一、springboot+mybatis整合redis cluster整合流程图

二、springboot+mybatis整合redis cluster具体实现
2.1 创建springboot+mybatis项目,引入jar
<!--springboot整合redis jar 开始-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--springboot整合redis jar 结束-->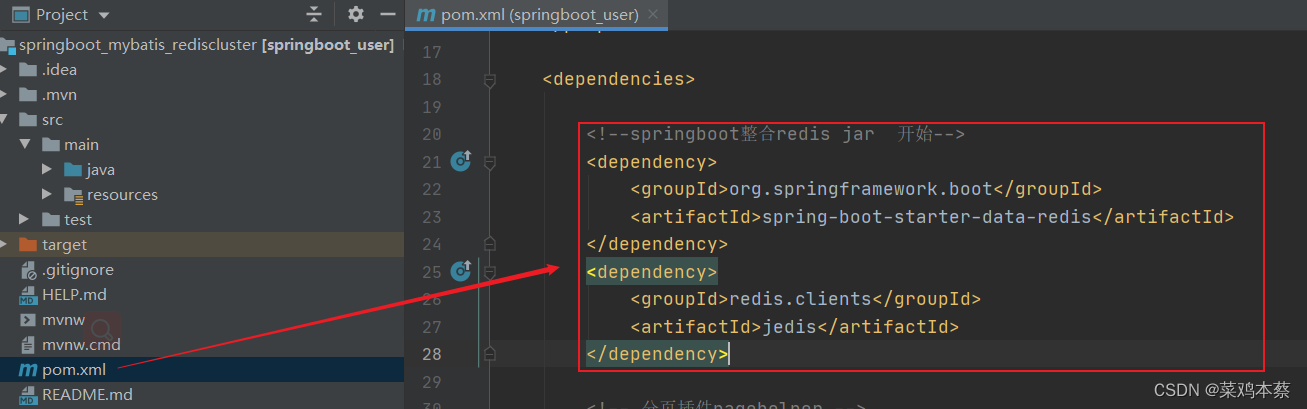
2.2 配置连接redis数据源
在resources文件夹下 添加一个配置 project.properties配置文件
# redis 数据源配置 springboot+mybatis+redis cluster
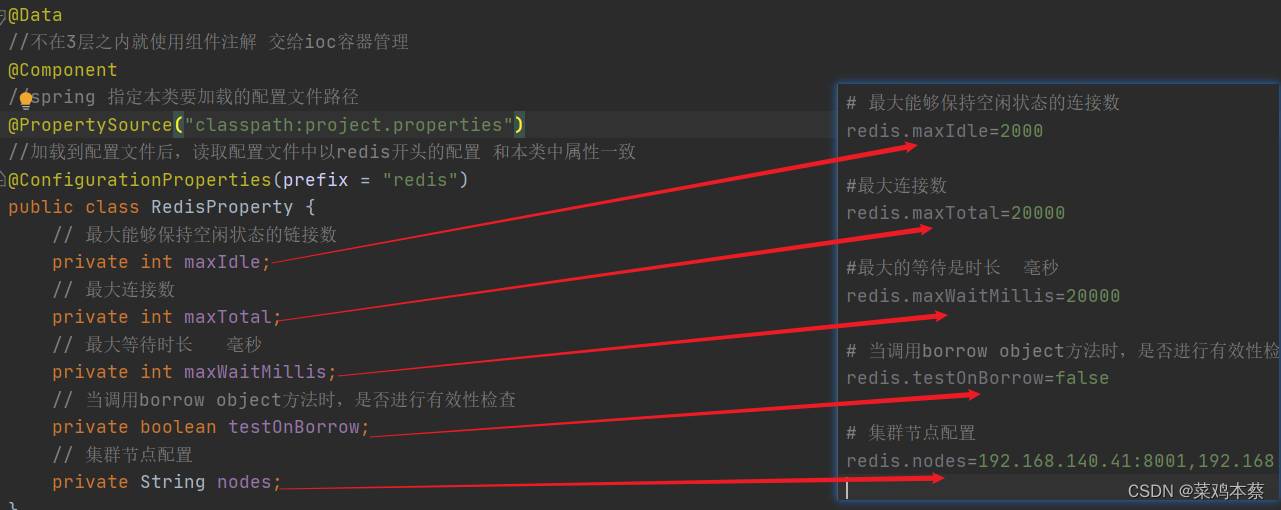
# 最大能够保持空闲状态的连接数
redis.maxIdle=2000
#最大连接数
redis.maxTotal=20000
#最大的等待是时长 毫秒
redis.maxWaitMillis=20000
# 当调用borrow object方法时,是否进行有效性检查
redis.testOnBorrow=false
# 集群节点配置 对应redis服务器创建的集群模式中的IP和端口
redis.nodes=192.168.140.41:8001,192.168.140.41:8002,192.168.140.42:8003,192.168.140.43:8004,192.168.140.43:8005,192.168.140.43:8006
2.3 springboot加载自定义配置文件
创建一个property文件夹存放自定义配置文件
配置文件
package com.aaa.springboot.property;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author :caicai
* @date :Created in 2022/8/12 13:30
* @description: redis配置属性类(springboot加载自定义配置文件)
* @modified By:
* @version:
*/
@Data
//不在3层之内就使用组件注解 交给ioc容器管理
@Component
//spring 指定本类要加载的配置文件路径
@PropertySource("classpath:project.properties")
//加载到配置文件后,读取配置文件中以redis开头的配置 和本类中属性一致
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "redis")
public class RedisProperty {
// 最大能够保持空闲状态的链接数
private int maxIdle;
// 最大连接数
private int maxTotal;
// 最大等待时长 毫秒
private int maxWaitMillis;
// 当调用borrow object方法时,是否进行有效性检查
private boolean testOnBorrow;
// 集群节点配置
private String nodes;
