01 本地环境配置
Anaconda 提供了一种处理包依赖关系的简便方法,为课程创建虚拟环境。
Jupyter notebook 在web浏览器中编写和执行代码。
02 KNN分类器
021 数据集预处理
0211模版导入 & jupyter notebook 图片展示设置
# Run some setup code for this notebook.
import random
import numpy as np
from cs231n.data_utils import load_CIFAR10
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from __future__ import print_function
# This is a bit of magic to make matplotlib figures appear inline in the notebook
# rather than in a new window.
%matplotlib inline
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (10.0, 8.0) # set default size of plots
plt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest'
plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray'
# Some more magic so that the notebook will reload external python modules;
# see http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1907993/autoreload-of-modules-in-ipython
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2
0212导入数据集
# Load the raw CIFAR-10 data.
cifar10_dir = 'cs231n/datasets/cifar-10-batches-py'
# Cleaning up variables to prevent loading data multiple times (which may cause memory issue)
try:
del X_train, y_train
del X_test, y_test
print('Clear previously loaded data.')
except:
pass
X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test = load_CIFAR10(cifar10_dir)
# As a sanity check, we print out the size of the training and test data.
print('Training data shape: ', X_train.shape)
print('Training labels shape: ', y_train.shape)
print('Test data shape: ', X_test.shape)
print('Test labels shape: ', y_test.shape)
结果:
Training data shape: (50000, 32, 32, 3)
Training labels shape: (50000,)
Test data shape: (10000, 32, 32, 3)
Test labels shape: (10000,)
训练数据:五万张32X32X3
测试数据:一万张32X32X3
0213展示训练照片
# Visualize some examples from the dataset.
# We show a few examples of training images from each class.
classes = ['plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck']# 列表的使用
num_classes = len(classes)#返回列表中元素的个数
samples_per_class = 7
for y, cls in enumerate(classes):# enumerate 显示index和value
idxs = np.flatnonzero(y_train == y)#找出某一类的index
idxs = np.random.choice(idxs, samples_per_class, replace=False)#np.random.choice(a, size, replace, p)从a中以p的概率分布取size个,repalce表明有无放回
for i, idx in enumerate(idxs):
plt_idx = i * num_classes + y + 1
plt.subplot(samples_per_class, num_classes, plt_idx)
plt.imshow(X_train[idx].astype('uint8'))
plt.axis('off')
if i == 0:
plt.title(cls)
plt.show()
结果:

0214选取数据集的一部分
# Subsample the data for more efficient code execution in this exercise
num_training = 5000
mask = list(range(num_training))
X_train = X_train[mask]
y_train = y_train[mask]
num_test = 500
mask = list(range(num_test))
X_test = X_test[mask]
y_test = y_test[mask]
0215将每张照片变成一行数据
# Reshape the image data into rows
X_train = np.reshape(X_train, (X_train.shape[0], -1))#shape[0]表示第一维的长度,-1表示未知自适应
X_test = np.reshape(X_test, (X_test.shape[0], -1))
print(X_train.shape, X_test.shape)
结果:
(5000, 3072) (500, 3072)
022KNN分类器实现
0221 k_nearest_neighbor.py
import numpy as np
class KNearestNeighbor(object):
""" a kNN classifier with L2 distance """
def __init__(self):#空函数
pass
def train(self, X, y):
"""
Train the classifier. For k-nearest neighbors this is just
memorizing the training data.
Inputs:
- X: A numpy array of shape (num_train, D) containing the training data
consisting of num_train samples each of dimension D.
- y: A numpy array of shape (N,) containing the training labels, where
y[i] is the label for X[i].
"""
self.X_train = X
self.y_train = y
def predict(self, X, k=1, num_loops=0):
"""
Predict labels for test data using this classifier.
Inputs:
- X: A numpy array of shape (num_test, D) containing test data consisting
of num_test samples each of dimension D.
- k: The number of nearest neighbors that vote for the predicted labels.
- num_loops: Determines which implementation to use to compute distances
between training points and testing points.
Returns:
- y: A numpy array of shape (num_test,) containing predicted labels for the
test data, where y[i] is the predicted label for the test point X[i].
"""
if num_loops == 0:
dists = self.compute_distances_no_loops(X)
elif num_loops == 1:
dists = self.compute_distances_one_loop(X)
elif num_loops == 2:
dists = self.compute_distances_two_loops(X)
else:
raise ValueError('Invalid value %d for num_loops' % num_loops) #Python的一种异常处理机制
return self.predict_labels(dists, k=k)
def compute_distances_two_loops(self, X):
"""
Compute the distance between each test point in X and each training point
in self.X_train using a nested loop over both the training data and the
test data.
