Spring IOC容器的初始化过程:Resource定位,BeanDefinition载入,向IOC容器注册BeanDefinition。整个过程由refresh()方法触发,三个过程由不同的模块完成,使用户更加灵活的对这三个过程剪裁和扩展。
BeanDefinition 就是POJO对象在IOC容器中的抽象。通过BeanDefinition 这个数据结构,使IOC容器能够方便的对POJO对象也就是Bean进行管理。将BeanDefinition 注册到hashmap中,也就是一个IOC容器中,通过hashmap持有这些BeanDefinition结构。就好比我们对物品整理归类,苹果,桃子,草莓都是水果,可以归到水果类,然后对水果进行统一的处理,比如放到冰箱保鲜。这里BeanDefinition就是苹果或桃子或李子,容器就是冰箱。
IOC容器的初始化过程不包括Bean依赖注入。Bean定义的载入和依赖注入是两个独立的过程。依赖注入一般发生在应用第一次通过getBean向容器索取Bean的时候。(配置lazyinit属性除外)
具体过程(以FileSystemXmlApplicationContext为例):
Resource定位:
指BeanDefinition资源定位。它由ResourceLoader通过统一的Resource接口完成,这个Resource对各种形式的BeanDefinition的使用提供了统一接口。在文件系统中的BeanDefinition可以用FileSystemResource抽象;在类路径中的BeanDefinition可以用ClassPathResource来抽象。Resource定位就是找水果的过程,水果可能在树上,也可能在地里长着。
BeanDefinition载入:
指把用户定义好的Bean表示成IOC容器的数据结构,这个数据结构就是BeanDefinition。
注册:
指向IOC容器注册这些BeanDefinition的过程。通俗的讲就是将BeanDefinition注入到一个hashmap中。
以FileSystemXmlApplicationContext为例来看下IOC容器初始化的过程。
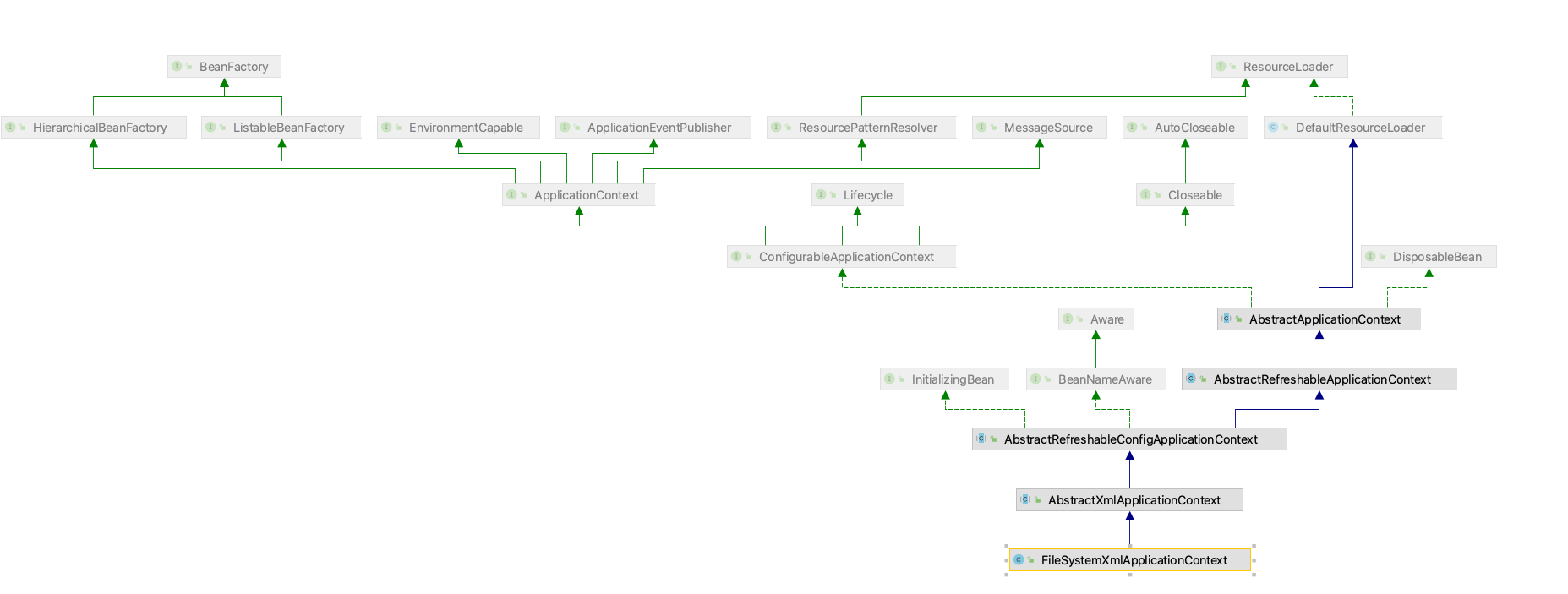
我们先看下FileSystemXmlApplicationContext继承关系:
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext源码:
package org.springframework.context.support;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
/**
* FileSystemXmlApplicationContext是一个支持xml定义BeanDefinition的ApplicationContext,
* 并且可以指定以文件形式的BeanDefinition的读入,这些文件可以使用文件路径和URL定义来表示。
* 在测试环境和独立应用环境中,这个ApplicationContext非常有用。
*/
public class FileSystemXmlApplicationContext extends AbstractXmlApplicationContext {
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext() {
}
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {
super(parent);
}
/**
* 从给定的xml文件中加载Bean定义,创建一个FileSystemXmlApplicationContext,并自动刷新上下文
* configLocation包含的是BeanDefinition所在的文件路径
*/
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException {
this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null);
}
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String... configLocations) throws BeansException {
this(configLocations, true, null);
}
/**
* 允许configLocation包含多个BeanDefinition的文件路径的同时,还允许指定自己的双亲IOC容器
*/
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
