# BST(二叉搜索树、二叉查找树、二叉排序树)
定义:
1、要么是一棵空树
2、如果不为空,那么其左子树节点的值都小于根节点的值;右子树节点的值都大于根节点的值
3、其左右子树也是二叉搜索树
# AVL tree(平衡二叉树)
定义:
平衡二叉树(Balanced Binary Tree)又被称为AVL树(有别于AVL算法),且具有以下性质:它是一 棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。平衡二叉树的常用算法有红黑树、AVL、Treap、伸展树等。
最小不平衡子树: 以离插入结点最近、且平衡因子绝对值大于 1 的结点作根结点的子树。
调整该子树的分为四种情况:
(1)LL形
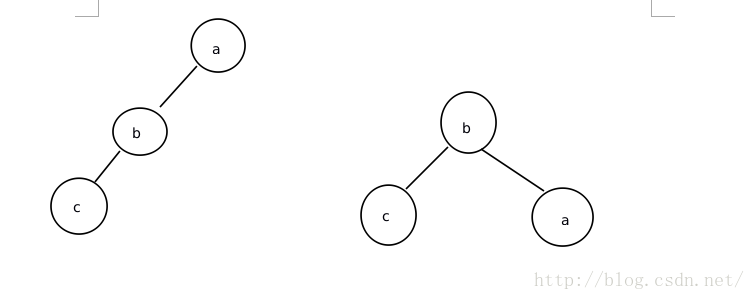
(2)LR形
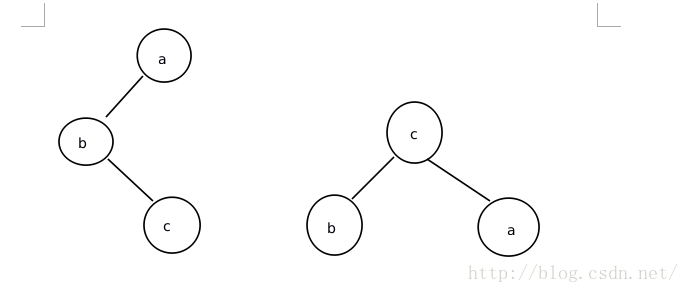
(3)RR形
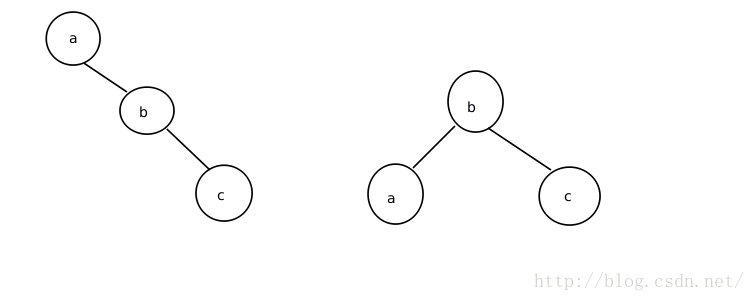
(4)RL形
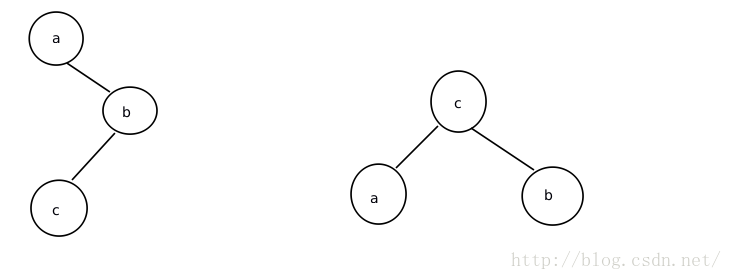
代码实现:
LR:
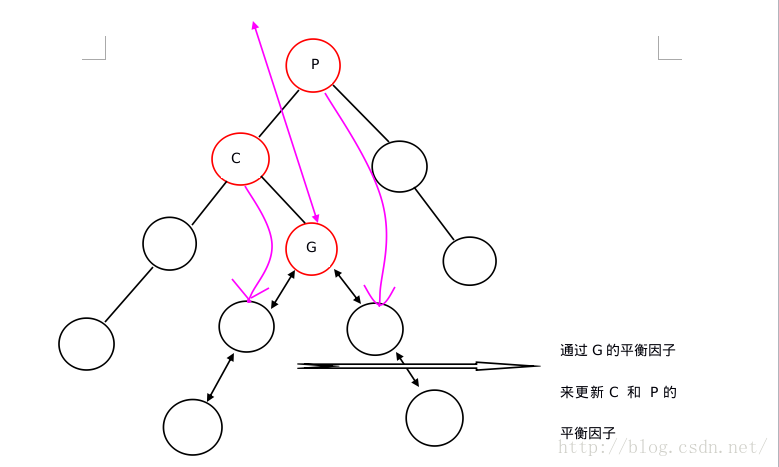
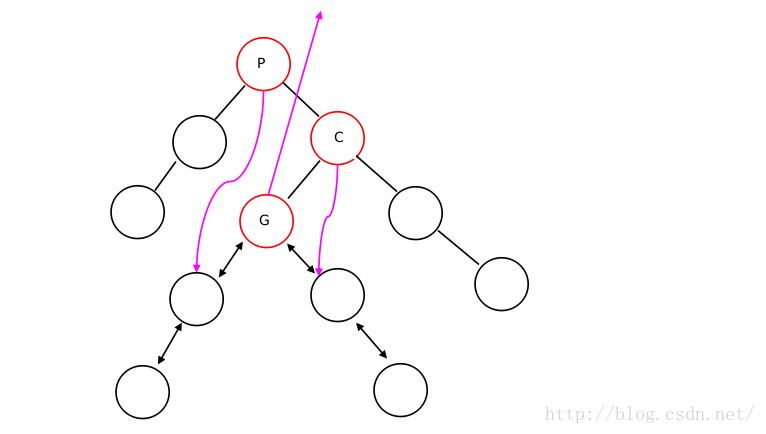
RL:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define FALSE 0
#define TRUE 1
typedef struct {
int key;
} element;
typedef struct tree_node {
struct tree_node *left_child;
element data;
short bf;
struct tree_node *right_child;
} tree_node, *tree_pointer;
int unbalanced = FALSE;
tree_pointer root = NULL;
void left_rotation(tree_pointer *parent, int *unbalanced);
void right_rotation(tree_pointer *parent, int *unbalanced);
void avl_insert(tree_pointer *parent, element x, int *unbalanced);
/*
*1.如果要插入的元素的父节点为空则为其分配内存并处理
*2.如果小于父节点的数据域则插入父节点的左孩子,并旋转
*3.如果大于父节点的数据域则插入父节点的右孩子,并旋转
*/
void avl_insert(tree_pointer *parent, element x, int *unbalanced) {
if(!*parent) {
*unbalanced = TRUE;
*parent = new tree_node();
(*parent)->left_child = (*parent)->right_child = NULL;
(*parent)->bf = 0;
(*parent)->data = x;
}
else if(x.key < (*parent)->data.key) {
avl_insert(&(*parent)->left_child, x, unbalanced);
if(*unbalanced) {
/*
* unbalanced表示是插完之后就不平衡了 和 判断还用不用处理平衡因子
*/
switch((*parent)->bf) {
case -1:
(*parent)->bf = 0;
*unbalanced = FALSE;
break;
case 0:
(*parent)->bf = 1;
break;
case 1:
left_rotation(parent,unbalanced);
}
}
}
else if(x.key > (*parent)->data.key) {
avl_insert(&(*parent)->right_child, x, unbalanced);
if(*unbalanced) {
switch((*parent)->bf) {
case 1:
(*parent)->bf = 0;
*unbalanced = FALSE;
break;
case 0:
(*parent)->bf = 1;
break;
case -1:
