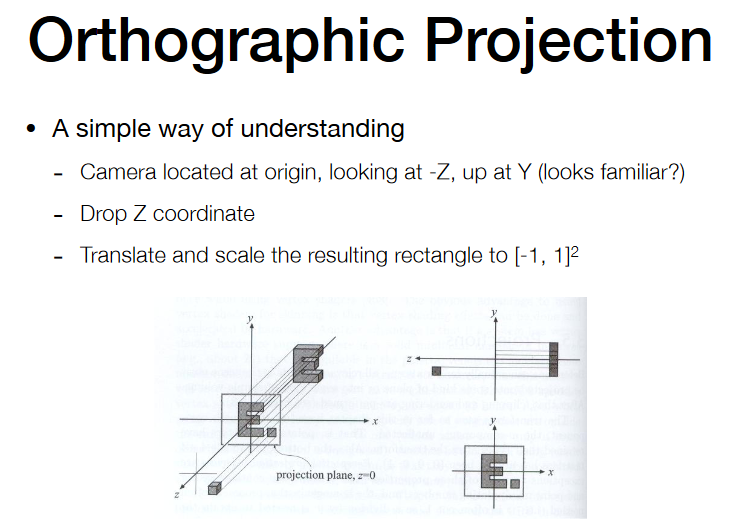
- Orthographic projection
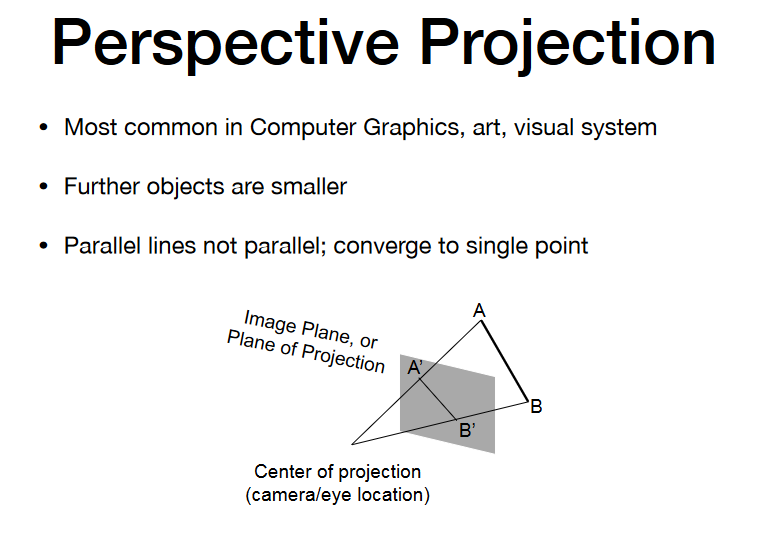
- Perspective projection
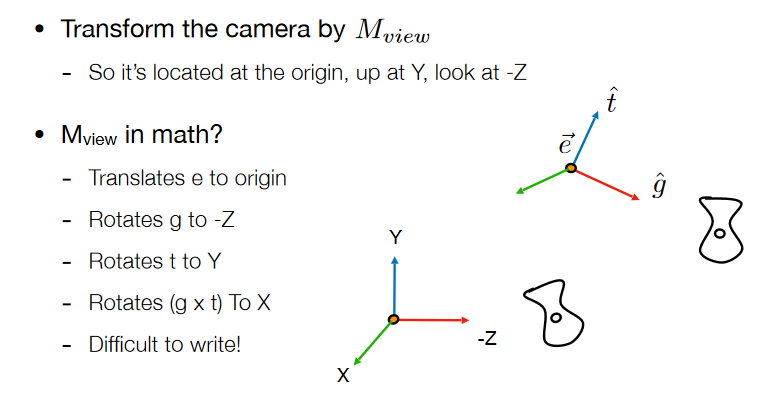
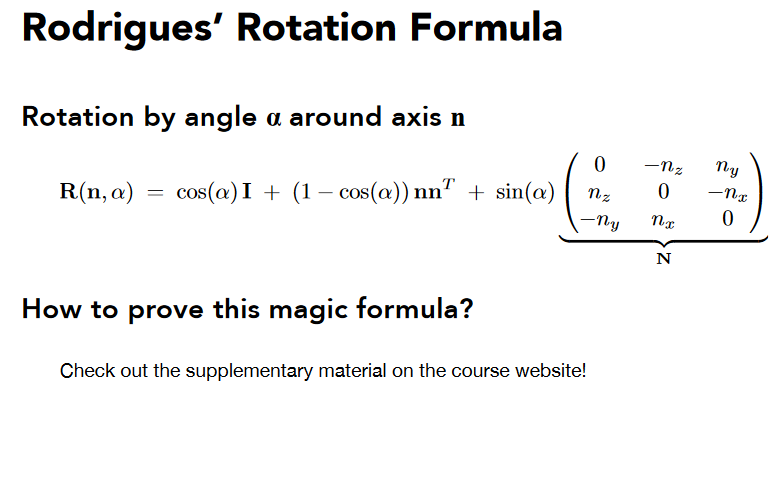
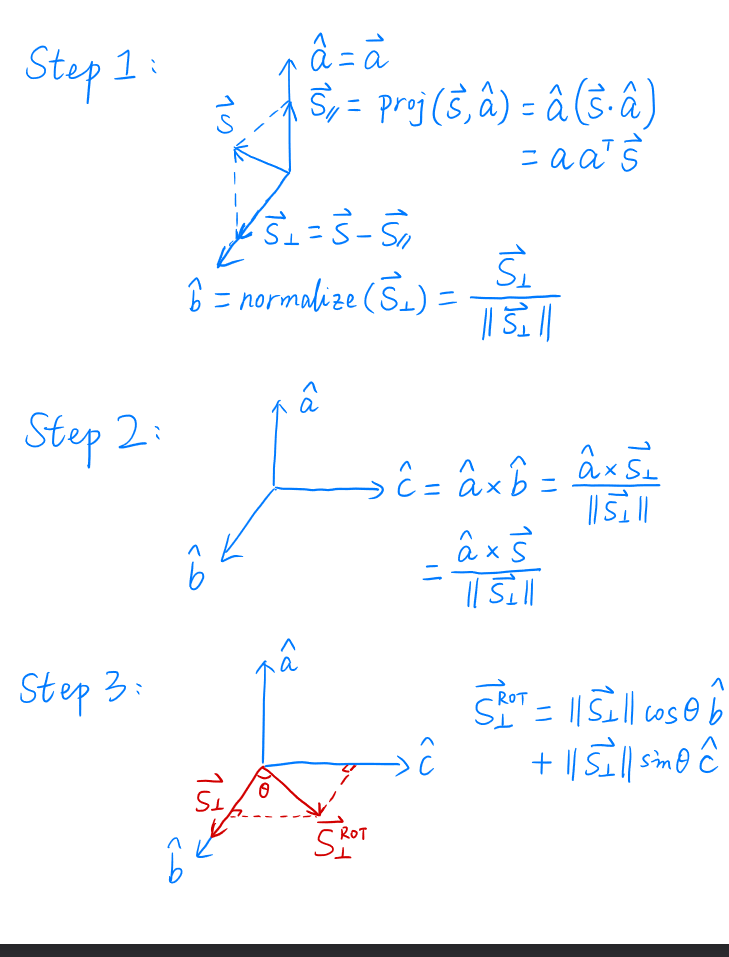
