我们知道要想绘制一些特别的效果的话,离不开Paint和Canvas,Paint是你所画图形的一些基本属性,按照面向对象的思想,你要把一个圆画在画布上,那么是有画笔和画布,比如你所画圆的颜色,粗细等都是画笔的属性,而决定所画的位置是由画布决定的,Paint类一些基本的方法上篇讲解了,今天就讲解下Canvas一些常用的方法,后期会配合讲一些自定义view的一些效果,这样更加理解Paint和Canvas一些方法怎么使用以及是怎么个意思,理论实践结合才是王道,进入正题
1):画点
public void drawPoint(float x, float y, Paint paint)
参数说明:
x:表示x轴方法的坐标
y:表示y轴方法的坐标 这坐标是相对于它的父view,而不是屏幕
paint:表示你所画点用到的画笔
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); canvas.drawPoint(100,200,mPaint); }效果:
怎么会什么都没有呢?这是因为犯了一个很低级的错误,你画笔都没设置宽度,怎么可能在画布上所画的能看见,所以添加这行代码即可:mPaint.setStrokeWidth(20); 就可以看见你所画的点了,
除了上面的方法绘制点以外,还有一次性绘制多个点,
public void drawPoints(float[] pts,Paint paint) 绘制多个点
参数说明:
pts:是一个float数组,存储的是点的集合,数组的长度必须>=2,而且数组长度必须是2的倍数,它是每2个数代表一个点,第一个数是x轴坐标,第二个参数表示是y轴坐标
paint:绘制点的画笔
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(100); float[] pts = {100,200,300,400,500,600}; canvas.drawPoints(pts,mPaint); }这代表绘制3个点(100,200),(300,400),(500,600)效果如下:
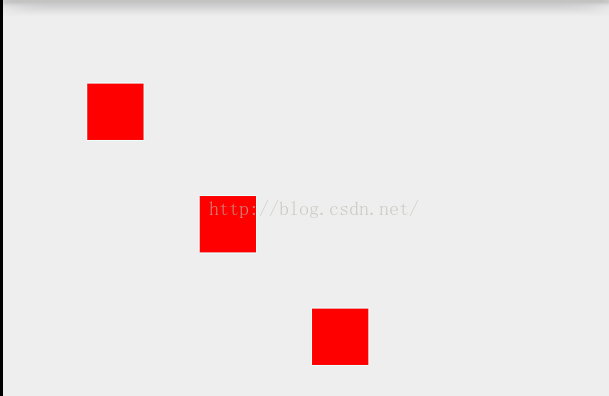
绘制多个点还有一个方法就是
public void drawPoints(float[] pts, int offset, int count,Paint paint)
参数说明:
pts:同上
offset:集合中跳过的数值个数,注意不是点的个数!一个点是两个数值,比如你offset=2就表示跳过一个点
count:参与绘制的数值的个数,指pts[]里人数值个数,而不是点的个数,因为一个点是两个数值 比如count=4就表示绘制2个点,因为一个点是等于2个数值(x轴和y轴)
paint:同上
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(100); float[] pts = {100,100,100,150,100,280,100,400,100,520,100,650}; canvas.drawPoints(pts,2,6,mPaint); }我上面是要绘制(100,100),(100,150),(100,280),(100,400),(100,520),(100,650)这6个点,offset=2表示跳过2个数值,就等于是从第二个点开始画,count=6就表示绘制6个数值,就是3个点,

2):画线
public void drawLine(float startX, float startY, float stopX, float stopY,Paint paint) 2点连接成一条线
参数说明:
startX:第一个点的起始x轴坐标
startY:第一个点的起始y轴坐标
stopX:结束点x轴坐标
stopY:结束点y轴坐标
paint:绘制线所用到的画笔
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(10); canvas.drawLine(100,100,800,800,mPaint); }效果:

这是画一条线,比如我要画多条线 是不是要循环调用这个方法呢?,肯定系统会给相应的方法
public void drawLines(float[] pts, Paint paint)
参数说明:
pts:这个和drawPoints中的参数是同一个意思,不解释
