1 原文
没有仔细看,只是看了一下模型结构。点击【原文】即可下载。
2 模型
对于监督学习问题,类别特征作为输入,一般One-hot,所以需要引入特征交互来做出更精确的预测;但是如果直接以product的方式来显示交互,对于稀疏输入数据集,只能观察到一些交叉特征;
所以FM被提出了,利用隐变量来做内积实现交互,但是FM也存在问题,也就是所有交互特征的权重是一样的;
但是在实际中,应该预测性较低的特征,其对应权重也较低。所以AFM就是基于这个思想,AFM模型的结构如下:

求解公式:
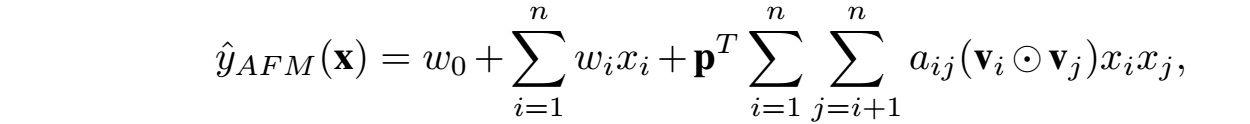
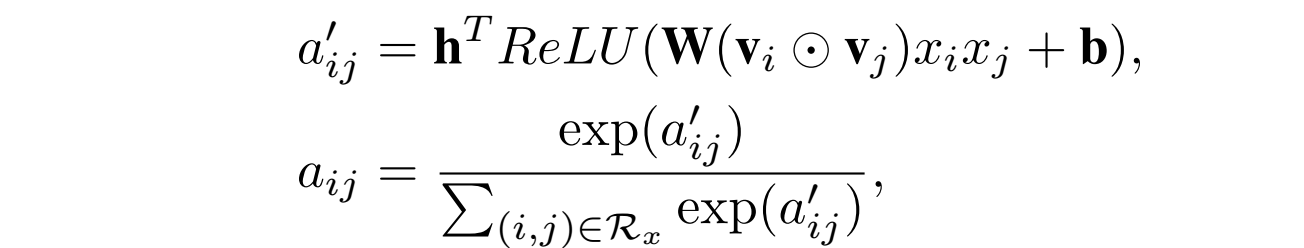
AFM可以用于不同的任务:回归、分类、排序等,一般对于回归问题是平方损失,二分类是Logloss,本文专注于平方损失,且使用SGD算法来最优化模型参数;
防止过拟合: 一般考虑L2和Dropout,文中没有同时使用L2+Dropout,效果不好;所以只用了L2在MLP层,如下所示:
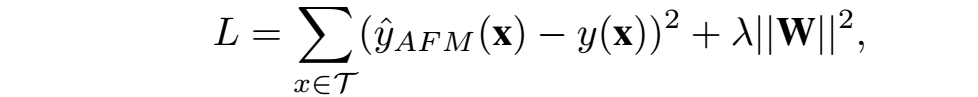
3 python
Embedding Size:K
Batch Size:N
Attention Size :A
Field Size (这里是field size 不是feature size!!!!): F
weights[‘attention_w’] 的维度为 K * A,
weights[‘attention_b’] 的维度为 A,
weights[‘attention_h’] 的维度为 A,
weights[‘attention_p’] 的维度为 K * 1
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from time import time
from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
class AFM(BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin):
def __init__(self, feature_size, field_size,
embedding_size=8,attention_size=10,
deep_layers=[32, 32], deep_init_size = 50,
dropout_deep=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],
deep_layer_activation=tf.nn.relu,
epoch=10, batch_size=256,
learning_rate=0.001, optimizer="adam",
batch_norm=0, batch_norm_decay=0.995,
verbose=False, random_seed=2016,
loss_type="logloss", eval_metric=roc_auc_score,
greater_is_better=True,
use_inner=True):
assert loss_type in ["logloss", "mse"],
"loss_type can be either 'logloss' for classification task or 'mse' for regression task"
self.feature_size = feature_size
self.field_size = field_size
self.embedding_size = embedding_size
self.attention_size = attention_size
self.deep_layers = deep_layers
self.deep_init_size = deep_init_size
self.dropout_dep = dropout_deep
self.deep_layers_activation = deep_layer_activation
self.epoch = epoch
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.optimizer_type = optimizer
self.batch_norm = batch_norm
self.batch_norm_decay = batch_norm_decay
self.verbose = verbose
self.random_seed = random_seed
self.loss_type = loss_type
self.eval_metric = eval_metric
self.greater_is_better = greater_is_better
self.train_result,self.valid_result = [],[]
self.use_inner = use_inner
self._init_graph()
def _init_graph(self):
self.graph = tf.Graph()
with self.graph.as_default():
tf.set_random_seed(self.random_seed)
self.feat_index = tf.placeholder(tf.int32,
shape=[None,None],
name='feat_index')
self.feat_value = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,
shape=[None,None],
name='feat_value')
self.label = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=[None,1],name='label')
self.dropout_keep_deep = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=[None],name='dropout_deep_deep')
self.train_phase = tf.placeholder(tf.bool,name='train_phase')
self.weights = self._initialize_weights()
# Embeddings
self.embeddings = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.weights['feature_embeddings'],self.feat_index) # N * F * K
feat_value = tf.reshape(self.feat_value,shape=[-1,self.field_size,1])
self.embeddings = tf.multiply(self.embeddings,feat_value) # N * F * K
# element_wise
element_wise_product_list = []
