SpringBoot外化配置源码解析
在前面章节我们讲解了 Spring Boot 的运作核心原理及启动过程中进行的一系列核心操作。
从本章开始,我们将针对在实践过程中应用的不同知识点的源代码进行解读和分析,内容上可能会与之前章节有所重叠,但这些重叠的内容更有助于我们在实践和应用中形成前后呼应,加深记忆学习效果。
本章将重点讲解 Spring Boot 外化配置文件相关内容,核心包括:外化配置文件、命令行参数、Profile 实现机制及 整个加载处理业务逻辑。
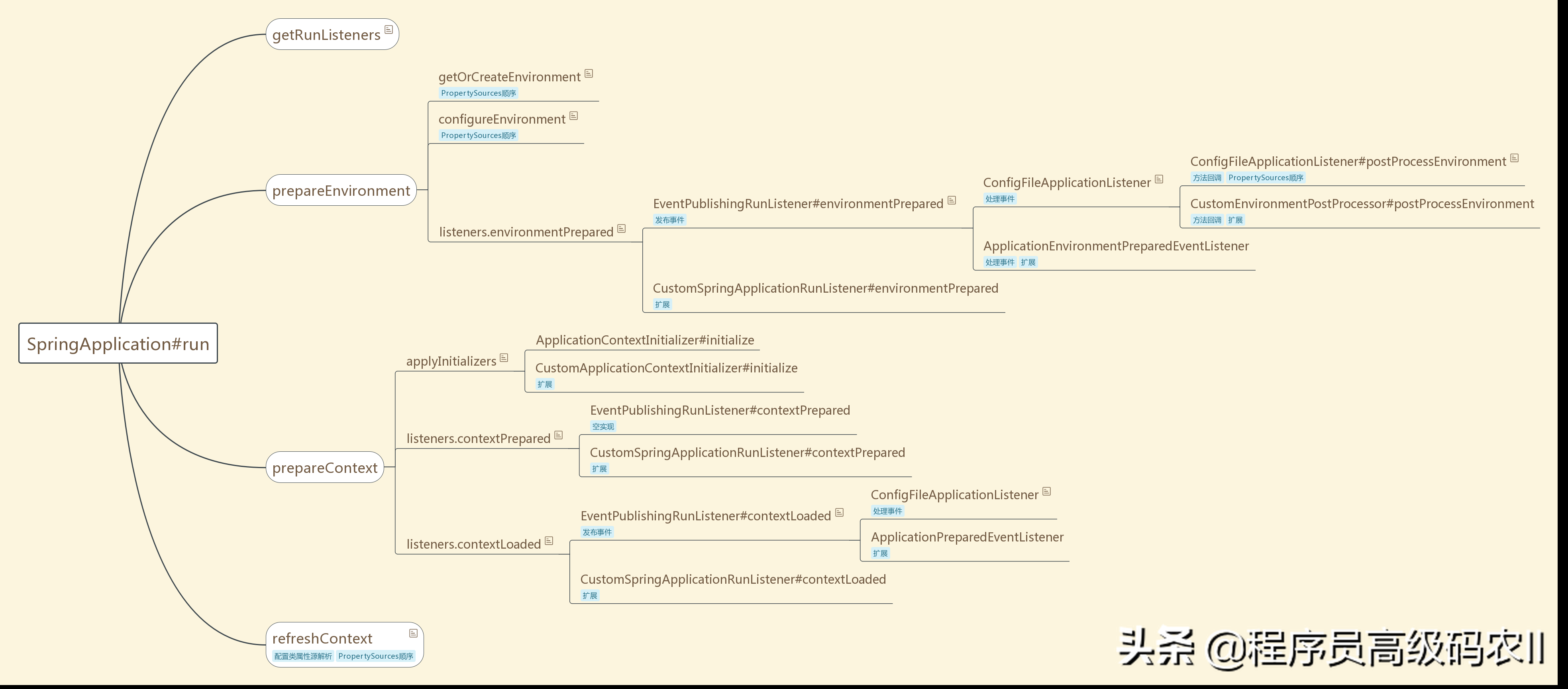
外化配置简介
Spring Boot 允许我们将配置进行外部化处理,以便我们使用相同的代码在不同的环境中运行。我们可以使用属性文件、YAML 文件、环境变量和命令参数来进行外化配置。这些配置中的属性可以通过@Value 注解直接注入到对应的 Bean 中,也可以通过 Spring 的Environment 抽象访问,还可以通过@ConfigurationProperties 绑定到结构化的对象上。
Spring Boot 设计了非常特殊的加载指定属性文件(PropertySource) 的顺序,以允许对属性值进行合理的覆盖。属性值会以下面的优先级进行设置。
-home 目 录 下 的 Devtools 全 局 设 置 属 性 (
~/.spring-boot-devtools.properties, 条件当devtools 激活时)。@ TestPropertySource 注解的测试用例。
- . @Spring BootTest#properties 注解的测试用例。
- .命令行参数。
- .来自 SPRING_ _APPLICATION JSON 的属性(内嵌在环境变量或系统属性中的内联JSON)。
- SrvletConfig 初始化参数。
- :ServletContext 初始化参数。
- java:comp/env 的 JNDI 属性。
- Java 系统属性(System.getProperties() 。
- .操作系统环境变量。
- : RandomValuePropertySource,只包含 random. *中的属性。
- jar 包外的 Profile-specific 应用属性(application-{profile} properties 和 YAML 变量)。
- :jar 包内的 Profile-specific 应用属性(application-{profile} properties 和 YAML 变量)。
- xjar 包外的应用配置(application properties 和 YAML 变量)。
- xjar 包内的应用配置(application.properties 和 YAML 变 量)。
- .@Configuration 类上的@ PropertySource 注解。
- .默认属性(通过 SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties 指定)。
在以上配置方式中,我们经常使用的包括:命令参数、属性文件、YAML 文件等内容,以下将围绕它们的运作及相关代码进行讲解。