paint:同上
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(10); float[] pts = {100,100,400,100,400,100,400,400,400,400,100,400,100,400,100,100}; canvas.drawLines(pts,mPaint); }这是由8个点构成了一个矩形,所以画矩形也可以这么画,但几乎不用,除非特殊的需求下会用:

绘制多条直线还有一个方法,
public void drawLines(float[] pts, int offset, int count, Paint paint)
参数说明:
pts:同上
offset:和drawPoints是一样
count:和drawPoints是一样
paint:同上
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(10); float[] pts = {100,100,400,100,400,100,400,400,400,400,100,400,100,400,100,100}; canvas.drawLines(pts,4,12,mPaint); }在这注意下count的返回时pts的数组长度-offset,在这offet是4而数组的长度为16,所以count的最大值不能超过12,刚才我就犯了这个错,
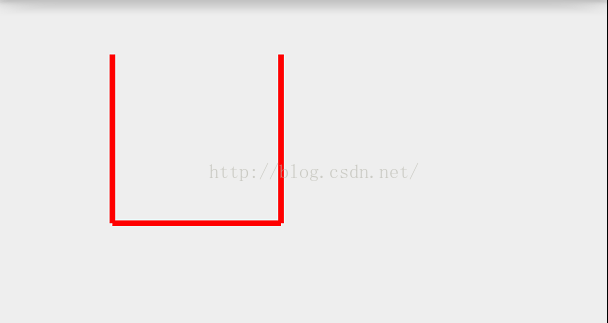
3):绘制矩形
我们知道2个点可以构成一个矩形,那么第一个绘制矩形的参数就出来了
public void drawRect(float left, float top, float right, float bottom, Paint paint)
参数说明:
left:第一个点距离x轴多少距离(单位像素)
top:第一个点距离y轴多少距离
right:第二个距离x轴多少距离
bottom:第二个点距离y轴多少距离
矩形的长度=right-left 矩形的高度为=bottom-top
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(10); canvas.drawRect(100,100,800,800,mPaint); }效果:

如果觉得一大遍红色区域不好看的话,可以设置下Paint的style样式即可,
而矩形在android有二个类,一个是Rect和RectF用法上没什么差别,主要是在精度上有差距,RectF精度更准确,其他没啥,
而Rect有三个构造函数
/** * Create a new empty Rect. All coordinates are initialized to 0. */ public Rect() {} /** * Create a new rectangle with the specified coordinates. Note: no range * checking is performed, so the caller must ensure that left <= right and * top <= bottom. * * @param left The X coordinate of the left side of the rectangle * @param top The Y coordinate of the top of the rectangle * @param right The X coordinate of the right side of the rectangle * @param bottom The Y coordinate of the bottom of the rectangle */ public Rect(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { this.left = left; this.top = top; this.right = right; this.bottom = bottom; } /** * Create a new rectangle, initialized with the values in the specified * rectangle (which is left unmodified). * * @param r The rectangle whose coordinates are copied into the new * rectangle. */ public Rect(Rect r) { if (r == null) { left = top = right = bottom = 0; } else { left = r.left; top = r.top; right = r.right; bottom = r.bottom; } }我们知道绘制矩形canvas还有一种方法