Inputs:
- X: A numpy array of shape (num_test, D) containing test data.
Returns:
- dists: A numpy array of shape (num_test, num_train) where dists[i, j]
is the Euclidean distance between the ith test point and the jth training
point.
"""
num_test = X.shape[0]#500
num_train = self.X_train.shape[0]#5000
dists = np.zeros((num_test, num_train))
for i in range(num_test):# 0 1 2 3 4
for j in range(num_train):
#####################################################################
# TODO: #
# Compute the l2 distance between the ith test point and the jth #
# training point, and store the result in dists[i, j]. You should #
# not use a loop over dimension. #
#####################################################################
dists[i][j] = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(self.X_train[j,:] - X[i,:])))
#####################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
#####################################################################
return dists
def compute_distances_one_loop(self, X):
"""
Compute the distance between each test point in X and each training point
in self.X_train using a single loop over the test data.
Input / Output: Same as compute_distances_two_loops
"""
num_test = X.shape[0]#500
num_train = self.X_train.shape[0]#5000
dists = np.zeros((num_test, num_train))
for i in range(num_test):
#######################################################################
# TODO: #
# Compute the l2 distance between the ith test point and all training #
# points, and store the result in dists[i, :]. #
#######################################################################
dists[i,:] = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(self.X_train-X[i,:]),axis = 1))
#######################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
#######################################################################
return dists
def compute_distances_no_loops(self, X):
"""
Compute the distance between each test point in X and each training point
in self.X_train using no explicit loops.
Input / Output: Same as compute_distances_two_loops
"""
num_test = X.shape[0]
num_train = self.X_train.shape[0]
dists = np.zeros((num_test, num_train))
#########################################################################
# TODO: #
# Compute the l2 distance between all test points and all training #
# points without using any explicit loops, and store the result in #
# dists. #
# #
# You should implement this function using only basic array operations; #
# in particular you should not use functions from scipy. #
# #
# HINT: Try to formulate the l2 distance using matrix multiplication #
# and two broadcast sums. #
#########################################################################
m=np.multiply(np.dot(X,self.X_train.T),-2)
n=np.sum(np.square(X),axis=1,keepdims = True)#当axis为0时,是压缩行,即将每一列的元素相加,将矩阵压缩为一行
#当axis为1时,是压缩列,即将每一行的元素相加,将矩阵压缩为一列
t=np.sum(np.square(self.X_train),axis=1)
dists=m+n+t
#########################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
#########################################################################
return dists
def predict_labels(self, dists, k=1):
"""
Given a matrix of distances between test points and training points,
predict a label for each test point.
Inputs:
- dists: A numpy array of shape (num_test, num_train) where dists[i, j]
gives the distance betwen the ith test point and the jth training point.
Returns:
- y: A numpy array of shape (num_test,) containing predicted labels for the
test data, where y[i] is the predicted label for the test point X[i].
"""
num_test = dists.shape[0]#500
y_pred = np.zeros(num_test)
for i in range(num_test):
# A list of length k storing the labels of the k nearest neighbors to
# the ith test point.
closest_y = []
#########################################################################
# TODO: #
# Use the distance matrix to find the k nearest neighbors of the ith #
# testing point, and use self.y_train to find the labels of these #
# neighbors. Store these labels in closest_y. #
# Hint: Look up the function numpy.argsort. #
#########################################################################
closest_y = self.y_train[np.argsort(dists[i,:])[:k]]
#########################################################################
# TODO: #
# Now that you have found the labels of the k nearest neighbors, you #
# need to find the most common label in the list closest_y of labels. #
# Store this label in y_pred[i]. Break ties by choosing the smaller #
# label. #
#########################################################################
y_pred[i] = np.argmax(np.bincount(closest_y))#bincount 统计0-最大值出现的次数
#agrmax返回最大值的索引
#########################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
#########################################################################
return y_pred
022使用分类器
from cs231n.classifiers import KNearestNeighbor
# Create a kNN classifier instance.
# Remember that training a kNN classifier is a noop:
# the Classifier simply remembers the data and does no further processing
classifier = KNearestNeighbor()
classifier.train(X_train, y_train)
# Test your implementation:
dists = classifier.compute_distances_two_loops(X_test)
print(dists.shape)#(500,5000)
#Now implement the function predict_labels and run the code below:
# We use k = 1 (which is Nearest Neighbor).
y_test_pred = classifier.predict_labels(dists, k=1)
# Compute and print the fraction of correctly predicted examples
num_correct = np.sum(y_test_pred == y_test)
accuracy = float(num_correct) / num_test
print('Got %d / %d correct => accuracy: %f' % (num_correct, num_test, accuracy))
y_test_pred = classifier.predict_labels(dists, k=5)
num_correct = np.sum(y_test_pred == y_test)
accuracy = float(num_correct) / num_test
print('Got %d / %d correct => accuracy: %f' % (num_correct, num_test, accuracy))
# Let's compare how fast the implementations are
def time_function(f, *args):
"""
Call a function f with args and return the time (in seconds) that it took to execute.
