前言
使用 Flutter 开发移动端有一段时间了,总结一下关于 UI 渲染方面的知识。 了解关于 Flutter 渲染方面的知识还是有必要的,可以帮助你开发更稳定,性能更高的应用。
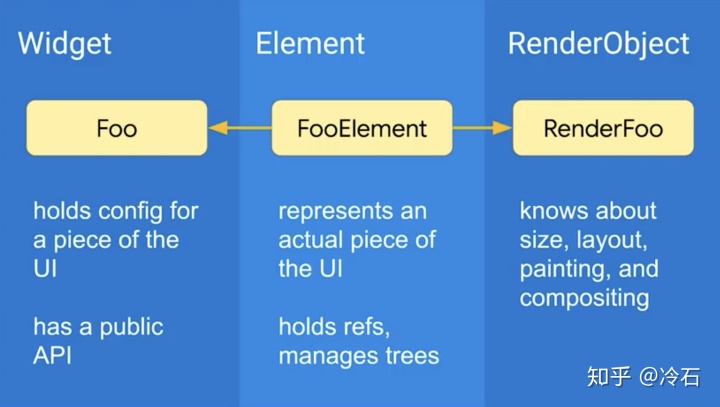
要解答这个问题,首先需要认识到 Flutter 中有三棵树:Widget 树,Element 树和 RenderObject 树。
当应用启动时 Flutter 会遍历并创建所有的 Widget 形成 Widget Tree,同时与 Widget Tree 相对应,通过调用 Widget 上的 createElement() 方法创建每个 Element 对象,形成 Element Tree。
最后调用 Element 的 createRenderObject() 方法创建每个渲染对象,形成一个 Render Tree。
然后需要知道 Widget,Element 和 RenderObject 到底是啥以及它们是干什么的。
什么是 Widget
Widget 是 Flutter 的核心部分,是用户界面的不可变描述信息。正如 Flutter 的口号 Everything’s a widget, 用 Flutter 开发应用就是在写 Widget 。
Flutter 的 Widget 不只表示 UI 控件,还表示一些功能性的组件,如路由跳转 Navigator,手势检测 GestureDetector 组件等。
@immutable
abstract class Widget extends DiagnosticableTree {
/// Initializes [key] for subclasses.
const Widget({ this.key });
final Key key;
/// ...
@protected
Element createElement();
/// ...
static bool canUpdate(Widget oldWidget, Widget newWidget) {
return oldWidget.runtimeType == newWidget.runtimeType
&& oldWidget.key == newWidget.key;
}
}Widget 的 canUpdate 方法通过比较新部件和旧部件的 runtimeType 和 key 属性是否相同来决定更新部件对应的 Element。
什么是 Element
Element 是实例化的 Widget 对象,通过 Widget 的 createElement() 方法,在特定位置使用 Widget 配置数据生成。
Element 用于管理应用 UI 的更新和更改,管理部件的生命周期,每个 Element 都包含对 Widget 和 RenderObject 的引用。

当 Widget 变化时,如果两个 Widget 的 runtimeType 和 key 属性相同的,那么新的 Element 会通过 Element.update() 更新旧的 Element,否则旧的 Element 会被删除,新生成的 Element 插入到树中。
abstract class Element extends DiagnosticableTree implements BuildContext {
/// Creates an element that uses the given widget as its configuration.
///
/// Typically called by an override of [Widget.createElement].
Element(Widget widget)
: assert(widget != null),
_widget = widget;
/// Change the widget used to configure this element.
///
/// The framework calls this function when the parent wishes to use a
/// different widget to configure this element. The new widget is guaranteed
/// to have the same [runtimeType] as the old widget.
///
/// This function is called only during the "active" lifecycle state.
@mustCallSuper
void update(covariant Widget newWidget) {
/// ...
}
/// Creates an instance of the [RenderObject] class that this
/// [RenderObjectWidget] represents, using the configuration described by this
/// [RenderObjectWidget].
///
/// This method should not do anything with the children of the render object.
/// That should instead be handled by the method that overrides
/// [RenderObjectElement.mount] in the object rendered by this object's
/// [createElement] method. See, for example,
/// [SingleChildRenderObjectElement.mount].
@protected
RenderObject createRenderObject(BuildContext context);
}什么是 RenderObject
RenderObject 用于应用界面的布局和绘制,保存了元素的大小,布局等信息,实例化一个 RenderObject 是非常耗能的。
当应用运行时 Flutter 使用 RenderObject 的数据绘制应用界面,最终形成一个 Render Tree。
abstract class RenderObject extends AbstractNode with DiagnosticableTreeMixin implements HitTestTarget {
/// Initializes internal fields for subclasses.
