步骤:
其中A是一个n*n的系数方阵 向量x和b分别是未知数和常量向量:
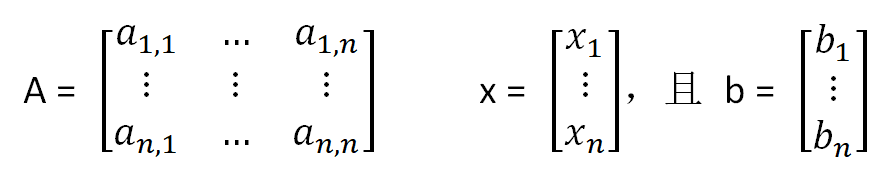
这个系统可能有0个、1个或者无穷多个解,这取决于系数矩阵A和向量b。求解线性系统的方法有很多,这里使用一种经典的方法——高斯消去法(https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/高斯消去法)。首先,我们对A和b进行交换,使得A变为一个上三角矩阵。上三角矩阵就是对角线之下的所有元素均为0。即如下形式:
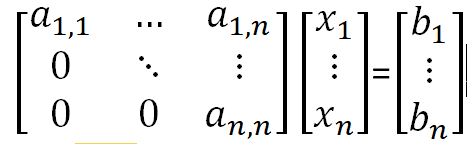
实现这个目标是很容易的。为了使a(i,j)变为0,我们先将它乘以一个常量,使它等于第j列上的另一个元素,比如说等于a(k,j)。然后,用第i个方程减去第k个方程,a(i,j)即变为0,矩阵第i行其他元素的值也相应发生改变。
如果这样一个变换最终使得对角线上所有元素都非0,方程组就有唯一解,此解可以通过”回代“求得。如果存在为0的元素,则意味着方程组有0个或者无穷多个解。
我们现在用c++来表示上述计算方法。首先,定义两个要使用的具体Matrix类型,以简化程序:
typedef Numeric_lib::Matrix<double, 2>Matrix2; // Matrix库下载地址 :http://www.stroustrup.com/Programming/Matrix/Matrix.h 整个库定义在名字空间 Numeric_lib 中
typedef Numeric_lib::Matrix<double, 1> Vector;
接下来我们将高斯消去法计算过程描述为程序:
Vector classic_gaussian_elimination(Matrix2 A,Vector b){
classical_elimination(A,b);
return back_substitution(A,b);
}
即,先为两个输入A和b创建拷贝(使用赋值函数),然后调用一个函数求解方程组,最后调用回代函数计算结果并将结果返回。关键之处在于,我们分解问题的方式和符号表示都完全来自于原始的数学描述。下面所要做的就是实现classic_elimination()和back_substitution()了,解决方案同意完全来自于数学教科书:
void classical_elimination(Matrix2&A,Vector& b){
const Index n=A.dim1();
//从第1列一直遍历到倒数第二列
//将对角线之下所以元素都填充0
for(Index j=0;j<n-1;++j){
const double pivot =A(j,j);
if(pivot==0)cerr<<"错误:其中有一对角线位为0"<<'n';
//将第i行在对角线之下的元素都填充为0
for(Index i=j+1;i<n;++i){
const double mult =A(i,j)/pivot;
A[i].slice(j)=scale_and_add(A[j].slice(j),-mult,A[i].slice(j)); //A[i].slice(j)表示从A[i][j]到这一行的末尾。
b(i)-=mult*b(j); //对b做对应变化
}
}
}
“pivot”表示当前行位于对角线上的元素,它必须是非0。因为需要用它作为除数;如果它为0,我们将放弃计算,抛出一个异常:
Vector back_substitution(const Matrix2&A,const Vector&b){
const Index n=A.dim1();
Vector x(n);
for(Index i=n-1;i>=0;--i){
double s=b(i)-dot_product(A[i].slice(i+1),x.slice(i+1));
if(double m=A(i,i))
x(i)=s/m;
else
throw Back_subst_failure(i);
}
return x;
}
完整示例程序:
#include<iostream>
#include"Matrix.h" //Matrix库下载地址 :http://www.stroustrup.com/Programming/Matrix/Matrix.h
#include"MatrixIO.h" //MatrixIO库下载地址 :http://www.stroustrup.com/Programming/Matrix/MatrixIO.h 仅为一维二维提供非常简单的I/O功能
using namespace Numeric_lib; //整个库定义在名字空间 Numeric_lib 中
using namespace std;
typedef Numeric_lib::Matrix<double, 2>Matrix2;
typedef Numeric_lib::Matrix<double, 1> Vector;
void classical_elimination(Matrix2& A, Vector& b) {
const Index n = A.dim1();
//从第1列一直遍历到倒数第二列
//将对角线之下所以元素都填充0
for (Index j = 0; j<n - 1; ++j) {
const double pivot = A(j, j);
if (pivot == 0)cerr<<"错误:其中有一对角线位为0"<<'n';
//将第i行在对角线之下的元素都填充为0
for (Index i = j + 1; i<n; ++i) {
const double mult = A(i, j) / pivot;
A[i].slice(j) = scale_and_add(A[j].slice(j), -mult, A[i].slice(j));
b(i) -= mult*b(j); //对b做对应变化
}
}
}
Vector back_substitution(const Matrix2&A, const Vector&b) {
const Index n = A.dim1();
Vector x(n);
for (Index i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
double s = b(i) - dot_product(A[i].slice(i + 1), x.slice(i + 1));