"""
import time
tic = time.time()
f(*args)
toc = time.time()
return toc - tic
two_loop_time = time_function(classifier.compute_distances_two_loops, X_test)
print('Two loop version took %f seconds' % two_loop_time)
one_loop_time = time_function(classifier.compute_distances_one_loop, X_test)
print('One loop version took %f seconds' % one_loop_time)
no_loop_time = time_function(classifier.compute_distances_no_loops, X_test)
print('No loop version took %f seconds' % no_loop_time)
# you should see significantly faster performance with the fully vectorized implementation
023交叉验证
num_folds = 5
k_choices = [1, 3, 5, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20, 50, 100]
X_train_folds = []
y_train_folds = []
################################################################################
# TODO: #
# Split up the training data into folds. After splitting, X_train_folds and #
# y_train_folds should each be lists of length num_folds, where #
# y_train_folds[i] is the label vector for the points in X_train_folds[i]. #
# Hint: Look up the numpy array_split function. #
################################################################################
X_train_folds = np.array_split(X_train, num_folds)
y_train_folds = np.array_split(y_train, num_folds)
################################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
################################################################################
# A dictionary holding the accuracies for different values of k that we find
# when running cross-validation. After running cross-validation,
# k_to_accuracies[k] should be a list of length num_folds giving the different
# accuracy values that we found when using that value of k.
k_to_accuracies = {}
################################################################################
# TODO: #
# Perform k-fold cross validation to find the best value of k. For each #
# possible value of k, run the k-nearest-neighbor algorithm num_folds times, #
# where in each case you use all but one of the folds as training data and the #
# last fold as a validation set. Store the accuracies for all fold and all #
# values of k in the k_to_accuracies dictionary. #
################################################################################
for k in k_choices:
for f in range(num_folds):
X_train_tmp = np.array(X_train_folds[:f] + X_train_folds[f + 1:])
y_train_tmp = np.array(y_train_folds[:f] + y_train_folds[f + 1:])
X_train_tmp = X_train_tmp.reshape(-1, X_train_tmp.shape[2])
y_train_tmp = y_train_tmp.reshape(-1)
X_va = np.array(X_train_folds[f])
y_va = np.array(y_train_folds[f])
classifier.train(X_train_tmp, y_train_tmp)
dists = classifier.compute_distances_no_loops(X_va)
y_test_pred = classifier.predict_labels(dists, k)
# Compute and print the fraction of correctly predicted examples
num_correct = np.sum(y_test_pred == y_va)
accuracy = float(num_correct) / y_va.shape[0]
if (k in k_to_accuracies.keys()):
k_to_accuracies[k].append(accuracy)
else:
k_to_accuracies[k] = []
k_to_accuracies[k].append(accuracy)
