Python 计算机视觉 knn算法和denseSIFT算法原理-图像内容分类-图像识别-手势识别
- 一、原理
- 1.K邻近分类法(KNN)
- 2.稠密SIFT(Dense SIFT)
- 二、代码实现
- 1.KNN算法分类二维数据集
- 2.d-sift实现
- 3.手势识别
一、原理
1.K邻近分类法(KNN)
KNN算法是分类算法中最典型最容易实现的算法。
工作原理:存在一个样本数据集合,也称为训练样本集,并且样本集中每个数据都存在标签,即我们知道样本集中每一数据与所属分类对应的关系。输入没有标签的数据后,将新数据中的每个特征与样本集中数据对应的特征进行比较,提取出样本集中特征最相似数据(最近邻)的分类标签。
一般来说,我们只选择样本数据集中前k个最相似的数据,这就是k近邻算法中k的出处,通常k是不大于20的整数。最后选择k个最相似数据中出现次数最多的分类作为新数据的分类。
所以我们可以总结出其算法步骤为:
-
计算测试对象到训练集中每个对象的距离
-
按照距离的远近排序
-
选取与当前测试对象最近的k的训练对象,作为该测试对象的邻居
-
统计这k个邻居的类别频率
-
k个邻居里频率最高的类别,即为测试对象的类别
2.稠密SIFT(Dense SIFT)
Dense SIFT算法,是一种对输入图像进行分块处理,再对每一块进行SIFT运算的特征提取过程。Dense SIFT根据可调的参数大小,来适当满足不同分类任务下对图像的特征表征能力;而传统的SIFT算法则是对整幅图像的处理,得到一系列特征点。
Dense-SIFT在非深度学习的模型中,常常是特征提取的第一步。采样的点提取SIFT描述子后,经过码书投影,投影在同一个码字上的采样点都代表了一组描述子相似的点。不同的码字(相当于直方图的每一个bin)之间,采样点的区分能力是不一样的。我们以下图图1为例,bin2代表的是一块很平坦的区域,于是dense采样时,很多点产生的描述子都会投影在bin2上。而bin1,bin3,bin4分别代表一块特有的区域,仅仅在dense采样到自行车,大提琴和眼睛等部位时,才能够形成类似的描述子。换而言之,bin2的重要性最低,而其他码字的重要性都很高。

通常来讲Dense SIFT更适用于图像分类识别的任务,而传统SIFT更适用于图像检索分割的任务,dense-SIFT在图像检索上的性能不如SIFT检测子的性能好。
二、代码实现
1.KNN算法分类二维数据集
knn分类器
其中K值的选择会影响分类的性能
from numpy import *
class KnnClassifier(object):
def __init__(self,labels,samples):
""" Initialize classifier with training data. """
self.labels = labels
self.samples = samples
def classify(self,point,k=3):
""" Classify a point against k nearest
in the training data, return label. """
# compute distance to all training points
dist = array([L2dist(point,s) for s in self.samples])
# sort them
ndx = dist.argsort()
# use dictionary to store the k nearest
votes = {}
for i in range(k):
label = self.labels[ndx[i]]
votes.setdefault(label,0)
votes[label] += 1
return max(votes, key=lambda x: votes.get(x))
def L2dist(p1,p2):
return sqrt( sum( (p1-p2)**2) )
def L1dist(v1,v2):
return sum(abs(v1-v2))
先随机创建两个不同的二维点集,其中一类使数据点成环状分布。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from numpy.random import randn
import pickle
from pylab import *
# create sample data of 2D points
n = 200
# two normal distributions
class_1 = 0.3 * randn(n,2) #200个随机点
class_2 = 1.5 * randn(n,2) + array([5,1])#分开两堆随机点
labels = hstack((ones(n),-ones(n)))#用标签分开前200和后200随机点
# save with Pickle
#with open('points_normal.pkl', 'w') as f:
with open('points_normal_test.pkl', 'wb') as f: #存文件
pickle.dump(class_1,f)
pickle.dump(class_2,f)
pickle.dump(labels,f)
# normal distribution and ring around it
print ("save OK!")
