遍历
就是按照某种次序访问树中的所有结点,且每个结点恰好访问一次。
也就是说,按照访问的次序,可以得到由树中所有结点排成一个序列。
树的遍历也可以看成人为的将非线性结构线性化。
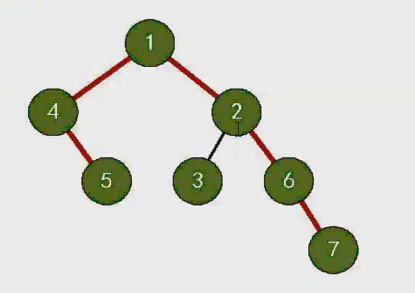
将整个二 叉树看做三部分:根、左子树、右子树、、如果规定先遍历左子树、再遍历右子树。那么根据根的遍历顺序就有三种遍历方式。
先序/根遍历DLR: 根 左子树 右子树
中序/根遍历LDR: 左子树 根 右子树
中序/根遍历LRD: 左子树 右子树 根
注意:由于树的递归定义,其实对三种遍历的概念其实也是一个递归的描述过程
先序遍历:1,4,5,2,3,6,7
中序遍历:4,5,1,3,2,6,7
后序遍历:5,4,3,7,6,2,1
分析流程:
递归实现遍历二叉树
先建立一个结点对象
public class Node {
Object Value; //结点值
Node leftChild; //左子树的引用
Node rightChild;//右子树的引用
public Node(Object value, Node leftChild, Node rightChild) {
super();
Value = value;
this.leftChild = leftChild;
this.rightChild = rightChild;
}
public Node(Object value) {
super();
Value = value;
}
}
实现遍历
public class BinaryTree {
private Node node;
public BinaryTree(Node node) {
super();
this.node = node;
}
public BinaryTree() {
super();
}
//判断是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
if (node !=null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
//先序遍历递归
public void preOrder(){
if (node !=null) {
//打印根结点
System.out.print(node.Value+" ");
//对左子树进行先序遍历
//构建一个二叉树,根是左子树的根
BinaryTree leftTree = new BinaryTree(node.leftChild);
leftTree.preOrder();
//对右子树进行先序遍历
//构建一个二叉树,根是左子树的根
BinaryTree rightTree = new BinaryTree(node.rightChild);
rightTree.preOrder();
}
}
//中序遍历
public void inOrderTraverse(){
System.out.println("中序遍历");
this.inOrderTraverse(node);
System.out.println("");
}
//中序遍历
private void inOrderTraverse(Node node){
if (node !=null) {
//构建一个二叉树,根是左子树的根
this.inOrderTraverse(node.leftChild);
//打印根结点的值
System.out.print(node.Value+" ");
//构建一个二叉树,根是左子树的根
this.inOrderTraverse(node.rightChild);
}
}
//后序遍历
public void postOrderTraverse(){
System.out.println("后序遍历");
this.postOrderTraverse(node);
System.out.println("");
}
//后序遍历
private void postOrderTraverse(Node node){
if(node !=null){
//遍历左子树
this.postOrderTraverse(node.leftChild);
//遍历右子树