for i in range(self.field_size):
for j in range(i+1,self.field_size):
element_wise_product_list.append(tf.multiply(self.embeddings[:,i,:],self.embeddings[:,j,:])) # None * K
self.element_wise_product = tf.stack(element_wise_product_list) # (F * F - 1 / 2) * None * K
self.element_wise_product = tf.transpose(self.element_wise_product,perm=[1,0,2],name='element_wise_product') # None * (F * F - 1 / 2) * K
#self.interaction
# attention part
num_interactions = int(self.field_size * (self.field_size - 1) / 2)
# wx+b -> relu(wx+b) -> h*relu(wx+b)
self.attention_wx_plus_b = tf.reshape(tf.add(tf.matmul(tf.reshape(self.element_wise_product,shape=(-1,self.embedding_size)),
self.weights['attention_w']),
self.weights['attention_b']),
shape=[-1,num_interactions,self.attention_size]) # N * ( F * F - 1 / 2) * A
self.attention_exp = tf.exp(tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(tf.nn.relu(self.attention_wx_plus_b),
self.weights['attention_h']),
axis=2,keep_dims=True)) # N * ( F * F - 1 / 2) * 1
self.attention_exp_sum = tf.reduce_sum(self.attention_exp,axis=1,keep_dims=True) # N * 1 * 1
self.attention_out = tf.div(self.attention_exp,self.attention_exp_sum,name='attention_out') # N * ( F * F - 1 / 2) * 1
self.attention_x_product = tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(self.attention_out,self.element_wise_product),axis=1,name='afm') # N * K
self.attention_part_sum = tf.matmul(self.attention_x_product,self.weights['attention_p']) # N * 1
# first order term
self.y_first_order = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.weights['feature_bias'], self.feat_index)
self.y_first_order = tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(self.y_first_order, feat_value), 2)
# bias
self.y_bias = self.weights['bias'] * tf.ones_like(self.label)
# out
self.out = tf.add_n([tf.reduce_sum(self.y_first_order,axis=1,keep_dims=True),
self.attention_part_sum,
self.y_bias],name='out_afm')
# loss
if self.loss_type == "logloss":
self.out = tf.nn.sigmoid(self.out)
self.loss = tf.losses.log_loss(self.label, self.out)
elif self.loss_type == "mse":
self.loss = tf.nn.l2_loss(tf.subtract(self.label, self.out))
if self.optimizer_type == "adam":
self.optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=self.learning_rate, beta1=0.9, beta2=0.999,
epsilon=1e-8).minimize(self.loss)
elif self.optimizer_type == "adagrad":
self.optimizer = tf.train.AdagradOptimizer(learning_rate=self.learning_rate,
initial_accumulator_value=1e-8).minimize(self.loss)
elif self.optimizer_type == "gd":
self.optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=self.learning_rate).minimize(self.loss)
elif self.optimizer_type == "momentum":
self.optimizer = tf.train.MomentumOptimizer(learning_rate=self.learning_rate, momentum=0.95).minimize(
self.loss)
#init
self.saver = tf.train.Saver()
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
self.sess = tf.Session()
self.sess.run(init)
# number of params
total_parameters = 0
for variable in self.weights.values():
shape = variable.get_shape()
variable_parameters = 1
for dim in shape:
variable_parameters *= dim.value
total_parameters += variable_parameters
if self.verbose > 0:
print("#params: %d" % total_parameters)