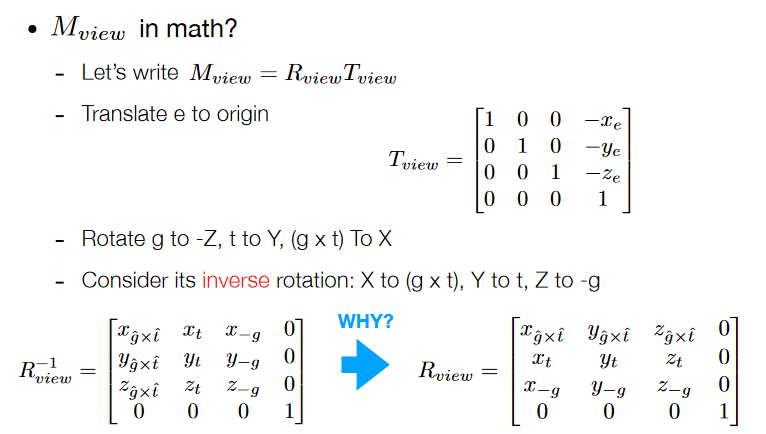
直接旋转并不好求,可以先求逆变换,而这个矩阵逆又等于矩阵转置
Projection transformation
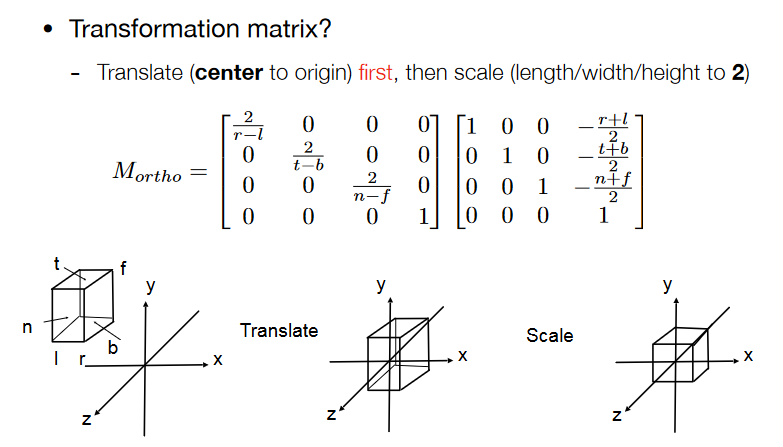
正交投影
z轴上,远小于近,(相机朝-z方向看)
 • Slightly different orders (to the “simple way”)
• Slightly different orders (to the “simple way”)
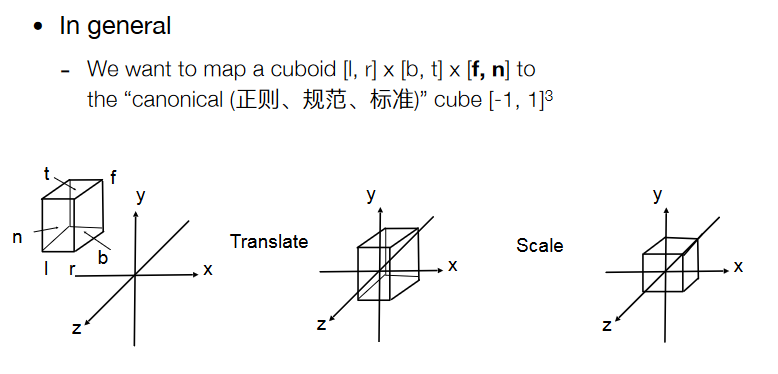
- Center cuboid by translating
- Scale into “canonical” cube
 • Caveat
• Caveat - Looking at / along -Z is making near and far not intuitive (n > f)
- FYI: that’s why OpenGL (a Graphics API) uses left hand coords.