#第二个分布
class_1 = 0.6 * randn(n,2)
r = 0.8 * randn(n,1) + 5
angle = 2*pi * randn(n,1)
class_2 = hstack((r*cos(angle),r*sin(angle)))
labels = hstack((ones(n),-ones(n)))
# save with Pickle
#with open('points_ring.pkl', 'w') as f:
with open('points_ring_test.pkl', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(class_1,f)
pickle.dump(class_2,f)
pickle.dump(labels,f)
print ("save OK!")
运行两次该脚本,第二次时修改一下保存的pkl文件名,这样我们就可以获得4个pkl文件,2个用来做训练,2个用来做测试。
接着我们用KNN分类器对数据点进行分类
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import pickle
from pylab import *
from PCV.classifiers import knn
from PCV.tools import imtools
pklist=['points_normal.pkl','points_ring.pkl']
figure()
# 用pickle载入二维数据点
for i, pklfile in enumerate(pklist):
with open(pklfile, 'rb') as f:
class_1 = pickle.load(f)
class_2 = pickle.load(f)
labels = pickle.load(f)
# 用pickle载入测试数据
with open(pklfile[:-4]+'_test.pkl', 'rb') as f:
class_1 = pickle.load(f)
class_2 = pickle.load(f)
labels = pickle.load(f)
model = knn.KnnClassifier(labels,vstack((class_1,class_2)))
# 在测试数据集的第一个数据点上进行测试
print (model.classify(class_1[0]))
用不同颜色标记出不同的分类,错误的分类点用圆点表示,并画出分界线
#画图
#define function for plotting
def classify(x,y,model=model):
return array([model.classify([xx,yy]) for (xx,yy) in zip(x,y)])
# lot the classification boundary
subplot(1,2,i+1)
imtools.plot_2D_boundary([-6,6,-6,6],[class_1,class_2],classify,[1,-1])#画出分界线
titlename=pklfile[:-4]
title(titlename)
show()
实验结果
n=200时:改变K值时不同结果图
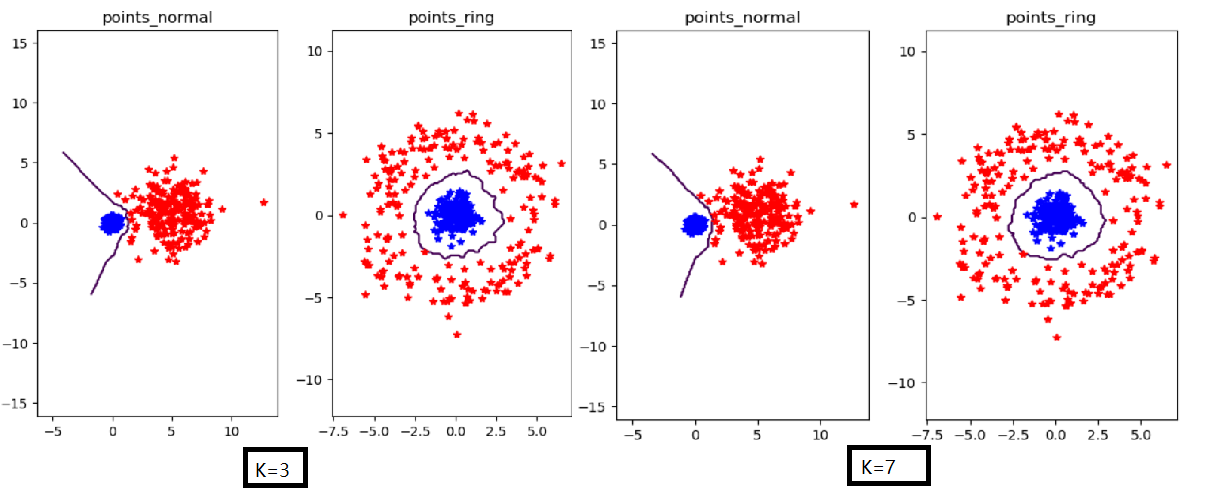
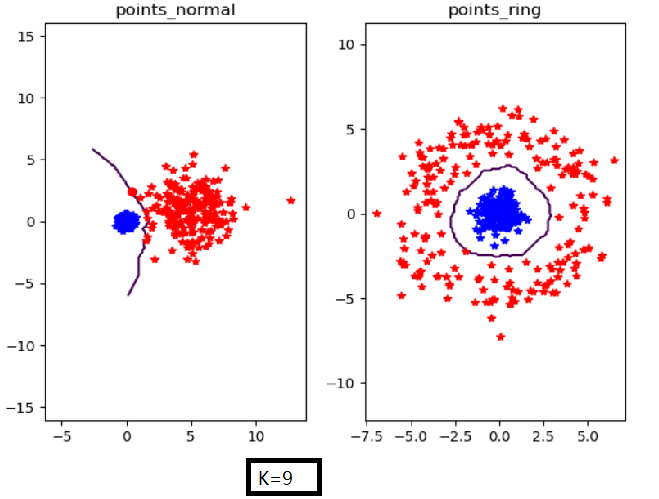
n=400,k=3时
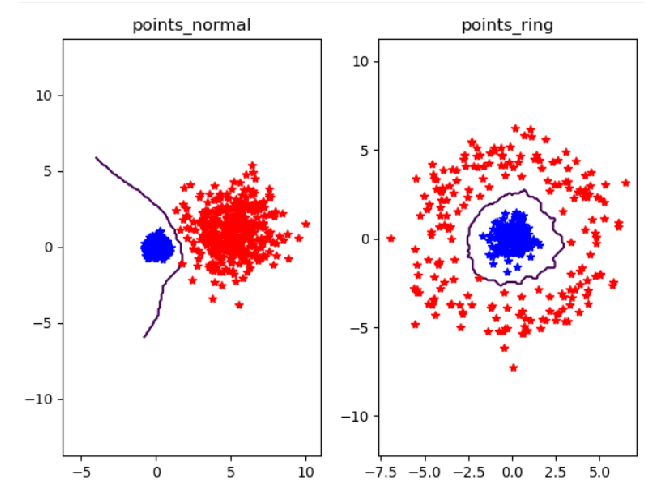
实验结论:当k较小时,分类数据点的效果就越准确。而数据样本的大小并不会影响分类效果。
2.d-sift实现
D-Sift文件
用密集采样的sift描述子处理一幅图像。
函数输入(特征大小size,位置之间的步长steps,是否强迫描述子的方位force_orientation(false比奥是所有的方位均朝上),用于调整图像大小的元组)
from PIL import Image
from numpy import *
import os
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