this(configLocations, true, parent);
}
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh) throws BeansException {
this(configLocations, refresh, null);
}
/**
* 在对象的初始化过程中,调用refresh函数载入BeanDefinition,
* 这个refresh()启动了BeanDefinition的载入过程
*/
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
/**
* 通过构造一个FileSystemResource来得到一个在文件系统中定位的BeanDefinition
*/
@Override
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
if (path != null && path.startsWith("/")) {
path = path.substring(1);
}
return new FileSystemResource(path);
}
}
从前面的类图中我们可以看出,FileSystemXmlApplicationContext已经通过继承AbstractApplicationContext具备了ResourceLoader读入以Resource定义的BeanDefinition的能力。因为AbstractApplicationContext的基类是DefaultResourceLoader。
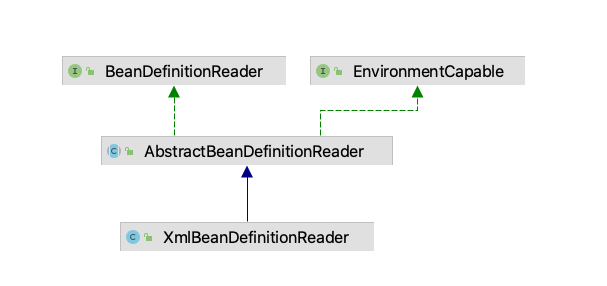
BeanDefinitionReader
在介绍IOC容器初始化过程之前,我们先了解一个类:BeanDefinition读取器-BeanDefinitionReader。BeanDefinitionReader利用ResouceLoader从指定位置加载Bean定义,将物理资源转化生成Resource。

图来自:https://blog.csdn.net/HNU_Csee_wjw/article/details/120406576
以编程的方式使用DefaultListableBeanFactory时,我们定义一个Resource来定位容器使用的BeanDefinition:ClassPathResource res = new ClassPathResource("beans.xml");
这里定义的Resource并不能由DefaultListableBeanFactory直接使用,而是通过BeanDefinitionReader来对这些信息进行处理。Spring为我们提供了一系列加载不同Resource的读取器的实现,使不同的容器可以配置相应的BeanDefinitionReader。比如FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的父类AbstractXmlApplicationContext用的读取器是XmlBeanDefinitionReader类型。
AbstractXmlApplicationContext
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
// 用给定的XmlBeanDefinitionReader加载BeanDefinition
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}
推荐阅读:SpringIOC源码解析(4)—— Resource、ResourceLoader、容器之间的微妙关系
下面我们进入正题,看一下FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的初始化流程:
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的初始化流程由父类AbstractApplicationContext的refresh()方法触发。
AbstractApplicationContext类refresh()方法:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// 子类启动refreshBeanFactory()
// FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 是AbstractApplicationContext的子类
// 在这一步执行refreshBeanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 准备用于此上下文的beanFactory