ApplicationArguments 参数处理
ApplicationArguments 提供了针对参数的解析和查询功能。在 Spring Boot 运行阶段的章节中 我 们 提 到 过 , 通 过 SpringApplication.run(args) 传 递 的 参 数 会 被 封 装 在ApplicationArguments 接口中。本节我们来详细了解一下 ApplicationArguments 接口。
接口定义及初始化
首先看一下 ApplicationArguments 接口的具体方法定义及功能介绍(注释部分)。
public interface ApplicationArguments {
//返回原始未处理的参数(通过 appl ication 传入的)
String[] getSourceArgs();
//返回所有参数名称的集合,如参数为: - foo=bar --debug, 则返回[ "foo", "debug"]
Set<String> getOpt ionNames();
//选项参数中是否包含指定名称的参数
boolean containsOpt ion(String name);
//根据选项参数的名称获取选项参数的值列表
List<String> getOptionValues(String name);//返回非选项参数列表
List<String> getNonOpt ionArgs();
}通过接口定义可以看出,ApplicationArguments 主要提供 了针对参数名称和值的查询,以及判断是否存在指定参数的功能。
在 Spring Boot 的初始化运行过程中,ApplicationArguments 接口的实例化操作默认是通过实现类
DefaultApplicationArguments 来完成的。
DefaultApplicationArguments 的 底 层 又 是 基 于 Spring 框 架 中 的 命 令 行 配 置 源SimpleCommandLinePropertySource 实 现 的 SimpleCommandLinePropertySource 是PropertySource 抽象类的派生类。
以下代码中内部类 Source 便是
SimpleCommandLinePropertySource 的子类。
public class DefaultApplicationArguments implements ApplicationArguments {
private final Source source;
private final String[] args;
public DefaultApplicationArguments(String[] args) {
Assert. notNull(args, "Args must not be null");
this.source = new Source(args);
this.args = args;
//在此省略 Appl icat ionArguments 的其他接口实现方法
private static class Source extends SimpleCommandL inePropertySource {
// ...