}2.4 配置rediscluster-config 使用配置连接配置数据源
使用spring-boot-starter-data-redis中提供的JedisConnectionFactory 连接redis集群
package com.aaa.springboot.config;
import com.aaa.springboot.property.RedisProperty;
import com.aaa.springboot.util.MyCustomCache;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisClusterConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisNode;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Configuration // 相当于 redis-cluster-config.xml <bean></bean>
public class RedisClusterConfig {
// 依赖注入
@Resource
private RedisProperty redisProperty;
/**
* 配置JedisConnectionFactory redis连接工厂
* @return
*/
@Bean //<bean id=jedisConnectionFactory class =org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory>
public JedisConnectionFactory jedisConnectionFactory(){
// 实例化对象 使用redis 集群 + redis连接池
// RedisClusterConfiguration clusterConfig, JedisPoolConfig poolConfig
JedisConnectionFactory jedisConnectionFactory = new JedisConnectionFactory(clusterConfig(),poolConfig());
// 返回对象
return jedisConnectionFactory;
}
/**
* 初始化 RedisClusterConfiguration redis 集群配置
* @return
*/
@Bean
public RedisClusterConfiguration clusterConfig() {
// 实例化
RedisClusterConfiguration redisClusterConfiguration = new RedisClusterConfiguration();
// 192.168.140.41:8001,192.168.140.41:8002,192.168.140.42:8003,192.168.140.43:8004,192.168.140.43:8005,192.168.140.43:8006
String nodes = redisProperty.getNodes();
// nodesArray=["192.168.140.41:8001","192.168.140.41:8002","192.168.140.42:8003",....]