def process_image_dsift(imagename,resultname,size=20,steps=10,force_orientation=False,resize=None):
im = Image.open(imagename).convert('L')
if resize!=None:
im = im.resize(resize)
m,n = im.size
if imagename[-3:] != 'pgm':
#create a pgm file
im.save('tmp.pgm')
imagename = 'tmp.pgm'
# create frames and save to temporary file
scale = size/3.0
x,y = meshgrid(range(steps,m,steps),range(steps,n,steps))
xx,yy = x.flatten(),y.flatten()
frame = array([xx,yy,scale*ones(xx.shape[0]),zeros(xx.shape[0])])
savetxt('tmp.frame',frame.T,fmt='%03.3f')
path = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname("__file__"),os.path.pardir))
path = path + "\python3-ch08\win32vlfeat\sift.exe "
if force_orientation:
cmmd = str(path+imagename+" --output="+resultname+
" --read-frames=tmp.frame --orientations")
else:
cmmd = str(path+imagename+" --output="+resultname+
" --read-frames=tmp.frame")
os.system(cmmd)
print ('processed', imagename, 'to', resultname)
计算dsift描述子
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift, dsift
from pylab import*
from PIL import Image
dsift.process_image_dsift('gesture/zhongshan.jpg','zhongshan.dsift',90,40,True)
l,d = sift.read_features_from_file('zhongshan.dsift')
im = array(Image.open('gesture/zhongshan.jpg'))
sift.plot_features(im,l,True)
title('dense SIFT')
show()
可视化结果:
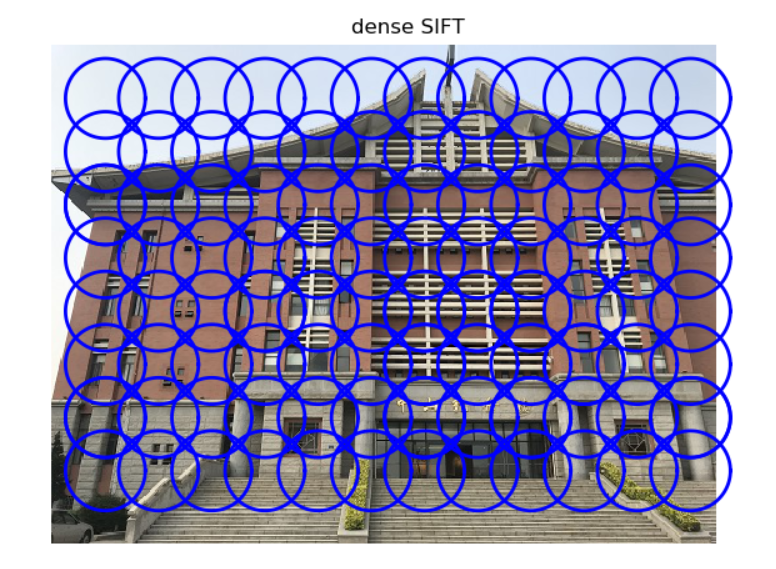
3.手势识别
5种手势
 我用了94张图片做训练集,50张图片做测试集,这样可以使结果更加准确
我用了94张图片做训练集,50张图片做测试集,这样可以使结果更加准确
先对所有图片进行尺寸调整,并生成sift文件
将所有图片的尺寸调整为了100x100,若不这么处理所有图片,可能会使图像特征向量长度不一致,导致比较出错。
def get_imagelist(path):
""" Returns a list of filenames for
all jpg images in a directory. """
return [os.path.join(path,f) for f in os.listdir(path) if f.endswith('.JPG')]
def read_gesture_features_labels(path):
# create list of all files ending in .dsift
featlist = [os.path.join(path,f) for f in os.listdir(path) if f.endswith('.dsift')]
# read the features
features = []