public void drawRect(Rect r, Paint paint)
参数说明:
r就是上面2个点封装成了一个矩形而已,
paint:同上,
如果是创建一个空构造的Rect,传递给drawRect的话,这个是看不见的,
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(10); mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); Rect rect = new Rect(); canvas.drawRect(rect,mPaint); }这样的话是什么都看不见,原因是它的2个点都是默认在(0,0)这就导致了矩形长度和宽度为0,可以通过 rect.width(); rect.height();去获取试试看,
那么矩形除了它有空参数的构造函数还有带4个参数也就是二个点,这和带一个参数的传递一个Rect是一样的,
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(10); mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); Rect rect = new Rect(100,100,300,600); canvas.drawRect(rect,mPaint); }效果:
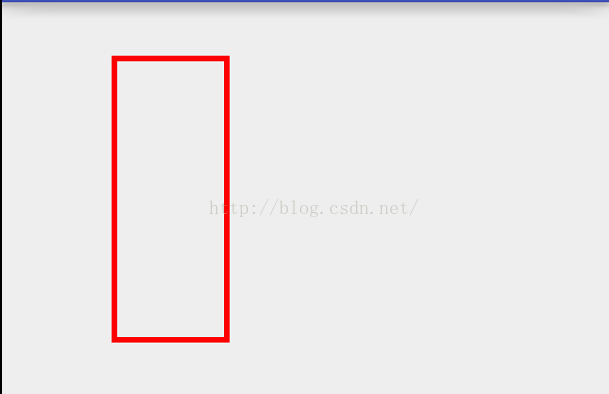
4):画圆角矩形
public void drawRoundRect(float left, float top, float right, float bottom, float rx, float ry,Paint paint)
参数说明:
left 第一个点x轴方向距离(像素)
top:第一个点y轴方向距离
right:第二个点x轴方向距离
bottom:第二个点y轴方向距离
rx:生成圆角椭圆的x轴半径
ry:生成圆角椭圆的y轴半径
paint:绘制圆角矩形所需的画笔
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(10); mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); canvas.drawRoundRect(100f,100f,600f,600f,20f,20f,mPaint); }效果:
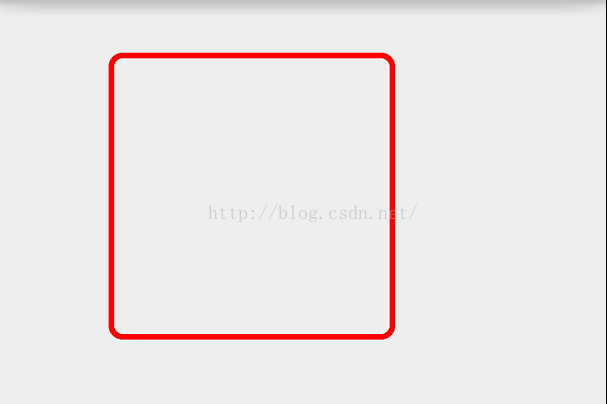
绘制圆角矩形还有一个方法: public void drawRoundRect(RectF rect, float rx, float ry, @NonNull Paint paint),这个无非是把上面的2个点构成了一个矩形而已,没差别,也很好理解
5):画圆
画圆要定一个圆心和半径
public void drawCircle(float cx, float cy, float radius,Paint paint)
参数说明:
cx:圆心x轴方向距离
cy:圆心y轴方向距离
radius:圆的半径
paint:绘制圆所需的画笔
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(10); mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); canvas.drawCircle(300,300,200,mPaint); }效果:

6):画椭圆
我们高中就学过一个椭圆是根据一个矩形的内切圆而定的,如图:
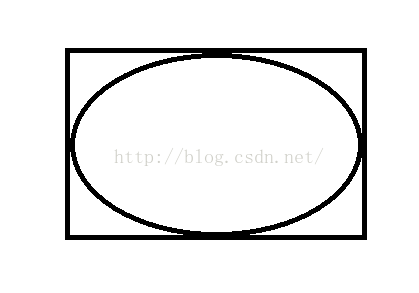