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 设置beanFactory的后置处理
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 在上下文中调用注册为bean的后置处理器。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 注册拦截bean创建的bean处理器。
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 初始化上下文中的消息源
initMessageSource();
// 为上下文初始化事件多播机制
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 初始化其他特殊的Bean
onRefresh();
// 检查监听的Bean并注册他们到容器中
registerListeners();
// 实例化所有剩余的(非懒加载)的单例
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 最后:发布容器事件
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// 为避免资源占用销毁在前面创建的单例
destroyBeans();
// 重置Reset 'active' 表示
cancelRefresh(ex);
// 向调用方抛出异常
throw ex;
}
finally {
// 重置Spring核心中的常见缺省缓存,因为我们可能不再需要单例bean的元数据。。。
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}先看一张流程图(为了突出关键步骤,只画了关键类,省略了参数):

FileSystemResource定位
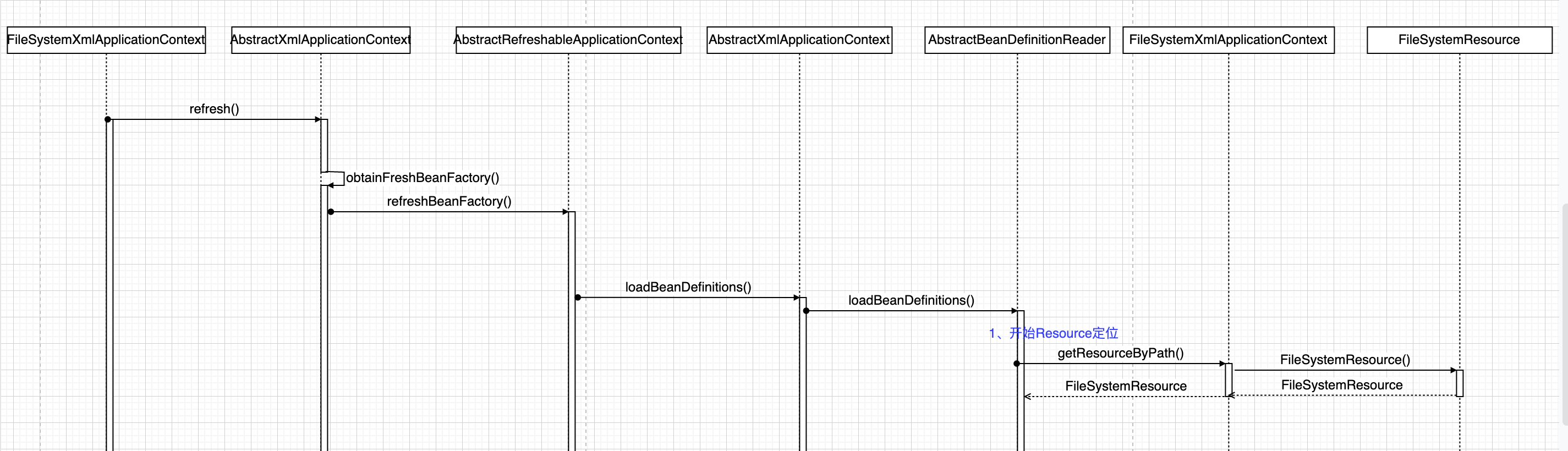
结合流程图可以看到,最后getResourceByPath()方法会被子类FileSystemXmlApplicationContext实现,返回一个FileSystemResource对象,完成BeanDefinition的定位。Spring通过FileSystemResource对象,可以进行相关的IO操作。
定位完成后,就可以用返回的Resource对象来进行BeanDefinition的载入了。
BeanDefinition载入
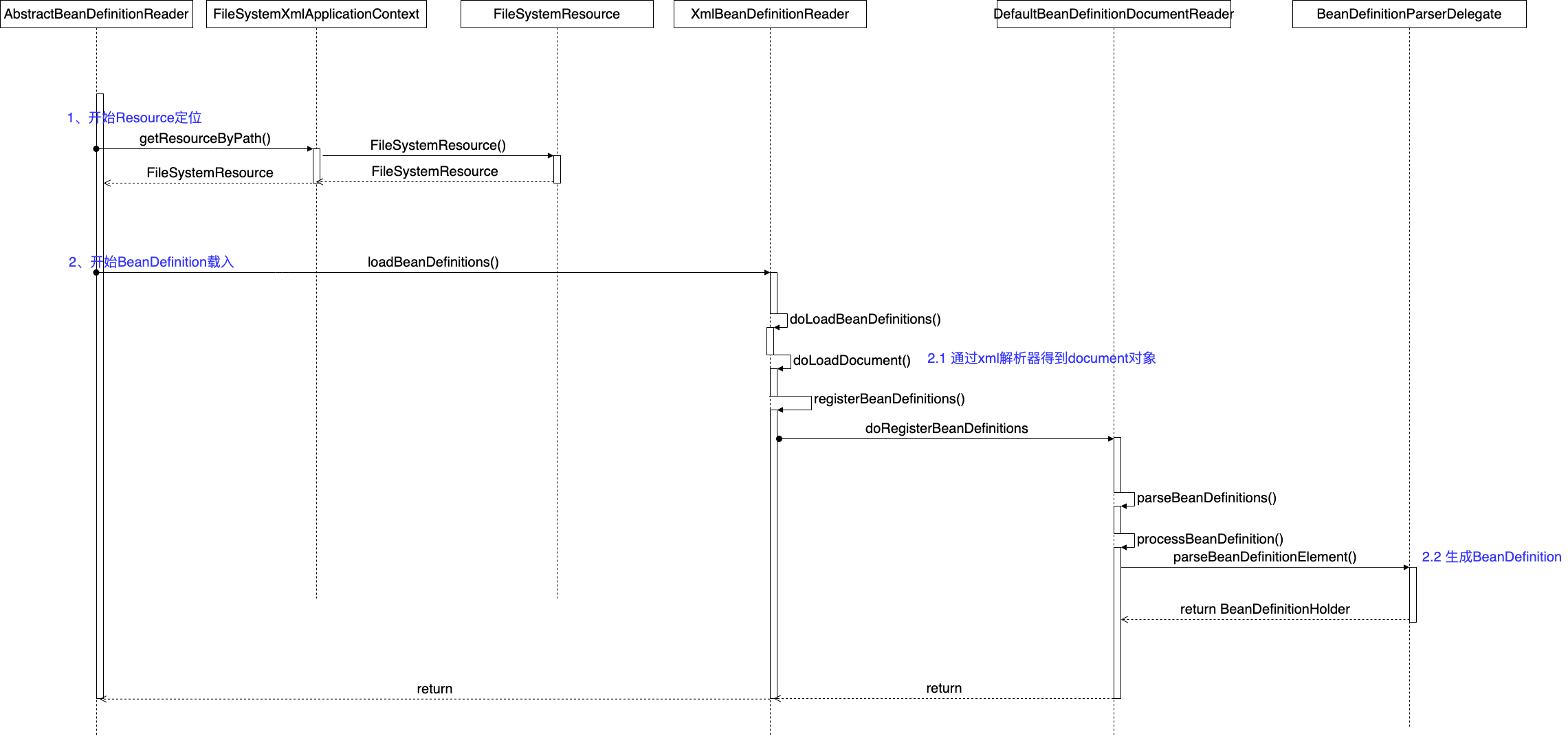
所谓BeanDefinition载入,就是把xml文件中定义的Bean定义,进过转换和层层解析,根据解析结果,将属性值封装成Property value对象设置到BeanDefinition中,处理成IOC容器中的数据结构。
入口在BeanDefinitionParserDelegate类的parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBean)方法。
核心处理方法是:
parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, String beanName, BeanDefinition containingBean)
我们重点看下:
// 解析bean定义本身,不考虑名称或别名。如果在解析bean定义期间出现问题可能返回null
// 只是把Bean的属性设置载入到BeanDefinition,不涉及对象的实例化过程。
// 对象的实例化在依赖注入时完成
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(
Element ele, String beanName, BeanDefinition containingBean) {
this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));
String className = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {
className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();
}
try {
String parent = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
// 生成需要的BeanDefinition对象,为Bean定义信息的载入做准备