正交投影
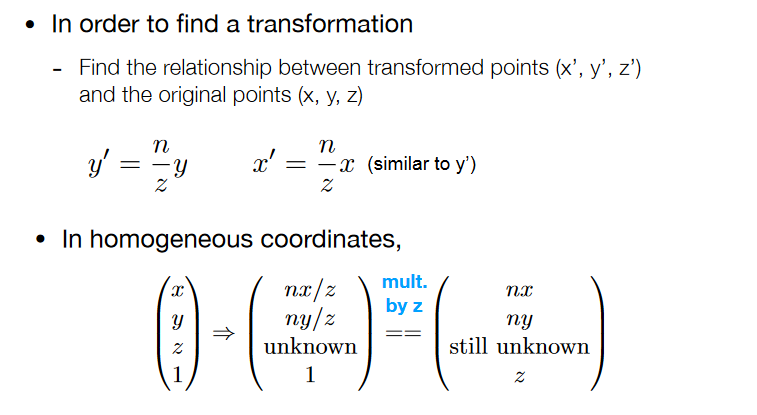
 • Recall: property of homogeneous coordinates
• Recall: property of homogeneous coordinates
- (x, y, z, 1), (kx, ky, kz, k != 0), (xz, yz, z2, z != 0) all represent
the same point (x, y, z) in 3D - e.g. (1, 0, 0, 1) and (2, 0, 0, 2) both represent (1, 0, 0)
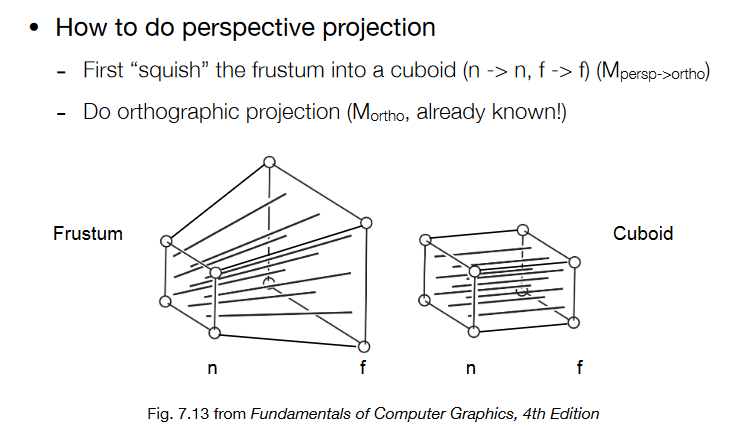