################################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
################################################################################
# Print out the computed accuracies
for k in sorted(k_to_accuracies):
for accuracy in k_to_accuracies[k]:
print('k = %d, accuracy = %f' % (k, accuracy))
结果:
k = 1, accuracy = 0.263000
k = 1, accuracy = 0.257000
k = 1, accuracy = 0.264000
k = 1, accuracy = 0.278000
k = 1, accuracy = 0.266000
k = 3, accuracy = 0.239000
k = 3, accuracy = 0.249000
k = 3, accuracy = 0.240000
k = 3, accuracy = 0.266000
k = 3, accuracy = 0.254000
k = 5, accuracy = 0.248000
k = 5, accuracy = 0.266000
k = 5, accuracy = 0.280000
k = 5, accuracy = 0.292000
k = 5, accuracy = 0.280000
k = 8, accuracy = 0.262000
k = 8, accuracy = 0.282000
k = 8, accuracy = 0.273000
k = 8, accuracy = 0.290000
k = 8, accuracy = 0.273000
k = 10, accuracy = 0.265000
k = 10, accuracy = 0.296000
k = 10, accuracy = 0.276000
k = 10, accuracy = 0.284000
k = 10, accuracy = 0.280000
k = 12, accuracy = 0.260000
k = 12, accuracy = 0.295000
k = 12, accuracy = 0.279000
k = 12, accuracy = 0.283000
k = 12, accuracy = 0.280000
k = 15, accuracy = 0.252000
k = 15, accuracy = 0.289000
k = 15, accuracy = 0.278000
k = 15, accuracy = 0.282000
k = 15, accuracy = 0.274000
k = 20, accuracy = 0.270000
k = 20, accuracy = 0.279000
k = 20, accuracy = 0.279000
k = 20, accuracy = 0.282000
k = 20, accuracy = 0.285000
k = 50, accuracy = 0.271000
k = 50, accuracy = 0.288000
k = 50, accuracy = 0.278000
k = 50, accuracy = 0.269000
k = 50, accuracy = 0.266000
k = 100, accuracy = 0.256000
k = 100, accuracy = 0.270000
k = 100, accuracy = 0.263000
k = 100, accuracy = 0.256000
k = 100, accuracy = 0.263000
可视化:
# plot the raw observations
for k in k_choices:
accuracies = k_to_accuracies[k]
plt.scatter([k] * len(accuracies), accuracies)
# plot the trend line with error bars that correspond to standard deviation
accuracies_mean = np.array([np.mean(v) for k,v in sorted(k_to_accuracies.items())])
accuracies_std = np.array([np.std(v) for k,v in sorted(k_to_accuracies.items())])
plt.errorbar(k_choices, accuracies_mean, yerr=accuracies_std)
plt.title('Cross-validation on k')
plt.xlabel('k')
plt.ylabel('Cross-validation accuracy')
plt.show()
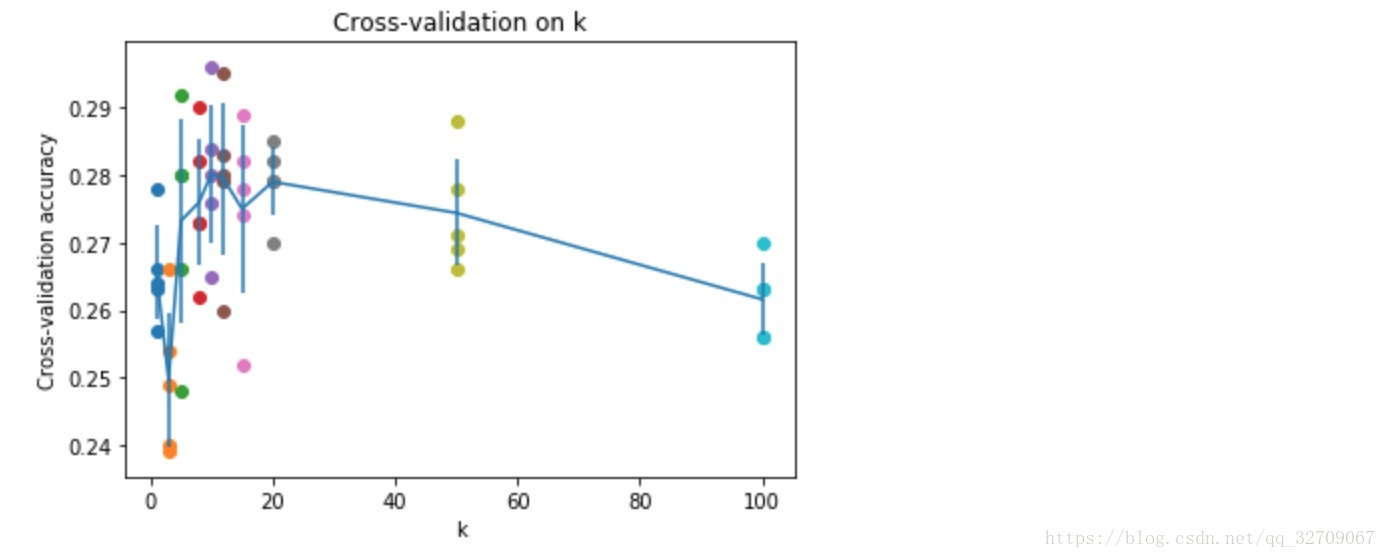
最佳选择:
# Based on the cross-validation results above, choose the best value for k,
# retrain the classifier using all the training data, and test it on the test
# data. You should be able to get above 28% accuracy on the test data.
best_k = 10
classifier = KNearestNeighbor()
classifier.train(X_train, y_train)
y_test_pred = classifier.predict(X_test, k=best_k)
# Compute and display the accuracy
num_correct = np.sum(y_test_pred == y_test)
accuracy = float(num_correct) / num_test
print('Got %d / %d correct => accuracy: %f' % (num_correct, num_test, accuracy))
Got 141 / 500 correct => accuracy: 0.282000
03个人总结
数学原理简单,但需要熟悉numpy的数据操作,常用函数的使用要非常熟悉。
最后
以上就是迷你冷风最近收集整理的关于cs231n------Assignment1-------KNN的全部内容,更多相关cs231n------Assignment1-------KNN内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复