for featfile in featlist:
l,d = sift.read_features_from_file(featfile)
features.append(d.flatten())
features = array(features)
# create labels
labels = [featfile.split('/')[-1][0] for featfile in featlist]
return features,array(labels)
filelist_train = get_imagelist('gesture/myself/train3/')
filelist_test = get_imagelist('gesture/myself/test3/')
imlist=filelist_train+filelist_test
for filename in imlist:
featfile = filename[:-3]+'dsift'
dsift.process_image_dsift(filename,featfile,20,10,resize=(100,100))
函数read_gesture_features_labels 生成dsift可视化:
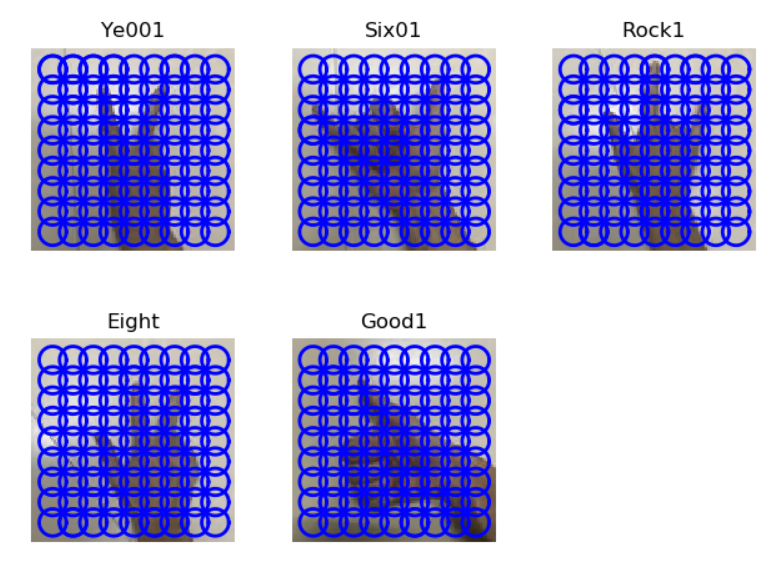
读取训练集,测试集的dsift文件
features,labels = read_gesture_features_labels('gesture/myself/train3/')
test_features,test_labels = read_gesture_features_labels('gesture/myself/test3/')
classnames = unique(labels)
开始用KNN来进行分类
# test kNN
k = 1
knn_classifier = knn.KnnClassifier(labels,features)
res = array([knn_classifier.classify(test_features[i],k) for i in
range(len(test_labels))])
# accuracy
acc = sum(1.0*(res==test_labels)) / len(test_labels)
print ('Accuracy:', acc)
生成分类的正确率:
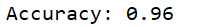
由于我的图片的背景没有太多冗余的障碍,并且训练集有足够的数量,得到的正确率相比有背景较乱的图片,较少的训练集更高一些。
最后用混淆矩阵来判断哪些手势是分类错误的
def print_confusion(res,labels,classnames):
n = len(classnames)
# confusion matrix
class_ind = dict([(classnames[i],i) for i in range(n)])
confuse = zeros((n,n))
for i in range(len(test_labels)):
confuse[class_ind[res[i]],class_ind[test_labels[i]]] += 1
print ('Confusion matrix for')
print (classnames)
print (confuse)
得到的混淆矩阵:
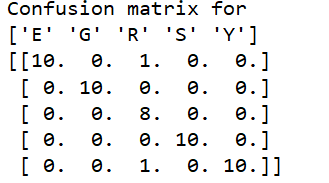
可看出Rock手势
有一个被判断成了Eight手势 ,一个被判断成了Ye手势
,一个被判断成了Ye手势 ,其余手势均正确。
,其余手势均正确。
手势识别完整代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from PCV.localdescriptors import dsift
import os
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from pylab import *
from PCV.classifiers import knn
def get_imagelist(path):
""" Returns a list of filenames for