}
}我们再来看 SimpleCommand inePropertySource 的构造方法,通过代码会发现默认使用Spring 的
SimpleCommandLineArgsParser 对 args 参加进行解析。
public class SimpleCommandL inePropertySource extends CommandL inePropertySou
rce<CommandL ineArgs> {
public SimpleCommandL inePropertySource(String... args) {
super(new SimpleCommand ineArgsParser() . parse(args));
// 重裁的构造方法
public SimpleCommandL inePropertySource(String name, String[] args) {
super(name, new SimpleCommandL ineArgsParser() . parse(args));
}
}除了构造方法之外,
SimpleCommandLinePropertySource 还提供 了不同类型参数信息的获取和检查是否存在的功能,代码如下。
public class SimpleCommandL inePropertySource extends Commandl inePropertySource<CommandL ineArgs> {
/获取选项参数数组
@0verride
public String[] getPropertyNames()
return StringUtils. toStringArray(this . source . getOpt ionNames());
/获取是否包含指定 name 的参数
@Override
protected boolean containsOption(String name) {
return this. source . containsOption(name );
/获取指定 name 的选项参数列表
@Override
@Nullable
protected List<String> getOptionValues(String name) {
return this . source . getOpt ionValues(name);
//获取非选项参数列表
protected List<String> getNonOptionArgs() {
return this. source . getNonOptionArgs();}
}ApplicationArguments 或者步说是
SimpleCommandLinePropertySource 对参数类型是有所区分的,即选项参数和非选项参数。
选项参数必须以“一”为前缀,参数值可为空,该参数我们可以通过 SpringBoot 属性处理后使用,比如在执行 jar jar 命令时,添加选项参数“--app.name=spring boot learn",在代码中可通过@Value 属性或其他方式获取到该参数的值。该参数可以通过逗号分隔多个参数值,或多次使用同一个参数来包含多个参数的值。
非选项参数并不要求以“--”前缀开始,可自行定义。非选项参数可以是除了传递的 VM 参数之外的其他参数。比如我们可以直接在 jar -jar 命令中定义参数为“non-option”的参数值。
以上所说的选项参数和非选项参数的解析是在
SimpleCommandLinePropertySource 构造方法中调用的 SimpleCommandLineArgsParser 中完成的,代码如下。
class SimpleCommandL ineArgsParser
//解析 args 参数,返回一个 完整的 CommandL ineArgs 对象
public CommandLineArgs parse(String... args) {
CommandL ineArgs commandLineArgs = new CommandL ineArgs();
//遍历参数
for (String arg : args) {
//解析选项参数,以"--"开头
if (arg. startsWith("--"))String optionText = arg. substring(2, arg.length());
String optionName;
String optionValue = null;
//判断是--foo=bar 参数格式, 还是 foo 参数格式, 并分别处理获取值
if (optionText . contains("=")) {
optionName = optionText . substring(0, optionText . index0f('='));
optionValue = optionText . substring(optionText . indexOf('=' )+1,
optionText. length());
} else
optionName = optionText;
if (optionName. isEmpty()|| (optionValue != null && opt ionValue.