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);
// 对当前的Bean元素进行属性解析,并设置description信息
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);
bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
// 对各种<bean>元素的信息进行解析
parseMetaElements(ele, bd);
parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
// 解析<bean>的构造函数设置
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);
// 解析<bean>的property设置
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd);
parseQualifierElements(ele, bd);
bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());
bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return bd;
}
// 这里是我们经常见到的异常处理(原来是在载入BeanDefinition时处理的)
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex);
}
catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) {
error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
return null;
}BeanDefinitionParserDelegate类:
解析<bean>的property设置,对property子元素进行解析,Array、List、Set、Map、prop等各种元素都会在这里解析,生成对应的数据对象。比如MangedList、ManagedArray、ManageSet等,是Spring对具体的BeanDefinition的数据封装。
/**
* 分析给定元素子元素属性
*/
public void parsePropertyElements(Element beanEle, BeanDefinition bd) {
NodeList nl = beanEle.getChildNodes();
// 遍历处理所以的子元素
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (isCandidateElement(node) && nodeNameEquals(node, PROPERTY_ELEMENT)) {
parsePropertyElement((Element) node, bd);
}
}
}
public void parsePropertyElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd) {
// 取得property的名字
String propertyName = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(propertyName)) {
error("Tag 'property' must have a 'name' attribute", ele);
return;
}
this.parseState.push(new PropertyEntry(propertyName));
try {
// 如果同一个Bean中已经有同名的property存在,则不进行解析,直接返回。
if (bd.getPropertyValues().contains(propertyName)) {
error("Multiple 'property' definitions for property '" + propertyName + "'", ele);
return;
}
Object val = parsePropertyValue(ele, bd, propertyName);
PropertyValue pv = new PropertyValue(propertyName, val);
parseMetaElements(ele, pv);
pv.setSource(extractSource(ele));
bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(pv);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
}
/**
* 取得每个property的值,也许是一个list或其他
*/
public Object parsePropertyValue(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd, String propertyName) {
String elementName = (propertyName != null) ?
"<property> element for property '" + propertyName + "'" :
"<constructor-arg> element";
// 应该只有一个子节点: 引用类型, 值类型, 集合等.
NodeList nl = ele.getChildNodes();
Element subElement = null;
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element && !nodeNameEquals(node, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT) &&
!nodeNameEquals(node, META_ELEMENT)) {
// Child element is what we're looking for.
if (subElement != null) {
error(elementName + " must not contain more than one sub-element", ele);
}
else {
subElement = (Element) node;
}
}
}
// 这里判断property的属性,是ref还是value。不允许同时是ref和value
boolean hasRefAttribute = ele.hasAttribute(REF_ATTRIBUTE);
boolean hasValueAttribute = ele.hasAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE);
if ((hasRefAttribute && hasValueAttribute) ||
((hasRefAttribute || hasValueAttribute) && subElement != null)) {
error(elementName +
" is only allowed to contain either 'ref' attribute OR 'value' attribute OR sub-element", ele);
}
// 如果是ref,创建一个RuntimeBeanReference类型的对象,封装ref的信息
if (hasRefAttribute) {
String refName = ele.getAttribute(REF_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) {
error(elementName + " contains empty 'ref' attribute", ele);
}
RuntimeBeanReference ref = new RuntimeBeanReference(refName);
ref.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return ref;
}
// 如果是value,创建一个TypedStringValue类型的对象,这个对象封装了value的信息
else if (hasValueAttribute) {
TypedStringValue valueHolder = new TypedStringValue(ele.getAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE));
valueHolder.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return valueHolder;
}
// 如果还有其他子元素,触发对子元素的解析
else if (subElement != null) {
return parsePropertySubElement(subElement, bd);
}
else {
// Neither child element nor "ref" or "value" attribute found.