这是用电脑自带的画画功能所画的,里面的内切圆就是依赖外面的矩形而形成的,以矩形的长为椭圆的X轴,矩形的宽为椭圆的Y轴,建立的椭圆图形
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(10); mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); RectF rect = new RectF(100,100,500,400); canvas.drawRect(rect,mPaint); mPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE); canvas.drawOval(rect,mPaint); }效果:
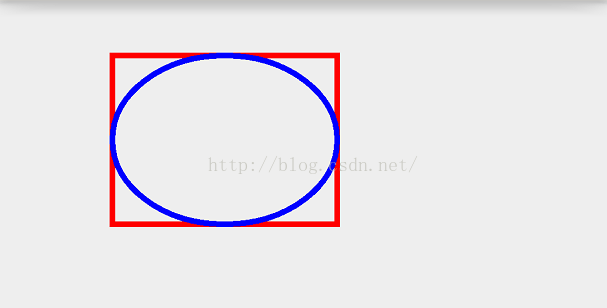
7):画弧
弧是根据椭圆来定的,而上面讲了椭圆是根据矩形来定的,所以弧也是根据矩形来定的,
public void drawArc(RectF oval, float startAngle, float sweepAngle, boolean useCenter,Paint paint)
参数说明:
oval:绘制弧所依赖的矩形
startAngle:弧开始的角度,以X轴正方向为0度
sweepAngle:弧持续的角度
useCenter:是否有弧的两边,True,还两边,False,只有一条弧
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(10); mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); RectF rect = new RectF(100,100,500,400); canvas.drawArc(rect,0,90,true,mPaint); }效果:
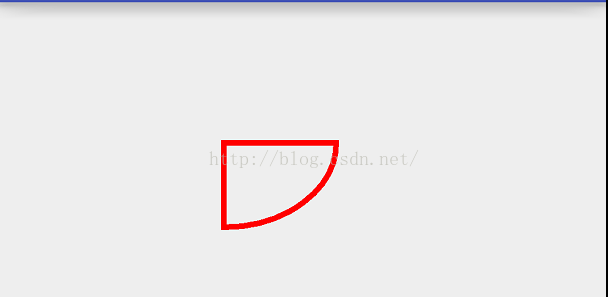
如果把第四个参数传false,

这个参数非常重要,在做一些进度条或者效果时,大部分都用到了这个,
这个如果把弧所依赖的椭圆和矩形都绘制出来,看效果也许会更好,
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(10); mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); RectF rect = new RectF(100,100,500,400); canvas.drawRect(rect,mPaint); mPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE); canvas.drawOval(rect,mPaint); mPaint.setColor(Color.YELLOW); canvas.drawArc(rect,0,90,true,mPaint); }效果:
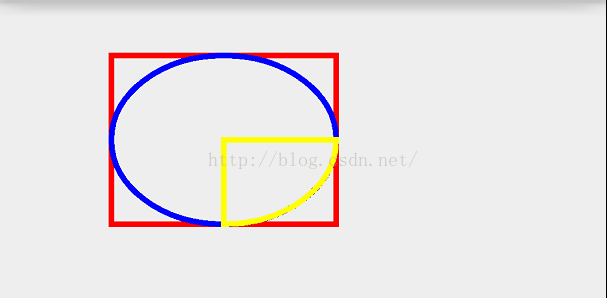
现在看到我们绘制的矩形,我们从中可以得出它的坐标点为圆心点,现在我把弧所持续的角度为-90,
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(10); mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); RectF rect = new RectF(100,100,500,400); canvas.drawRect(rect,mPaint); mPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE); canvas.drawOval(rect,mPaint); mPaint.setColor(Color.YELLOW); canvas.drawArc(rect,0,-90,true,mPaint); }效果:
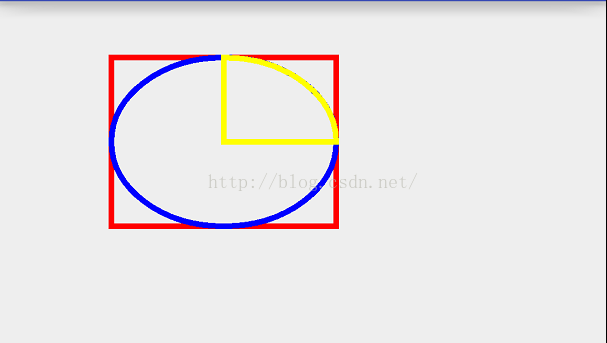
发现当所持续的角度为-90度是逆时针转90的,从这可以得出一个简单的结论:当所持续的角度为正数是顺时针,当所持续的角度为负数时,是逆时针,
现在还有一个参数startAngle就是弧开始的角度,之前是传入0,现在改为90,
