slam十四讲--习题一
习题1 Ax=b, 已知A,b要如何解x?
若A可逆,rank(A)=rank(A,b)=n. x=A^-1 * b 即A满秩(/ 非奇异 / det(A)不等于0),可以解出x的唯一解
若rank(A)<rank(A,b) x无解。
若rank(A)=rank(A,b)<n, x多解。
习题2 高斯分布
正态分布(Normal distribution)又名高斯分布(Gaussian distribution),是一个在数学、物理及工程等领域都非常重要的概率分布,在统计学的许多方面有着重大的影响力。
若随机变量X服从一个数学期望为μ、标准方差为σ2的高斯分布,记为:
X∼N(μ,σ2),
则其概率密度函数为
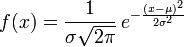
代表在均值为 ,方差为
的情况下,需要标准化一下:
,标准化之后方差变为1,标准化的意义在于将数据点
到均值
的距离转化为数据点
到均值的距离等于多少个总体的标准差
,这样,就消除了数据分布差异和量纲对概率计算的影响,此时的概率密度函数为:
可见,高斯分布的概率密度计算核心在于计算数据点到中心的距离,并且除以标准差将这个绝对距离转化为相对距离,然后通过距离平方的指数衰减计算概率密度。
它的高维形式:
习题3
c++ 类: http://www.cnblogs.com/mr-wid/archive/2013/02/18/2916309.html
STL : http://www.runoob.com/cplusplus/cpp-stl-tutorial.html
习题7
Linuc目录结构: http://www.cnblogs.com/JCSU/articles/2770249.html
习题9 vim的使用:
------------------------------
Lesson 1 SUMMARY
1. The cursor is moved using either the arrow keys or the hjkl keys.
h (left) j (down) k (up) l (right)
2. To start Vim from the shell prompt type: vim FILENAME <ENTER>
3. To exit Vim type: <ESC> :q! <ENTER> to trash all changes.
OR type: <ESC> :wq <ENTER> to save the changes.
4. To delete the character at the cursor type: x
5. To insert or append text type:
i type inserted text <ESC> insert before the cursor
A type appended text <ESC> append after the line
NOTE: Pressing <ESC> will place you in Normal mode or will cancel
an unwanted and partially completed command
-------------------------------
Lesson 2 SUMMARY
1. To delete from the cursor up to the next word type: dw
2. To delete from the cursor to the end of a line type: d$
3. To delete a whole line type: dd
4. To repeat a motion prepend it with a number: 2w
5. The format for a change command is:
operator [number] motion
where:
operator - is what to do, such as d for delete
[number] - is an optional count to repeat the motion
motion - moves over the text to operate on, such as w (word),
$ (to the end of line), etc.
6. To move to the start of the line use a zero: 0
7. To undo previous actions, type: u (lowercase u)
To undo all the changes on a line, type: U (capital U)
To undo the undo's, type: CTRL-R
--------------------------------
Lesson 3 SUMMARY
1. To put back text that has just been deleted, type p . This puts the deleted text AFTER the cursor (if a line was deleted it will go on the line below the cursor).
2. To replace the character under the cursor, type r and then the character you want to have there.
3. The change operator allows you to change from the cursor to where the motion takes you.
eg. Type ce to change from the cursor to the end of the word,
c$ to change to the end of a line.
4. The format for change is:
c [number] motion
---------------------------------------------
Lesson 4 SUMMARY
1. CTRL-G displays your location in the file and the file status.
G moves to the end of the file.
number G moves to that line number.
gg moves to the first line.
2. Typing / followed by a phrase searches FORWARD for the phrase.
Typing ? followed by a phrase searches BACKWARD for the phrase.
After a search type n to find the next occurrence in the same direction
or N to search in the opposite direction.
CTRL-O takes you back to older positions, CTRL-I to newer positions.
3. Typing % while the cursor is on a (,),[,],{, or } goes to its match.
4. To substitute new for the first old in a line type :s/old/new
To substitute new for all 'old's on a line type :s/old/new/g
To substitute phrases between two line #'s type :#,#s/old/new/g
To substitute all occurrences in the file type :%s/old/new/g
To ask for confirmation each time add 'c' :%s/old/new/gc
----------------
Lesson 5 SUMMARY
1. :!command executes an external command.
Some useful examples are:
(MS-DOS) (Unix)
:!dir :!ls - shows a directory listing.
:!del FILENAME :!rm FILENAME - removes file FILENAME.
2. :w FILENAME writes the current Vim file to disk with name FILENAME.
3. v motion :w FILENAME saves the Visually selected lines in file FILENAME.
4. :r FILENAME retrieves disk file FILENAME and puts it below the cursor position.
5. :r !dir reads the output of the dir command and puts it below the cursor position.
------------------
Lesson 6 SUMMARY
1. Type o to open a line BELOW the cursor and start Insert mode.
Type O to open a line ABOVE the cursor.
2. Type a to insert text AFTER the cursor.
Type A to insert text after the end of the line.
3. The e command moves to the end of a word.
4. The y operator yanks (copies) text, p puts (pastes) it.
5. Typing a capital R enters Replace mode until <ESC> is pressed.
6. Typing ":set xxx" sets the option "xxx". Some options are:
'ic' 'ignorecase' ignore upper/lower case when searching
'is' 'incsearch' show partial matches for a search phrase
'hls' 'hlsearch' highlight all matching phrases
You can either use the long or the short option name.
7. Prepend "no" to switch an option off: :set noic
-----------------
Lesson 7 SUMMARY
1. Type :help or press <F1> or <Help> to open a help window.
2. Type :help cmd to find help on cmd .
3. Type CTRL-W CTRL-W to jump to another window
4. Type :q to close the help window
5. Create a vimrc startup script to keep your preferred settings.
6. When typing a : command, press
参考文献:
维基百科
知乎--李亮德:https://www.zhihu.com/question/36339816/answer/385944057
最后
以上就是爱笑牛排最近收集整理的关于【SLAM十四讲】 第一讲习题的全部内容,更多相关【SLAM十四讲】内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。









发表评论 取消回复