isEmpty()))-
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid argument syntax: ”+
arg);
commandL ineArgs . addOpt ionArg( optionName, optionValue);
} else {
//处理非选项参数
commandL ineArgs . addNon0pt ionArg(arg);
return commandLineArgs;
}
}通过
SimpleCommandLineArgsParser 的代码可以看出,Spring 对参数的解析是按照指定的 参 数 格 式 分 别 解 析 字 符 串 中 的 值 来 实 现 的 。 最 终 , 解 析 的 结 果 均 封 装 在CommandLineArgs 中。而 CommandLineArgs 类 只是命令行参数的简单表示形式,内部分为“选项参数和“非选项参数”。
class CommandL ineArgs
private final Map<String, List<String>> optionArgs = new HashMap<>();
private final List<String> nonOptionArgs = new ArrayList<>();
CommandLineArgs 的核心存储结构包括:存储选项参数的
Map<String,List<String>> optionArgs 和存储非选项参数的 List<String>nonOptionArgs。同时,针对这两个核心存储结构,Spring Boot 也提供了读写操作的方法。
SimpleCommandLineArgsParser 解 析 获 得 的 CommandLineArgs 对 象 , 最 终 会 被SimpleCommand-LinePropertySource 的 构 造 方 法 通 过 super 调 用 , 一 层 层 地 传 递 到PropertySource 类的构造方法, 最终封装到对应的属性当中。
public abstract class PropertySource<T> {//参数类别名称
protected final String name;
//参数封装类
protected final T source;以在
SimpleCommandLinePropertySource 中的使用为例,最终封装在 PropertySource 中的结构为: name 为“commandLineArgs",source 为解析出 的 CommandLineArgs 对象。
而
DefaultApplicationArguments的内部类Source作为SimpleCommandLinePropertySource 的子类存储了以上解析的数据内容。同时,args 参数的原始值存储在 DefaultApplicationArguments 的 String[ ] args 属性中。
使用实例
在实践中我们可能会遇到这样的疑问:如何访问应用程序变量?或者,如何访问通过SpringApplication.run(args) 传 入 的 参 数 ? 下 面 我 们 以 具 体 的 例 子 来 说 明 如 何 通 过ApplicationArguments 获得对应的参数。
ApplicationArguments 接口的使用非常简单,在我们使用参数值的 Bean 中直接注入ApplicationArguments 即可,然后调用其方法即可获得对应的参数值。
注入 ApplicationArguments,并提供打印所需参数信息的方法,代码如下。
@Component
public class ArgsBean {
@Resource
private ApplicationArguments arguments;
public void printArgs() {
System. out. println("#非选项参数数量:”+ arguments . getNonOptionArgs().s
ize());
System. out. println("#选项参数数量:”+ arguments . getOpt ionNames(). size
());
System. out. println("#非选项参数具体参数:");
arguments . getNonOpt ionArgs(). forEach(System. out::println);
System. out.println("#选项参数具体参数:");
arguments . getOptionNames() . forEach(optionName -> {
System. out . println("--"+ optionName + "=" + arguments . getOptionValue
(optionName));
});
}在 main 方法中获得 ArgsBean 实例化对象,并调用其 printArgs 方法, 代码如下。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Spring
SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication(SpringL earnApplication.clas
ConfigurableApplicationContext context =app. run(args);
ArgsBean bean = context. getBean(ArgsBean. class);
bean. printArgs();
}启动项目,控制台打印结果,代码如下。
非选项参数数量: 1
#选项参数数量:2
#非选项参数具体参数:
nonaoptin 休会
#选项
参数:
- --jdk . support=[1.7,1.8,1.8+]
- - app . name=[ springBootLearn]
以上只是示例,在上面的介绍中也提到了,选项参数可通过@Value 直接注入 Bean 中使用。
关于ApplicationArguments 其他方法的使用以此类推即可!
本文给大家讲解的内容是外化配置简介、ApplicationArguments参数处理
- 下篇文章给大家讲解的是命令参数的获取和配置文件的加载;
- 觉得文章不错的朋友可以转发此文关注小编;
- 感谢大家的支持!
最后
以上就是懵懂含羞草最近收集整理的关于SpringBoot外化配置源码解析:外化配置简介、参数处理SpringBoot外化配置源码解析外化配置简介ApplicationArguments 参数处理本文给大家讲解的内容是外化配置简介、ApplicationArguments参数处理的全部内容,更多相关SpringBoot外化配置源码解析:外化配置简介、参数处理SpringBoot外化配置源码解析外化配置简介ApplicationArguments内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复