挤压
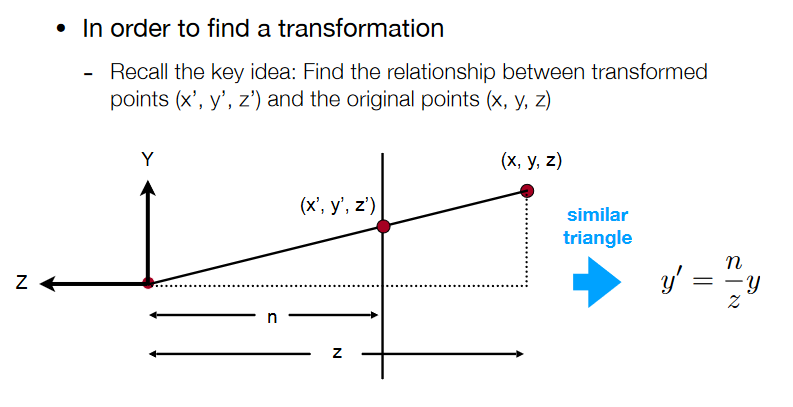
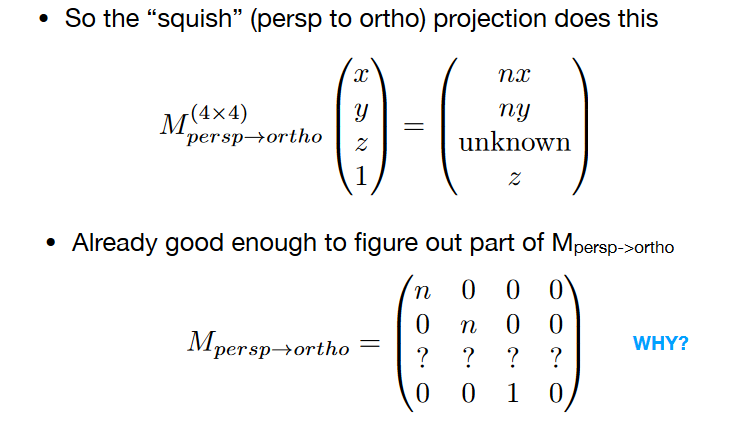

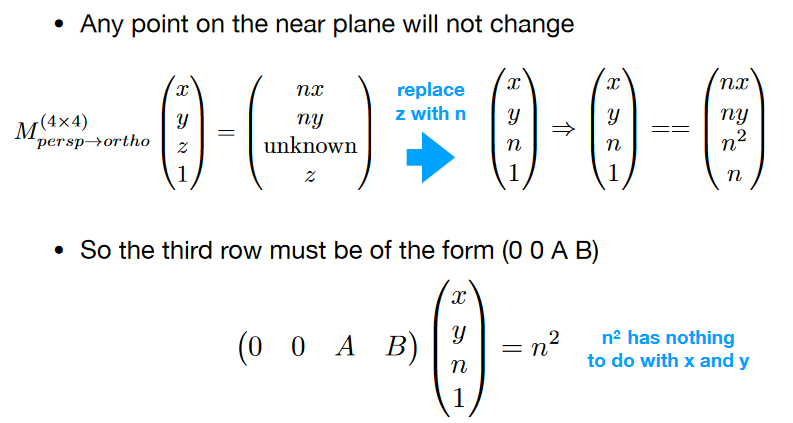
取远平面的中心点:
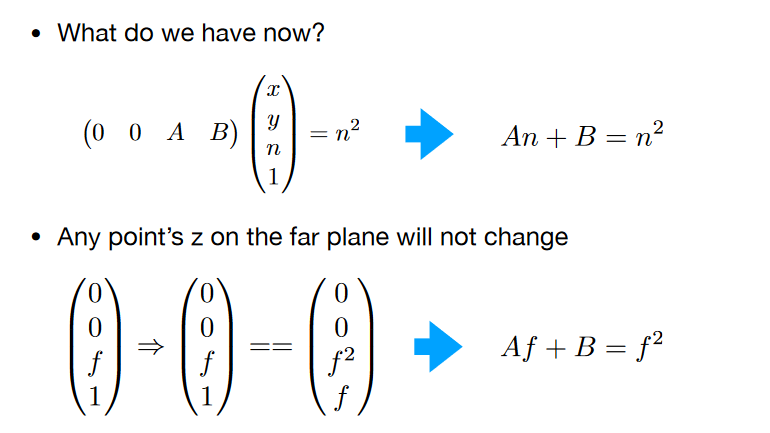
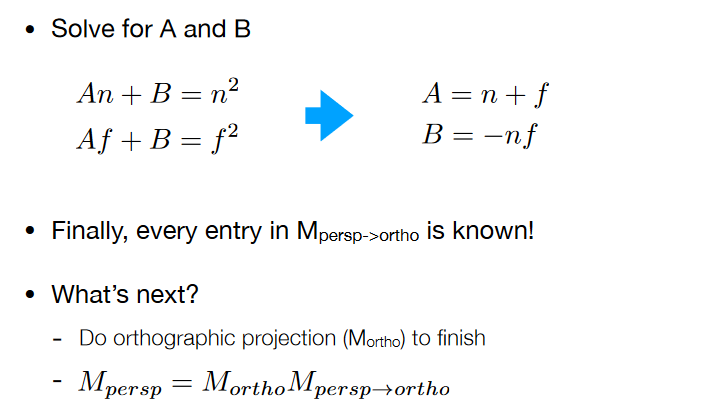
最后
以上就是洁净柜子最近收集整理的关于计算机图形学笔记1.变换向量 Vectors矩阵变换的全部内容,更多相关计算机图形学笔记1.变换向量内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复