right_rotation(parent, unbalanced);
}
}
}
else {
*unbalanced = FALSE;
printf("该元素已经存在!n");
}
}
void left_rotation(tree_pointer *parent, int *unbalanced) {
tree_pointer grand_child, child;
child = (*parent)->left_child;
if(child->bf == 1) {
//LL
(*parent)->left_child = child->right_child;
child->right_child = *parent;
(*parent)->bf = 0;
(*parent) = child;
} else {
//LR
grand_child = child->right_child;
child->right_child = grand_child->left_child;
grand_child->left_child = child;
(*parent)->left_child = grand_child->right_child;
grand_child->right_child = (*parent);
switch(grand_child->bf) {
case 1:
(*parent)->bf = -1;
child->bf = 0;
case 0:
(*parent)->bf = child->bf = 0;
case -1:
(*parent)->bf = 0;
child->bf = 1;
}
(*parent) = grand_child;
}
(*parent)->bf = 0;
*unbalanced = FALSE;
}
void right_rotation(tree_pointer *parent, int *unbalanced) {
tree_pointer grand_child, child;
child = (*parent)->right_child;
if(child->bf == -1) {
//RR
(*parent)->right_child = child->left_child;
child->left_child = (*parent);
(*parent) = child;
} else {
//RL
grand_child = child->left_child;
child->left_child = grand_child->right_child;
grand_child->right_child = child;
(*parent)->right_child = grand_child->left_child;
grand_child->left_child = (*parent);
switch(grand_child->bf) {
case 1:
(*parent)->bf = 0;
child->bf = -1;
case 0:
(*parent)->bf = child->bf = 0;
case -1:
(*parent)->bf = 1;
child->bf = 0;
}
(*parent) = grand_child;
}
(*parent)->bf = 0;
*unbalanced = FALSE;
}
void raverse(tree_pointer root) {
if(root) {
printf("%d ",root->data.key);
raverse(root->left_child);
raverse(root->right_child);
}
}
int main() {
int arr[11] = {15,6,18,3,7,17,20,2,4,13,9};
element arr_x[11];
for(int i = 0; i<11; i++) {
arr_x[i].key = arr[i];
// cout<<arr_x[i].key<<endl;
avl_insert(&root, arr_x[i], &unbalanced);
}
raverse(root);
printf("n");
return 0;
}
最后
以上就是俭朴学姐最近收集整理的关于数据结构 — AVL tree(平衡二叉树)的全部内容,更多相关数据结构内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复