String[] nodesArray = nodes.split(",");
// 对节点集合进行遍历
for (String node : nodesArray) {
// node: 第一次:"192.168.140.41:8001" 第二次 "192.168.140.41:8002"
// 在次分割 获取ip 和 端口
String[] nodeip = node.split(":");
// 实例化节点
RedisNode redisNode = new RedisNode(nodeip[0], Integer.valueOf(nodeip[1]));
// 添加节点到集群配置类中
redisClusterConfiguration.addClusterNode(redisNode);
}
return redisClusterConfiguration;
}
/**
* 初始化JedisPoolConfig redis连接池配置
* @return
*/
@Bean
public JedisPoolConfig poolConfig() {
// 实例化连接池配置
JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig();
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxIdle(redisProperty.getMaxIdle());
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxTotal(redisProperty.getMaxTotal());
jedisPoolConfig.setTestOnBorrow(redisProperty.isTestOnBorrow());
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(redisProperty.getMaxWaitMillis());
return jedisPoolConfig;
}
/**
* 特殊的bean配置 在springboot启动时也会被执行
* 没有返回值,目的是调用静态注入方法,把当前配置完成的jedisConnectionFactory
* 赋值给MyCustomCache中的属性
*/
@Bean
public void setJCF(){
// 调用MyCustomCache 静态方法,把jedisConnectionFactory注入进去
MyCustomCache.setJedisConnectionFactory(jedisConnectionFactory());
}
}
2.5 编写mybatis自定义缓存类
通过mybatis调用redis集群缓存。 实际使用的mybatis二级缓存,调用第三方缓存。
https://mybatis.net.cn/sqlmap-xml.html#cache
MyBatis 内置了一个强大的事务性(一旦进行CUD,缓存就会被清空)查询(只有查询有缓存)缓存机制,它可以非常方便地配置和定制。默认情况下,只启用了本地的会话缓存(只开启了一级缓存,无论想不想用,都是开启),它仅仅对一个会话中的数据进行缓存(一级缓存是基于SqlSession)。 要启用全局的二级缓存,只需要在你的 SQL 映射文件中添加一行(二级缓存需要自己开启,二级缓存是语句XxxMapper.xml) <cache>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.aaa.springboot.dao.DeptDao">
<!-- 开启二级缓存-->
<cache type="com.aaa.springboot.util.MyCustomCache"></cache>
<select id="queryInfo" resultType="com.aaa.springboot.entity.DeptEntity">
select * from tb_dept
<where>
<if test="dname!=null and dname!=''">
and dname like concat("%",#{dname},"%")
</if>
<if test="loc!=null and loc!=''">
and loc like concat("%",#{loc},"%")
</if>
</where>
</select>
<insert id="addInfo">
insert into tb_dept(dname,loc) values (#{dname},#{loc})
</insert>
<update id="updateInfo">
update tb_dept set dname=#{dname},loc=#{loc} where dept_no = #{deptNo}
</update>