def _initialize_weights(self):
weights = dict()
#embeddings
weights['feature_embeddings'] = tf.Variable(
tf.random_normal([self.feature_size,self.embedding_size],0.0,0.01),
name='feature_embeddings')
weights['feature_bias'] = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([self.feature_size,1],0.0,1.0),name='feature_bias')
weights['bias'] = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1),name='bias')
# attention part
glorot = np.sqrt(2.0 / (self.attention_size + self.embedding_size))
weights['attention_w'] = tf.Variable(np.random.normal(loc=0,scale=glorot,size=(self.embedding_size,self.attention_size)),
dtype=tf.float32,name='attention_w')
weights['attention_b'] = tf.Variable(np.random.normal(loc=0,scale=glorot,size=(self.attention_size,)),
dtype=tf.float32,name='attention_b')
weights['attention_h'] = tf.Variable(np.random.normal(loc=0,scale=1,size=(self.attention_size,)),
dtype=tf.float32,name='attention_h')
weights['attention_p'] = tf.Variable(np.ones((self.embedding_size,1)),dtype=np.float32)
return weights
def get_batch(self,Xi,Xv,y,batch_size,index):
start = index * batch_size
end = (index + 1) * batch_size
end = end if end < len(y) else len(y)
return Xi[start:end],Xv[start:end],[[y_] for y_ in y[start:end]]
# shuffle three lists simutaneously
def shuffle_in_unison_scary(self, a, b, c):
rng_state = np.random.get_state()
np.random.shuffle(a)
np.random.set_state(rng_state)
np.random.shuffle(b)
np.random.set_state(rng_state)
np.random.shuffle(c)
def predict(self, Xi, Xv,y):
"""
:param Xi: list of list of feature indices of each sample in the dataset
:param Xv: list of list of feature values of each sample in the dataset
:return: predicted probability of each sample
"""
# dummy y
feed_dict = {self.feat_index: Xi,
self.feat_value: Xv,
self.label: y,
self.dropout_keep_deep: [1.0] * len(self.dropout_dep),
self.train_phase: True}
loss = self.sess.run([self.loss], feed_dict=feed_dict)
return loss
def fit_on_batch(self,Xi,Xv,y):
feed_dict = {self.feat_index:Xi,
self.feat_value:Xv,
self.label:y,
self.dropout_keep_deep:self.dropout_dep,
self.train_phase:True}
loss,opt = self.sess.run([self.loss,self.optimizer],feed_dict=feed_dict)
return loss
def fit(self, Xi_train, Xv_train, y_train,
Xi_valid=None, Xv_valid=None, y_valid=None,
early_stopping=False, refit=False):
has_valid = Xv_valid is not None
for epoch in range(self.epoch):
t1 = time()
self.shuffle_in_unison_scary(Xi_train, Xv_train, y_train)
total_batch = int(len(y_train) / self.batch_size)
for i in range(total_batch):
Xi_batch, Xv_batch, y_batch = self.get_batch(Xi_train, Xv_train, y_train, self.batch_size, i)
self.fit_on_batch(Xi_batch, Xv_batch, y_batch)
if has_valid:
y_valid = np.array(y_valid).reshape((-1,1))
loss = self.predict(Xi_valid, Xv_valid, y_valid)
print("epoch",epoch,"loss",loss)
参考
1、原文 https://www.ijcai.org/proceedings/2017/0435.pdf
2、代码 https://github.com/liulin7576/DL_CTR/tree/master/AFM
3、代码 https://github.com/princewen/tensorflow_practice/tree/master/recommendation/Basic-AFM-Demo
最后
以上就是魁梧手机最近收集整理的关于《Attentional Factorization Machines》AFM模型及python实现1 原文2 模型3 python参考的全部内容,更多相关《Attentional内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复