RenderObject() {
_needsCompositing = isRepaintBoundary || alwaysNeedsCompositing;
}
/// The render object at (or below) this location in the tree.
///
/// If this object is a [RenderObjectElement], the render object is the one at
/// this location in the tree. Otherwise, this getter will walk down the tree
/// until it finds a [RenderObjectElement].
RenderObject get renderObject {
RenderObject result;
void visit(Element element) {
assert(result == null); // this verifies that there's only one child
if (element is RenderObjectElement)
result = element.renderObject;
else
element.visitChildren(visit);
}
visit(this);
return result;
}
void layout(Constraints constraints, { bool parentUsesSize = false }) {
/// ...
}
/// ...
void paint(PaintingContext context, Offset offset) {
/// ...
}
}为什么需要三棵树
使用三棵树的目的是尽可能复用 Element。
复用 Element 对性能非常重要,因为 Element 拥有两份关键数据:Stateful widget 的状态对象及底层的 RenderObject。
当应用的结构很简单时,或许体现不出这种优势,一旦应用复杂起来,构成页面的元素越来越多,重新创建 3 棵树的代价是很高的,所以需要最小化更新操作。
当 Flutter 能够复用 Element 时,用户界面的逻辑状态信息是不变的,并且可以重用之前计算的布局信息,避免遍历整棵树。
举个例子说明
创建一个简单的 Flutter 应用,代码如下
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(
MaterialApp(
color: Colors.white,
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
builder: (context, child) => HomePage(),
),
);
}
class HomePage extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_HomePageState createState() => _HomePageState();
}
class _HomePageState extends State<HomePage> {
bool _isWorld = true;
Widget _buildWorld() {
return RichText(
text: TextSpan(
text: 'Hello world',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.black),
),
);
}
Widget _buildFlutter() {
return RichText(
text: TextSpan(