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(10); mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); RectF rect = new RectF(100,100,500,400); canvas.drawRect(rect,mPaint); mPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE); canvas.drawOval(rect,mPaint); mPaint.setColor(Color.YELLOW); canvas.drawArc(rect,90,-90,true,mPaint); }效果:
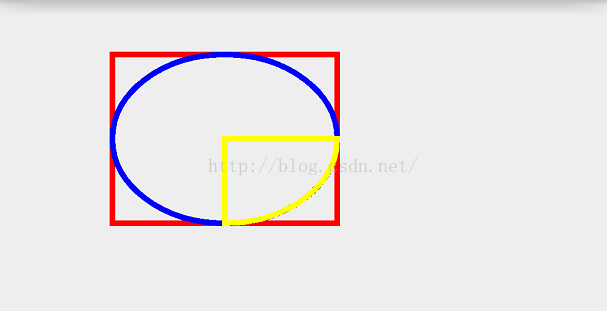
现在画图来解释上面第二个和第三个参数如下图:
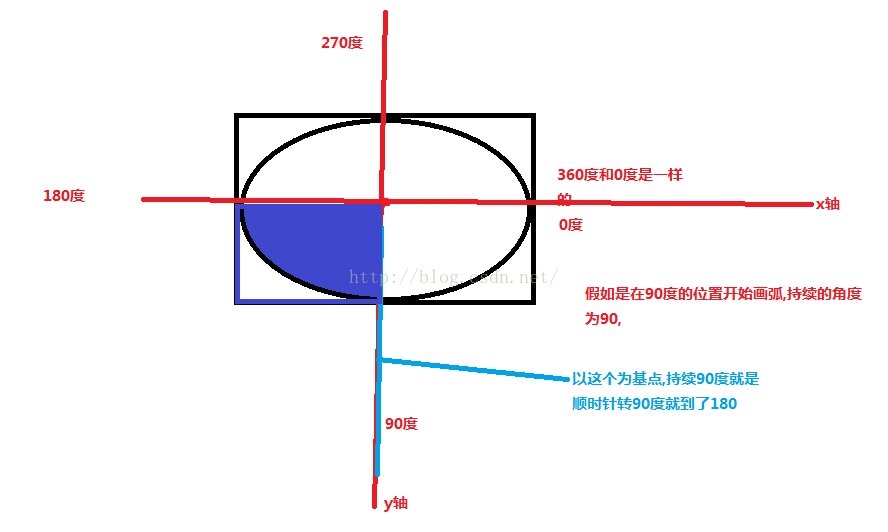
8):画多边形
public void drawPath(Path path, Paint paint)
参数说明:
path;路径
paint:所画路径需要的画笔
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(10); mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(100,100); path.lineTo(100,500); path.lineTo(600,500); path.close(); canvas.drawPath(path,mPaint); }moveTo()方法是绘制多边形的起点,lineTo()是连接上一个点,构成一条线,path的close()方法一定要记得调用,close()能保证多边形构成的线能闭合,
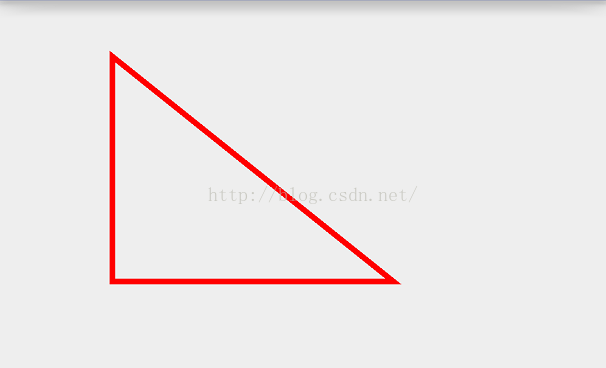
我们发现Path类有很多add各种图形的方法:
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(10); mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(100,100); path.lineTo(100,500); path.lineTo(600,500); path.close(); path.addCircle(100,100,30, Path.Direction.CW); path.addCircle(100,200,30, Path.Direction.CW); path.addCircle(100,300,30, Path.Direction.CW); path.addCircle(100,400,30, Path.Direction.CW); path.addCircle(100,500,30, Path.Direction.CW); canvas.drawPath(path,mPaint); }效果:
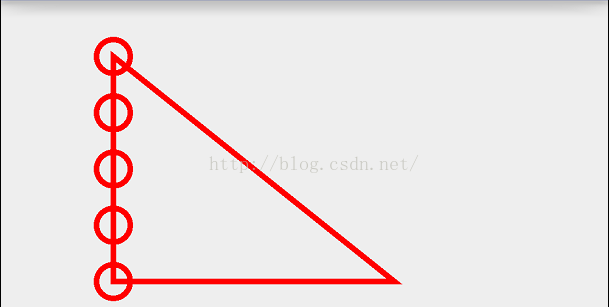
这是在Path上添加圆,当然还可以添加其他图形了,
9):画带文字的多边形
public void drawTextOnPath(String text,Path path, float hOffset,float vOffset,Paint paint)
参数说明:
text:绘制到path上的文字
path:路径
float hOffset : 与路径起始点的水平偏移距离
float vOffset : 与路径中心的垂直偏移量
paint:同上
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(5); mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); String text="杭州9月份要开G20峰会,杭州9月份要开G20峰会"; Path path = new Path(); Path path1 = new Path(); path.addCircle(300,300,200, Path.Direction.CCW); path1.addCircle(800,300,200, Path.Direction.CCW); canvas.drawPath(path,mPaint); canvas.drawPath(path1,mPaint); mPaint.setTextSize(50);//设置字体 mPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE); mPaint.setAntiAlias(true); canvas.drawTextOnPath(text,path,0,0,mPaint); canvas.drawTextOnPath(text,path1,20,20,mPaint); }效果:
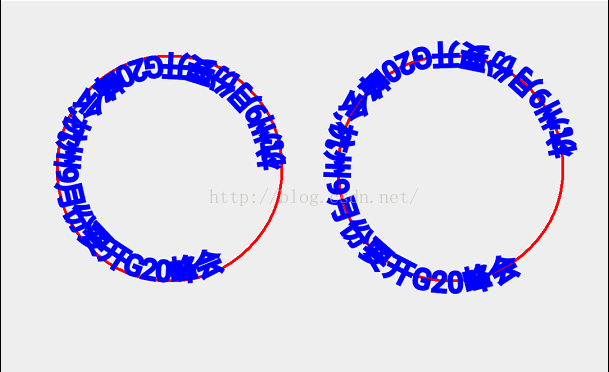
分析图:
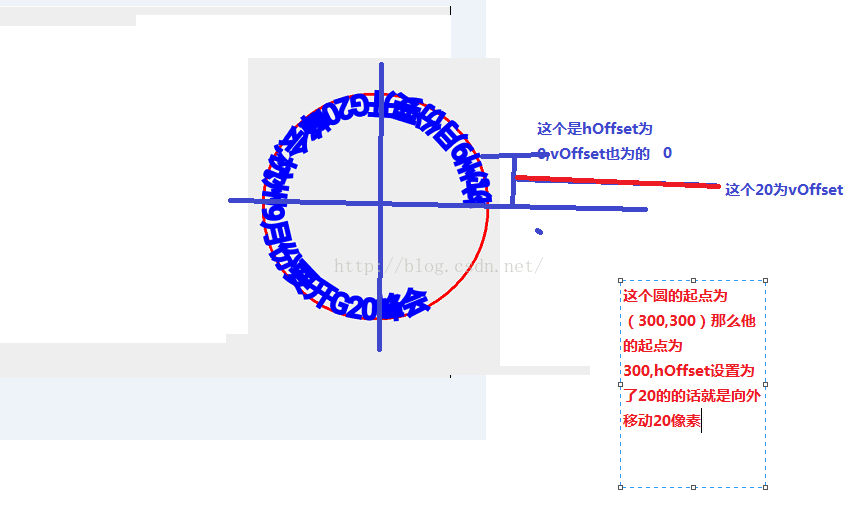
path.addCircle(300,300,200, Path.Direction.CCW);方法的第四个参数讲下,
Path.Direction有两个值:
Path.Direction.CCW:是counter-clockwise缩写,指创建逆时针方向的矩形路径;
Path.Direction.CW:是clockwise的缩写,指创建顺时针方向的矩形路径
源码:
/** * Specifies how closed shapes (e.g. rects, ovals) are oriented when they * are added to a path. */ public enum Direction { /** clockwise */ CW (1), // must match enum in SkPath.h /** counter-clockwise */ CCW (2); // must match enum in SkPath.h Direction(int ni) { nativeInt = ni; } final int nativeInt; }它就是Paint中的一个枚举, clockwise翻译为顺时针方向,而counter-clockwise就为逆时针方向了,比如你画一个圆肯定是看不出来是顺时针还是逆时针,因为它所出的效果是一样的,但是如果你往这个path上绘制一段文字就可以看出来了,
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(5); mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); String text="杭州9月份要开G20峰会,杭州9月份要开G20峰会"; Path path = new Path(); Path path1 = new Path(); path.addCircle(300,300,200, Path.Direction.CCW); path1.addCircle(800,300,200, Path.Direction.CW); canvas.drawPath(path,mPaint); canvas.drawPath(path1,mPaint); mPaint.setTextSize(50);//设置字体 mPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE); mPaint.setAntiAlias(true); canvas.drawTextOnPath(text,path,0,0,mPaint); canvas.drawTextOnPath(text,path1,0,0,mPaint); }
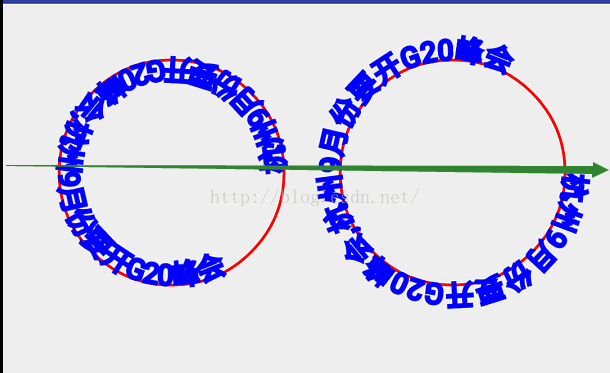
这样第一个就是逆时针方向 第二个就是顺时针方向了,
10):画文字
这里就不讲drawText()了,在讲Paint中这个讲的比较详细,可以去看看那个博客,绘制文字讲的是这个方法
public void drawPosText(char[] text, int index, int count,float[] pos,Paint paint)
参数说明:
text:所绘制文字的数组
index:从第几个数组小标位置开始绘制
count:绘制多少文字
paint:同上
pos:是所绘制所在位置的坐标的集合
