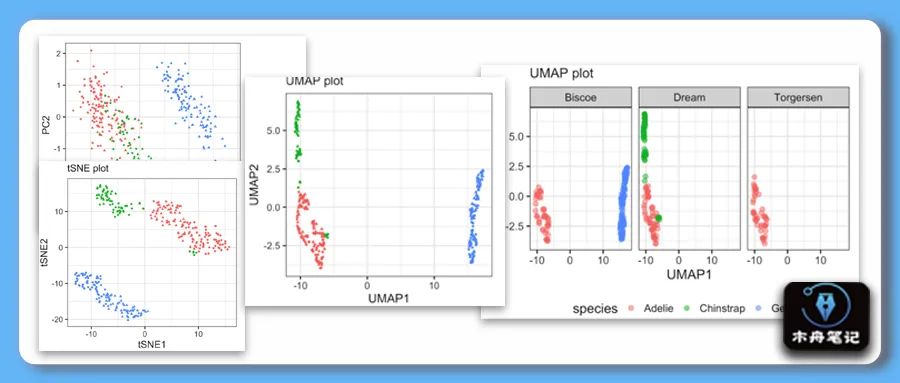
在组学分析中,一般通过降维算法得到低纬度如二维或三维的新坐标数据,再结合可视化技术去展示样本的在新坐标的空间分布,接着加上统计检验结果证实整体组学水平上组间的差异性。降维算法有基于线性模型的PCA,也有基于非线性的tSNE和UMAP等方法。
示例数据和代码领取
详见:R实战| PCA、tSNE、UMAP三种降维方法在R中的实现
PCA
主成分分析(Principal Component Analysis,PCA)是最常用的无监督学习方法。
rm(list = ls())
library(tidyverse)
library(broom)
library(palmerpenguins)
# 示例数据
penguins <- penguins %>%
drop_na() %>%
select(-year)
head(penguins)
# 使用prcomp()进行PCA
# PCA前对数值型数据进行标准化
pca_fit <- penguins %>%
select(where(is.numeric)) %>%
scale() %>%
prcomp()
# 查看成分重要性
summary(pca_fit)
# 可视化PC1和PC2
pca_fit %>%
augment(penguins) %>%
rename_at(vars(starts_with(".fitted")),
list(~str_replace(.,".fitted",""))) %>%
ggplot(aes(x=PC1,
y=PC2,
color=species,
shape=sex))+
geom_point()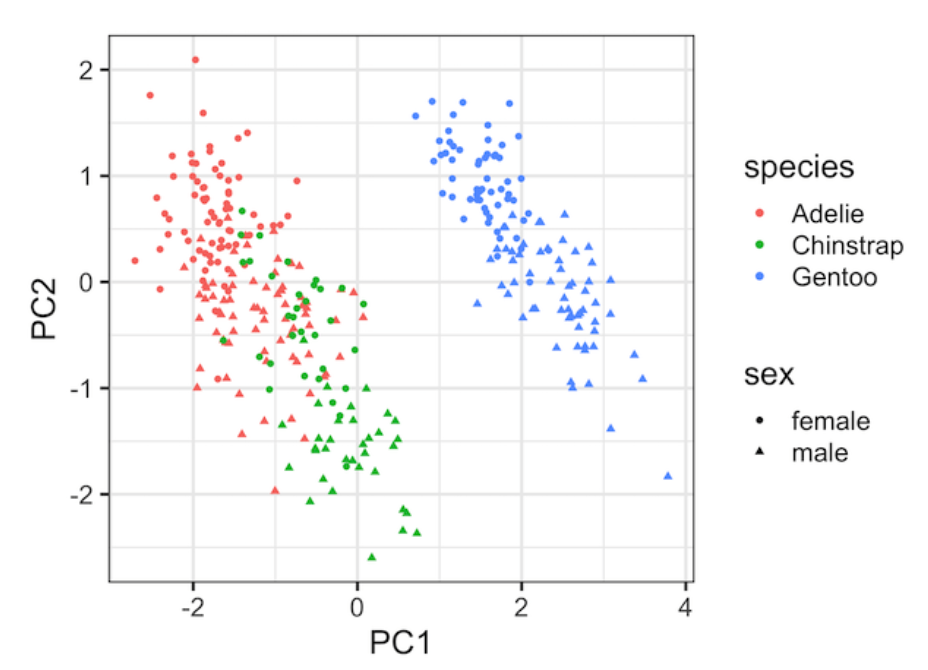
UMAP
数据预处理
## UMAP
rm(list = ls())