error(elementName + " must specify a ref or value", ele);
return null;
}
}
/**
* 分析属性或构造函数arg元素的值、ref或集合子元素。
* @param ele 属性元素的子元素;我们还不知道是哪个
* @param defaultValueType 任何的默认类型(类名)
* {@code <value>} 可能创建的标记
*/
public Object parsePropertySubElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd, String defaultValueType) {
if (!isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
return parseNestedCustomElement(ele, bd);
}
// 节点是Bean
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder nestedBd = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, bd);
if (nestedBd != null) {
nestedBd = decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, nestedBd, bd);
}
return nestedBd;
}
// 节点是引用类型
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, REF_ELEMENT)) {
// 对任何bean的任何名称的通用引用。
String refName = ele.getAttribute(BEAN_REF_ATTRIBUTE);
boolean toParent = false;
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) {
// 对同一XML文件中另一个bean的id的引用。
refName = ele.getAttribute(LOCAL_REF_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) {
// 对父上下文中另一个bean的id的引用。
refName = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_REF_ATTRIBUTE);
toParent = true;
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) {
error("'bean', 'local' or 'parent' is required for <ref> element", ele);
return null;
}
}
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) {
error("<ref> element contains empty target attribute", ele);
return null;
}
RuntimeBeanReference ref = new RuntimeBeanReference(refName, toParent);
ref.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return ref;
}
// 节点是idref类型
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, IDREF_ELEMENT)) {
return parseIdRefElement(ele);
}
// 节点是value
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, VALUE_ELEMENT)) {
return parseValueElement(ele, defaultValueType);
}
// 节点是null
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, NULL_ELEMENT)) {
// 对象是null,创建一个TypedStringValue类型的对象为其保留地址空间
TypedStringValue nullHolder = new TypedStringValue(null);
nullHolder.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return nullHolder;
}
// 节点是数组类型
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, ARRAY_ELEMENT)) {
return parseArrayElement(ele, bd);
}
// 节点是List集合类型
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, LIST_ELEMENT)) {
return parseListElement(ele, bd);
}
// 节点是Set集合类型
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, SET_ELEMENT)) {
return parseSetElement(ele, bd);
}
// 节点是Map类型
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, MAP_ELEMENT)) {
return parseMapElement(ele, bd);
}
// 节点是props类型
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, PROPS_ELEMENT)) {
return parsePropsElement(ele);
}
else {
error("Unknown property sub-element: [" + ele.getNodeName() + "]", ele);
return null;
}
}我们看一下List这样的属性配置是如何被解析的:
// 返回ManagedList类型的对象
public List<Object> parseListElement(Element collectionEle, BeanDefinition bd) {
String defaultElementType = collectionEle.getAttribute(VALUE_TYPE_ATTRIBUTE);
NodeList nl = collectionEle.getChildNodes();
ManagedList<Object> target = new ManagedList<Object>(nl.getLength());
target.setSource(extractSource(collectionEle));
target.setElementTypeName(defaultElementType);
target.setMergeEnabled(parseMergeAttribute(collectionEle));
// 具体的List元素解析过程
parseCollectionElements(nl, target, bd, defaultElementType);