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(5); mPaint.setTextSize(60); mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); float []pos=new float[]{140,200, 200,300, 320,400, 440,500}; char[] text={'杭','州','您','好'}; canvas.drawPosText(text,0,4,pos,mPaint); }效果:

讲了这么多canvas所能绘制的东西,现在通过上面讲的来画一个轨迹或者涂鸦功能,
之前讲过通过Path来绘制多边形,这个就是通过Path来实现的,
package com.example.canvasdemo; import android.content.Context; import android.graphics.Canvas; import android.graphics.Color; import android.graphics.Paint; import android.graphics.Path; import android.util.AttributeSet; import android.view.MotionEvent; import android.view.View; /** * Created by admin on 2016/5/18. */ public class TestCanvasView extends View { private Paint mPaint; private Path mPath; public TestCanvasView(Context context) { this(context,null); } public TestCanvasView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs,0); } public TestCanvasView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); mPaint = new Paint(); mPath = new Path(); } @Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(5); mPaint.setTextSize(60); mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); canvas.drawPath(mPath,mPaint); } @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { switch (event.getAction()){ case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: mPath.moveTo(event.getX(),event.getY()); return true; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: mPath.lineTo(event.getX(),event.getY()); invalidate(); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: break; } return super.onTouchEvent(event); } }效果:
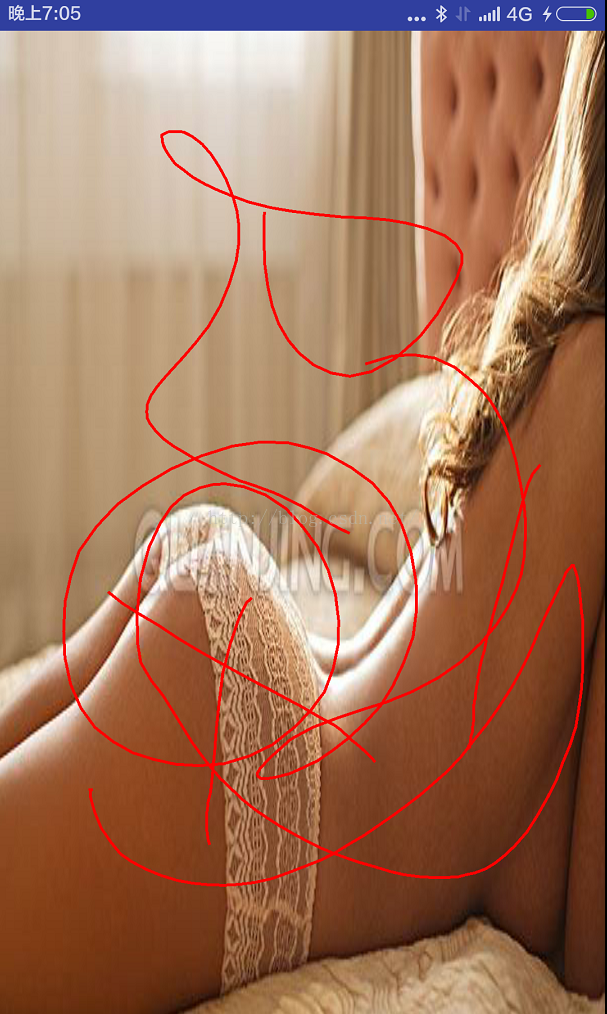

可以发挥你的艺术细胞在这美女身上随便乱画了
canvas还有一个重要的方法就是裁剪,canvas提供了很多关于裁剪的方法如下:
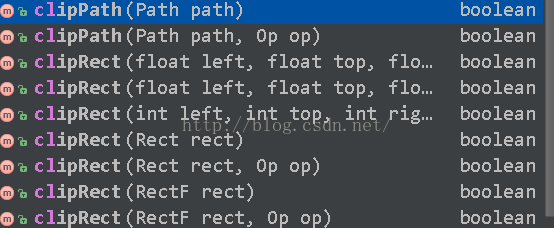
现在拿clipRect()方法来做例子,首先你裁剪得先在画布上绘制出图形来后才可以裁剪,不然你在画布上什么也没有,那裁剪个毛线,