if (double m = A(i, i))
x(i) = s / m;
else
cerr<<"错误:其中有一对角线位为0"<<'n';
}
return x;
}
Vector classic_gaussian_elimination(Matrix2 A, Vector b) {
classical_elimination(A, b);
return back_substitution(A, b);
}
int main() {
double val2[3][3] = {2,1,-1,-3,-1,2,-2,1,2 };
double val1[3] = {8,-11,-3 };
Matrix2 A(val2);
Vector b(val1);
cout<<classic_gaussian_elimination(A, b);
}
改进:
pivot为0的问题是可以避免的,我们可以对行进行排列,从而将0和较小的值从对角线上移开,这样就得到了一个更鲁棒的方案。“更鲁棒”是指对于舍入误差不敏感。但是,随着我们将0置于对角线之下,元素值也会发生改变。因此,我们必须反复进行重排序,以将较小的值从对角线上移开(即,不能一次重排矩阵后就直接使用经典算法):
void elim_with_partial_pivot(Matrix2& A, Vector& b) {
const Index n = A.dim1();
for (Index j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
Index pivot_row = j;
//查找一个合适的主元:
for (Index k = j + 1; k < n; ++k)
if (abs(A(k, j)) > abs(A(pivot_row, j))) pivot_row = k;
//如果我们找到了一个更好的主元,交换两行:
if (pivot_row != j) {
A.swap_rows(j, pivot_row);
std::swap(b(j), b(pivot_row));
}
//消去:
for (Index i = j + 1; i < n; ++i) {
const double pivot = A(j, j);
if (pivot == 0)error("can't solve:pivot==0");
const double mult = A(i, j) / pivot;
A[i].slice(j) = scale_and_add(A[j].slice(j), -mult, A[i].slice(j));
b(i) -= mult*b(j);
}
}
}
在这里我们使用了swap_rows()和scale_and_multipy(),这样程序更符合习惯,我们也不必显式编写循环代码了。
随机数测试:
void solve_random_system(Index n) {
Matrix2 A = random_matrix(n);
Vector b = random_vector(n);
cout << "A=" << A << 'n';
cout << "b=" << b << 'n';
try {
Vector x = classic_gaussian_elimination(A, b);
cout << "classic elim solution is x =" << x << 'n';
Vector v = A*x;
cout << "A*x=" << v << 'n';
}
catch (const exception& e) {
cerr << e.what() << 'n';
}
}
程序在三种情况下会进入catch语句:
- 代码中有bug。
- 输入内容使classic_elimination出现错误(elim_with_partial_pivot在很多情况下可以做得更好)。
- 舍入误差导致问题。
为了测试我们的程序,我们输出 A*x,其值应该与b相单。但考虑到存在舍入误差,若其值与b足够接近就认为结果正确,这也是为什么测试程序中没有采用下面语句来判断结果是否正确的原因:
if(A*b!=b)error ("substitution failed");
在计算机中,浮点数只是实数的近似,因此我们必须接受近似的计算结果。一般来说,应该避免使用==和!=来判断是否正确。
Matrix库中并没有定义矩阵与向量的乘法运算,因此我们为测试程序定义这个运算:
Vector operator*(const Matrix2&m, const Vector&u) {
const Index n = m.dim1();
Vector v(n);
for (Index i = 0; i < n; ++i) v(i) = dot_product(m[i], u);
return v;
}
random_matrix()和random_vector()是随机数的简单应用。Index是索引类型,它是用typedef定义的。
完整程序:
#include<iostream>
#include<random>
#include <time.h>
#include"Matrix.h" //Matrix库下载地址 :http://www.stroustrup.com/Programming/Matrix/Matrix.h
#include"MatrixIO.h"//MatrixIO库下载地址 :http://www.stroustrup.com/Programming/Matrix/MatrixIO.h
using namespace Numeric_lib;//整个库定义在名字空间 Numeric_lib 中
using namespace std;
typedef Numeric_lib::Matrix<double, 2>Matrix2;
typedef Numeric_lib::Matrix<double, 1> Vector;
void classical_elimination(Matrix2& A, Vector& b) {
const Index n = A.dim1();
//从第1列一直遍历到倒数第二列
//将对角线之下所以元素都填充0
for (Index j = 0; j<n - 1; ++j) {
const double pivot = A(j, j);
if (pivot == 0)cerr<<"错误:其中有一对角线位为0"<<'n';