<delete id="delInfo">
delete from tb_dept where dept_no = #{deptNo}
</delete>
</mapper>mybatis 二级缓存详解:
1、所有 select 语句的结果将会被缓存 除非自己配置去掉缓存useCache="false"
2、所有 insert、update 和 delete 语句会刷新缓存。(增删改是改变数据库数据,改变之后一定要重新缓存)除非自己配置不刷新 flushCache="false"
3、缓存会使用最近最少使用算法(LRU, Least Recently Used)算法来清除不需要的缓存。(当1025个热点数据准备缓存时,先把缓存最近最少使用的踢出去)
默认策略可以通过 eviction="FIFO" 改为先进先出
4、缓存不会定时进行刷新(也就是说,没有刷新间隔)。如果想定时刷新(定时把所有缓存内容清空)配置flushInterval=""
5、缓存会保存列表或对象(无论查询方法返回哪种)的 1024 个引用(一共有多少个被缓存)。
6、缓存会被视为读/写缓存 (readOnly="false"),这意味着获取到的对象并不是共享的,可以安全地被调用者修改,而不干扰其他调用者或线程所做的潜在修改。
如果配置的是readOnly="false" 每次请求获取缓存数据时,缓存会把当前缓存的数据复制一份返回给调用或者线程,修改复制品,对原来缓存没有任何影响,
速度慢,但是安全性好。。。。 浪费内存
如果配置的是readOnly="true" 每一个请求获取缓存数据时,都是同一份数据,如果有请求改了,其他人拿到的也会被修改,速度快,因为没有复制品
但是安全性不好。。。 节省内存
编写缓存类
package com.aaa.springboot.util;
import org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnection;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.JdkSerializationRedisSerializer;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;
/**
* @author :caicai
* @date :Created in 2022/8/12 14:18
* @description:自定义的缓存类 用于调用第三方缓存(我们在这调用的是redis cluster 缓存)
* 必须要实现 Cache接口
* @version:
*/
public class MyCustomCache implements Cache {
// 定义缓存对象的唯一识别 mybatis官网要求必须提供一个接收String参数作为id的构造器
private String id;
// 使用在springboot 启动时,加载配置文件
// 实例化 jedisConnectionFactory 对象,来进行数据存入和获取及删除相关操作
private static JedisConnectionFactory jedisConnectionFactory;
// 实例话读写锁对象 多个请求同时对缓存中某一个操作时的策略
private ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
// 无法使用正常注入,使用该对象 所以使用一个静态方法注入 给当前jedisConnectionFactory对象来赋值
public static void setJedisConnectionFactory(JedisConnectionFactory jedisConnectionFactory){
MyCustomCache.jedisConnectionFactory=jedisConnectionFactory;
}
/**
* 提供一个接收有String参数 作为id的构造器(官网要求)
* @return
*/
public MyCustomCache(String id) {
if (null == id){
throw new RuntimeException("id不能为空,必须传递!!");
}
this.id = id;
}
/**
* 获取缓存对象id
* @return
*/
@Override
public String getId() {
return this.id;
}
/**
* 向redis集群中写入缓存对象
* @param key
* @param value
*/
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
// 通过实例化连接redis集群的工厂类 获取一个redis连接 静态属性在非静态方法中可以直接使用 静态属性在类加载时就被放入到所有内存共享区域-方法区 所有对象都是共享