library(tidyverse)
library(palmerpenguins)
#install.packages("umap")
library(umap)
theme_set(theme_bw(18))
penguins <- penguins %>%
drop_na() %>%
select(-year)%>%
mutate(ID=row_number())
penguins_meta <- penguins %>%
select(ID, species, island, sex)使用umap包进行umap分析
set.seed(142)
umap_fit <- penguins %>%
select(where(is.numeric)) %>%
column_to_rownames("ID") %>%
scale() %>%
umap()
umap_df <- umap_fit$layout %>%
as.data.frame()%>%
rename(UMAP1="V1",
UMAP2="V2") %>%
mutate(ID=row_number())%>%
inner_join(penguins_meta, by="ID")
umap_df %>% head()可视化
# 可视化
umap_df %>%
ggplot(aes(x = UMAP1,
y = UMAP2,
color = species,
shape = sex))+
geom_point()+
labs(x = "UMAP1",
y = "UMAP2",
subtitle = "UMAP plot")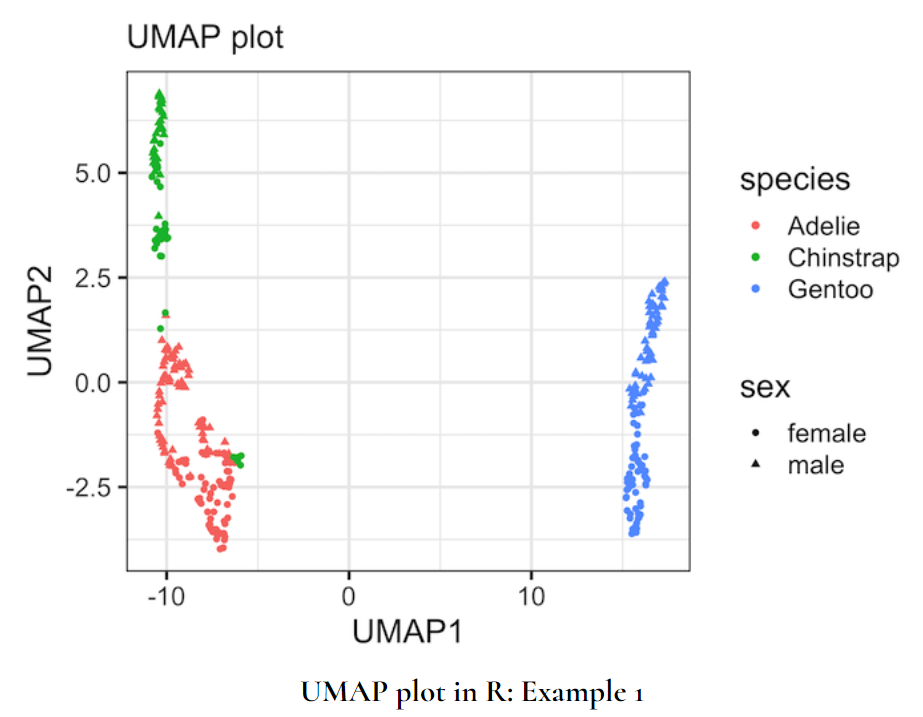
# 分面
umap_df %>%
ggplot(aes(x = UMAP1,
y = UMAP2,
color = species)) +