return target;
}
protected void parseCollectionElements(
NodeList elementNodes, Collection<Object> target, BeanDefinition bd, String defaultElementType) {
for (int i = 0; i < elementNodes.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = elementNodes.item(i);
// node需要是element类型
if (node instanceof Element && !nodeNameEquals(node, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT)) {
// 将node添加到taget中,并递归解析下一层子元素
target.add(parsePropertySubElement((Element) node, bd, defaultElementType));
}
}
}经过这样层层解析,我们就将xml文件中定义的Definition加载到了IOC容器中,并在容器中建立了映射,完成了IOC容器管理Bean对象的准备工作。这些数据结构可以以AbstractBeanDefinition为入口,让IOC容器执行索引、查询和操作。你没有看错,这一小节,经过了这么多的处理,就是对xml文件解析,把内容处理成BeanDefinition。看迷茫的同学可以结合类图,往回倒一下处理的入口。
这时候IOC容器BeanDefinition中存在的还只是一些静态的配置信息,要想让容器起作用,还需完成数据向容器的注册
BeanDefinition在IOC容器中的注册
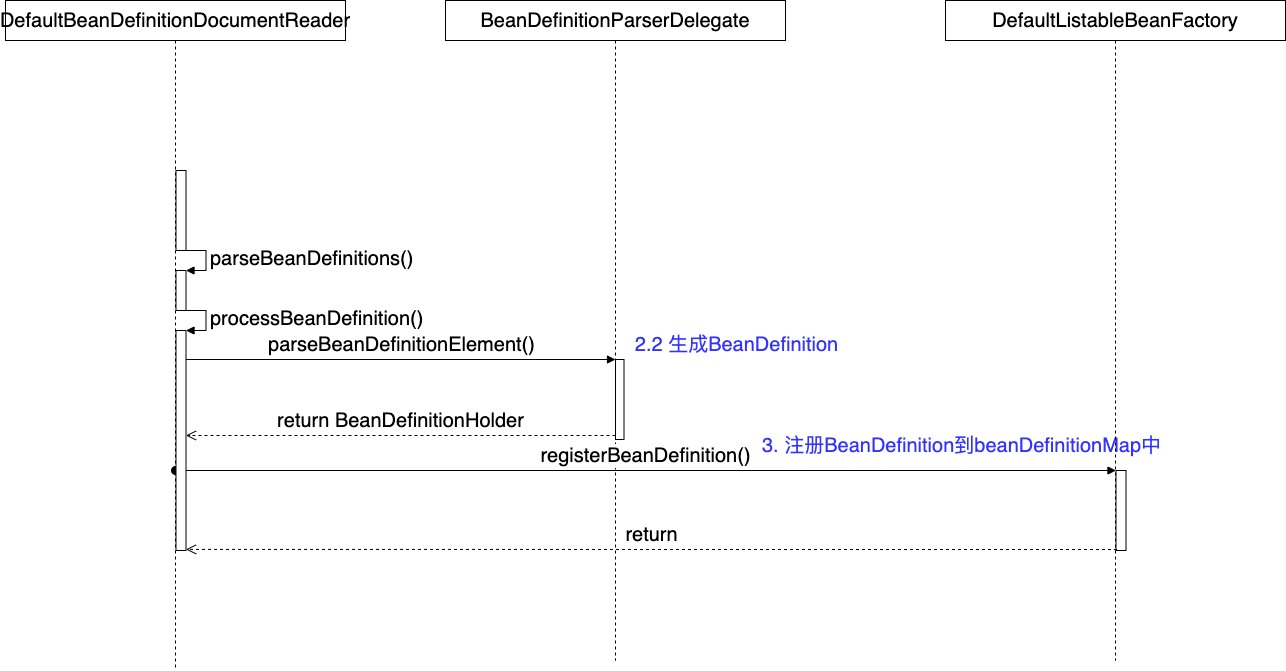
我们回到DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader类
/**
* 处理给定的bean元素,解析bean定义并将其注册到注册表中。
*/
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
// BeanDefinition载入
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// 注册实例
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event.
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}将BeanDefinition载入后,开始注册BeanDefinition到IOC容器。
注册的关键代码,在DefaultListableBeanFactory类:
在DefaultListableBeanFactory中,是通过一个hashmap来持有载入的BeanDefinition的:
/** Map of bean definition objects, keyed by bean name */
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition>(256);@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
BeanDefinition oldBeanDefinition;
// 如果有相同名字的Bean已经在IOC容器中注册了,如果不允许覆盖,则抛出异常
oldBeanDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (oldBeanDefinition != null) {
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Cannot register bean definition [" + beanDefinition + "] for bean '" + beanName +
"': There is already [" + oldBeanDefinition + "] bound.");
}
else if (oldBeanDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
oldBeanDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(oldBeanDefinition)) {
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + oldBeanDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + oldBeanDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
// 覆盖old beanDefinition
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
// 检查此工厂的bean创建阶段是否已启动,即,是否有任何bean被标记为同时创建。
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// 加锁
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
if (this.manualSingletonNames.contains(beanName)) {
Set<String> updatedSingletons = new LinkedHashSet<String>(this.manualSingletonNames);
updatedSingletons.remove(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames = updatedSingletons;
}
}
}
else {
// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames.remove(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (oldBeanDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
}到此,完成了BeanDefinition的注册,完成了IOC容器的初始化过程。此时使用的IOC容器DefaultListableBeanFactory中已经建立了整个Bean的配置信息,而且这些BeanDefinition已经可以被容器使用了,并且可以在BeanDefinitionMap中被检索到和使用。通过容器对这些Bean信息进行处理和维护。
最后
以上就是奋斗咖啡最近收集整理的关于Spring源码阅读-IOC容器初始化过程Resource定位:BeanDefinition载入:注册:以FileSystemXmlApplicationContext为例来看下IOC容器初始化的过程。的全部内容,更多相关Spring源码阅读-IOC容器初始化过程Resource定位:BeanDefinition载入:注册:以FileSystemXmlApplicationContext为例来看下IOC容器初始化内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复