1.首先创建maven工程(略),项目结构如下
2.pom文件配置
2.1 添加<profiles标签>,在<profiles>分别定义各个<profile>用来配置开发,测试以及生产的全局变量,代码如下:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>tca</groupId>
<artifactId>maven</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<junit.version>4.12</junit.version>
<slf4j.version>1.7.7</slf4j.version>
<spring.version>4.3.8.RELEASE</spring.version>
</properties>
<!-- 整个项目都需要依赖的jar包 -->
<dependencies>
<!-- 单元测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 日志 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>${slf4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-oxm</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<profiles>
<profile>
<!-- 本地环境 -->
<id>dev</id>
<properties>
<test.username>dev</test.username>
<test.password>dev</test.password>
</properties>
<!-- 默认激活本环境 -->
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
</profile>
<profile>
<!-- 测试环境 -->
<id>test</id>
<properties>
<test.username>test</test.username>
<test.password>test</test.password>
</properties>
</profile>
<profile>
<!-- 生产环境 -->
<id>pro</id>
<properties>
<test.username>pro</test.username>
<test.password>pro</test.password>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
<build>
<!-- 所有子项目都需要 -->
<plugins>
<!-- JDK版本 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<!-- maven插件 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<testFailureIgnore>true</testFailureIgnore>
<!-- 跳过单元测试 -->
<skip>true</skip>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>${project.basedir}/src/main/resources</directory>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
</project>注:
1.为保证项目完整性,所以将整个pom文件粘贴上来
2.<profiles>标签是定义在<project>下的子标签,我们在<profiles>里分别定义三个<profile>标签,分别代表三个环境,开发,测试和线上,在<profile>标签下我们通常添加下列几个子标签:
<id>标签表示当前环境的唯一标识符,之后使用maven打包时具体选择哪个<profile>环境需要用到该参数
<properties>标签用于定义该环境下的全局变量(<key>value</key>格式)
<activation>标签用于定义默认打包环境,配置如下(表示打包时默认选择当前<profile>):
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>2.2 <resources>标签用于指定上述<profile>中定义的全局变量可被哪些资源引用,配置如下:
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>${project.basedir}/src/main/resources</directory>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>如上图所示,表示可以被src/main/resources类路径下的资源引用。因为正常我们在.properties配置文件中引用。${project.basedir}表示项目根目录,即pom文件所在的目录
3.实际应用
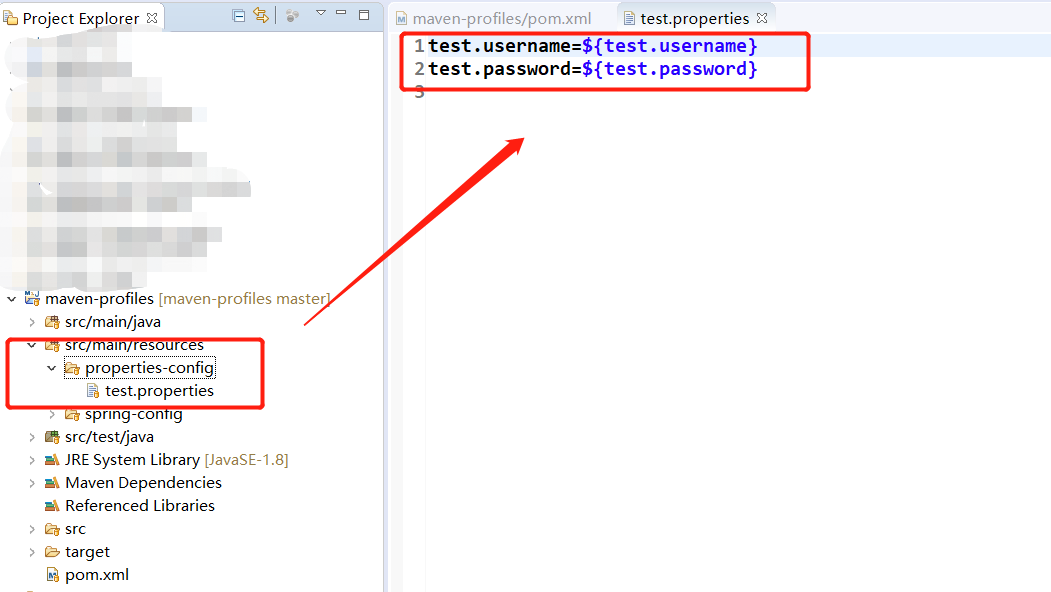
一般,我们在各个<profile>中定义的全局变量的<key>值是相同的,只是value不同,如代码:

我们在properties文件中进行引用, 使用${}符号,${}内的值就是上述全局变量的key,这样我们在打包时就会根据所选的<profile>模板来引用不同的值:
4.打包
切换到项目根目录下,即pom文件所在的目录,使用命令:
<!-- profile-id代表上述定义profile时下的<id>标签的值 -->
mvn clean package -P profile-id如,打包为生产环境,只需要 mvn clean package -P pro
5.验证
切换到项目根目录下,使用mvn clean package -P pro命令打包,用解压器打开打包之后的jar包(jar包位于项目根目录下的target目录下),观察test.properties文件,如下:
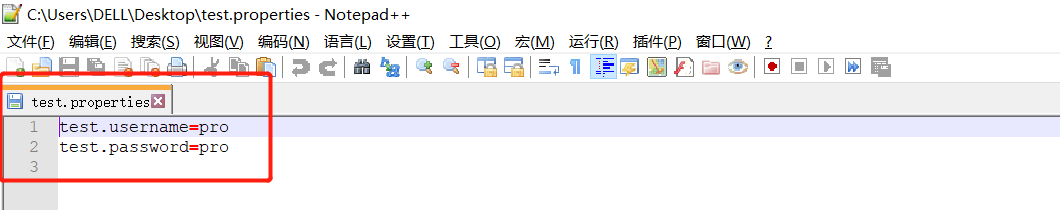
验证成功!
最后
以上就是隐形花瓣最近收集整理的关于maven的profile构建不同环境打包的全部内容,更多相关maven内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复