this.postOrderTraverse(node.rightChild);
System.out.print(node.Value+" ");
}
}
//高度
public int getHeight() {
System.out.println("二叉树的高度是:");
return this.getHeight(node);
}
private int getHeight(Node node) {
if(node == null){
return 0;
}else {
//获取左子树的高度
int nl = this.getHeight(node.leftChild);
//获取右子树的高度
int nr = this.getHeight(node.rightChild);
//返回左子树、右子树较大的高度并加1
return nl > nr ? nl+1:nr+1;
}
}
//结点数
public int size() {
System.out.println("二叉数结点的个数:");
return this.size(node);
}
private int size(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}else {
//获取左子树的结点数
int nl = this.size(node.leftChild);
//获取右子树的结点数
int nr = this.size(node.rightChild);
//返回左右子树的和加1;
return nl+nr+1;
}
}
}
测试
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建树
Node node5 = new Node(5, null, null);
Node node4 = new Node(4, null, node5);
Node node3 = new Node(3, null, null);
Node node7 = new Node(7, null, null);
Node node6 = new Node(6, null, node7);
Node node2 = new Node(2,node3, node6);
Node node1 = new Node(1,node4, node2);
BinaryTree btree = new BinaryTree(node1);
//判断二叉树是否为空
System.out.println(btree.isEmpty());
//先序遍历递归
System.out.println("先序遍历");
btree.preOrder();
System.out.println("");
//中序遍历递归
btree.inOrderTraverse();
//后序遍历递归
btree.postOrderTraverse();
//二叉树的高度
int h = btree.getHeight();
System.out.println(h);
//二叉树的结点数量
int n = btree.size();
System.out.println(n);
}
}
运行结果:
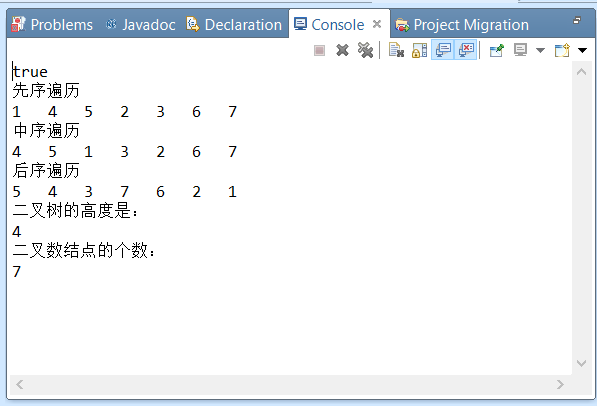
对一个二叉树的层次遍历,不能用递归的方法,借助队列来实现。
原理:先把根放进队列里面,然后在出栈,在根释放之前,把根的两个孩子都放到队列里面,并且是自左向右放的,相当于把一层结点处理完了,把第二层的结点也放进队列里面,然后在处理的第二层结点,在释放之前把第三层的结点自左向在放在结点里面,然后在处理第三层的结点,在处理第在层的结点的过程中把第四层的结点放进队列里面,因为队列是先进先出,所以要先放左边的,再放右边的;当所有的结点为空的时候结束 。
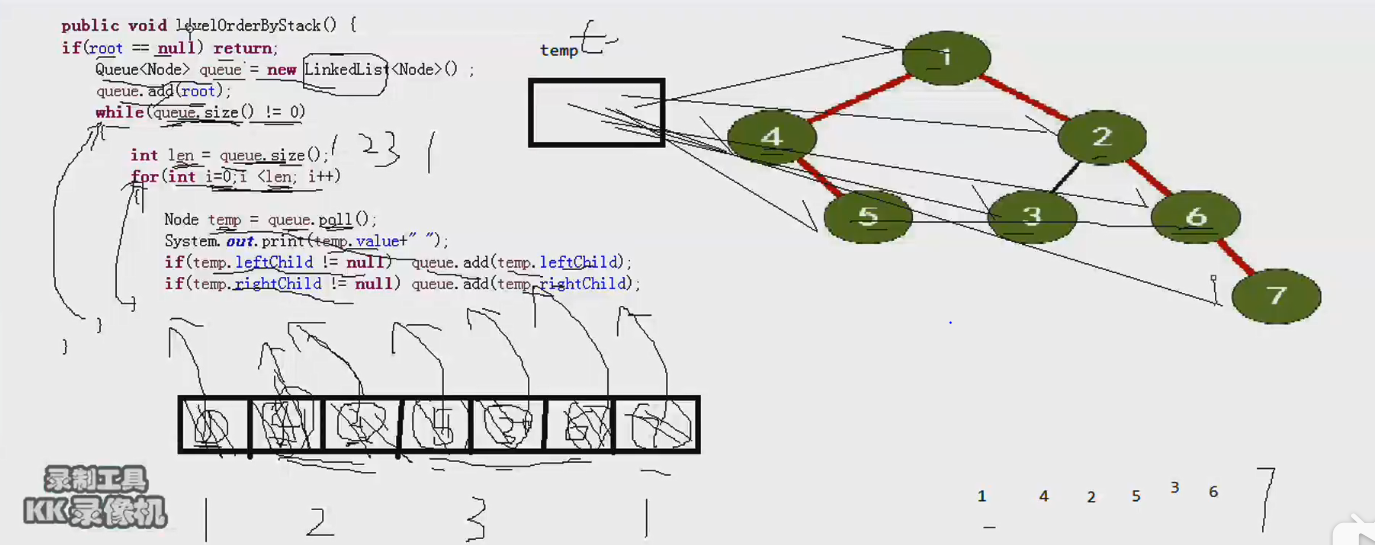
中序非递归遍历
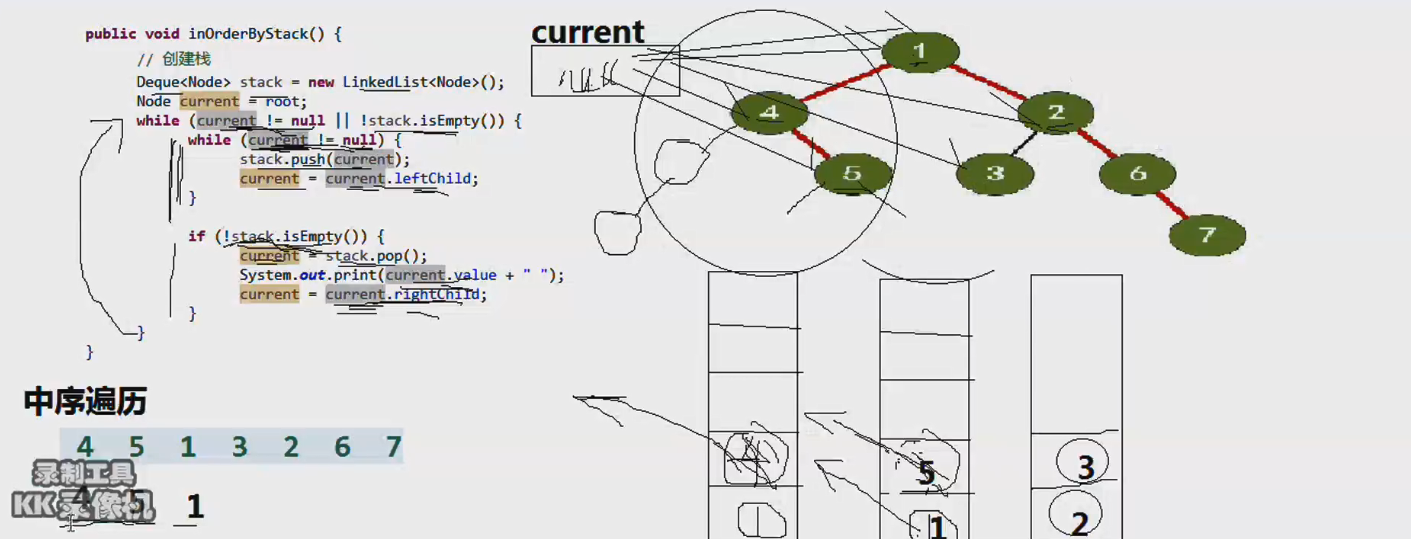
最后
以上就是欣慰果汁最近收集整理的关于二叉树的遍历(递归与队列)的全部内容,更多相关二叉树内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复