文章目录
- 前言
- 一、MTCNN
- 二、代码实现
- 1.引入库
- 2.函数定义
- nms
- PNet处理代码
- RNet处理代码
- ONet处理代码
- LNet处理代码
- 效果
前言
本文基于MxNet实现人脸识别,使用算法MTCNN
一、MTCNN
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1604/1604.02878.pdf
网络结构:
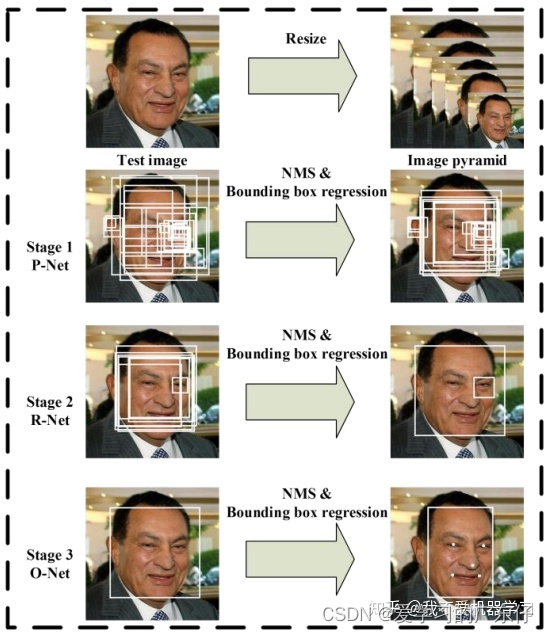
首先将图像重新缩放为不同大小的范围(称为图像金字塔),然后第一个模型(Proposal Network 或 P-Net)提出候选面部区域;第二个模型(Refine Network 或 R-Net)过滤边界框;第三个模型(Output Network或 O-Net)输出边界框和面部特征点位置。
上图表示 CNN 三个阶段。在第一阶段,它通过浅层 CNN 快速生成候选窗口。然后,它通过更复杂的 CNN 对窗口进行细化以拒绝大量非人脸窗口。最后,它使用更强大的 CNN 来细化结果并输出面部标志位置。
模型被称为多任务网络,因为级联中的三个模型(P-Net、R-Net 和 O-Net)中的每一个都在三个任务上进行训练,例如进行三种类型的预测:人脸分类、边界框回归和人脸 landmark 定位。
三个模型不直接连接,相反,前一阶段的输出作为输入送到下一阶段。这允许在阶段之间执行额外的处理;例如,非极大值抑制 (NMS) 用于在将第一阶段 P-Net 提出的候选边界框提供给第二阶段 R-Net 模型之前对其进行过滤。
- 候选网络 (P-Net):该网络结构主要获得了人脸区域的候选窗口和边界框的回归向量,并用该边界框做回归,对候选窗口进行校准,然后通过非极大值抑制 (NMS) 来合并高度重叠的候选框。
- 细化网络 (R-Net):该网络结构还是通过边界框的回归和 NMS 来去掉那些假正例的区域。只是由于该网络结构和P-Net网络结构有差异,多了一个全连接层,所以会取得更好的抑制假正例的作用。
- 输出网络 (O-Net):该层比 R-Net 层又多了一层卷积层,所以处理的结果会更精细。作用和 R-Net 层作用一样。但是该层对人脸区域进行了更多的监督,同时还会输出 人脸的5 个 Landmark(界标)。
二、代码实现
1.引入库
import os,time,math,cv2
import numpy as np
from multiprocessing import Pool
from itertools import repeat
import mxnet as mx
2.函数定义
nms
def nms(boxes, overlap_threshold, mode='Union'):
if len(boxes) == 0:
return []
if boxes.dtype.kind == "i":
boxes = boxes.astype("float")
pick = []
x1, y1, x2, y2, score = [boxes[:, i] for i in range(5)]
area = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
idxs = np.argsort(score)
while len(idxs) > 0:
last = len(idxs) - 1
i = idxs[last]
pick.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[idxs[:last]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[idxs[:last]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[idxs[:last]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[idxs[:last]])
w = np.maximum(0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h
if mode == 'Min':
overlap = inter / np.minimum(area[i], area[idxs[:last]])
else:
overlap = inter / (area[i] + area[idxs[:last]] - inter)
idxs = np.delete(idxs, np.concatenate(([last], np.where(overlap > overlap_threshold)[0])))
return pick
PNet处理代码
total_boxes = []
for batch in sliced_index:
local_boxes = self.Pool.map(detect_first_stage_warpper,zip(repeat(img), self.PNets[:len(batch)], [scales[i] for i in batch], repeat(self.threshold[0])))
total_boxes.extend(local_boxes)
total_boxes = [i for i in total_boxes if i is not None]
if len(total_boxes) == 0:
return None
RNet处理代码
input_buf = np.zeros((num_box, 3, 24, 24), dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(num_box):
tmp = np.zeros((tmph[i], tmpw[i], 3), dtype=np.uint8)
tmp[dy[i]:edy[i] + 1, dx[i]:edx[i] + 1, :] = img[y[i]:ey[i] + 1, x[i]:ex[i] + 1, :]
input_buf[i, :, :, :] = adjust_input(cv2.resize(tmp, (24, 24)))
output = self.RNet.predict(input_buf)
passed = np.where(output[1][:, 1] > self.threshold[1])
total_boxes = total_boxes[passed]
if total_boxes.size == 0:
return None
ONet处理代码
input_buf = np.zeros((num_box, 3, 48, 48), dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(num_box):
tmp = np.zeros((tmph[i], tmpw[i], 3), dtype=np.float32)
tmp[dy[i]:edy[i] + 1, dx[i]:edx[i] + 1, :] = img[y[i]:ey[i] + 1, x[i]:ex[i] + 1, :]
input_buf[i, :, :, :] = adjust_input(cv2.resize(tmp, (48, 48)))
output = self.ONet.predict(input_buf)
passed = np.where(output[2][:, 1] > self.threshold[2])
total_boxes = total_boxes[passed]
if total_boxes.size == 0:
return None
LNet处理代码
关键点代码
input_buf = np.zeros((num_box, 15, 24, 24), dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(5):
x, y = points[:, i], points[:, i + 5]
x, y = np.round(x - 0.5 * patchw), np.round(y - 0.5 * patchw)
[dy, edy, dx, edx, y, ey, x, ex, tmpw, tmph] = self.pad(np.vstack([x, y, x + patchw - 1, y + patchw - 1]).T,
width,
height)
for j in range(num_box):
tmpim = np.zeros((tmpw[j], tmpw[j], 3), dtype=np.float32)
tmpim[dy[j]:edy[j] + 1, dx[j]:edx[j] + 1, :] = img[y[j]:ey[j] + 1, x[j]:ex[j] + 1, :]
input_buf[j, i * 3:i * 3 + 3, :, :] = adjust_input(cv2.resize(tmpim, (24, 24)))
output = self.LNet.predict(input_buf)
pointx = np.zeros((num_box, 5))
pointy = np.zeros((num_box, 5))
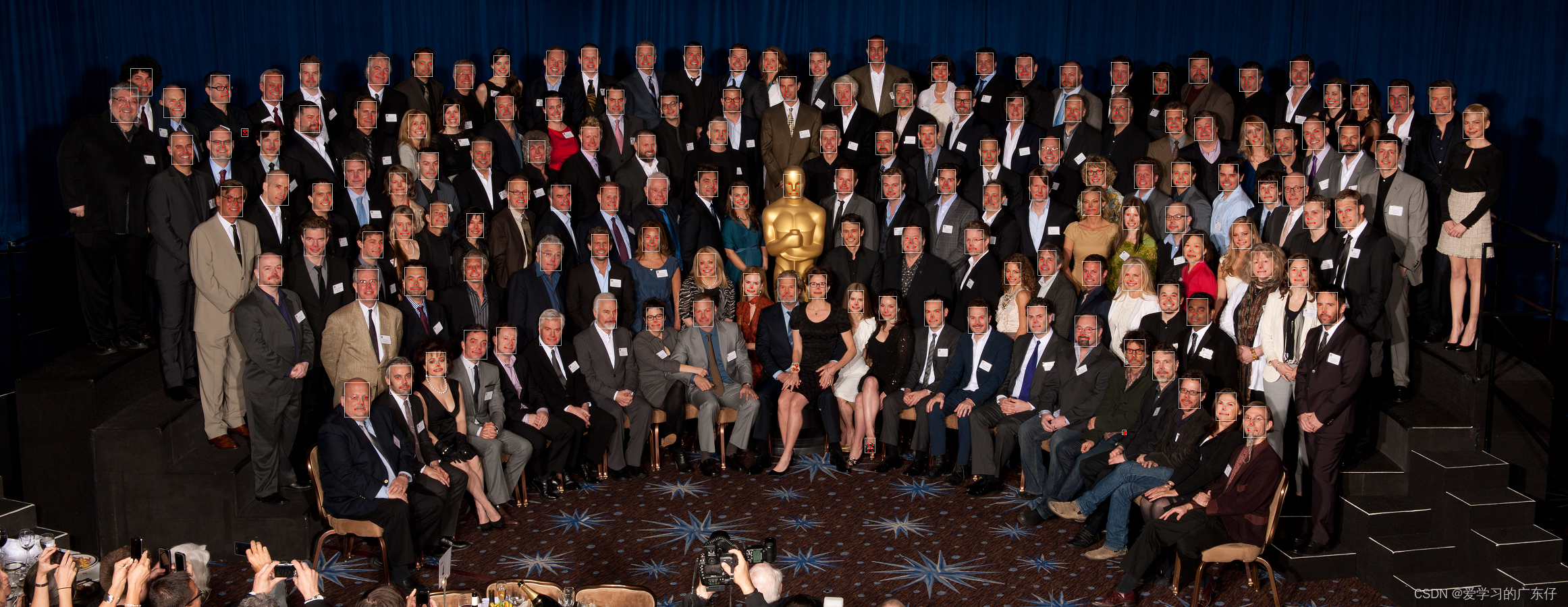
效果

最后
以上就是快乐月饼最近收集整理的关于基于Mxnet实现MTCNN人脸识别【附部分源码】前言一、MTCNN二、代码实现的全部内容,更多相关基于Mxnet实现MTCNN人脸识别【附部分源码】前言一、MTCNN二、代码实现内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复