RedisConnection connection = jedisConnectionFactory.getConnection();
// 因为存储时存储的时字节数组类型 所以key 和 value 都要经过序列化
// 使用springboot整合redis提供的序列化方式
JdkSerializationRedisSerializer jdkSerializationRedisSerializer = new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer();
// 使用该类,序列化 key 和 value a=1 变为:aserialize = 1serialize
byte[] serializeKey = jdkSerializationRedisSerializer.serialize(key);
byte[] serializeValue = jdkSerializationRedisSerializer.serialize(value);
// 通过RedisConnection 可以执行redis所有命令
// 在此使用spring类型操作,向集群中存入数据 存入的key 和value都是序列化过的字节数组
connection.set(serializeKey,serializeValue);
// 这里面不要手动关闭连接,因为配置的有连接池,连接的使用和关闭由连接池来完成
// connection.close();
}
/**
* 通过 key 获取缓存对象
* @param key
* @return
*/
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
// 通过实例化连接 redis 集群的工厂类 获取一个redis 连接静态属性在非静态方法中可以直接使用 静态属性在类加载时就被放入到所有内存共享区域-方法区 所有对象都是共享
RedisConnection connection = jedisConnectionFactory.getConnection();
// 因为存储时存储的是自己数组类型 所以key 和 value 都要经过序列化
// 使用springboot整合redis提供的序列化方式
JdkSerializationRedisSerializer jdkSerializationRedisSerializer = new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer();
// 序列化变字节数组 serializekey = a
byte[] serializeKey = jdkSerializationRedisSerializer.serialize(key);
//通过序列化的key获取到序列化后的值
byte[] serializeValue = connection.get(serializeKey);
// 反序列化后并返回 1serialize --> 1
return jdkSerializationRedisSerializer.deserialize(serializeValue);
}
/**
* 根据 key 删除缓存对象
* @param key
* @return
*/
@Override
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
// 通过实例化连接 redis 集群的工厂类 获取一个redis 连接
RedisConnection connection = jedisConnectionFactory.getConnection();
// 使用springboot整合redis提供的序列化方式
JdkSerializationRedisSerializer jdkSerializationRedisSerializer = new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer();
// 序列 key 变为字节数组
byte[] serializeKey = jdkSerializationRedisSerializer.serialize(key);
// 删除时也要使用序列化后的key 这种写法当在大量缓存进行删除时,效率会低 每次都会执行删除
// connection.del(serializeKey);
// 设置该 key 失效 0为立马失效 立马失效,就获取不到,等同于删除 底层redis使用惰性删除 定期批量清理失效的key 批量操作,而不是一个一个操纵,提高效率
return connection.expireAt(serializeKey,0);
}
/**
* 清空所有缓存书库
*/
@Override
public void clear() {