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.mipmap.meinv); canvas.drawColor(Color.BLUE); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); //设置画笔颜色 mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);//填充样式改为描边 mPaint.setStrokeWidth(5);//设置画笔宽度 canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap, bitmap.getWidth(),10,mPaint); canvas.clipRect(bitmap.getWidth(), bitmap.getHeight(), bitmap.getWidth()+bitmap.getWidth()/2 , bitmap.getHeight()+bitmap.getHeight()/2); canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap, bitmap.getWidth(), bitmap.getHeight(), mPaint); }效果:

第一张是原图做对比用的,现在重点讲下
public boolean clipRect(int left, int top, int right, int bottom)
参数说明:
left:第一个点所在x轴方向坐标
top:第一个点所在y轴方向坐标值,
right:第二个坐标所在x轴方向坐标值
bottom:第二个坐标所在y轴方向坐标值
刚才上面所说的关于裁剪是关于图形的是错的,裁剪是针对在画布上进行裁剪,
比如我要裁剪一个三角形:
@Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.mipmap.meinv); canvas.drawColor(Color.BLUE); mPaint.setColor(Color.RED); //设置画笔颜色 mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);//填充样式改为描边 mPaint.setStrokeWidth(5);//设置画笔宽度 canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap, bitmap.getWidth(), 10, mPaint); // canvas.clipRect(bitmap.getWidth(), bitmap.getHeight(), bitmap.getWidth() + bitmap.getWidth() / 2, bitmap.getHeight() + bitmap.getHeight() / 2); Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(bitmap.getWidth(), bitmap.getHeight()); path.lineTo(bitmap.getWidth(),bitmap.getHeight()+200); path.lineTo(bitmap.getWidth()+200,bitmap.getHeight()+200); path.close(); canvas.clipPath(path); canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap, bitmap.getWidth(), bitmap.getHeight(), mPaint); }效果:
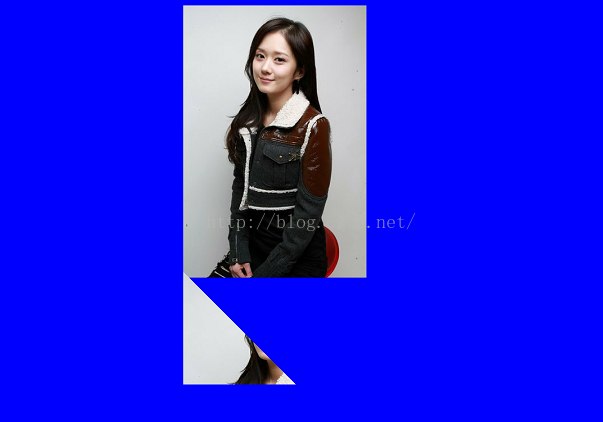

现在我把上面最后二行代码顺序调一下:
canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap, bitmap.getWidth(), bitmap.getHeight(), mPaint);
canvas.clipPath(path);
效果:
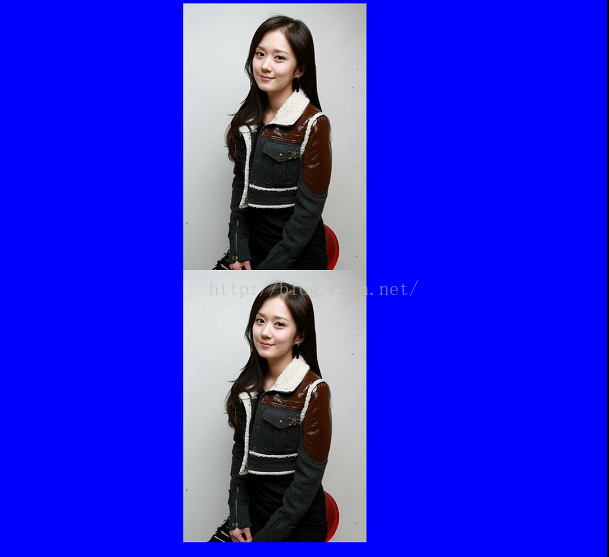
你会发现裁剪没起作用,从此可以得出一个结论
结论:
裁剪要在绘制前面对canvas进行clip,否则无效.
明天继续 困
最后
以上就是故意大船最近收集整理的关于android canvas常用的方法解析(一)的全部内容,更多相关android内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复