geom_point(size=3, alpha=0.5)+
facet_wrap(~island)+
labs(x = "UMAP1",
y = "UMAP2",
subtitle="UMAP plot")+
theme(legend.position="bottom")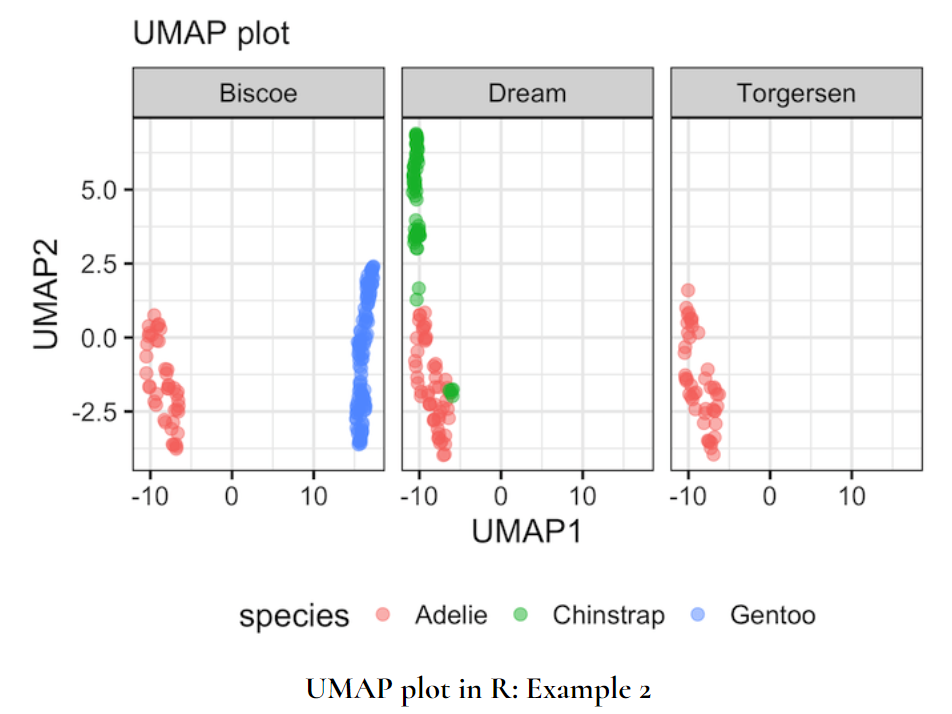
# 圈出异常样本
library(ggforce)
umap_df %>%
ggplot(aes(x = UMAP1,
y = UMAP2,
color = species,
shape = sex)) +
geom_point() +
labs(x = "UMAP1",
y = "UMAP2",
subtitle="UMAP plot") +
geom_circle(aes(x0 = -5, y0 = -3.8, r = 0.65),
color = "green",
inherit.aes = FALSE)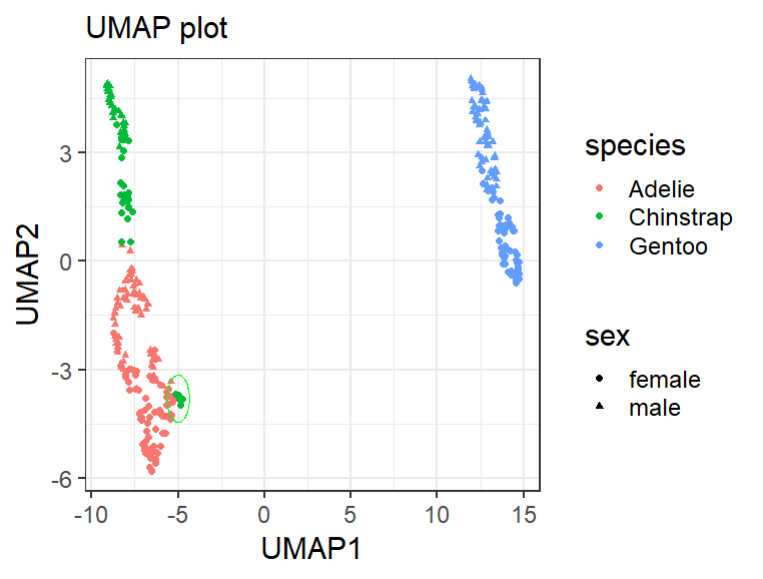
tSNE
数据预处理
## tSNE
rm(list = ls())
library(tidyverse)
library(palmerpenguins)
library(Rtsne)
theme_set(theme_bw(18))
penguins <- penguins %>%
drop_na() %>%
select(-year)%>%
mutate(ID=row_number())
penguins_meta <- penguins %>%
select(ID,species,island,sex)使用Rtsne 包进行tSNE 分析
set.seed(142)
tSNE_fit <- penguins %>%
select(where(is.numeric)) %>%