text: 'Hello flutter',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.black),
),
);
}
void changeText() {
setState(() {
_isWorld = !_isWorld;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
body: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Center(
child: _isWorld ? _buildWorld() : _buildFlutter(),
),
SizedBox(height: 20.0),
// Padding(padding: EdgeInsets.only(top: 20.0)),
IconButton(icon: Icon(Icons.refresh), onPressed: changeText)
],
),
);
}
}显示效果

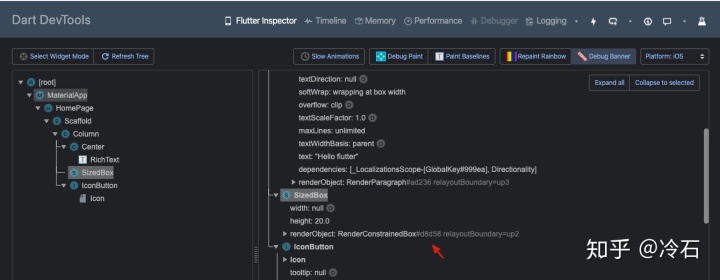
打开 Dart DevTools,可以看到应用的 Widget Tree,此时 RichText 控件的 RenderObject 的 ID 是 #6276a
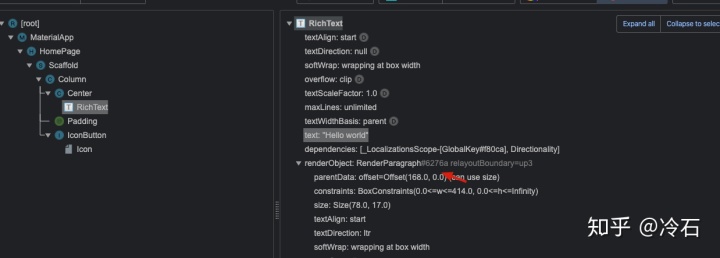
点击图标将文字变成 Hello flutter 时
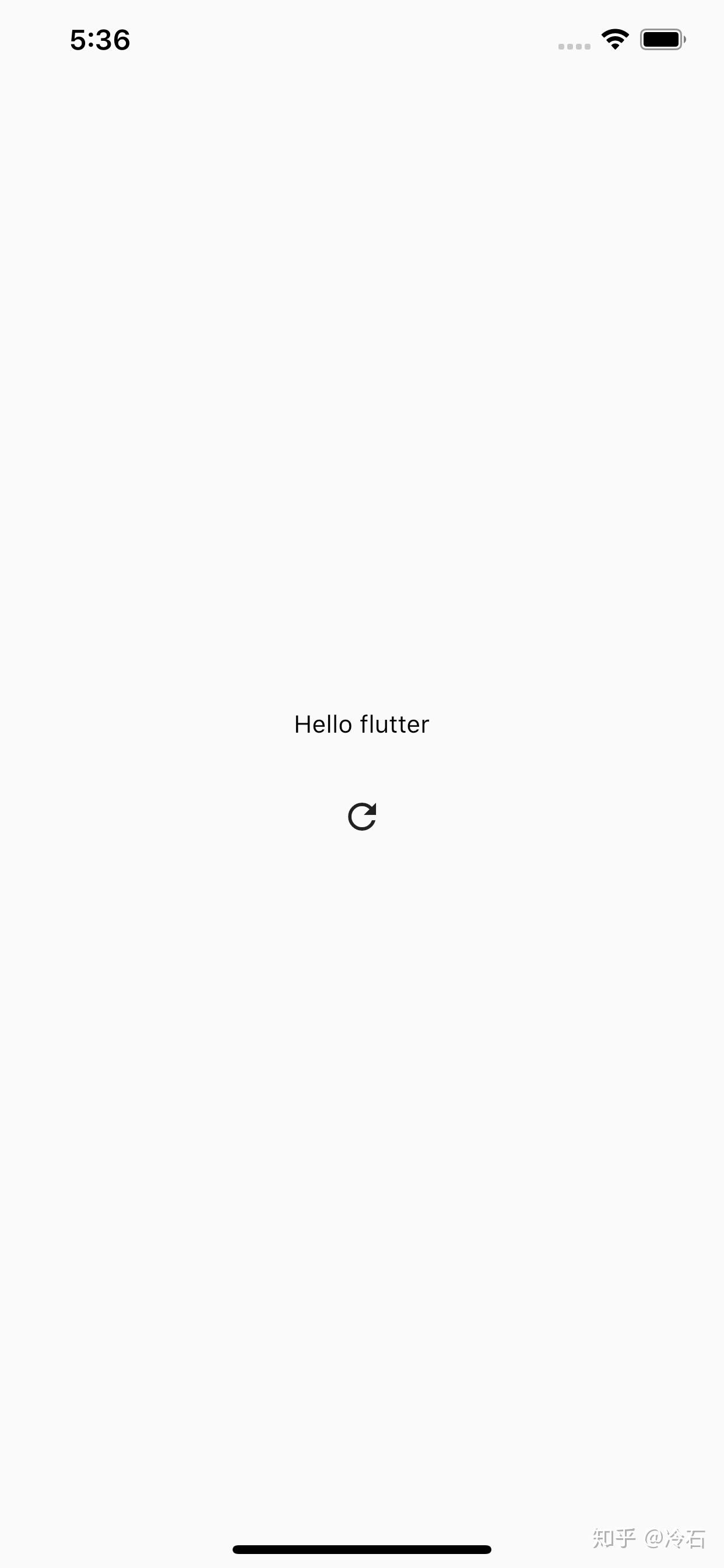
刷新浏览器页面再次查看 RichText 的 RenderObject 的 ID 依然是 #6276a

可以发现 Flutter 只是更新了文字数据,复用了 RichText 对应的 Element 和 RenderObject。
而使用 SizedBox 部件取代 Padding 部件时。
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
body: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Center(
child: RichText(
text: TextSpan(
text: 'Hello $text',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.black),
),
),
),
SizedBox(height: 20.0),
// Padding(padding: EdgeInsets.only(top: 20.0)),
IconButton(icon: Icon(Icons.refresh), onPressed: changeText)
],
),
);
}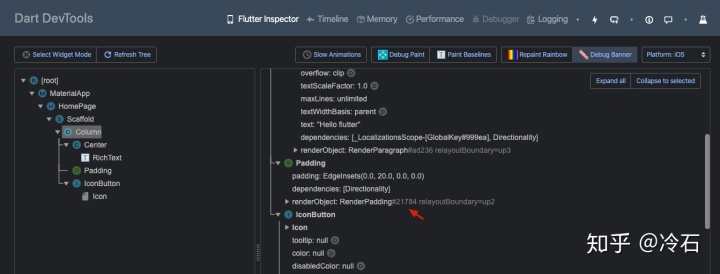
Padding 部件对应的 Element 和 RenderObject 都会被从树中移除,使用 SizedBox 新生成的替代。
总结
Widget是应用界面的声明信息。Element链接Widget和RenderObject,管理界面的更新和修改。RenderObject保存具体的布局信息,负责绘制 UI。
参考
How Flutter renders Widgetsyoutu.be How Flutter renders Widgetsmedium.com 14.1:Flutter UI系统book.flutterchina.club Flutter 是如何渲染的? - 冷石的博客coldstone.fun
最后
以上就是震动香水最近收集整理的关于flutter textspan_Flutter 是如何渲染的?的全部内容,更多相关flutter内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复