查看current工作路径:
1 >>> importos2 >>>os.getcwd()3 'D:\python'
更改工作路径:
1 >>> os.chdir('E:\forpython') #要用双斜杠
读入文件:
1 >>> red_data = open('《红楼梦》.txt')2 >>> print(red_data.readline())3 《红楼梦》4 >>> print(red_data.readline())5 曹雪芹 高鄂 著6 >>>print(red_data.readline())7 第一回 甄士隐梦幻识通灵 贾雨村风尘怀闺秀8 >>>red_data.seek(0)9 010 >>> print(red_data.readline())11 《红楼梦》
刷屏了。。。
1 >>> for each_line inred_data:2 print(red_data.readline(),end = 't')
处理完了之后:
1 >>> red_data.close()
对字符串的split:
1 >>> test = 'man said:'how are you''
2 >>>test3 "man said:'how are you'"
4 >>> (role,line_spoken) = test.split(":") # 多重赋值5 >>>role6 'man said'
7 >>>line_spoken8 "'how are you'"
head frist Python里面文件的资源链接:http://python.itcarlow.ie/resources.html
查看BulitInFunction的帮助文档:
1 >>> help(test.split)
很奇怪,用help(split)会报错。。。这个有待研究
1 >>> help("split")2 No Python documentation found for 'split'.3 Use help() to get the interactive help utility.4 Use help(str) for help on the str class.
看看help()会有什么结果:
1 >>>help()2
3 Welcome to Python 3.6's help utility!
4
5 If this isyour first time using Python, you should definitely check out6 the tutorial on the Internet at http://docs.python.org/3.6/tutorial/.7
8 Enter the name of any module, keyword, ortopic to get help on writing9 Python programs and using Python modules. To quit this help utility and
10 return to the interpreter, just type "quit".11
12 To get a list of available modules, keywords, symbols, ortopics, type13 "modules", "keywords", "symbols", or "topics". Each module also comes14 with a one-line summary of what it does; to list the modules whose name15 or summary contain a given string such as "spam", type "modules spam".16
17 help>
1 help>split2 No Python documentation found for 'split'.3 Use help() to get the interactive help utility.4 Use help(str) for help on the str class.
没办法。。。去百度一下吧
1 help("open")
这样用在split上还是会报错。。。不管了
打开在headfirst Python support site下载的sketch.txt,跑一下程序:
1 >>> data = open('sketch.txt')2 >>> for each_line indata:3 (role,line_spoken) = each_line.split(':',1)4 print(role,end=' ')5 print('said:',end=' ')6 print(line_spoken,end=' ')7 >>> data.close()
打印一部分后会报错:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "", line 2, in
(role,line_spoken) = each_line.split(':',1)
ValueError: not enough values to unpack (expected 2, got 1)
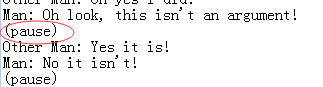 因为这一段中没有':'
因为这一段中没有':'
解决办法:
1 >>> for each_line indata:2 if not each_line.find(':') == -1: # 返回要查找字符所在的位置3 (role,line_spoken) = each_line.split(':',1)4 print(role,end=' ')5 print('said:',end=' ')6 print(line_spoken,end=' ')
检查文件是否存在:
1 >>> os.path.exists('123.xlsx')
异常错误处理机制:
1 >>> for each_line indata:2 try:3 (role,line_spoken) = each_line.split(':',1)4 print(role,end=' ')5 print('said:',end=' ')6 print(line_spoken,end=' ')7 except:8 pass
指定处理异常的类型:
>>> for each_line indata:try:
(role,line_spoken)= each_line.split(':',1)
print(role,end=' ')
print('said:',end=' ')
print(line_spoken,end=' ')
except ValueError:
pass
分别将两个人的台词保存到两个列表中:
1 >>> man=[]2 >>> other_man=[]3 >>> for each_line indata:4 try:5 (role,line_spoken)=each_line.split(':',1)6 line_spoken=line_spoken.strip()7 if role=='Man':8 man.append(line_spoken)9 elif role=='Other Man':10 other_man.append(line_spoken)11 except ValueError:12 pass
写出文件:
1 >>> out1=open('man.txt','w')2 >>> out2=open('other_man.txt','w')3 >>> print(man,file=out1)4 >>> print(other_man,file=out2)5 >>>out1.close()6 >>> out2.close()
完成写入后一定要关闭文件,即:out1.close() 这称为刷新输出
1 >>> try:2 man_file=open('man's word.txt','w')3 other_file=open('other man's word.txt','w')4 print(man,file=man_file)5 print(other_man,file=other_file)6
7 except IOError:8 print('File error')9 finally:10 man_file.close()11 other_file.close()
使用finally确保文件的关闭
打印异常错误:
1 exceptIOError as err:2 print('File error:'+err)
使用with:
1 >>> try:2 with open('1.txt','w') as data1:3 print(man,file=data1)4 with open('2.txt','w') as data2:5 print(other_man,file=data2)6 exceptIOError as err:7 print('file error:',str(err))
不需要close了,这样代码更简洁
修改上次的print_it_all,
1 >>> def print_it_all(thelist,indent=False,level=0,fn=sys.stdout):2 for each_item inthelist:3 ifisinstance(each_item,list):4 print_it_all(each_item,indent,level+1,fn)5 else:6 ifindent:7 for tap_stop inrange(level):8 print('t',end='',file=fn)9 print(each_item,file=fn)
再用print_it_all把数据输出到外部文件:
1 >>> with open('aaa.txt','w') as mdf:2 print_it_all(man,fn=mdf)
pickle:个人理解是对数据的封装(封装就是只能通过Python打开这个文件),并且持久的储存数据
1 >>> with open('man_data.txt','wb') as man_file:2 pickle.dump(man,man_file)3
5 >>> new_man=[]6 >>> with open('man_data.txt','rb') as man_file:7 new_man=pickle.load(man_file)
最后
以上就是粗心泥猴桃最近收集整理的关于python外部输入_Python学习笔记:外部数据的输入、存储等操作的全部内容,更多相关python外部输入_Python学习笔记:外部数据内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。

![读取外部输入的方式Python3 中 sys.argv[ ]的用法解释](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg13.png)






发表评论 取消回复