最近在看SpringMVC源码,从中看到了比较优秀的设计模式所以来分享下。
1.适配器模式(Adapter):将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另外一个接口,Adapter模式使得原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的那些类可以在一起工作
具体的详细知识可以参考这篇文章
http://haolloyin.blog.51cto.com/1177454/346128
http://blog.csdn.net/xtu_xiaoxin/article/details/8796499
适用场景:
1、已经存在的类的接口不符合我们的需求;
2、创建一个可以复用的类,使得该类可以与其他不相关的类或不可预见的类(即那些接口可能不一定兼容的类)协同工作;
3、在不对每一个都进行子类化以匹配它们的接口的情况下,使用一些已经存在的子类。
2.SpringMvc中的适配器(HandlerAdapter)
SpringMVC中的适配器到底是解决以上哪个问题的呢?我们来一步一步看看源码,看看Spring是怎么做的
首先我们找到前端控制器DispatcherServlet可以把它理解为适配器模式中的Client,它的主要作用在于通过处理映射器(HandlerMapper)来找到相应的Handler(即Controlle(宽泛的概念Controller,以及HttpRequestHandler,Servlet,等等)r),并执行Controller中相应的方法并返回ModelAndView,
mappedHandler.getHandler()其实就是通过Spring容器中获取到的(宽泛的概念Controller,以及HttpRequestHandler,Servlet,等等)Controller
先短暂回顾下流程
1.DispatcherServlet中的doDispatch
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 此处通过HandlerMapping来映射Controller
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// 获取适配器
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// 通过适配器调用controller的方法并返回ModelAndView
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
2.为什么要使用适配器模式呢?
Controller可以理解为Adaptee(被适配者)其中之一
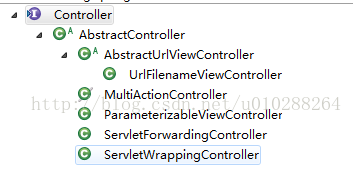
可以看到处理器(宽泛的概念Controller,以及HttpRequestHandler,Servlet,等等)的类型不同,有多重实现方式,那么调用方式就不是确定的,如果需要直接调用Controller方法,需要调用的时候就得不断是使用if else来进行判断是哪一种子类然后执行。那么如果后面要扩展(宽泛的概念Controller,以及HttpRequestHandler,Servlet,等等)Controller,就得修改原来的代码,这样违背了开闭原则(对修改关闭,对扩展开放)。
3.SpringMvc 是如何使用适配器模式来解决以上问题的呢?
Spring创建了一个适配器接口(HandlerAdapter)使得每一种处理器(宽泛的概念Controller,以及HttpRequestHandler,Servlet,等等)有一种对应的适配器实现类,让适配器代替(宽泛的概念Controller,以及HttpRequestHandler,Servlet,等等)执行相应的方法。这样在扩展Controller 时,只需要增加一个适配器类就完成了SpringMVC的扩展了。
public interface HandlerAdapter {
boolean supports(Object handler);
ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception;
}
supports()方法传入处理器(宽泛的概念Controller,以及HttpRequestHandler,Servlet,等等)判断是否与当前适配器支持如果支持则从DispatcherServlet中的HandlerAdapter实现类中返回支持的适配器实现类。handler方法就是代理Controller来执行请求的方法并返回结果。
在DispatchServlert中的doDispatch方法中
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
此代码通过调用DispatchServlert 中getHandlerAdapter传入Controller(宽泛的概念Controller,以及HttpRequestHandler,Servlet,等等),来获取对应的HandlerAdapter 的实现子类,从而做到使得每一种Controller有一种对应的适配器实现类
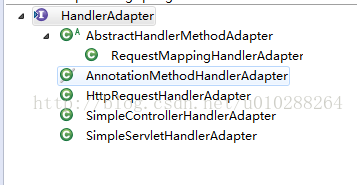
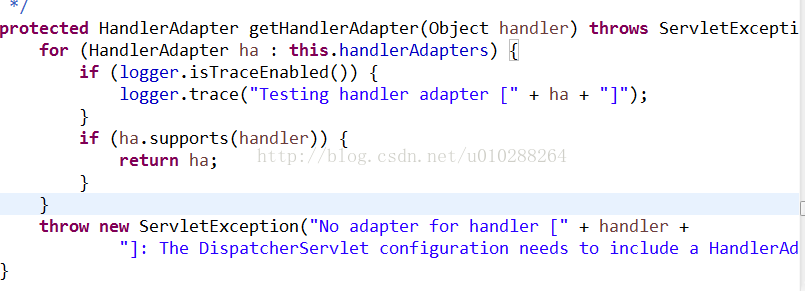
返回后就能通过对应的适配实现类代理Controller(宽泛的概念Controller,以及HttpRequestHandler,Servlet,等等)来执行请求的方法
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
其中一个处理器适配器就是我们常说的最熟悉的Controller类适配器
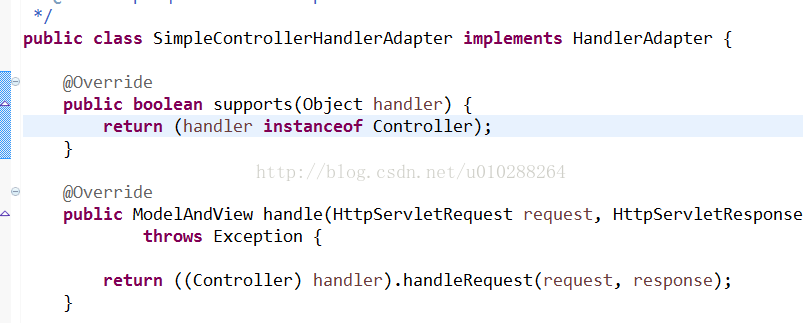
原文地址
最后
以上就是闪闪水池最近收集整理的关于从SpringMVC来看适配器模式的全部内容,更多相关从SpringMVC来看适配器模式内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复