all jpg images in a directory. """
return [os.path.join(path,f) for f in os.listdir(path) if f.endswith('.JPG')]
def read_gesture_features_labels(path):
# create list of all files ending in .dsift
featlist = [os.path.join(path,f) for f in os.listdir(path) if f.endswith('.dsift')]
# read the features
features = []
for featfile in featlist:
l,d = sift.read_features_from_file(featfile)
features.append(d.flatten())
features = array(features)
# create labels
labels = [featfile.split('/')[-1][0] for featfile in featlist]
return features,array(labels)
def print_confusion(res,labels,classnames):
n = len(classnames)
# confusion matrix
class_ind = dict([(classnames[i],i) for i in range(n)])
confuse = zeros((n,n))
for i in range(len(test_labels)):
confuse[class_ind[res[i]],class_ind[test_labels[i]]] += 1
print ('Confusion matrix for')
print (classnames)
print (confuse)
filelist_train = get_imagelist('gesture/myself/train3/')
filelist_test = get_imagelist('gesture/myself/test3/')
imlist=filelist_train+filelist_test
# process images at fixed size (50,50)
for filename in imlist:
featfile = filename[:-3]+'dsift'
dsift.process_image_dsift(filename,featfile,10,5,resize=(100,100))
features,labels = read_gesture_features_labels('gesture/myself/train3/')
test_features,test_labels = read_gesture_features_labels('gesture/myself/test3/')
classnames = unique(labels)
# test kNN
k = 1
knn_classifier = knn.KnnClassifier(labels,features)
res = array([knn_classifier.classify(test_features[i],k) for i in
range(len(test_labels))])
# accuracy
acc = sum(1.0*(res==test_labels)) / len(test_labels)
print ('Accuracy:', acc)
print_confusion(res,test_labels,classnames)
问题解决:
在运行手势识别代码时候,之前遇到了无法生成disift文件,却发现没有出现任何报错问题。后发现是文件后缀名要区分大小写。。。
最后
以上就是忐忑白云最近收集整理的关于计算机视觉 图像内容分类- K-近邻(KNN)算法和denseSIFT算法原理-手势识别的全部内容,更多相关计算机视觉内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复