column_to_rownames("ID") %>%
scale() %>%
Rtsne()
tSNE_df <- tSNE_fit$Y %>%
as.data.frame() %>%
rename(tSNE1="V1",
tSNE2="V2") %>%
mutate(ID=row_number())
tSNE_df <- tSNE_df %>%
inner_join(penguins_meta, by="ID")
tSNE_df %>% head()可视化
tSNE_df %>%
ggplot(aes(x = tSNE1,
y = tSNE2,
color = species,
shape = sex))+
geom_point()+
theme(legend.position="bottom")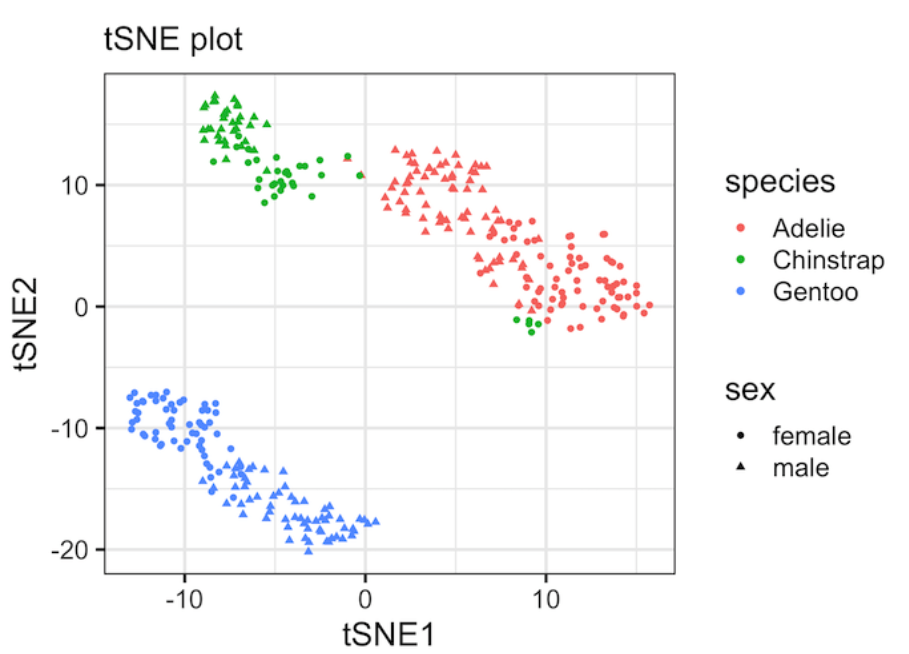
参考
-
How To Make tSNE plot in R - Data Viz with Python and R (datavizpyr.com)
-
How to make UMAP plot in R - Data Viz with Python and R (datavizpyr.com)
-
How To Make PCA Plot with R - Data Viz with Python and R (datavizpyr.com)
往期内容
-
CNS图表复现|生信分析|R绘图 资源分享&讨论群!
-
组学生信| Front Immunol |基于血清蛋白质组早期诊断标志筛选的简单套路

最后
以上就是健康长颈鹿最近收集整理的关于R实战| PCA、tSNE、UMAP三种降维方法在R中的实现的全部内容,更多相关R实战|内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复