// 通过实例化连接redis集群的工厂类,获取一个redis连接 静态属性在非静态方法中可以直接使用 静态属性在类加载时就被放入到所有内存共享区域-方法区 所有对象都是共享
RedisConnection connection = jedisConnectionFactory.getConnection();
// flushDb redis 每个实例对象默认分为16库 清空当前库
// connection.flushDb();
// flushAll 清空所有库
connection.flushAll();
}
/**
* 获取当前缓存中对象数量
* @return
*/
@Override
public int getSize() {
// 通过实例化连接redis集群的工厂类,获取一个redis连接
RedisConnection connection = jedisConnectionFactory.getConnection();
// 使用 dbSize
Long aLong = connection.dbSize();
// 转为 int 类型,并返回
return Integer.valueOf(aLong.toString());
}
/**
* 缓存读写锁 (缓存读写策略)
* @return
*/
@Override
public ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock() {
return readWriteLock;
}
}
2.6 整合测试
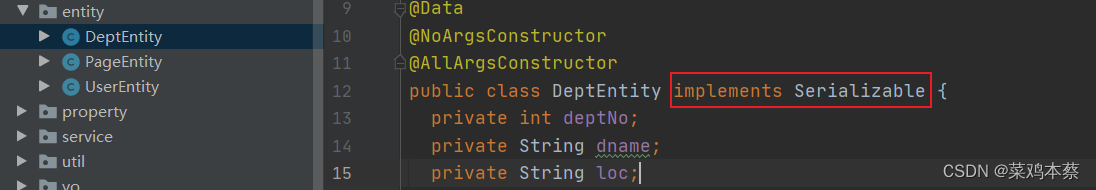
1、注意所有的实体类必须序列化 (只要使用了mybatis二级缓存,就需要这么做)
2、 启动redis集群,使用客户端命令测试是否正常
使用脚本启动集群:
./shelldir/redis-start-stop.sh
使用客户端命令测试:
/usr/redis/bin/redis-cli -c -h 192.168.140.43 -p 8005
192.168.140.43:8005> cluster info 发现正常

3、启动sbm项目,使用swagger做查询 测试
http://localhost:16666/swagger-ui/index.html#/
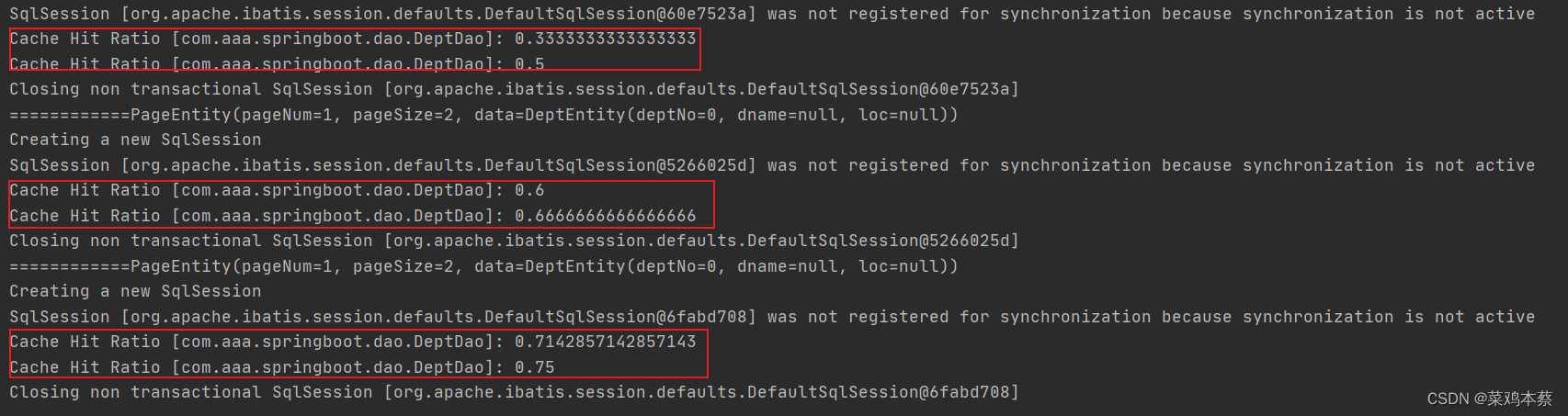
第一次请求时,在idea控制台可以看到执行语句(sql语句),说明是从数据获取
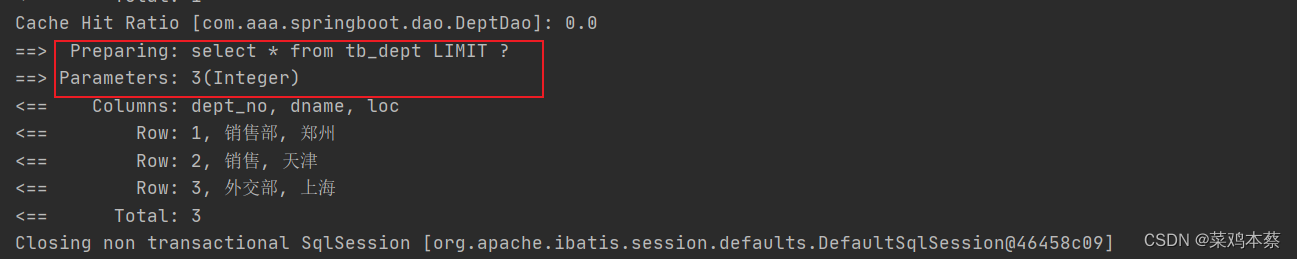
第二次: 清空控制台,再次请求,发现控制台就不再执行语句,而是看到cache hit Ratio 命中率
请求两次,从缓存中取了一次 1/2

第三次:2次从缓存中获取 2/3

第四次:3次从缓存中获取 3/4

。。。。。
4、查看缓存是否存在
/usr/redis/bin/redis-cli -c -h 192.168.140.41 -p 8001
缓存到那个节点不确定 要一个一个试

5、清空缓存,再次请求,再观察控制台
/usr/redis/bin/redis-cli -c -h 192.168.140.41 -p 8001
192.168.140.41:8001> flushdb
/usr/redis/bin/redis-cli -c -h 192.168.140.43 -p 8005
192.168.140.43:8005> flushdb
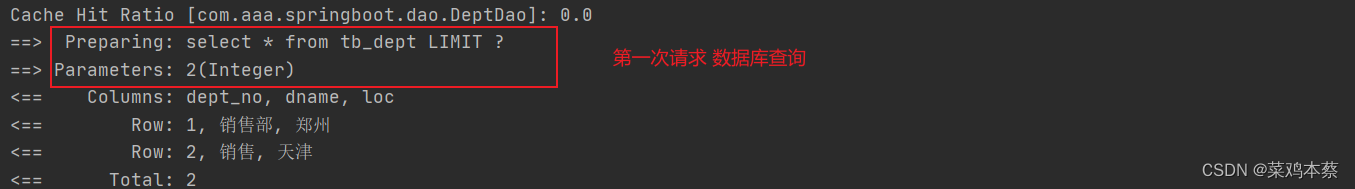
说明清空缓存后,会再次从数据获取
继续刷新请求
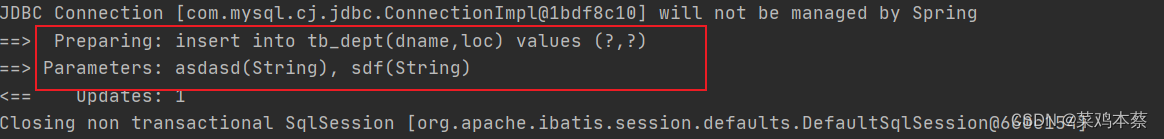
增删改后,再次观察控制台(增删改后,一定会自动清空缓存,再次从数据库查询,再次缓存)
先执行添加操作
在此查询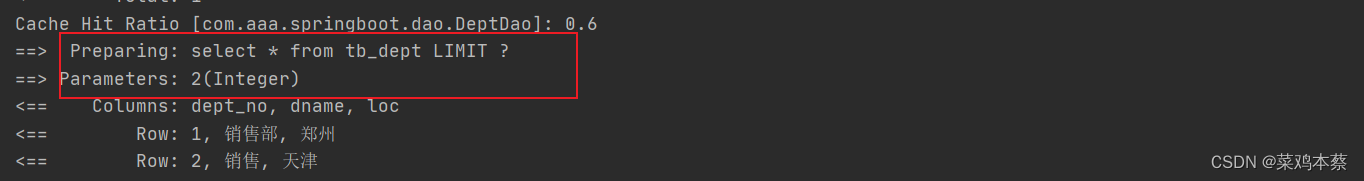
查询方法和CUD方法必须同一个mapper才会CUD后,清空缓存,重新缓存
最后
以上就是体贴羊最近收集整理的关于redis05_springboot+mybatis整合redis cluster一、springboot+mybatis整合redis cluster整合流程图二、springboot+mybatis整合redis cluster具体实现的全部内容,更多相关redis05_springboot+mybatis整合redis内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。

![redis java 存储图片_Redis 存储图片 [base64/url/path]vs[object]](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg3.png)






发表评论 取消回复