//将第i行在对角线之下的元素都填充为0
for (Index i = j + 1; i<n; ++i) {
const double mult = A(i, j) / pivot;
A[i].slice(j) = scale_and_add(A[j].slice(j), -mult, A[i].slice(j));
b(i) -= mult*b(j); //对b做对应变化
}
}
}
Vector back_substitution(const Matrix2&A, const Vector&b) {
const Index n = A.dim1();
Vector x(n);
for (Index i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
double s = b(i) - dot_product(A[i].slice(i + 1), x.slice(i + 1));
if (double m = A(i, i))
x(i) = s / m;
else
;
}
return x;
}
void elim_with_partial_pivot(Matrix2& A, Vector& b) {
const Index n = A.dim1();
for (Index j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
Index pivot_row = j;
//查找一个合适的主元:
for (Index k = j + 1; k < n; ++k)
if (abs(A(k, j)) > abs(A(pivot_row, j))) pivot_row = k;
//如果我们找到了一个更好的主元,交换两行:
if (pivot_row != j) {
A.swap_rows(j, pivot_row);
std::swap(b(j), b(pivot_row));
}
//消去:
for (Index i = j + 1; i < n; ++i) {
const double pivot = A(j, j);
if (pivot == 0)error("can't solve:pivot==0");
const double mult = A(i, j) / pivot;
A[i].slice(j) = scale_and_add(A[j].slice(j), -mult, A[i].slice(j));
b(i) -= mult*b(j);
}
}
}
Vector classic_gaussian_elimination(Matrix2 A, Vector b) {
elim_with_partial_pivot(A, b);
//classical_elimination(A, b);
return back_substitution(A, b);
}
Vector operator*(const Matrix2&m, const Vector&u) {
const Index n = m.dim1();
Vector v(n);
for (Index i = 0; i < n; ++i) v(i) = dot_product(m[i], u);
return v;
}
int max0 = 10;
Vector random_vector(Index n) {
Vector v(n);
default_random_engine ran{(unsigned int)(time(0)+2)};
uniform_int_distribution<> ureal{ 0,max0 };
for (Index i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
v(i) = ureal(ran);
}
return v;
}
Matrix2 random_matrix(Index n) {
Matrix2 v(n,n);
default_random_engine ran{ (unsigned int)time(0) };
uniform_int_distribution<> ureal{ 0,max0 };
for (Index i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (Index j = 0; j < n; ++j)
v[i][j] = ureal(ran);
}
return v;
}
void solve_random_system(Index n) {
Matrix2 A = random_matrix(n);
Vector b = random_vector(n);
cout << "A=" << A << 'n';
cout << "b=" << b << 'n';
try {
Vector x = classic_gaussian_elimination(A, b);
cout << "classic elim solution is x =" << x << 'n';
Vector v = A*x;
cout << "A*x=" << v << 'n';
}
catch (const exception& e) {
cerr << e.what() << 'n';
}
}
int main() {
/*double val2[3][3] = {2,1,-1,-3,-1,2,-2,1,2 };
double val1[3] = {8,-11,-3 };
Matrix2 A(val2);
Vector b(val1);
cout<<classic_gaussian_elimination(A, b);
*/
solve_random_system(4);
}
c++程序设计原理与实践(进阶篇)
转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/l2017/p/7856623.html
最后
以上就是优美菠萝最近收集整理的关于实现求解线性方程(矩阵、高斯消去法)------c++程序设计原理与实践(进阶篇)...的全部内容,更多相关实现求解线性方程(矩阵、高斯消去法)------c++程序设计原理与实践(进阶篇)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复